Review Papers in Energy and Environment
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Eugenio Meloni
Dr. Eugenio Meloni
 Dr. Eugenio Meloni
Dr. Eugenio Meloni
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Salerno, Via Giovanni Paolo II 132, 84084 Fisciano, Italy
Interests: heterogeneous catalysis; soot abatement; process intensification; catalytic filters for soot abatement; microwave-assisted processes; hydrogen production; structured catalysts preparation and characterization; non-thermal plasma; steam reforming; dry reforming; water gas shift
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. José Carlos Magalhães Pires
Dr. José Carlos Magalhães Pires
 Dr. José Carlos Magalhães Pires
Dr. José Carlos Magalhães Pires
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
LEPABE—Laboratory for Process Engineering, Environment, Biotechnology and Energy, Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias, 4200-465 Porto, Portugal
Interests: CO
2 capture; wastewater treatment; microalgal biofuels; process modelling
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Juri Belikov
Dr. Juri Belikov
 Dr. Juri Belikov
Dr. Juri Belikov
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Software Science, School of Information Technologies, Tallinn University of Technology, Akadeemia tee 15a, 12618 Tallinn, Estonia
Interests: nonlinear control systems; power systems; renewable energy; computational intelligence
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Iva Ridjan Skov
Dr. Iva Ridjan Skov
 Dr. Iva Ridjan Skov
Dr. Iva Ridjan Skov
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
The Technical Faculty of IT and Design Sustainable Energy Planning Research Group, Aalborg University, 2450 Copenhagen, Denmark
Interests: electrofuels; power-to-x; carbon capture and utilization; smart energy systems; renewable energy sources
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Giorgio Vilardi
Dr. Giorgio Vilardi
 Dr. Giorgio Vilardi
Dr. Giorgio Vilardi
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Chemical Engineering Materials Environment, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
Interests: process intensification; methanation; P2G; exergy; industrial and environmental catalysis; nano-catalysts production; adsorption; plant units design and modeling; process development and scale-up; dynamic modeling; wastewater treatment
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Antonio Zuorro
Prof. Dr. Antonio Zuorro
 Prof. Dr. Antonio Zuorro
Prof. Dr. Antonio Zuorro
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Chemical Engineering, Materials & Environment, Sapienza – University of Rome, Via Eudossiana 18, 00184 Rome, Italy
Interests: advanced oxidation processes; green processes; agroindustrial waste valorization; biochemical engineering; microalgae; pesticide removal; wastewater treatment; value-added compounds
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Energy and environmental applications are acquiring an increasing importance. Energy and the environment are indispensable for sustainable development. The demand for environmental resources, especially water, food, and fuels, has grown enormously as population growth and consumption rates have increased dramatically.
The attention of the scientific community is already focused on these topics, and the increasing number of research papers present in the literature indicates their importance.
This Topical Collection is focused on “Review papers in Energy and Environment”, featuring the state-of-the-art in this field. Reviews related to all aspects of green energy and the environment, such as biofuel and bioenergy, energy storage and networks, catalysis for sustainable processes, and materials for energy and the environment are welcome to this Topical Collection.
Dr. Eugenio Meloni
Dr. Alberto-Jesus Perea-Moreno
Dr. José Carlos Magalhães Pires
Dr. Juri Belikov
Dr. Iva Ridjan Skov
Dr. Giorgio Vilardi
Prof. Dr. Antonio Zuorro
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Hydrogen storage and (bio)hydrogen production
- Biofuel and bioenergy
- Catalysis for sustainable processes
- Clean processing and utilization of fossil resources
- Climate change and pollution control
- CO2 capture, storage, and utilization
- Energy storage and network
- Green solvents for energy conversion
- Hydrogen energy and fuel cells
- Life cycle analysis
- Materials for energy and environment
- Simulation in energy and environment
- Solar energy and photovoltaics
- Electrification of chemical processes
- Energy management for water
- Zero-energy buildings
- Wind energy
- Legislations, regulations, and standards of energy
- Microalgal biofuels
- Biosequestration of greenhouse gases
- Negative emissions technologies
- Electrofuels
- Power-to-x fuels
- Process simulation and dynamics
- Circular and green economy
- Zero-liquid-discharge plants
- Process intensification and integration
- Green process development
- Waste-to-chemicals
- Waste-to-energy
- Wastewater/wastegas treatment
- Waste-to-syngas
Published Papers (32 papers)
Open AccessReview
A Review Analysis of Electricity Generation Studies with Social Life Cycle Assessment
by
Georgios Archimidis Tsalidis, Maria Batsioula, George F. Banias and Evina Katsou
Viewed by 770
Abstract
This review explores the social impacts of electricity production by applying the framework of Social Life Cycle Assessment (S-LCA). The authors adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines to select studies that were published post-2010 and used S-LCA
[...] Read more.
This review explores the social impacts of electricity production by applying the framework of Social Life Cycle Assessment (S-LCA). The authors adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines to select studies that were published post-2010 and used S-LCA in the context of various electricity sources, including bioelectricity, solar, wind, and hydropower. The search yielded 13 eligible studies that employed both generic and site-specific assessment strategies, primarily relying on the Social Hotspot Database and Product Social Impact Life Cycle Assessment database for generic evaluations. The findings emphasize the Workers stakeholder as the most frequently examined, with significant attention also given to the Local Community, Society, Value Chain Actors, and Consumer stakeholders when social databases are employed. The studies primarily assessed socioeconomic impact subcategories related to labor practices, health and safety, and economic contributions, as well as a tailored set of self-developed social impacts and indicators specific to the energy sources and geographical contexts examined. This review demonstrates the crucial role of S-LCA in revealing the socio-economic impacts of electricity generation and the need to consider the impacts on Local Community and Society stakeholders through site-specific assessments. Such insights are crucial for guiding policy reforms and industry practices towards more socially responsible energy production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Optimization of Energy Consumption in a Wastewater Treatment Plant: An Overview
by
Nikolaos Tsalas, Spyridon K. Golfinopoulos, Stylianos Samios, Georgios Katsouras and Konstantinos Peroulis
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2471
Abstract
Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, a cornerstone of environmental health for thriving biodiversity and undisturbed natural processes. This balance is crucial for the sustainability of ecosystems, directly influencing human health, biodiversity, and the overall quality of
[...] Read more.
Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, a cornerstone of environmental health for thriving biodiversity and undisturbed natural processes. This balance is crucial for the sustainability of ecosystems, directly influencing human health, biodiversity, and the overall quality of our natural environment. WWTPs contribute to this equilibrium by efficiently removing pollutants and harmful substances from wastewater, thus averting the degradation of water bodies that are essential for numerous ecological processes. WWTPs encompass multiple stages of wastewater and sludge treatment and are significant energy consumers globally, especially in secondary treatment, particularly the activated sludge method which is the most common method. With an upcoming directive from the European Union aiming to reduce energy consumption in WWTPs, this paper focuses on a literature review examining global practices implemented across all stages of WWTP treatment processes. It summarizes the key points of each study, focusing primarily on the outcomes of each application. This document concludes with an in-depth review of each study and provides general conclusions for each group of studies. The objective is to identify methods that have effectively reduced energy consumption and enhanced the overall energy efficiency of WWTPs. The main conclusions indicate that the studies encompass a wide range of applications that achieve significant reductions in energy consumption. However, additional testing of these applications in more diverse operating environments through trials could further enhance their reliability and increase acceptance among WWTP operators.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Integrated Underground Analyses as a Key for Seasonal Heat Storage and Smart Urban Areas
by
Dimitra Rapti, Francesco Tinti and Carlo Antonio Caputo
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 681
Abstract
The design and performance of a shallow geothermal system is influenced by the geological and hydrogeological context, environmental conditions and thermal demand loads. In order to preserve the natural thermal resource, it is crucial to have a balance between the supply and the
[...] Read more.
