Development of Pb-Free Nanocomposite Solder Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
3. Result and Discussion
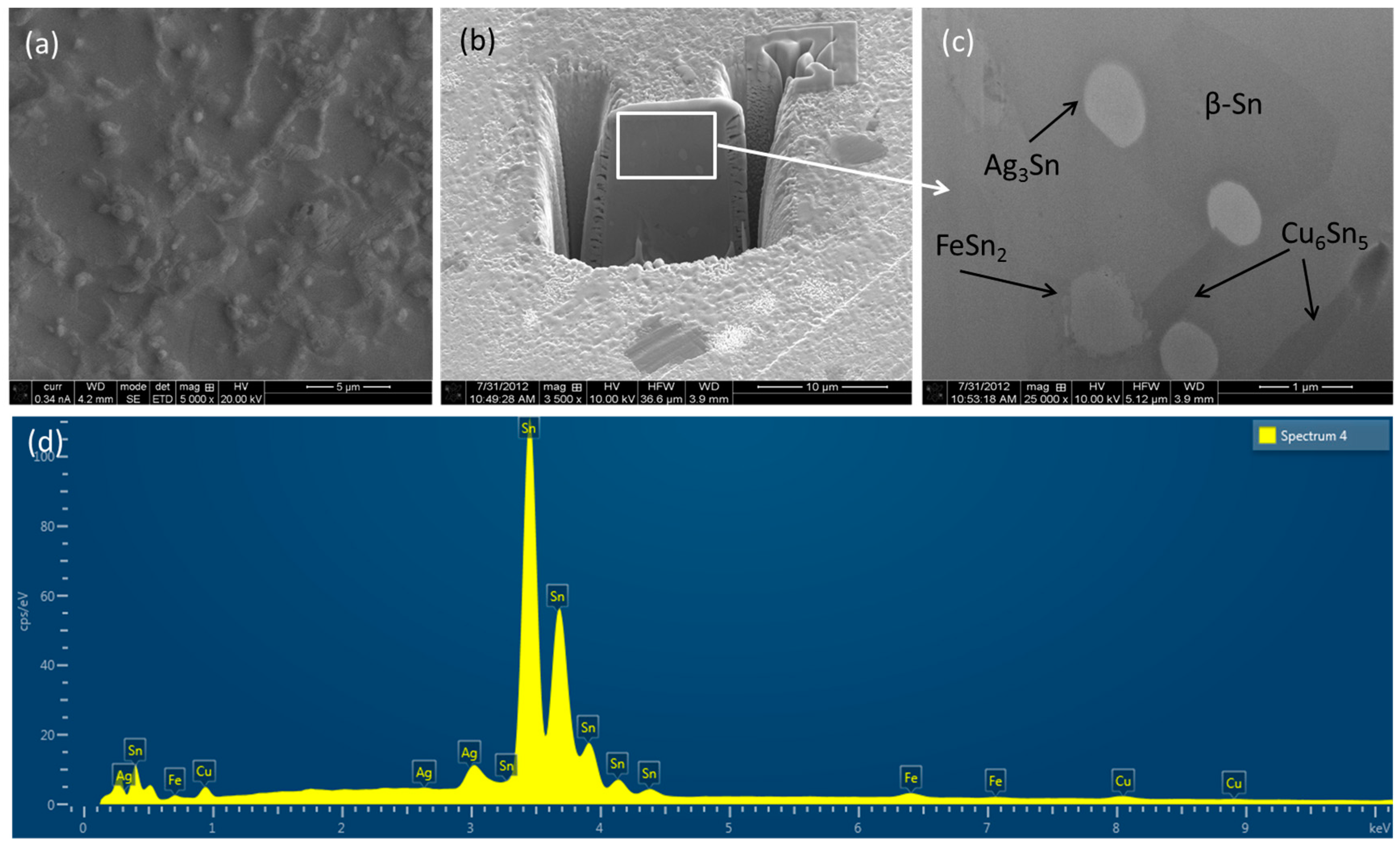
