The Origin of the Yellow Luminescence Band in Be-Doped Bulk GaN
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
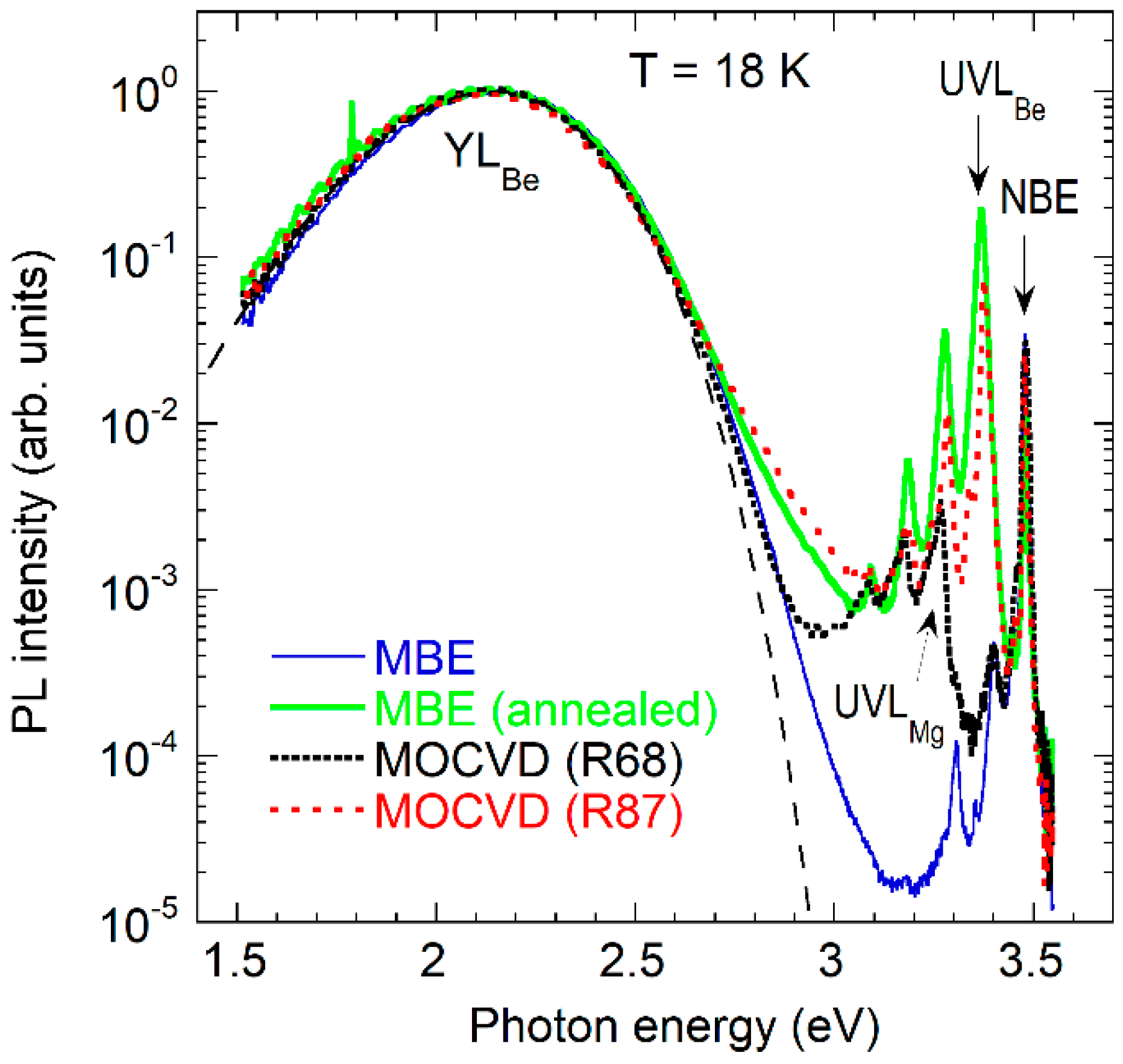
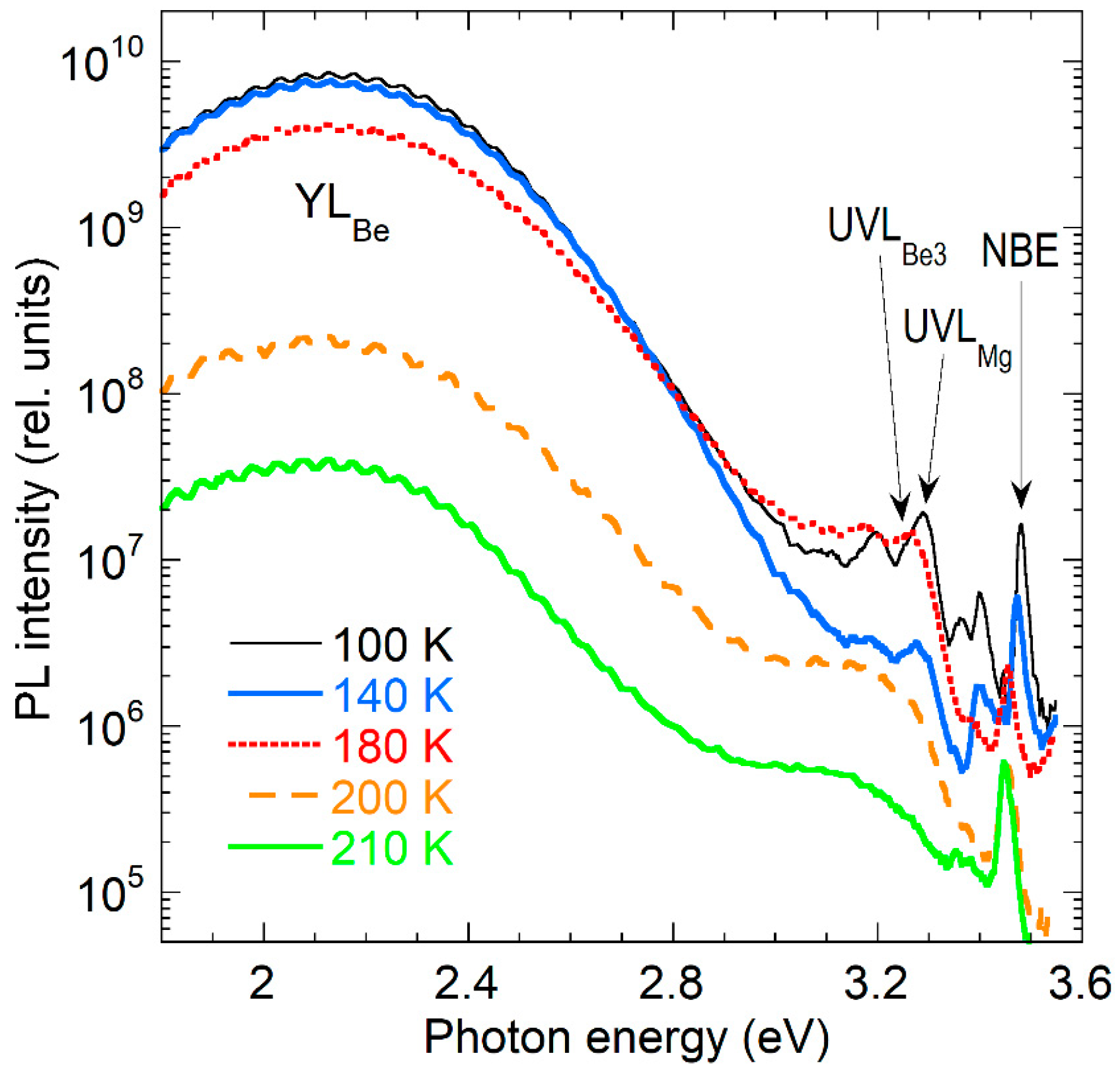
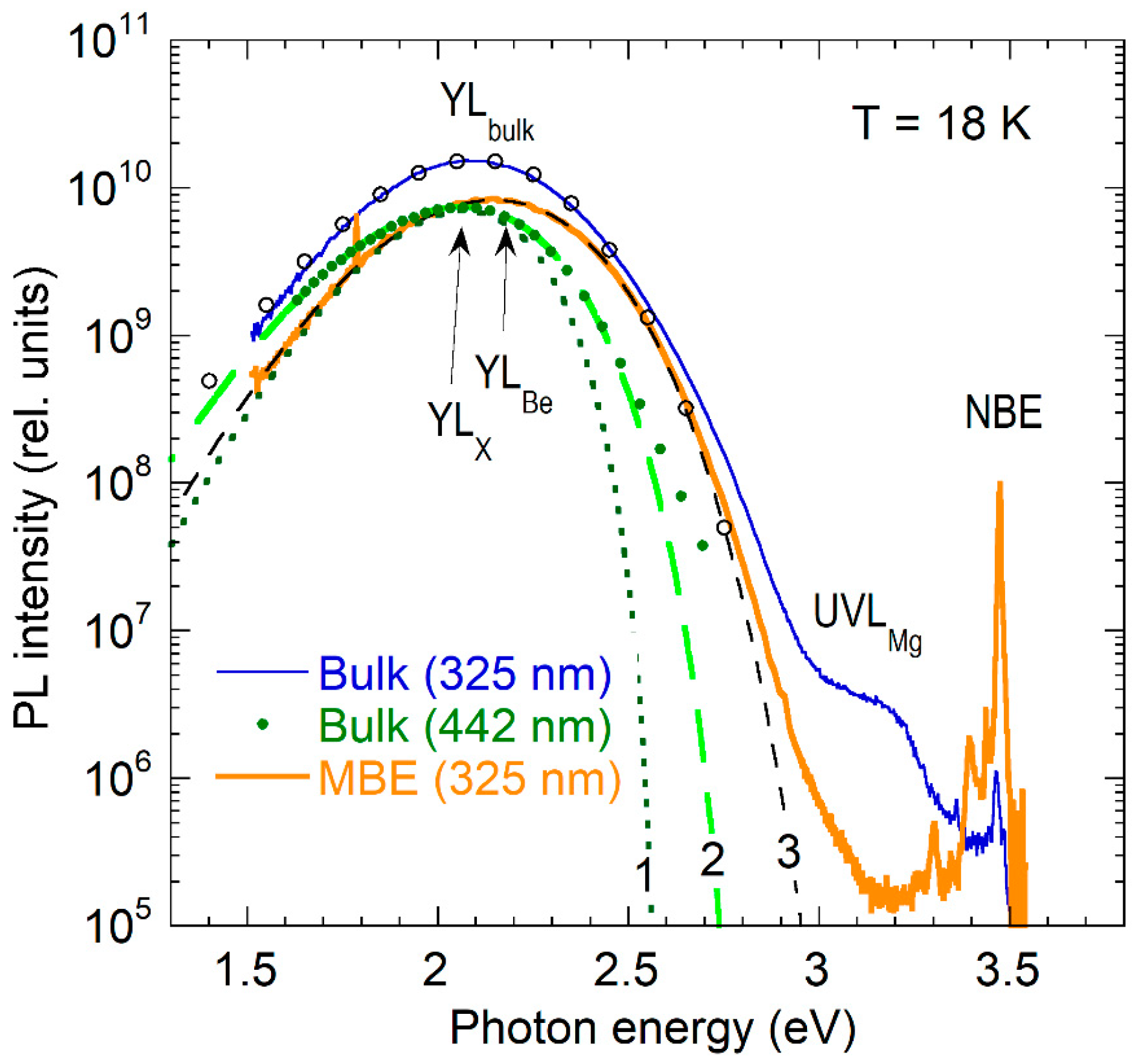
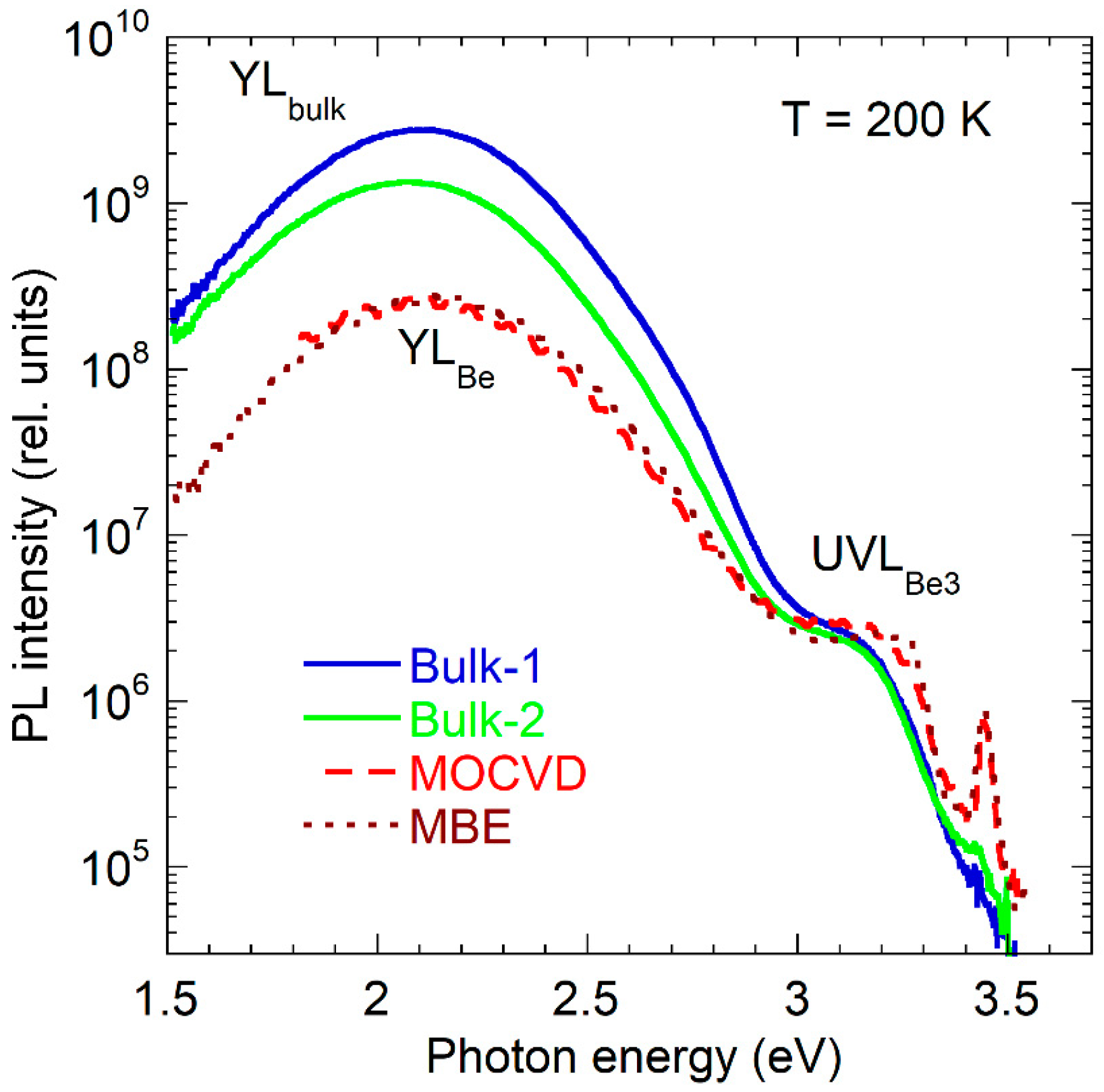
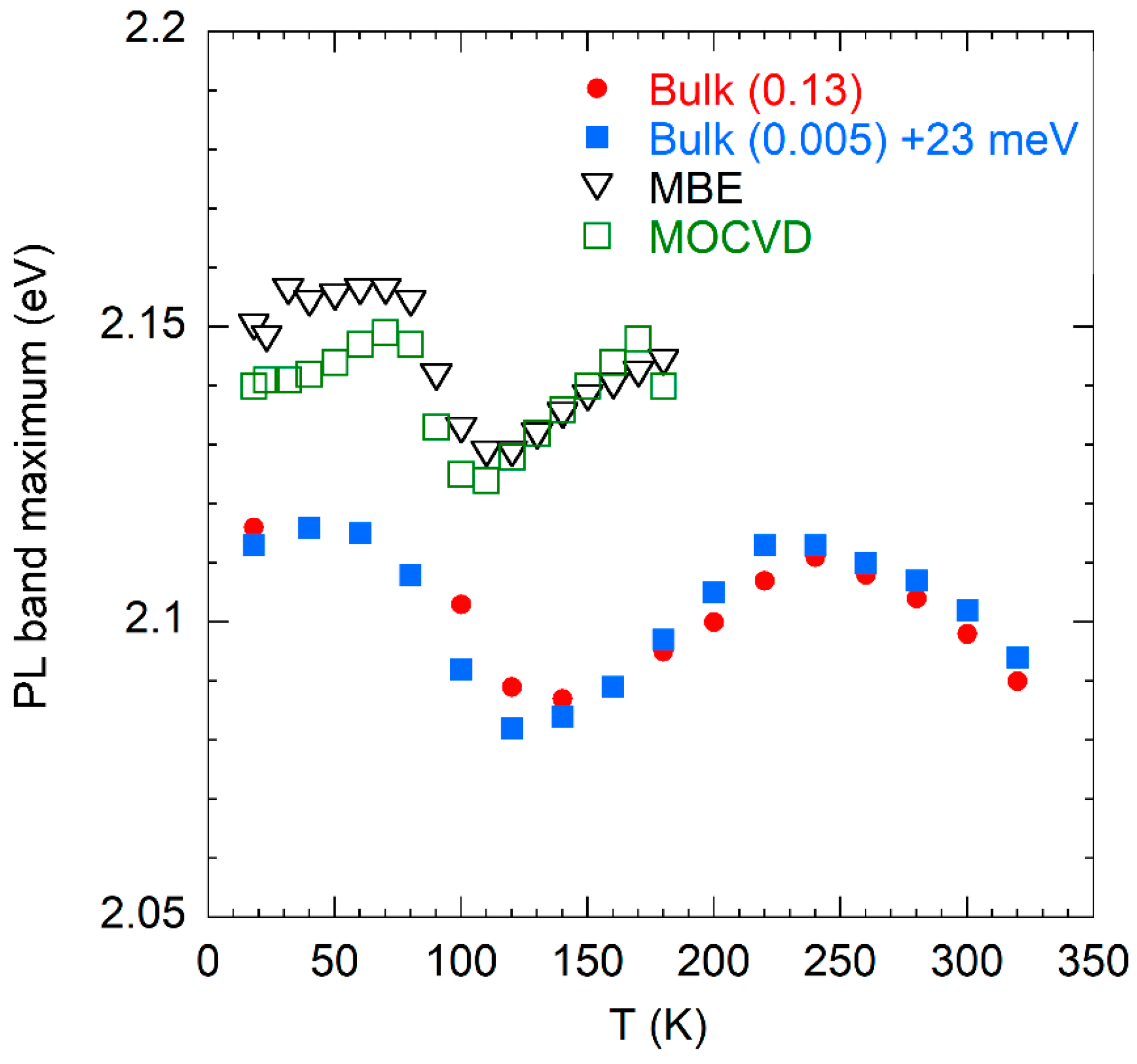
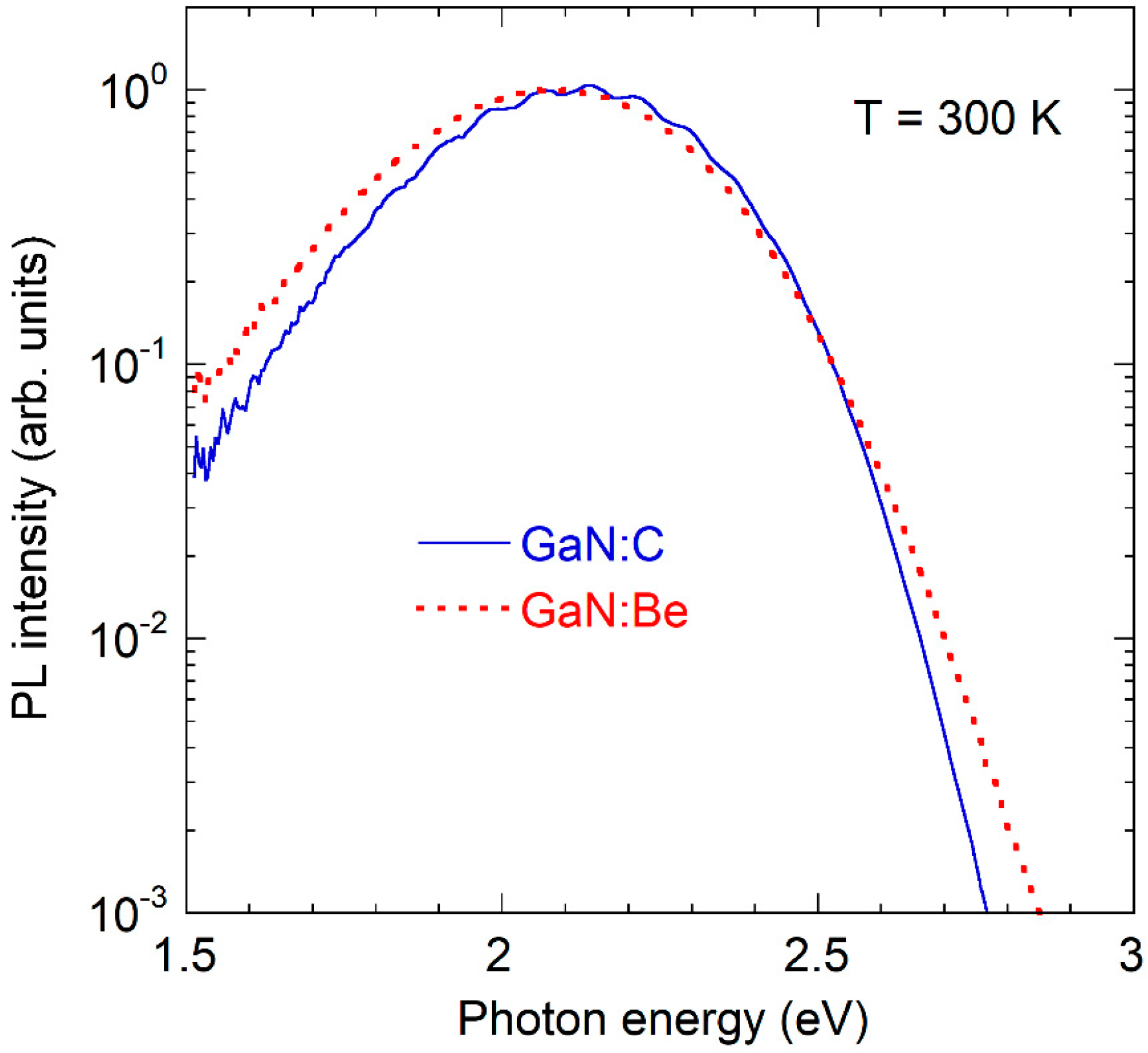
3.1. PL Bands in Be-Doped GaN Grown by MOCVD and MBE Techniques
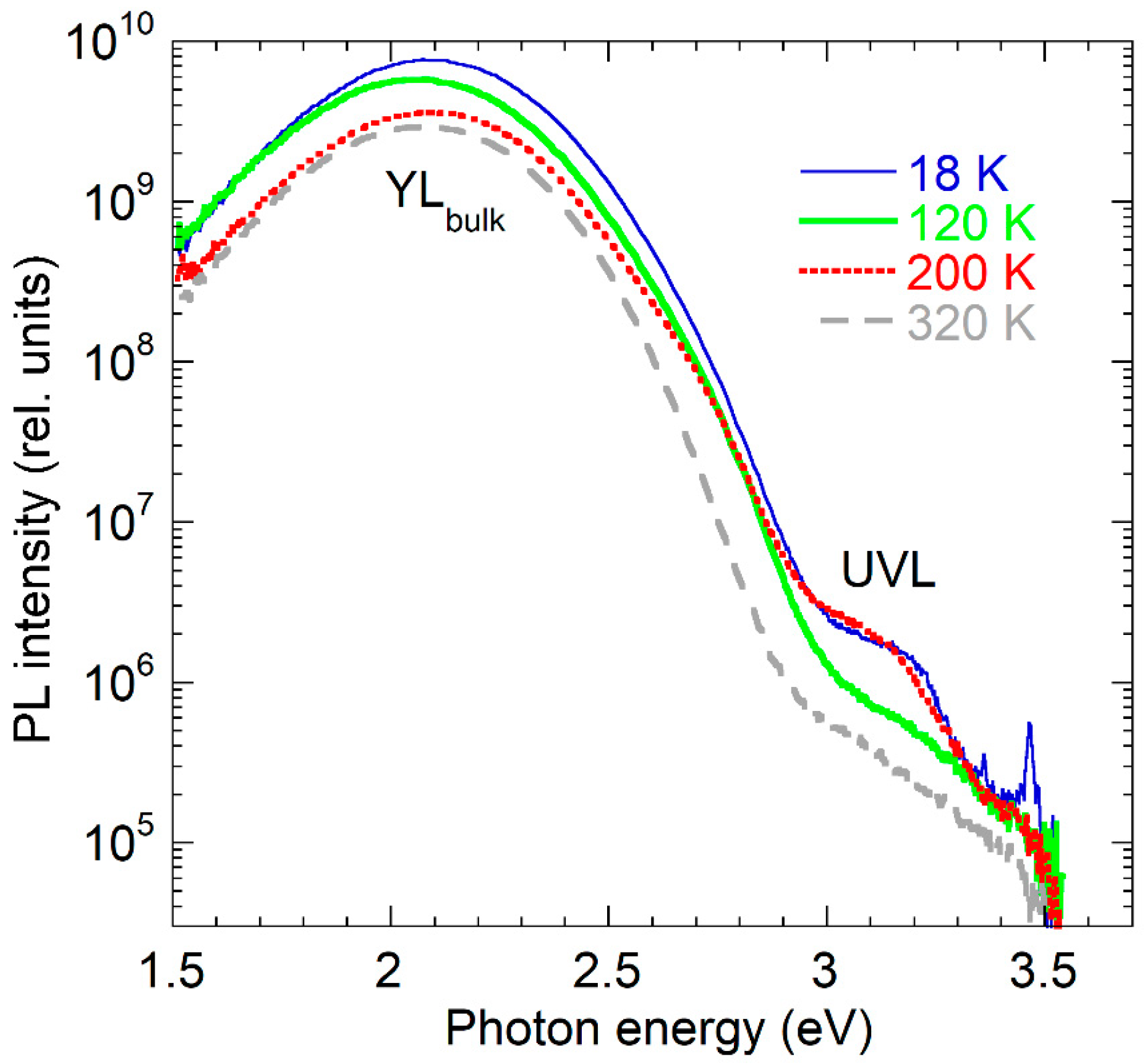
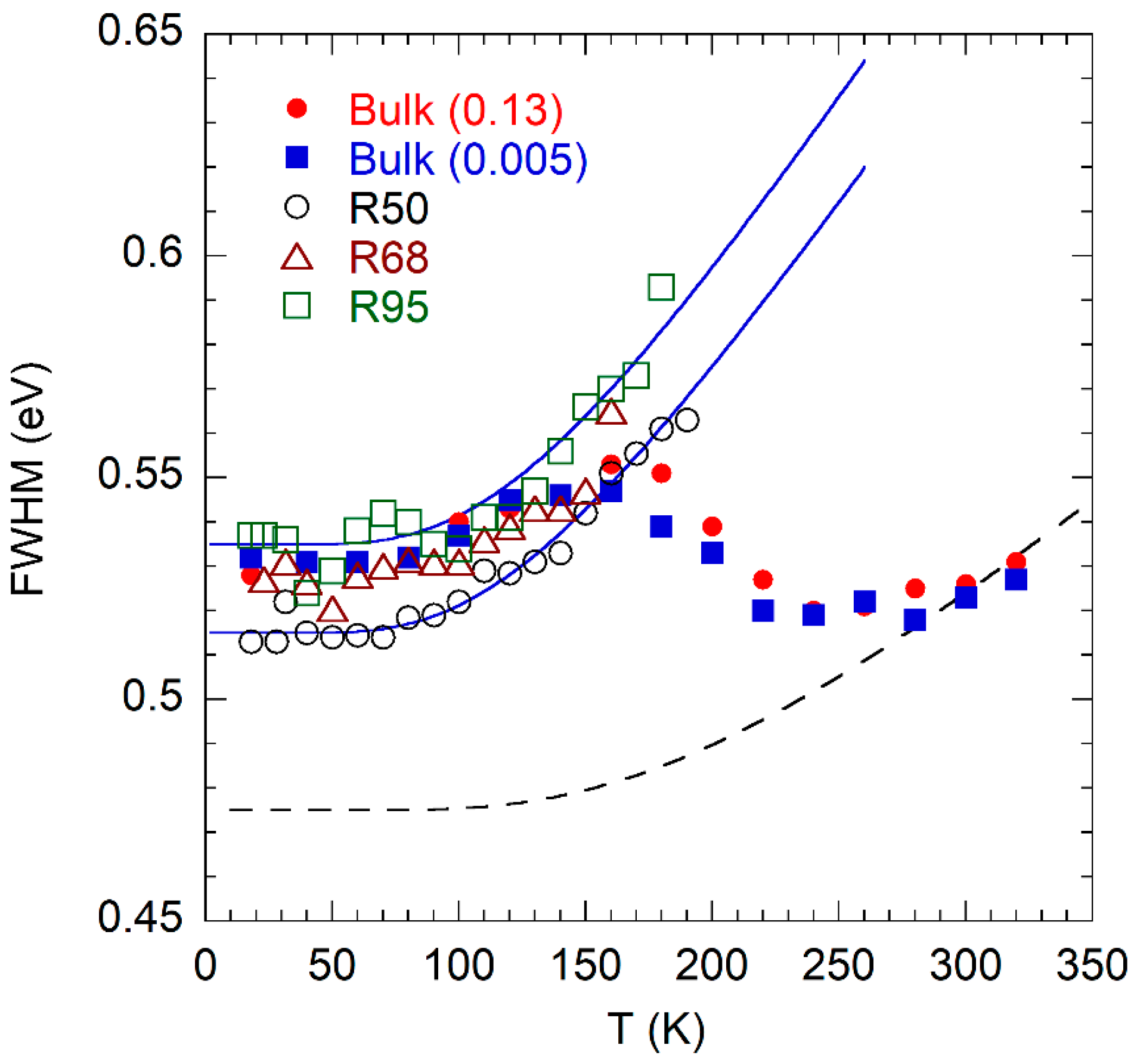
3.2. The Yellow Band in Bulk GaN:Be Grown by High-Pressure Technique
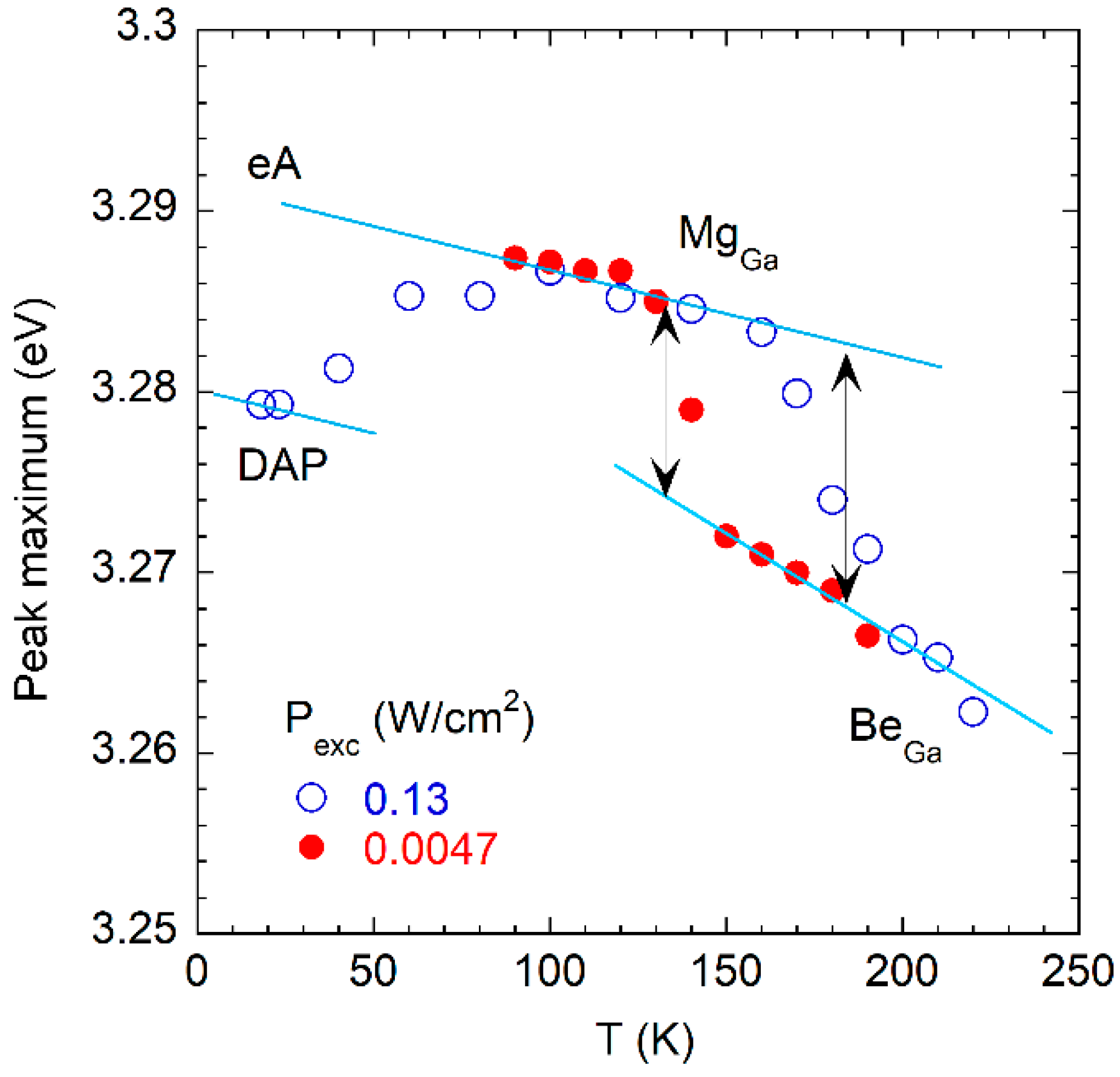
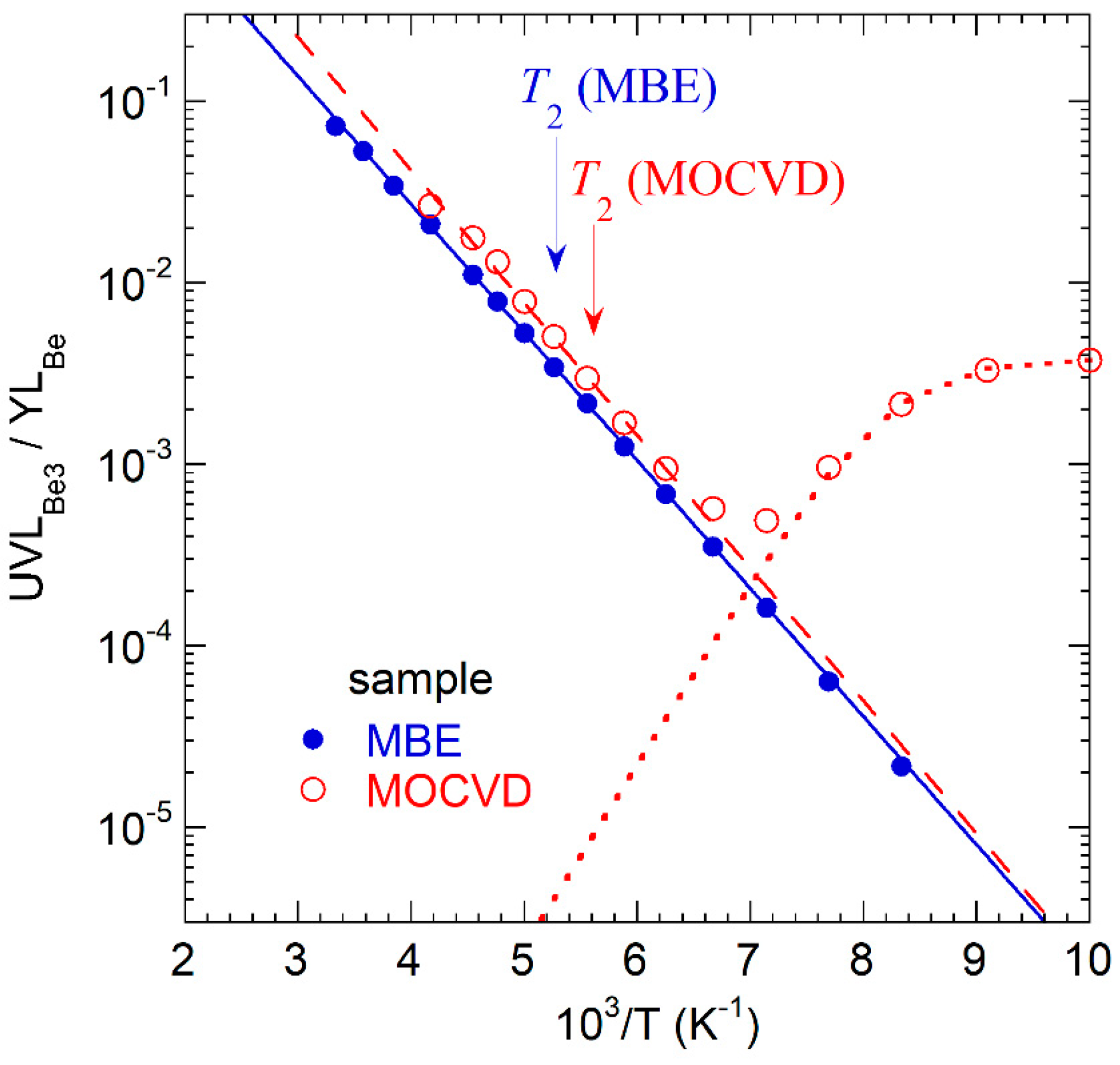
4. Discussion
4.1. Type of Transition
4.2. On Identification of the YLX Band in Bulk GaN
4.2.1. Can the YLX Band Be the CN-Related YL1 Band?
4.2.2. Can the YLX Band Be Caused by the BeGaON Complex?
4.3. Interpretation of Other Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morkoç, H. Handbook of Nitride Semiconductors and Devices; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pearton, S.J.; Zolper, J.C.; Shul, R.J.; Ren, F. GaN: Processing, defects, and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, S. GaN-based light-emitting diodes on various substrates: A critical review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 056501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.A.; Wang, F.; Costinett, D. Review of Commercial GaN Power Devices and GaN-Based Converter Design Challenges. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Electron. 