The design and performance of a shallow geothermal system is influenced by the geological and hydrogeological context, environmental conditions and thermal demand loads. In order to preserve the natural thermal resource, it is crucial to have a balance between the supply and the demand for the renewable energy. In this context, this article presents a case study where an innovative system is created for the storage of seasonal solar thermal energy underground, exploiting geotechnical micropiles technology. The new geoprobes system (energy micropile; EmP) consists of the installation of coaxial geothermal probes within existing micropiles realized for the seismic requalification of buildings. The underground geothermal system has been realized, starting from the basement of an existing holiday home Condominium, and was installed in dry subsoil, 20 m-deep below the parking floor. The building consists of 140 apartments, with a total area of 5553 m
2, and is located at an altitude of about 1490 m above sea level. Within the framework of a circular economy, energy saving and the use of renewable sources, the design of the geothermal system was based on geological, hydrogeological and thermophysical analytical studies, in situ measurements (e.g., Lefranc and Lugeon test during drilling; Rock Quality Designation index; thermal response tests; acquisition of temperature data along the borehole), numerical modelling and long-term simulations. Due to the strong energy imbalance of the demand from the building (heating only), and in order to optimize the underground annual balance, both solar thermal storage and geothermal heat extraction/injection to/from a field of 380 EmPs, with a relative distance varying from 1 to 2 m, were adopted. The integrated solution, resulting from this investigation, allowed us to overcome the standard barriers of similar geological settings, such as the lack of groundwater for shallow geothermal energy exploitation, the lack of space for borehole heat exchanger drilling, the waste of solar heat during the warm season, etc., and it can pave the way for similar renewable and low carbon emission hybrid applications as well as contribute to the creation of smart buildings/urban areas.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Future Distribution Networks: A Review
by
Zahid Javid, Ilhan Kocar, William Holderbaum and Ulas Karaagac
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1625
Abstract
This manuscript presents a comprehensive review of recent advancements in electrical distribution networks, with a specific focus on the incorporation of direct current (DC) applications. The research aims to comprehensively address the current and future aspects of DC, spanning from the distribution level
[...] Read more.
This manuscript presents a comprehensive review of recent advancements in electrical distribution networks, with a specific focus on the incorporation of direct current (DC) applications. The research aims to comprehensively address the current and future aspects of DC, spanning from the distribution level to the utilization level. The renewed interest in DC power systems has led to the investigation of several transitional challenges in recent years. A significant portion of these efforts has been dedicated to determining the feasibility of applying DC to specific use cases. Additionally, the literature has explored design considerations such as system architecture and voltage levels, the integration of DC into existing distribution networks, load flow (LF) computations, and the distinct safety concerns associated with DC power systems. In this paper, the various research endeavors are categorized, evaluated, and scrutinized to assess the current state of the transition from a purely alternating current (AC) distribution system to a solely DC or hybrid AC/DC distribution system. A bibliometric analysis is conducted, constructing a network of co-occurrence based on author-provided keywords, which reveals the primary research foci in this domain. The barriers hindering the widespread adoption of DC distribution systems and potential solutions are also discussed. Moreover, this article synthesizes ongoing efforts to address these obstacles and delineates future research directions by emphasizing the existing knowledge gaps.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Methods for Quantifying Expansion in Lithium-Ion Battery Cells Resulting from Cycling: A Review
by
Tessa Krause, Daniel Nusko, Luciana Pitta Bauermann, Matthias Vetter, Marcel Schäfer and Carlo Holly
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2548
Abstract
Significant efforts are being made across academia and industry to better characterize lithium ion battery cells as reliance on the technology for applications ranging from green energy storage to electric mobility increases. The measurement of short-term and long-term volume expansion in lithium-ion battery
[...] Read more.
Significant efforts are being made across academia and industry to better characterize lithium ion battery cells as reliance on the technology for applications ranging from green energy storage to electric mobility increases. The measurement of short-term and long-term volume expansion in lithium-ion battery cells is relevant for several reasons. For instance, expansion provides information about the quality and homogeneity of battery cells during charge and discharge cycles. Expansion also provides information about aging over the cell’s lifetime. Expansion measurements are useful for the evaluation of new materials and the improvement of end-of-line quality tests during cell production. These measurements may also indicate the safety of battery cells by aiding in predicting the state of charge and the state of health over the lifetime of the cell. Expansion measurements can also assess inhomogeneities on the electrodes, in addition to defects such as gas accumulation and lithium plating. In this review, we first establish the mechanisms through which reversible and irreversible volume expansion occur. We then explore the current state-of-the-art for both contact and noncontact measurements of volume expansion. This review compiles the existing literature on four approaches to contact measurement and eight noncontact measurement approaches. Finally, we discuss the different considerations when selecting an appropriate measurement technique.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Mapping Global Research on Green Energy and Green Investment: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Study
by
Aleksy Kwilinski
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1137
Abstract
The spillover effects of climate change require the exploration and implementation of appropriate ways to reduce ecological issues while simultaneously maintaining economic and social well-being. The expansion of green energy allows for a reduction in the negative anthropogenic impact on the environment without
[...] Read more.
The spillover effects of climate change require the exploration and implementation of appropriate ways to reduce ecological issues while simultaneously maintaining economic and social well-being. The expansion of green energy allows for a reduction in the negative anthropogenic impact on the environment without restricting economic growth or social welfare. However, the expansion of green energy necessitates additional green investment. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of studies on the interactions between green energy and green investment. The study is based on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and employs Scopus Tools Analysis and VOSviewer version 1.6.20 software. The metadata for the investigation were compiled from scientific databases in Scopus. The findings allow for the identification of the most prolific countries and authors and their collaborative efforts, which contribute to the theoretical landscape of green energy and green investment. The study also illustrates the evolution of the investigation of the linkages between green energy and green investment. Furthermore, the results enable the identification of core scientific clusters in the analysis of green energy and green investment: the first cluster focuses on renewable energy and sustainable development; the second on government and green energy; and the third on green investment as the catalyst for green energy. The results of the meta-analysis facilitate the identification of new research areas related to the connection between green investment and green energy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Energizing the Now: Navigating the Critical Landscape of Today’s Energy Challenges—An In-Depth Review
by
Catalin Popescu, Simona Andreea Apostu, Irina Gabriela Rădulescu, Jianu Daniel Mureșan and Alina Gabriela Brezoi
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1475
Abstract
Today’s energy challenges are multifaceted. Over the past 30–40 years, energy issues have been discussed and published on an extensive scale. The green transition involves concrete actions related to increasing energy efficiency, replacing fossil fuels with alternative fuels, producing energy using renewable resources,
[...] Read more.
Today’s energy challenges are multifaceted. Over the past 30–40 years, energy issues have been discussed and published on an extensive scale. The green transition involves concrete actions related to increasing energy efficiency, replacing fossil fuels with alternative fuels, producing energy using renewable resources, creating various means of transport that use electric motors, identifying technical solutions that generate an increased energy yield in the case of buildings, and waste reduction, reuse and recycling. In order to attain a climate-neutral environment, it is mandatory to impose regulations, measures and actions to help decarbonize the energy sector. The analysis of published articles on these issues is the subject of this large and information-dense review. Concretely, the transition to climate neutrality will generate obvious advantages at an economic, social and technological level, for example, the opportunity for economic growth, new business models and new markets, and the generation of new jobs or technological development. At the same time, this paper underscores the need for a multifaceted approach, integrating technological innovation, policy intervention and global cooperation for an effective energy transformation. The review suggests future issues and research directions, focusing on viable strategies for energy transition and its socio-economic environmental impacts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Fundamentals, Operation and Global Prospects for the Development of Biogas Plants—A Review
by
Gulnar Gadirli, Agnieszka A. Pilarska, Jacek Dach, Krzysztof Pilarski, Alicja Kolasa-Więcek and Klaudia Borowiak
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2698
Abstract
As the global demand for renewable energy continues to rise, biogas production has emerged as a promising solution for sustainable energy generation. This review article presents the advantages of biogas technologies (mainly agricultural, based on waste of animal and plant origin) and extensively
[...] Read more.
