- Article
Synergistic Integration of Drop-Casting with Sonication and Thermal Treatment for Fabrication of MWCNT-Coated Conductive Cotton Fabrics
- Muhammad Shahbaz and
- Hiroshi Furuta
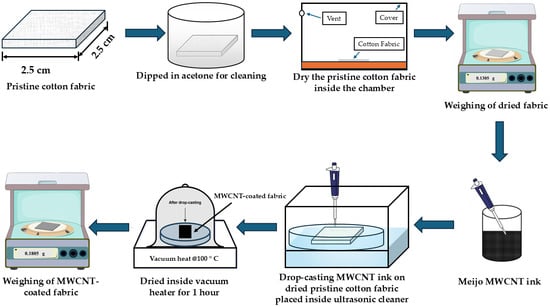
This study introduces a synergistic drop-casting, sonication, and thermal treatment (DSTT) method for fabricating multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)-coated conductive cotton fabrics. The process produced uniform MWCNT networks with a minimum sheet resistance of 0.072 ± 0.004 kΩ/sq. at ~30 wt.% loading. Scanning electron microscopy confirmed an improved MWCNT network. Reproducibility was demonstrated for different fabric sizes, with resistance values remaining consistent within experimental errors. Stability tests showed only minor changes in sheet resistance after 16 weeks of ambient storage and periodic manual bending. Compared to conventional methods such as room-temperature drying, vacuum drying, and sonication alone, DSTT consistently performed better, yielding fabrics with lower resistance and more reliable conductivity. These results highlight DSTT as a reproducible and scalable method for producing conductive cotton fabrics suitable for smart textiles and wearable electronics.
14 January 2026