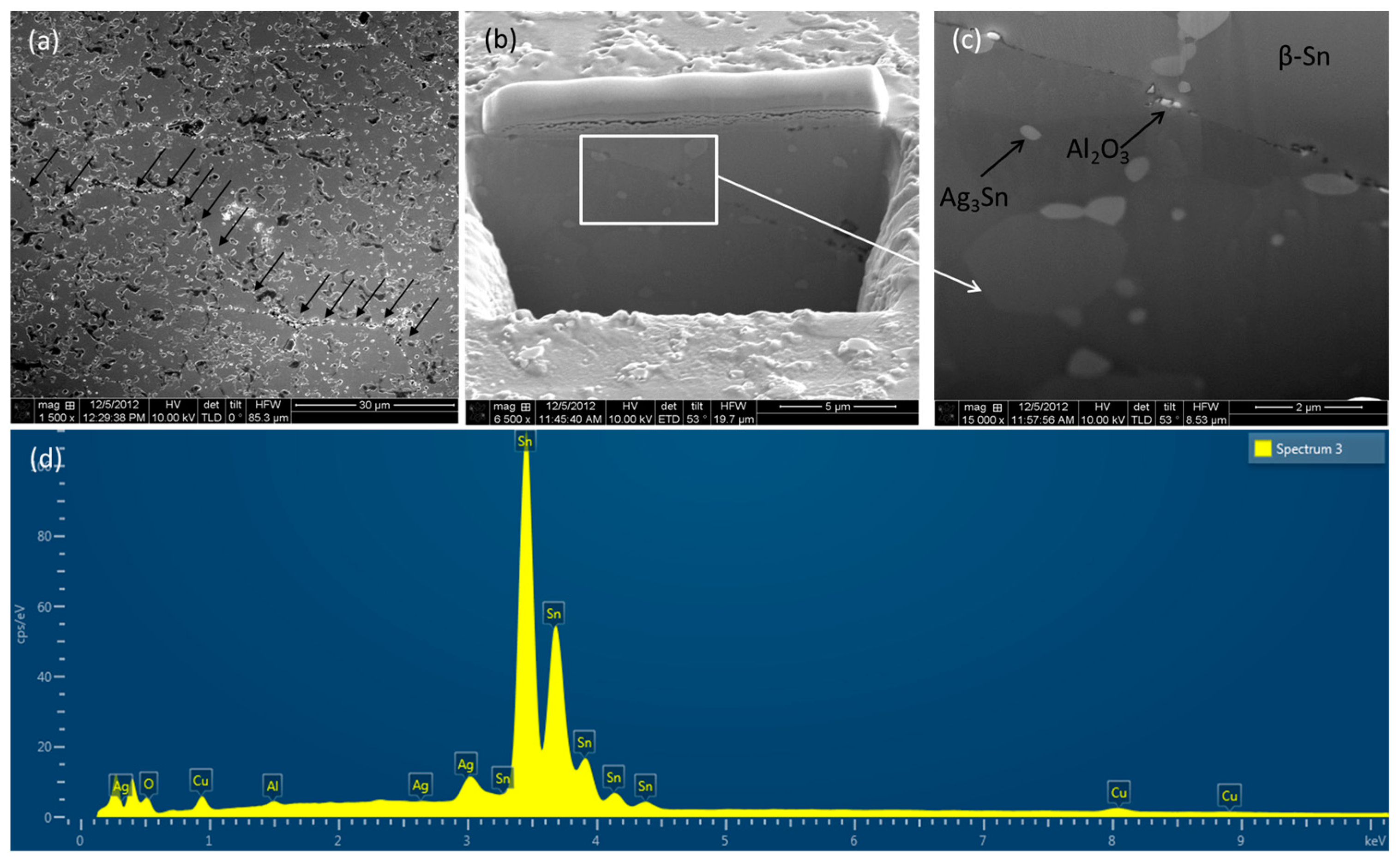
3.1. Microstructure of Solder Alloys
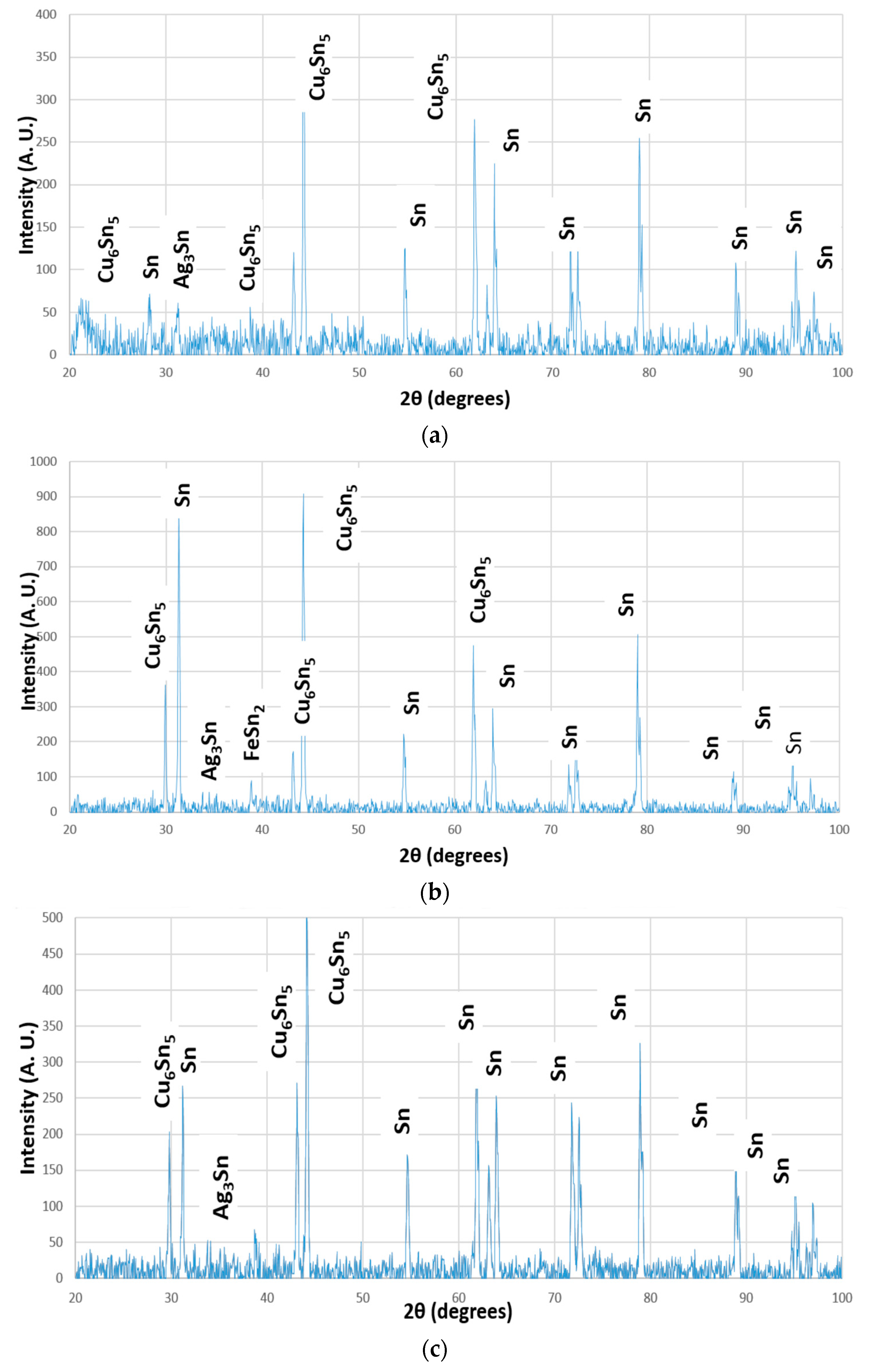
3.2. Different Phases of Solder Alloys