As the global demand for renewable energy continues to rise, biogas production has emerged as a promising solution for sustainable energy generation. This review article presents the advantages of biogas technologies (mainly agricultural, based on waste of animal and plant origin) and extensively discusses the main principles of biogas production in the anaerobic digestion (AD). In this respect, the main parameters of the process, which require monitoring and decisive for its efficiency are described, therefore: temperature, pH value, retention time and organic loading rate (OLR). The principles of substrate selection are also discussed and the necessity and advantages of the use of organic waste according to the model of a circular economy and the concept of sustainable development, are indicated. It is emphasized that according to the new European regulations, the crops classified as food cannot be considered energy crops. The part on biogas production is summarised with an explanation of the necessity to treat and purify biogas. Biogas purification is important from the point of view of the efficiency of its conversion into electricity. A special place in this paper is devoted to the design, construction, functioning and operation of biogas plants, based on both scientific and practical aspects. In conclusion of this chapter, the economic aspects and profitability of operating biogas plants are discussed. Cost and benefit analyses are the major tool used for the systematic evaluation of the financial costs and potential benefits associated with the operation of biogas plants. The important fact is that the return on investment can be achieved within a few years, provided the activities are well-planned and executed. In addition to the fundamental issues of the operation of biogas plants, this article presents the global situation regarding the development of biogas plants, discussing in detail the specific needs and limitations on different continents. It is a interesting and extensive part of this article. The global agricultural biogas market is at very different levels of development. Most such installations are located in Asia and Europe. China has the highest number of biogas plants, with more than 100,000 biogas plants, followed by Germany with over 10,000 plants. In addition to the 100,000 biogas plants, China also has a large number of household biogas units, which gives a total of approx. 40 million operating units. The article concludes with a discussion of opportunities and barriers to the development of biogas plants, pointing to: financial issues, access to feedstock, political regulations, public awareness and the geopolitical situation. The most frequently cited reasons for investment failure include economic problems, lack of professional knowledge.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
State-of-the-Art and Recent Advances in the Abatement of Gaseous Pollutants from Waste-to-Energy
by
Marco Schiavon, Marco Ravina, Mariachiara Zanetti and Deborah Panepinto
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1417
Abstract
Despite their key role in integrated waste management, direct (incineration) and indirect (gasification/pyrolysis) waste combustion processes are still opposed by some of the general public due to the past emission levels of air pollutants. In fact, although the release of air pollutants (especially
[...] Read more.
Despite their key role in integrated waste management, direct (incineration) and indirect (gasification/pyrolysis) waste combustion processes are still opposed by some of the general public due to the past emission levels of air pollutants. In fact, although the release of air pollutants (especially dioxin) to the atmosphere from waste combustion processes has gradually decreased over the years, thanks to the introduction of stricter regulations and more advanced removal technologies, there is still an unsolved problem regarding the public acceptance of waste-to-energy facilities. The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of the state-of-the-art air pollution control (APC) technologies used in waste combustion facilities. Air pollution control technologies are designed to reduce or eliminate the emissions of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. These technologies are important for safeguarding public health, protecting ecosystems, complying with regulations, and promoting a more sustainable and resilient future for both local and global communities. This paper will highlight the complexity behind emission control and the efforts made by this sector over the years. This paper will also propose suggested configurations based on the interactions/complementarity between different APC technologies and recent findings to improve their performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Critical Review of the Environmental Performance of Bifacial Photovoltaic Panels
by
Manfredi Picciotto Maniscalco, Sonia Longo, Gabriele Miccichè, Maurizio Cellura and Marco Ferraro
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1864
Abstract
Bifacial photovoltaic (BPV) panels represent one of the main solar technologies that will be used in the near future for renewable energy production, with a foreseen market share in 2030 of 70% among all the photovoltaic (PV) technologies. Compared to monofacial panels, bifaciality
[...] Read more.
Bifacial photovoltaic (BPV) panels represent one of the main solar technologies that will be used in the near future for renewable energy production, with a foreseen market share in 2030 of 70% among all the photovoltaic (PV) technologies. Compared to monofacial panels, bifaciality can ensure a gain in energy production per unit panel area together with a competitive cost. However, it is of paramount importance to identify whether there is also an environmental benefit when adopting bifacial technologies as opposed to traditional monofacial ones. To obtain a proper insight into the environmental impact, this paper reviews the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies of bifacial solar panels, identifying the most crucial processes and materials that raise environmental burdens. The analysis also contributes to determining whether the major aspects that influence energy production in real operation scenarios and, most of all, that can ensure the gain associated with bifaciality, are considered and how these can further affect the overall environmental impacts. In this sense, it was found that the installation parameters like the mounting structure, or the choice of ground material to raise the albedo as well as the diffuse irradiation that hits the rear surface of thepanel, are commonly not considered during LCA analysis. However, none of the analyzed studies address the issue in a comprehensive way, hampering an effective comparison between both the different works and traditional monofacial PV panels. Recommendations for future LCAs are finally proposed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
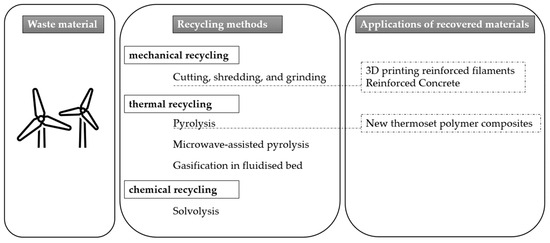
Unlocking the Potential of Wind Turbine Blade Recycling: Assessing Techniques and Metrics for Sustainability
by
Sandra Sorte, Nelson Martins, Mónica S. A. Oliveira, German L. Vela and Carlos Relvas
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2681
Abstract
The rapid growth of the wind energy industry has resulted in a significant increase in Wind Turbine Blade (WTB) waste, posing challenges for recycling due to the composite materials used in their construction. Several proposed techniques, including mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes, have
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth of the wind energy industry has resulted in a significant increase in Wind Turbine Blade (WTB) waste, posing challenges for recycling due to the composite materials used in their construction. Several proposed techniques, including mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes, have been considered for wind-blade recycling, but determining the most effective approach remains a critical issue. This study presents the first comprehensive systematic review of available wind-blade recycling processes, evaluating their economic, technical, and environmental performance. Additionally, we consider the physical and mechanical properties of the recycled materials, which can aid in identifying potential markets for these materials. Among the various recycling technologies, microwave pyrolysis emerges as the most promising technique for recycling large quantities of WTB, despite some challenges and uncertainties surrounding its effectiveness and feasibility at an industrial scale. However, the optimal recycling technique for WTB will depend on multiple factors, including the blade material, the desired environmental impact, and the economic feasibility of the process. Based on this review, mechanical recycling appears to be more energy-efficient, while the fluidised bed recycling process demonstrates a lower primary energy demand, global warming potential, and power consumption. These findings provide valuable guidance for decision-makers in the wind energy industry to develop effective waste management strategies and plans for sustainable wind energy development. Addressing WTB waste and implementing efficient recycling techniques will be critical in mitigating environmental impacts and promoting sustainability in the renewable energy sector as the wind energy industry grows.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
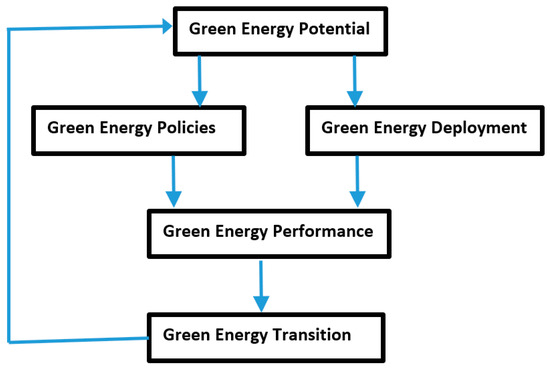
A Review and Analysis of Green Energy and the Environmental Policies in South Asia
by
Hassan Qudrat-Ullah
Viewed by 1421
Abstract
This paper explores the challenges and opportunities for green energy and environment transition in South Asia, a region that faces the dilemma of meeting its growing energy demand while reducing its greenhouse gas emissions and environmental vulnerability. The region has rich renewable energy
[...] Read more.