2016, 4, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.J. Photoluminescence as a diagnostic of semiconductors. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. 1982, 5, 89–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Morkoç, H. Luminescence properties of defects in GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A. Measurement and analysis of photoluminescence in GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, T.; Aoki, M. Mechanism of Yellow Luminescence in GaN. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 19, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankove, J.I.; Hutchby, J.A. Photoluminescence of ion-implanted GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 5387–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A. On the Origin of the Yellow Luminescence Band in GaN. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 2023, 260, 2200488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.L.; Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Carbon impurities and the yellow luminescence in GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 97, 152108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; McNamara, J.D.; Zhang, F.; Monavarian, M.; Usikov, A.; Helava, H.; Makarov, Y.; Morkoç, H. Zero-phonon line and fine structure of the yellow luminescence band in GaN. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 035201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Vorobiov, M.; Demchenko, D.O.; Özgür, Ü.; Morkoç, H.; Lesnik, A.; Hoffmann, M.P.; Hörich, F.; Dadgar, A.; Strittmatter, A. Two charge states of the CN acceptor in GaN: Evidence from photoluminescence. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 125207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, F.; Beyer, J.; Röder, C.; Beyer, C.; Richter, E.; Irmscher, K.; Heitmann, J. Current Status of Carbon-Related Defect Luminescence in GaN. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 2021, 218, 2100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suski, T.; Perlin, P.; Teisseyre, H.; Leszczynski, M.; Grzegory, I.; Jun, J.; Boćkowski, M.; Porowski, S. Mechanism of yellow luminescence in GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 2188–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Usikov, A.; Helava, H.; Makarov, Y.; Prozheeva, V.; Makkonen, I.; Tuomisto, F.; Leach, J.H.; Udwary, K. Evaluation of the concentration of point defects in GaN. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshchikov, M.A. Photoluminescence from defects in GaN. In Proceedings of SPIE 12421, Gallium Nitride Materials and Devices XVIII; Fujioka, H., Morkoç, H., Schwarz, U., Eds.; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023; p. 1242109. [Google Scholar]
- Ilegems, M.; Dingle, R. Luminescence of Be- and Mg-doped GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 4234–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Skromme, B. Spectroscopic Characterization of Ion-Implanted GaN. In GaN and Related Alloys—2002; Materials Research Society Symposium—Proceedings; Wetzel, C., Yu, E.T., Speck, J.S., Rizzi, A., Arakawa, Y., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 743, pp. 755–760. [Google Scholar]