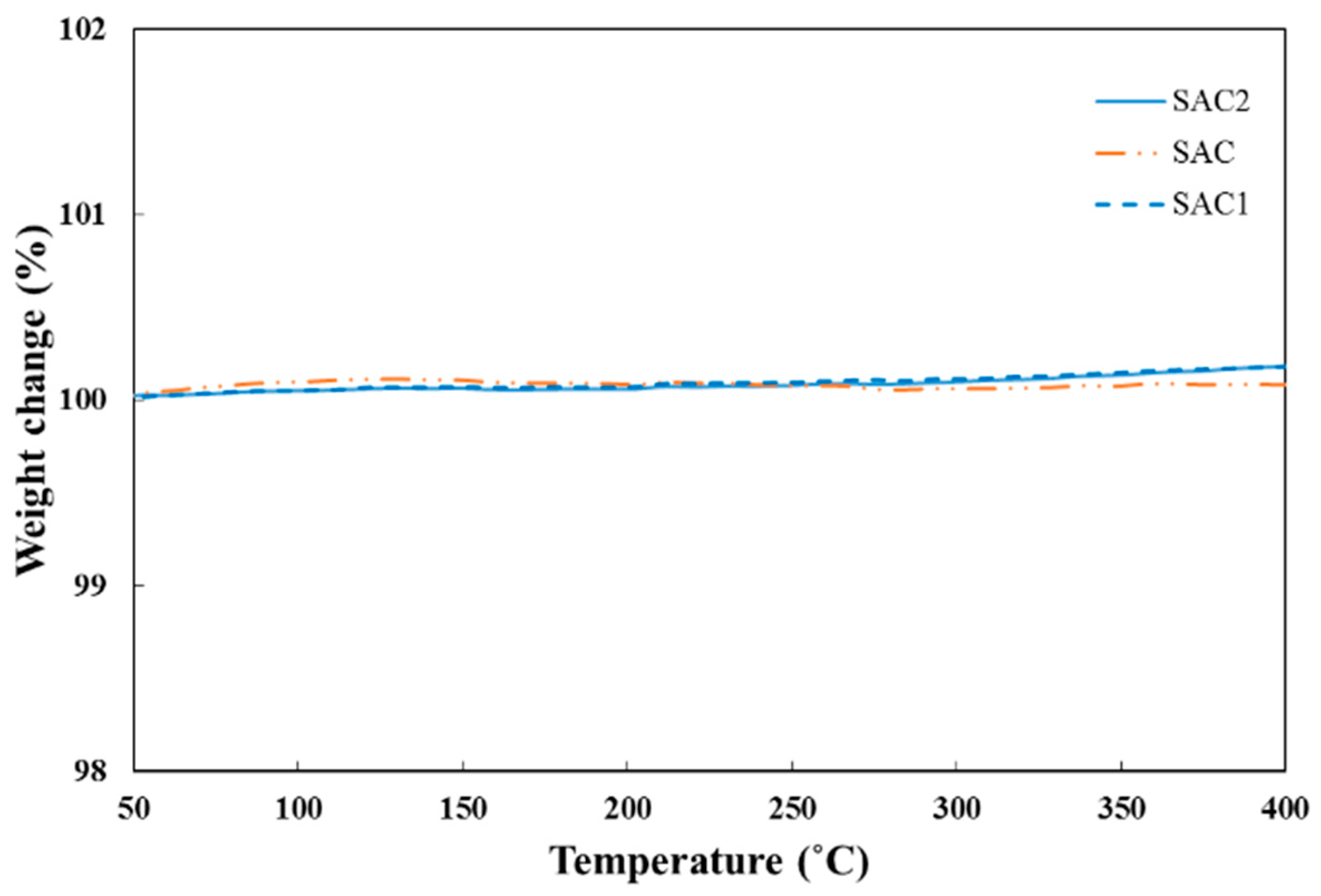
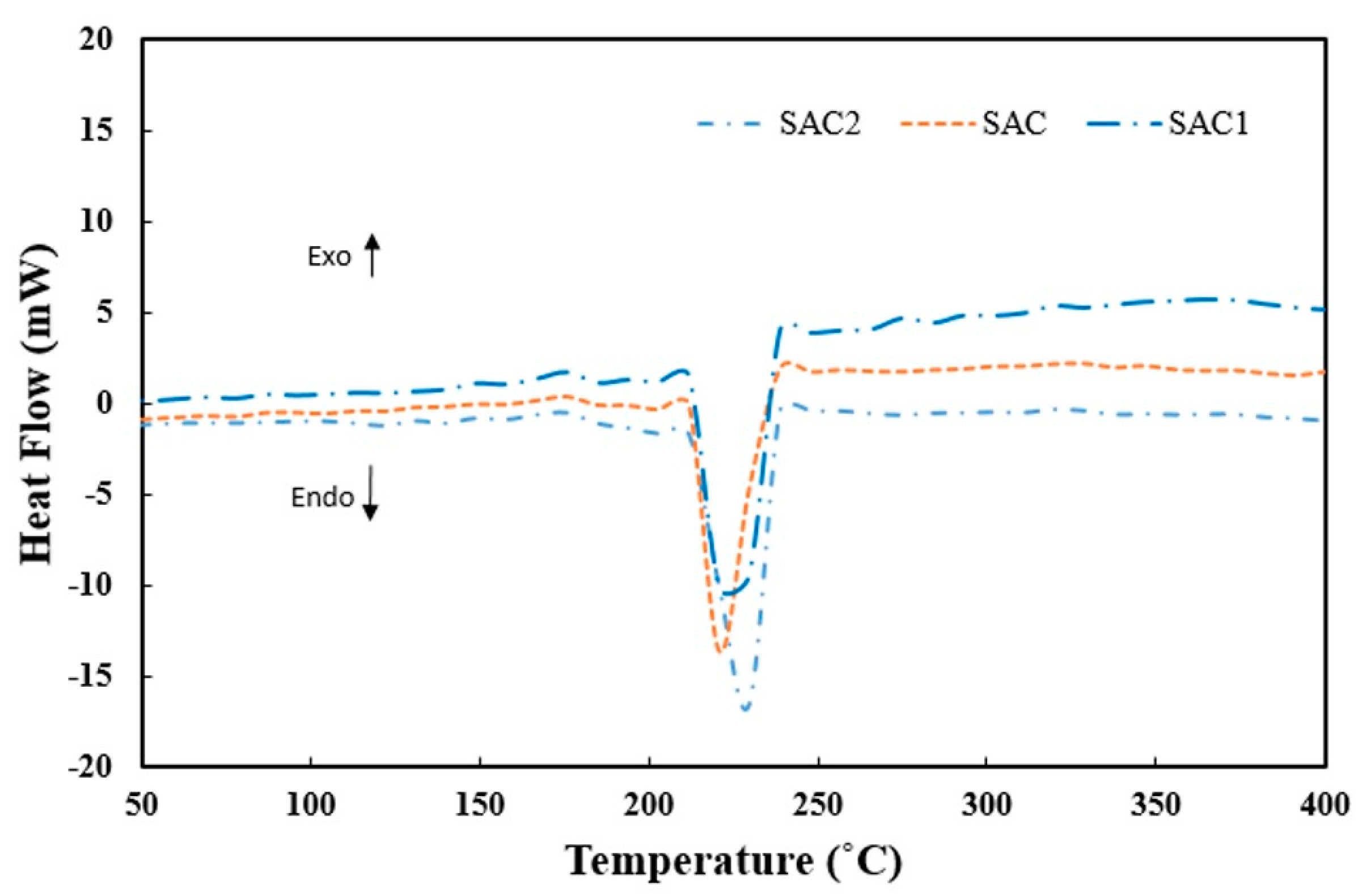
3.3. Thermal Analysis of Solder Alloys
4. Conclusions
- Fe-bearing solder nanocomposite form relatively larger primary β-Sn grains compared to monolithic Sn–Ag–Cu alloy. Fe addition also helps to form FeSn2 IMCs dispersed in matrix and foreseen to restrict grain/ IMCs growth during aging/reflowing.
- Addition of Al2O3 nanoparticles refine β-Sn grain size, dispersed in the matrix with preferential trend to be accumulated along grain boundaries.