This paper explores the challenges and opportunities for green energy and environment transition in South Asia, a region that faces the dilemma of meeting its growing energy demand while reducing its greenhouse gas emissions and environmental vulnerability. The region has rich renewable energy sources and potential for energy efficiency improvement, but it also relies heavily on fossil fuels and suffers from various barriers and constraints that hinder its green energy development. The region needs policies that can achieve economic growth, social welfare, and environmental sustainability coherently and effectively. Utilizing the thematic literature review approach, this paper examines the literature on four main topics: (1) the estimation of green energy resources potential and scenarios in South Asia; (2) the comparison of green energy targets and policies in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) countries; (3) the evaluation of green energy deployment and performance in different sectors; and (4) the identification of green energy transition challenges and opportunities in South Asia. This paper fills some research gaps in the literature by providing a comprehensive, comparative, holistic, and integrated analysis of green energy and environment policies in South Asia, using various data sources, methods, frameworks, criteria, indicators, scenarios, impacts, trade-offs, drivers, barriers, best practices, lessons learned, and policy recommendations. This paper also develops a conceptual model for the green energy transition in South Asia, which consists of five key variables: green energy potential, green energy policies, green energy deployment, green energy performance, and green energy transition. The main findings and implications of this paper are that South Asia has a huge opportunity to pursue a green energy and environment transition that can address its multiple challenges and aspirations, but this requires overcoming various obstacles and constraints that hinder its progress. This paper suggests some policy options and strategies to enhance the green energy and environment policies in South Asia, such as developing a clear and consistent policy framework, enhancing regional cooperation and collaboration, leveraging information technology and data analytics, emphasizing sustainability and resilience, and engaging with other stakeholders and partners.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Comprehensive Review of a Decade of Field PV Soiling Assessment in QEERI’s Outdoor Test Facility in Qatar: Learned Lessons and Recommendations
by
Brahim Aïssa, Rima J. Isaifan, Benjamin W. Figgis, Amir A. Abdallah, Dunia Bachour, Daniel Perez-Astudillo, Antonio Sanfilippo, Juan Lopez-Garcia and Veronica Bermudez Benito
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 1936
Abstract
Soiling of photovoltaic (PV) modules is a major issue due to its critical impact on PV performance and reliability, especially in the desert and arid regions such as the state of Qatar. Soiling frequently results in a severe reduction in PV power generation,
[...] Read more.
Soiling of photovoltaic (PV) modules is a major issue due to its critical impact on PV performance and reliability, especially in the desert and arid regions such as the state of Qatar. Soiling frequently results in a severe reduction in PV power generation, which drastically affects the economical profitability of the PV plant, and therefore, must be mitigated. The most common way of mitigating PV soiling is surface cleaning. However, the latter could consequently increase the associated operation and maintenance (O&M) cost of the PV site. However, previous studies indicated that even if the best-optimized cleaning schemes are used, the actual global solar-power production can still be reduced by about 4%, which is associated with at least EUR 5 billion in annual revenue losses worldwide. This loss is expected to reach a conservative value of EUR 7 billion in 2023. Accordingly, investigating the interplayed physics phenomena related to the various soiling processes, the site-specific O&M costs, along with a techno-economical assessment of state-of-the-art soiling mitigation strategies (including innovative anti-soiling coating materials) is of paramount importance. The goal of this comprehensive report is to provide the solar community at large, and those focusing on the desert environment in particular, with real field measurements that provide key findings and challenges in addressing soiling research obtained from multiyear testing at the Outdoor Test Facility (OTF) field station, located in the desert environment of the city of Doha, in the state of Qatar.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A State-of-the-Art Review of Structural Testing of Tidal Turbine Blades
by
Tenis Ranjan Munaweera Thanthirige, Jamie Goggins, Michael Flanagan and William Finnegan
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2474
Abstract
Over the last two decades, the tidal energy industry has laid the groundwork for creating commercially viable tidal power generation projects to strengthen sustainable energy policies around the world. At the end of 2021, the cumulative installation of tidal stream technology that has
[...] Read more.
Over the last two decades, the tidal energy industry has laid the groundwork for creating commercially viable tidal power generation projects to strengthen sustainable energy policies around the world. At the end of 2021, the cumulative installation of tidal stream technology that has been deployed in Europe reached 30.2 MW, where the majority of the installations are by small and medium-sized companies. Due to a growing demand among investors related to the global tidal energy industry, the reliability and safety of operational-stage tidal energy systems’ components are becoming increasingly important. In this context, companies, universities and research institutes are focusing on conducting large- and small-scale tests of tidal turbine elements to validate their projected design life, and major attention is being given to assessing the structural integrity of turbine blades. This review paper focuses on structural tests that have been reported for axial flow tidal turbine blades manufactured using composite materials around the world, highlighting the testing standards, equipment and instrumentation required. Overall, this review article discusses the state of the art in the structural testing of tidal turbine blades. In addition, it highlights the global concerns and research gaps to ensure the long-term sustainability of axial flow tidal turbine blades. In addition, the information contained in this article will be useful for formulating a smooth and reliable mechanism to enhance the evaluation process of the structural properties of tidal turbine blades in the future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Actualization and Adoption of Renewable Energy Usage in Remote Communities in Canada by 2050: A Review
by
Obiora S. Agu, Lope G. Tabil and Edmund Mupondwa
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3603
Abstract
Remote community initiatives for renewable energy are rapidly emerging across Canada but with varying numbers, success rates, and strategies. To meet low-carbon transition goals, the need to coordinate technology deployment and long-term policy to guide the adoption is critical. Renewable resources such as
[...] Read more.
Remote community initiatives for renewable energy are rapidly emerging across Canada but with varying numbers, success rates, and strategies. To meet low-carbon transition goals, the need to coordinate technology deployment and long-term policy to guide the adoption is critical. Renewable resources such as wind, solar, hydro, and biomass can provide energy at a subsidized cost, create sustainable infrastructure, and provide new economic viability in social value integration. The renewable energy transition is crucial to Canada in sustaining remote and indigenous communities by providing local, clean, and low-carbon-emission energy for heat, power, and possibly transportation. This paper identified 635 renewable resources projects deployed to improve and increase electricity supply. To an extent, balancing demand within the remote and indigenous communities of Canada and highlighting sustainable renewable energy development through ownership participation within the communities is achievable before 2050 and beyond through energy efficiency and the social value of energy. The article identifies clean energy targets as mandated by the different provinces in Canada to reach net-zero GHG emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Heterogeneous Catalytic Conversion of Terpenes into Biofuels: An Open Pathway to Sustainable Fuels
by
Magín Lapuerta, Indira Tobío-Pérez, Marianela Ortiz-Alvarez, David Donoso, Laureano Canoira and Ramón Piloto-Rodríguez
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2814
Abstract
The production and use of terpene-based fuels represents a renewable source of energy in the transportation sector, especially in the aviation sector. The literature on the conversion of terpenes into valuable compounds is not new but has been based on the production of
[...] Read more.