- Demchenko, D.O.; Vorobiov, M.; Andrieiev, O.; Myers, T.H.; Reshchikov, M.A. Shallow and deep states of beryllium acceptor in GaN: Why photoluminescence experiments do not reveal small polarons for defects in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 027401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Lindemuth, J.; Engel, Z.; Matthews, C.M.; McCrone, T.M.; Doolittle, W.A. Substantial P-Type Conductivity of AlN Achieved via Beryllium Doping. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, W.A.; Matthews, C.M.; Ahmad, H.; Lee, S.; Ghosh, A.; Marshall, E.N.; Tang, A.L.; Manocha, P.; Yoder, D. Prospectives for AlN electronics and optoelectronics and the important role of alternative synthesis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobiov, M.; Andrieiev, O.; Demchenko, D.O.; Reshchikov, M.A. Point Defects in Beryllium Doped GaN. Phys. Rev B 2021, 104, 245203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Andrieiev, O.; Vorobiov, M.; Demchenko, D.O.; McEwen, B.; Shahedipour-Sandvik, F. Photoluminescence from GaN implanted with Be and F. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 2023, 260, 2300131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Vorobiov, M.; Andrieiev, O.; Demchenko, D.O.; McEwen, B.; Shahedipour-Sandvik, F. Dual Nature of the BeGa Acceptor in GaN: Evidence from Photoluminescence. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 108, 075202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lany, S.; Zunger, A. Dual nature of acceptors in GaN and ZnO: The curious case of the shallow MgGa deep state. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 142114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teisseyre, H.; Lyons, J.L.; Kaminska, A.; Jankowski, D.; Jarosz, D.; Boćkowski, M.; Suchocki, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Identification of yellow luminescence centers in Be-doped GaN through pressure-dependent studies. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 22LT03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, M.; Thonke, K.; Teisseyre, H.; Boćkowski, M. Extremely Slow Decay of Yellow Luminescence in Be-Doped GaN and Its Identification. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 2018, 255, 1800126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teisseyre, H.; Boćkowski, M.; Grzegory, I.; Kozanecki, A.; Damilano, B.; Zhydachevskii, Y.; Kunzer, M.; Holc, K.; Schwarz, U.T. An effective light converter for white light emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 011107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegory, I.; Boćkowski, M.; Porowski, S. Bulk Crystal Growth of Electronic, Optical and Optoelectronic Materials; Capper, P., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Suski, T.; Litwin-Staszewska, E.; Perlin, P.; Wisniewski, P.; Teisseyre, H.; Grzegory, I.; Boćkowski, M.; Porowski, S.; Saarinen, K.; Nissilä, J. Optical and electrical properties of Be doped GaN bulk crystals. J. Crystal Growth 2001, 230, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, F.; Prozheeva, V.; Makkonen, I.; Myers, T.H.; Boćkowski, M.; Teisseyre, H. Amphoteric Be in GaN: Experimental Evidence for Switching between Substitutional and Interstitial Lattice Sites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 196404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, E.R.; Freitas, J.A., Jr.; Storm, D.F.; Teisseyre, H.; Boćkowski, M. Optical and magnetic resonance studies of Be-doped GaN bulk crystals. J. Crystal Growth 2014, 403, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerjaud, B.; Côte, D.; Naud, C.; Bouanani-Rahbi, R.; Wasik, D.; Pakula, K.; Baranowski, J.M.; Suski, T.; Litwin-Staszewska, E.; Boćkowski, M.; et al. The role of oxygen and hydrogen in GaN. Phys. B 2001, 308–310, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willoughby, W.R.; Zvanut, M.E.; Dashdorj, J.; Boćkowski, M. A model for Be-related photo-absorption in compensated GaN:Be substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 115701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willoughby, W.R.; Zvanut, M.E.; Boćkowski, M. Photo-EPR study of compensated defects in Be-doped GaN substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 075701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Demchenko, D.O.; McNamara, J.D.; Fernández-Garrido, S.; Calarco, R. Green luminescence in Mg-doped GaN. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 035207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Kvasov, A.A.; Bishop, M.F.; McMullen, T.; Usikov, A.; Soukhoveev, V.; Dmitriev, V.A. Tunable and abrupt thermal quenching of photoluminescence in high-resistivity Zn-doped GaN. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 075212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanyuk, A.P.; Osipov, V.V. Edge luminescence of direct-gap semiconductors. Sov. Phys. Usp. 1981, 24, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Albarakati, N.M.; Monavarian, M.; Avrutin, V.; Morkoç, H. Thermal quenching of the yellow luminescence in GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 161520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Demchenko, D.O.; Vorobiov, M.; Andrieiev, O.; McEwen, B.; Shahedipour-Sandvik, F.; Sierakowski, K.; Jaroszynski, P.; Boćkowski, M. Photoluminescence related to Ca in GaN. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 106, 035206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A. Giant shifts of photoluminescence bands in GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 055701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyd, J.; Scuseria, G.E.; Ernzerhof, M. Hybrid functionals based on a screened Coulomb potential. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 8207–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.L.; Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Impact of Group-II Acceptors on the Electrical and Optical Properties of GaN. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 08JJ04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wei, S.-H. Origin of Deep Be Acceptor Levels in Nitride Semiconductors: The Roles of Chemical and Strain Effects. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 11, 034019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Source | BeGa (−/0) | BeGaON (0/+) | CN (−/0) | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep | Shallow | Deep | Deep | ||||||
| EA | ħωmax | EA | ħωmax | EA | ħωmax | EA | ħωmax | ||
| VDW 1 | 0.55 | 1.80 | 0.26 | 2.08 | 0.90 | 2.14 | [11,27,44] | ||
| DD 2 | 0.58 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 3.20 | – | – | 0.93 | 2.08 | [13,20,23] |
| SHW 3 | 0.65 | 1.67 | [45] | ||||||
| LZ 4 | 0.45 | 2.02 | 0.15 | ~3.3 | [26] | ||||
| Experiment | 0.33 0.38 | 2.15 | 0.236 | 3.26 | 0.8–0.9 | 2.06 | 0.916 | 2.17 | [12,25] and this work |
| Scenario | Concentration of Defects (cm−3) | Hole-Capture Coefficient (cm3/s) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BeGa | BeGaON | ON | CN | BeGa | BeGaON | CN | |
| 1 (X = CN) | 1017 | 3 × 1019 | 1017 | 1018 | 10−6 | 10−9 | 4 × 10−7 |
| 2 (X = BeGaON) | 1018 | 3 × 1019 | 1018 | 1018 | 10−6 | 10−7 | 4 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reshchikov, M.A.; Bockowski, M. The Origin of the Yellow Luminescence Band in Be-Doped Bulk GaN. Solids 2024, 5, 29-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids5010003
Reshchikov MA, Bockowski M. The Origin of the Yellow Luminescence Band in Be-Doped Bulk GaN. Solids. 2024; 5(1):29-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleReshchikov, Michael A., and Michal Bockowski. 2024. "The Origin of the Yellow Luminescence Band in Be-Doped Bulk GaN" Solids 5, no. 1: 29-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids5010003