- Neither Fe nor Al2O3 nanoparticle addition cause any significant effect on thermal behavior compared to Sn–Ag–Cu solder alloys.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, C.M.; Anderson, I.E.; Smith, J.F. A Viable Tin-Lead Solder Substitute: Sn-Ag-Cu. J. Electron. Mater. 1994, 23, 595–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.E.; Cook, B.A.; Harringa, J.L.; Terpstra, R.L. Sn-Ag-Cu Solders and Solder Joints: Alloy Development, Microstructure, and Properties. JOM 2002, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Chen, J. Nanoindentation of lead-free solders in microelectronic packaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 448, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.F.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, Z.F. Coarsening mechanisms, texture evolution and size distribution of Cu6Sn5 between Cu and Sn-based solders. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 131, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chawla, N.; Chawla, K.K.; Koopman, M. Deformation behaviour of (Cu, Ag)—Sn intermetallics by nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Takemoto, T. Mechanical properties evolution of Sn-3.5Ag based lead-free solders by nanoindentation. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, E.; Petzow, G. Ueber den Auf-bau des Systems Silber-Kupfer-Zinn. Zeitschrift fuer Metallkunde 1959, 50, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Loomans, M.E.; Fine, M.E. Tin-silver-copper eutectic temperature and composition Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31A, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.W.; Boettinger, W.J.; Kattner, U.R.; Biancaniello, F.S.; Handwerker, C.A. Experimental and thermodynamic assessment of Sn-Ag-Cu solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 2000, 29, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.K.; Dong, Y.; Shankar, S.; Littlefair, G. Milling of nanoparticles reinforced Al-based metal matrix composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellvarajoo, S.; Abdullah, M.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Pb-free Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder pastes added with NiO nanoparticles after reflow soldering process. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.L.; Gupta, M. Development of lead-free Sn—0.7Cu/Al2O3 nanocomposite solders with superior strength. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 095403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.A.M.; McDonald, S.D.; Nogita, K. Effects of Ni and TiO2 additions in as-reflowed and annealed Sn0.7Cu solders on Cu substrates. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 242, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjani, V.L.; Rao, B.S.S.C.; Sarkar, R.; Kamat, S.V. The influence of addition of nano sized molybdenum and nickel particles on creep behavior of Sn–Ag lead free solder alloy. J. Alloys Comp. 2012, 542, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.B.; Benabou, L.; Le, V.N.; Hwang, H.; Lu, D.B. Viscoplastic characterization and post-rupture microanalysis of a novel lead-free solder with small additions of Bi, Sb and Ni. J. Alloys Comp. 2017, 694, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.L.; Yu, D.Q.; Law, C.M.T.; Wang, L. Properties of lead-free solder alloys with rare earth element additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2004, 44, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.A.; Vellinga, W.P.; Geers, M.G.D. Microstructure evolution in a Pb-free solder alloy during mechanical fatigue. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 431, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.S.S.C.; Weng, J.; Shen, L.; Lee, T.K.; Zeng, K.Y. Morphology and mechanical properties of intermetallic compounds in SnAgCu solder joints. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Fang, Z.Z.; Liang, J.; Dariavach, N. Microstructural Analysis of Lead-Free Solder Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2505–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Koopman, M.; Chawla, N.; Chawla, K.K. Young’s modulus of (Cu, Ag)–Sn intermetallics measured by nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 364, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, A.K.; Pramanik, A.; Islam, M.N. Failure mechanisms of nanoparticle reinforced metal matrix composite. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 774, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawah, D.A.A.; Said, S.B.M.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Che, F.X. Microstructure, mechanical, and thermal properties of the Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy bearing Fe for electronics applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 551, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, G.E. Mechanical Metallurgy, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: Minato-ku, Tokyo, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, A.K.; Eddine, W.Z.; Celis, J.P.; Matteazzi, P. Characterisation and tribological investigation on thermally processed nanostructured Fe-based and Cu-based cermet materials. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmer, J.W.; Specht, E.D.; Kumar, M. Microstructure and In Situ Observations of Undercooling for Nucleation of β-Sn Relevant to Lead-Free Solder Alloys. J. Elelctron. Mater. 2010, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; Punch, J.; Collins, M.; Ryan, C. Effect of Ag content on the microstructure of Sn-Ag-Cu based solder alloys. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2008, 20, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basak, A.K.; Pramanik, A.; Riazi, H.; Silakhori, M.; Netting, A.K.O. Development of Pb-Free Nanocomposite Solder Alloys. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020028
Basak AK, Pramanik A, Riazi H, Silakhori M, Netting AKO. Development of Pb-Free Nanocomposite Solder Alloys. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasak, Animesh K., Alokesh Pramanik, Hamidreza Riazi, Mahyar Silakhori, and Angus K. O. Netting. 2018. "Development of Pb-Free Nanocomposite Solder Alloys" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020028
APA StyleBasak, A. K., Pramanik, A., Riazi, H., Silakhori, M., & Netting, A. K. O. (2018). Development of Pb-Free Nanocomposite Solder Alloys. Journal of Composites Science, 2(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020028