The production and use of terpene-based fuels represents a renewable source of energy in the transportation sector, especially in the aviation sector. The literature on the conversion of terpenes into valuable compounds is not new but has been based on the production of products for cosmetics and pharmaceutics. Several established chemical routes are also a way to develop drop-in fuels. The present work explores all the main chemical processes that can transform terpenes into more valuable fuels or additives, focusing on the use of heterogeneous catalysis, catalyst type, operating conditions, and reaction performance.
α-pinene is the most studied catalyst, since it is the main component of turpentine. Isomerization is the most frequently applied chemical pathway used to enhance fuel properties, and a wide group of heterogeneous catalysts have been reported, with sulphonic acid resin catalysts, transition metals, alumina, and silicates being the most used. This work also explores the current production and commercialization of terpenes, as well as the challenges for their use as fuels at a commercial scale. The future challenge is to discover new catalysts or to improve the performance of the current products and reduce production costs. The feasibility of the production and commercialization of terpene-derived fuels is also linked to oil prices.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
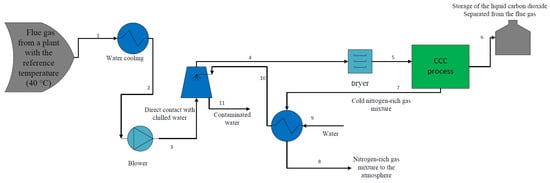
A Review on Process Modeling and Simulation of Cryogenic Carbon Capture for Post-Combustion Treatment
by
Hossein Asgharian, Florin Iov, Samuel Simon Araya, Thomas Helmer Pedersen, Mads Pagh Nielsen, Ehsan Baniasadi and Vincenzo Liso
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2992
Abstract
The cryogenic carbon capture (CCC) process is a promising post-combustion CO
2 removal method. This method is very novel compared with conventional and well-developed methods. However, cryogenic carbon capture is not yet commercially available despite its techno-economic benefits. Thus, a model-based design approach
[...] Read more.
The cryogenic carbon capture (CCC) process is a promising post-combustion CO
2 removal method. This method is very novel compared with conventional and well-developed methods. However, cryogenic carbon capture is not yet commercially available despite its techno-economic benefits. Thus, a model-based design approach for this process can provide valuable information. This paper will first introduce the cryogenic carbon capture process. Then, a comprehensive literature overview that focuses on different methods for modeling the process at the component level will be given. The modelling methods which are deemed most effective are presented more in depth for each of the key system components. These methods are compared with each other in terms of complexity and accuracy and the simplest methods with an acceptable level of precision for modelling a specific component in the CCC process are recommended. Furthermore, potential research areas in modeling and simulation of the CCC process are also highlighted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
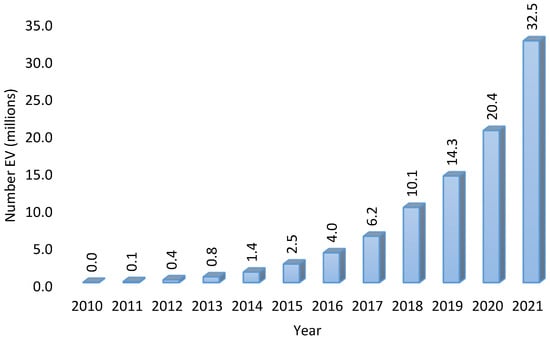
Open AccessReview
Control Strategies of Electric Vehicles Participating in Ancillary Services: A Comprehensive Review
by
Adlan Pradana, Mejbaul Haque and Mithulanathan Nadarajah
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3352
Abstract
With the emergence of the electric vehicle (EV) era in which the vehicle’s embedded batteries can be exploited for grid support purposes, the role of EVs participating in ancillary services via vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology cannot be disregarded. Although there are many forms of
[...] Read more.
With the emergence of the electric vehicle (EV) era in which the vehicle’s embedded batteries can be exploited for grid support purposes, the role of EVs participating in ancillary services via vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology cannot be disregarded. Although there are many forms of ancillary services, the most common services delivered by EVs are frequency regulation, frequency contingency, inertia, and voltage regulation. Numerous research studies have been conducted to propose the most effective control strategies for electric vehicle ancillary services (EVASs). In this paper, a comprehensive review is carried out on various control strategies for EVs with respect to their participation in ancillary services. The methodology applied for this review comprises a combination of thematic and historical reviews. The review explores the benefits and limitations of these control strategies and provides a clear understanding of the research gaps in the EVAS area. This review will provide a useful framework and a strong point of reference for researchers working in V2G controls for providing EVASs to a grid. V2G will be a way forward for future grids to accommodate more renewable resources and achieve sustainability pathways.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
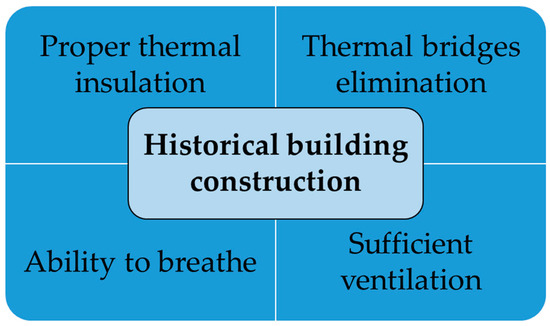
Open AccessReview
Microclimatic Monitoring—The Beginning of Saving Historical Sacral Buildings in Europe
by
Michal Poljak and Radoslav Ponechal
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2167
Abstract
A suitable indoor climate positively affects the lifespan of historical building structures. The path to an agreeable climate begins with monitoring current conditions. Considerable attention is given to monitoring the indoor climate of historical buildings. The motivation for monitoring air temperature and surface
[...] Read more.
A suitable indoor climate positively affects the lifespan of historical building structures. The path to an agreeable climate begins with monitoring current conditions. Considerable attention is given to monitoring the indoor climate of historical buildings. The motivation for monitoring air temperature and surface temperatures, relative air humidity or airflow can be, for example, the installation of heating, the occurrence of biotic damage, and others. Through the analysis of the most frequently used keywords, a strong connection was found, for example, between thermal comfort and the church. This review also summarises the various reasons for conducting microclimate monitoring studies in historical religious buildings on the European continent. It is supplemented with an evaluation of the monitoring methodology from the chosen period of the year point of view, the measured parameters, and the length of the interval between the recordings of quantities. It was found that in more than one-third of the cases, the recording time was less than or equal to 15 min, but mostly less than or equal to 1 h. Quite often, monitoring results are used to calibrate a simulation model describing the hydrothermal behaviour of a historical object under various operation alternatives (e.g., influence of ventilation, climate change, occupancy, etc.). This way, it is possible to test various intelligent systems in the virtual world without much risk before they are used in an actual building application.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Wastewater as a Renewable Energy Source—Utilisation of Microbial Fuel Cell Technology
by
Renata Toczyłowska-Mamińska and Mariusz Ł. Mamiński
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3816
Abstract
An underappreciated source of renewable energy is wastewater, both municipal and industrial, with global production exceeding 900 km
3 a year. Wastewater is currently perceived as a waste that needs to be treated via energy-consuming processes. However, in the current environmental nexus, traditional
[...] Read more.
An underappreciated source of renewable energy is wastewater, both municipal and industrial, with global production exceeding 900 km
3 a year. Wastewater is currently perceived as a waste that needs to be treated via energy-consuming processes. However, in the current environmental nexus, traditional wastewater treatment uses 1700–5100 TWh of energy on a global scale. The application of modern and innovative treatment techniques, such as microbial fuel cells (MFC), would allow the conversion of wastewater’s chemical energy into electricity without external energy input. It has been demonstrated that the chemically bound energy in globally produced wastewater exceeds 2.5 × 10
4 TWh, which is sufficient to meet Europe’s annual energy demand. The aim of this paper is to answer the following questions. How much energy is bound in municipal and industrial wastewaters? How much of that energy can be extracted? What benefits will result from alternative techniques of waste treatment? The main finding of this report is that currently achieved energy recovery efficiencies with the use of microbial fuel cells technology can save about 20% of the chemical energy bound in wastewater, which is 5000 TWh on a global scale. The recovery of energy from wastewater via MFC technology can reach as much as 15% of global energy demands.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
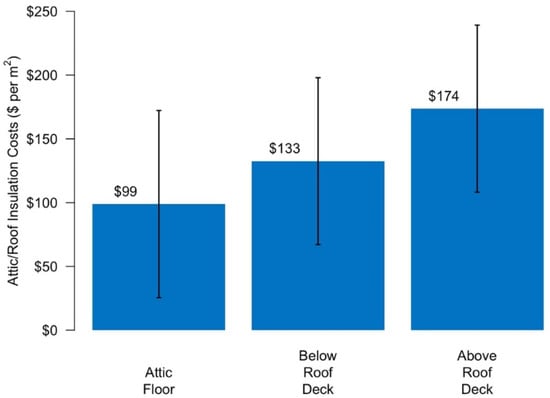
Home Energy Upgrades as a Pathway to Home Decarbonization in the US: A Literature Review
by
Brennan D. Less, Núria Casquero-Modrego and Iain S. Walker
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3790
Abstract
This work aims to characterize how home energy upgrade projects and programs in the US have evolved over the past decade. It also identifies what changes are needed to drive expansion of the US energy retrofit market in such a way that addresses
[...] Read more.
This work aims to characterize how home energy upgrade projects and programs in the US have evolved over the past decade. It also identifies what changes are needed to drive expansion of the US energy retrofit market in such a way that addresses carbon emissions from buildings, improves resilience and upgrades the housing stock. This review focuses on whole-home energy upgrades, targeting deep energy retrofit savings of >30%. The topics we cover include trends in home electrification, US and European home energy upgrade programs, energy upgrade measure costs, business economics, and health effects. Key changes in project design noted in this review include: (1) the electrification of dwellings with rapidly improving heat pump systems and low-cost solar photovoltaic technology; and (2) a shift away from high-cost building envelope strategies and towards more traditional home performance/weatherization envelope upgrades. Promising program design strategies covered include: (1) end-use electrification programs; (2) novel financing approaches; (3) the use of carbon-based program and project metrics; and (4) “one-stop shop” programs. Based on the existing market barriers, we suggest that the industry should adopt new project performance metrics. Additionally, market drivers are needed to spur widespread energy upgrades in the US housing stock. Costs must be reduced, and projects designed to appeal to homeowners and contractors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
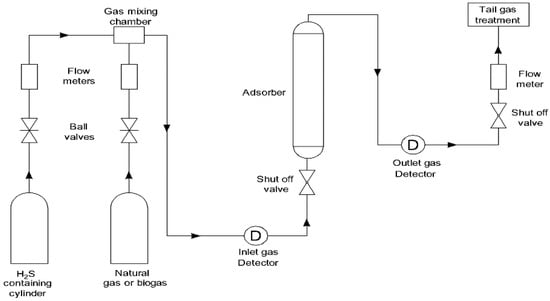
Recent Attempts on the Removal of H2S from Various Gas Mixtures Using Zeolites and Waste-Based Adsorbents
by
Mirzokhid Abdirakhimov, Mohsen H. Al-Rashed and Janusz Wójcik
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3706
Abstract
Natural gas, biogas, and refinery gas all include H
2S, which has adverse effects not only on the environment and human health but also on the equipment and catalysts that are employed in the relevant processes. H
2S is removed from
[...] Read more.
Natural gas, biogas, and refinery gas all include H
2S, which has adverse effects not only on the environment and human health but also on the equipment and catalysts that are employed in the relevant processes. H
2S is removed from the aforementioned gases using a variety of techniques in order to fulfill the necessary sales criteria and for reasons of safety. The adsorption method stands out among various other approaches due to its straightforward operation, high level of efficiency, and low overall cost. This technique makes use of a variety of adsorbents, such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), activated carbon, and zeolites. The use of zeolite-based adsorbents is by far the most common of these various types. This is due to the specific properties of zeolite-based adsorbents, which include a high adsorption capacity, the ability to be regenerated, a high temperature stability, a diversity of types, the possibility of modification, high efficiency, and low cost. In addition, research is being done on adsorbents that are made from inexpensive raw materials in order to remove H
2S. This article focuses on zeolites, zeolite modifications, and wastes as an adsorbent for the removal of H
2S, all of which have been investigated fruitfully in recent years, as well as the promising applications of zeolites.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Are Wetlands as an Integrated Bioremediation System Applicable for the Treatment of Wastewater from Underground Coal Gasification Processes?
by
Jacek Borgulat, Katarzyna Ponikiewska, Łukasz Jałowiecki, Aleksandra Strugała-Wilczek and Grażyna Płaza
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2248
Abstract
Underground coal gasification (UCG) can be considered as one of the clean coal technologies. During the process, the gas of industrial value is produced, which can be used to produce heat and electricity, liquid fuels or can replace natural gas in chemistry. However,
[...] Read more.
Underground coal gasification (UCG) can be considered as one of the clean coal technologies. During the process, the gas of industrial value is produced, which can be used to produce heat and electricity, liquid fuels or can replace natural gas in chemistry. However, UCG does carry some environmental risks, mainly related to potential negative impacts on surface and groundwater. Wastewater and sludge from UCG contain significant amounts of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, phenols, ammonia, cyanides and hazardous metals such as arsenic. This complicated matrix containing high concentrations of hazardous pollutants is similar to wastewater from the coke industry and, similarly to them, requires complex mechanical, chemical and biological treatment. The focus of the review is to explain how the wetlands systems, described as one of bioremediation methods, work and whether these systems are suitable for removing organic and inorganic contaminants from heavily contaminated industrial wastewater, of which underground coal gasification wastewater is a particularly challenging example. Wetlands appear to be suitable systems for the treatment of UCG wastewater and can provide the benefits of nature-based solutions. This review explains the principles of constructed wetlands (CWs) and provides examples of industrial wastewater treated by various wetland systems along with their operating principles. In addition, the physicochemical characteristics of the wastewater from different coal gasifications under various conditions, obtained from UCG’s own experiments, are presented.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Electrified Hydrogen Production from Methane for PEM Fuel Cells Feeding: A Review
by
Eugenio Meloni, Giuseppina Iervolino, Concetta Ruocco, Simona Renda, Giovanni Festa, Marco Martino and Vincenzo Palma
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 4710
Abstract
The greatest challenge of our times is to identify low cost and environmentally friendly alternative energy sources to fossil fuels. From this point of view, the decarbonization of industrial chemical processes is fundamental and the use of hydrogen as an energy vector, usable
[...] Read more.
The greatest challenge of our times is to identify low cost and environmentally friendly alternative energy sources to fossil fuels. From this point of view, the decarbonization of industrial chemical processes is fundamental and the use of hydrogen as an energy vector, usable by fuel cells, is strategic. It is possible to tackle the decarbonization of industrial chemical processes with the electrification of systems. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of the latest research on the electrification of endothermic industrial chemical processes aimed at the production of H
2 from methane and its use for energy production through proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC). In particular, two main electrification methods are examined, microwave heating (MW) and resistive heating (Joule), aimed at transferring heat directly on the surface of the catalyst. For cases, the catalyst formulation and reactor configuration were analyzed and compared. The key aspects of the use of H
2 through PEM were also analyzed, highlighting the most used catalysts and their performance. With the information contained in this review, we want to give scientists and researchers the opportunity to compare, both in terms of reactor and energy efficiency, the different solutions proposed for the electrification of chemical processes available in the recent literature. In particular, through this review it is possible to identify the solutions that allow a possible scale-up of the electrified chemical process, imagining a distributed production of hydrogen and its consequent use with PEMs. As for PEMs, in the review it is possible to find interesting alternative solutions to platinum with the PGM (Platinum Group Metal) free-based catalysts, proposing the use of Fe or Co for PEM application.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
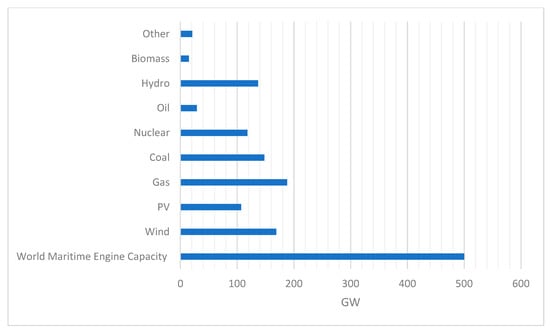
The Maritime Sector and Its Problematic Decarbonization: A Systematic Review of the Contribution of Alternative Fuels
by
Vinicius Andrade dos Santos, Patrícia Pereira da Silva and Luís Manuel Ventura Serrano
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 5133
Abstract
The present study seeks to select the most important articles and reviews from the Web of Science database that approached alternative fuels towards the decarbonization of the maritime sector. Through a systematic review methodology, a combination of keywords and manual refining found a
[...] Read more.
The present study seeks to select the most important articles and reviews from the Web of Science database that approached alternative fuels towards the decarbonization of the maritime sector. Through a systematic review methodology, a combination of keywords and manual refining found a contribution of 103 works worldwide, the European continent accounting for 57% of all publications. Twenty-two types of fuels were cited by the authors, liquefied natural gas (LNG), hydrogen, and biodiesel contributing to 49% of the mentions. Greenhouse gases, sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxide, and particulate matter reductions are some of the main advantages of cleaner sources if used by the vessels. Nevertheless, there is a lack of practical research on new standards, engine performance, cost, and regulations from the academy to direct more stakeholders towards low carbon intensity in the shipping sector.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
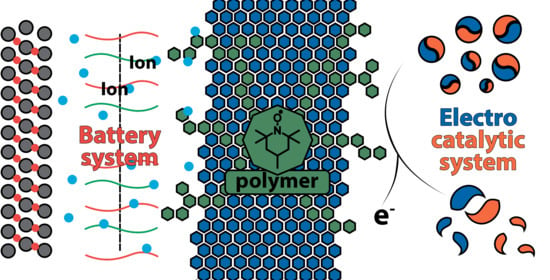
Key Features of TEMPO-Containing Polymers for Energy Storage and Catalytic Systems
by
Anatoliy A. Vereshchagin, Arseniy Y. Kalnin, Alexey I. Volkov, Daniil A. Lukyanov and Oleg V. Levin
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4590
Abstract
The need for environmentally benign portable energy storage drives research on organic batteries and catalytic systems. These systems are a promising replacement for commonly used energy storage devices that rely on limited resources such as lithium and rare earth metals. The redox-active TEMPO
[...] Read more.
The need for environmentally benign portable energy storage drives research on organic batteries and catalytic systems. These systems are a promising replacement for commonly used energy storage devices that rely on limited resources such as lithium and rare earth metals. The redox-active TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl-4-yl) fragment is a popular component of organic systems, as its benefits include remarkable electrochemical performance and decent physical properties. TEMPO is also known to be an efficient catalyst for alcohol oxidation, oxygen reduction, and various complex organic reactions. It can be attached to various aliphatic and conductive polymers to form high-loading catalysis systems. The performance and efficiency of TEMPO-containing materials strongly depend on the molecular structure, and thus rational design of such compounds is vital for successful implementation. We discuss synthetic approaches for producing electroactive polymers based on conductive and non-conductive backbones with organic radical substituents, fundamental aspects of electrochemistry of such materials, and their application in energy storage devices, such as batteries, redox-flow cells, and electrocatalytic systems. We compare the performance of the materials with different architectures, providing an overview of diverse charge interactions for hybrid materials, and presenting promising research opportunities for the future of this area.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
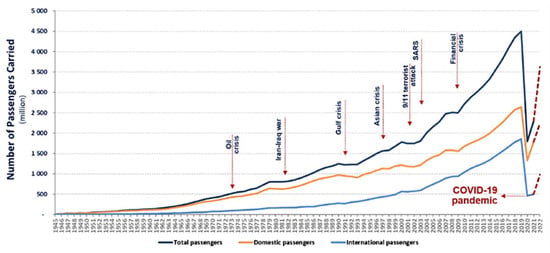
Use of Sustainable Fuels in Aviation—A Review
by
Eduardo Cabrera and João M. Melo de Sousa
Cited by 77 | Viewed by 19374
Abstract
As the push for carbon-neutral transport continues, the aviation sector is facing increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. Furthermore, commercial air traffic is expected to resume the continuous growth experienced until the pandemic, highlighting the need for reduced emissions. The use of
[...] Read more.
As the push for carbon-neutral transport continues, the aviation sector is facing increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. Furthermore, commercial air traffic is expected to resume the continuous growth experienced until the pandemic, highlighting the need for reduced emissions. The use of alternative fuels plays a key role in achieving future emission goals, while also lowering the dependency on fossil fuels. The so-called sustainable aviation fuels (SAF), which encompass bio and synthetic fuels, are currently the most viable option, but hydrogen is also being considered as a long-term solution. The present paper reviews the production methods, logistical and technological barriers, and potential for future mass implementation of these alternative fuels. In general, biofuels currently present higher technological readiness levels than other alternatives. Sustainable mass production faces critical feedstock-related challenges that synthetic fuels, together with other solutions, can overcome. All conventional fuel replacements, though with different scopes, will be important in meeting long-term goals. Government support will play an important role in accelerating and facilitating the transition towards sustainable aviation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Route from Green H2 Production through Bioethanol Reforming to CO2 Catalytic Conversion: A Review
by
Eugenio Meloni, Marco Martino, Giuseppina Iervolino, Concetta Ruocco, Simona Renda, Giovanni Festa and Vincenzo Palma
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 3653
Abstract
Currently, a progressively different approach to the generation of power and the production of fuels for the automotive sector as well as for domestic applications is being taken. As a result, research on the feasibility of applying renewable energy sources to the present
[...] Read more.
Currently, a progressively different approach to the generation of power and the production of fuels for the automotive sector as well as for domestic applications is being taken. As a result, research on the feasibility of applying renewable energy sources to the present energy scenario has been progressively growing, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Following more than one approach, the integration of renewables mainly involves the utilization of biomass-derived raw material and the combination of power generated via clean sources with conventional power generation systems. The aim of this review article is to provide a satisfactory overview of the most recent progress in the catalysis of hydrogen production through sustainable reforming and CO
2 utilization. In particular, attention is focused on the route that, starting from bioethanol reforming for H
2 production, leads to the use of the produced CO
2 for different purposes and by means of different catalytic processes, passing through the water–gas shift stage. The newest approaches reported in the literature are reviewed, showing that it is possible to successfully produce “green” and sustainable hydrogen, which can represent a power storage technology, and its utilization is a strategy for the integration of renewables into the power generation scenario. Moreover, this hydrogen may be used for CO
2 catalytic conversion to hydrocarbons, thus giving CO
2 added value.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
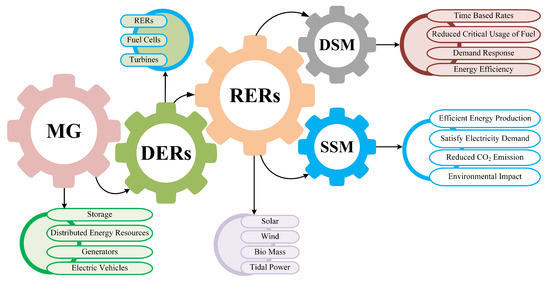
Smart Grid, Demand Response and Optimization: A Critical Review of Computational Methods
by
Ussama Assad, Muhammad Arshad Shehzad Hassan, Umar Farooq, Asif Kabir, Muhammad Zeeshan Khan, S. Sabahat H. Bukhari, Zain ul Abidin Jaffri, Judit Oláh and József Popp
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 11602
Abstract
In view of scarcity of traditional energy resources and environmental issues, renewable energy resources (RERs) are introduced to fulfill the electricity requirement of growing world. Moreover, the effective utilization of RERs to fulfill the varying electricity demands of customers can be achieved via
[...] Read more.
In view of scarcity of traditional energy resources and environmental issues, renewable energy resources (RERs) are introduced to fulfill the electricity requirement of growing world. Moreover, the effective utilization of RERs to fulfill the varying electricity demands of customers can be achieved via demand response (DR). Furthermore, control techniques, decision variables and offered motivations are the ways to introduce DR into distribution network (DN). This categorization needs to be optimized to balance the supply and demand in DN. Therefore, intelligent algorithms are employed to achieve optimized DR. However, these algorithms are computationally restrained to handle the parametric load of uncertainty involved with RERs and power system. Henceforth, this paper focuses on the limitations of intelligent algorithms for DR. Furthermore, a comparative study of different intelligent algorithms for DR is discussed. Based on conclusions, quantum algorithms are recommended to optimize the computational burden for DR in future smart grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Olive Mill Wastewater Valorization through Steam Reforming Using Multifunctional Reactors: Challenges of the Process Intensification
by
Cláudio Rocha, Miguel Angel Soria and Luís M. Madeira
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4024
Abstract
Olive oil mill wastewater (OMW) is a polluting stream derived from the production of olive oil and is a source of environmental pollution; this is relevant in many countries around the world, but particularly in all the Mediterranean region where major producers are
[...] Read more.
Olive oil mill wastewater (OMW) is a polluting stream derived from the production of olive oil and is a source of environmental pollution; this is relevant in many countries around the world, but particularly in all the Mediterranean region where major producers are located. In this effluent, several pollutants are present—namely, sugars, fatty acids, and polyphenols, among others. Nowadays, to reduce the pollutant load, several treatment techniques are applied, but these technologies have numerous cost and efficiency problems. For this reason, the steam reforming of the OMW (OMWSR) presents as a good alternative, because this process decreases the pollutant load of the OMW and simultaneously valorizes the waste with the production of green H
2, which is consistent with the perspective of the circular economy. Currently, the OMWSR is an innovative treatment alternative in the scientific field and with high potential. In the last few years, some groups have studied the OMWSR and used innovative reactor configurations, aiming to improve the process’ effectiveness. In this review, the OMW treatment/valorization processes, the last developments on catalysis for OMWSR (or steam reforming of similar species present in the effluent), as well as the last advances on OMWSR performed in multi-functional reactors are addressed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
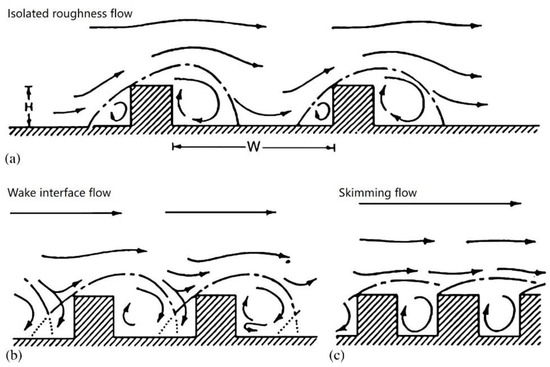
A Review on the Dispersion and Distribution Characteristics of Pollutants in Street Canyons and Improvement Measures
by
Weixun Lv, Yan Wu and Jianbin Zang
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3474
Abstract
The air quality in a street canyon seriously affects the exposure level of pollutants for pedestrians and is directly related to the indoor air quality (IAQ) of surrounding buildings. In order to improve the street canyon environment, it is necessary to clarify the
[...] Read more.
The air quality in a street canyon seriously affects the exposure level of pollutants for pedestrians and is directly related to the indoor air quality (IAQ) of surrounding buildings. In order to improve the street canyon environment, it is necessary to clarify the distribution and dispersion characteristics of pollutants. Through field tests, wind tunnel experiments, and numerical simulation, the current research studied the nature of pollutants in street canyons and provided some improvement measures. This paper comprehensively introduces the characteristics of pollutants in street canyons and reviews past studies on the following parts: (a) the dispersion principle and main impact factors of pollutants in street canyons, (b) the spatial and temporal distribution of pollutants in street canyons, (c) the relationship between pollutants in street canyons and indoor air quality, and (d) improvement measures of the street canyon environment. The dispersion of pollutants is dominated by the air exchange between the street canyon and the upper atmosphere, which is strengthened when the wind speed is high or when the temperature in the street canyon is obviously higher than the surrounding area. The heat island effect is beneficial for pollutant dispersion, while the inversion layer has a negative influence. Dense buildings mean lower pollutant diffusion capacity, which causes pollutants to easily gather. Pollutants tend to accumulate on the leeward side of buildings. The concentration of pollutants decreases with the increase of height and drops to the background level at a height of several hundred meters. The temporal distribution of pollutants in street canyons varies in diurnal, weekly, and annual periods, and the concentration peaks in the winter morning and summer evening. Besides, pollutants in street canyons have a significant influence on IAQ. To improve the street canyon environment, green belts and other facilities should be reasonably set up in the streets. Future research should pay attention to comprehensive test data, solving disagreement conclusions, and quantitative evaluation of the various impact factors on pollutants, etc.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
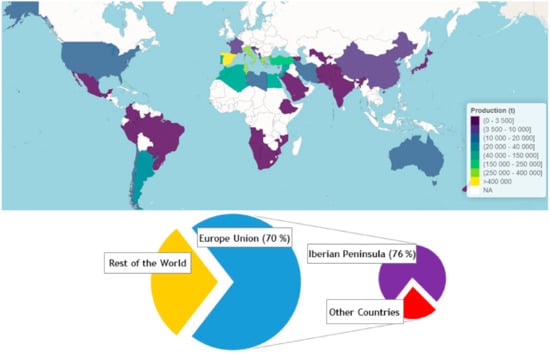
PAH and POP Presence in Plastic Waste and Recyclates: State of the Art
by
Juan A. Conesa, Samuel S. Nuñez, Núria Ortuño and Julia Moltó
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 4688
Abstract
The presence of different pollutants in recycled plastics is reviewed in this article. The desirable circular economy of plastics should be linked to the availability of clean recycled plastics with a non-significant and small to nil amount of substances of concern. Different researchers
[...] Read more.
The presence of different pollutants in recycled plastics is reviewed in this article. The desirable circular economy of plastics should be linked to the availability of clean recycled plastics with a non-significant and small to nil amount of substances of concern. Different researchers found polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), such as brominated flame retardants (BFRs), pesticides, dioxins and furans (PCDD/Fs and PBDD/Fs) in plastic recyclates. This represents an added difficulty to the effective recycling process of plastics that reduces the demand for energy and materials, in addition to posing a great environmental danger since they represent a vector of accumulation of the contaminants that will finally appear in the most unexpected products. Life Cycle Analysis of the plastic wastes recycling process indicates a great saving of energy, water and CO
2 emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures