Advances in Plant Breeding
A topical collection in Plants (ISSN 2223-7747). This collection belongs to the section "Plant Genetics, Genomics and Biotechnology".
Viewed by 67475Editors
Interests: genetics and plant breeding; sustainable agriculture; horticulture; forestry; biostatistics; biodiversity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: Solanaceae breeding; vegetable genetic resources; plant genomics; tolerance to abiotic stresses; adaptation to climate change; introgression breeding
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: biodiversity; biostatistics; ecology; fruit quality; genetics and plant breeding; horticulture; trees
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: breeding for quality; abiotic stress breeding; genetic diversity; phenomics; introgression breeding
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
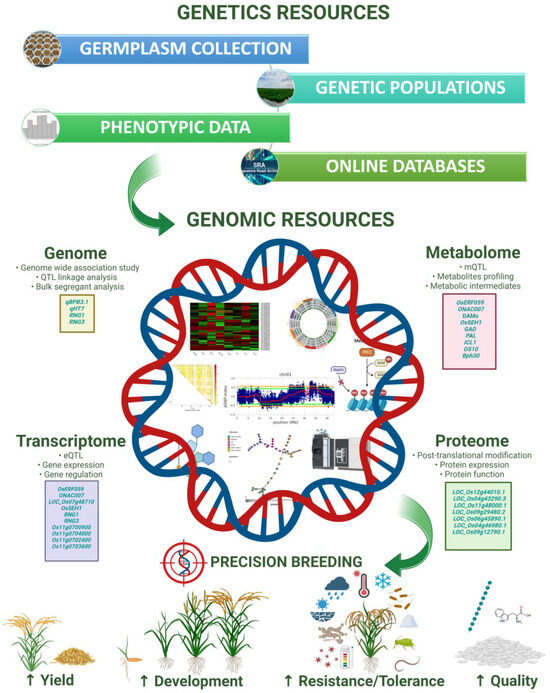
The efficient management of plant genetic resources, represented by the diversity of cultivated species but also by spontaneous flora that can provide genes of interest for resistance to abiotic and biotic stress, is of paramount importance for present and future agriculture and its sustainability. The broadening genetic bases of crop production and the need for a greater efficiency in the use of resources (energy, fertilizers, water, etc.) must be taken into account in the current conditions and for the development of sustainable agriculture and food systems. New improved cultivars are one of the most important factors in agricultural production, playing an essential role in ensuring a sustainable agriculture. This Special Issue aims to promote research on plant breeding, aimed at the topical problems of mankind: the continuous growth of the world’s population, which is already 7.8 billion; climate change and the action of multiple and various factors of abiotic stress; restriction in available land areas with favorable conditions for the cultivation of agricultural plants; impoverishment and the crisis of fresh water; desertification; salinization; aggressiveness and intensification of the attack of pathogens and harmful insects, or the appearance of new pathogens or strains of virulence; and the development of agricultural products with better quality. Along with classical breeding objectives and achievements, aimed at satisfying the current requirements of producers and farmers, traders, industry, market, and consumers or users, in this Special Issue we expect contributions about the use and application of innovative modern methodologies in plant breeding for the development of new crop varieties for current and future agriculture. This includes the development of varieties for suboptimal cultivation conditions to achieve sustainable agricultural production and increased food quality and security, but also to supply the raw materials for innovative industrial products and the living needs of mankind.
Prof. Dr. Radu E. Sestras
Prof. Dr. Jaime Prohens
Prof. Dr. Adriana F. Sestra
Dr. Mariola Plazas
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- conventional plant breeding
- objectives and methods of plant breeding
- genetic resources in plant breeding
- abiotic and biotic stress traits
- breeding for quality
- achievements and perspectives in plant breeding
- broadening the genetic base of crops
- conservation and use of genetic resources
- gene background
- hybridization
- polyploidy
- mutations
- inbreeding and heterosis
- biotechnology and molecular tools in plant breeding
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Designing novel strategies for improving old crops: A Vicia sativa review
Authors: Elena Ramírez-Parra & Lucía De la Rosa
Affiliation: INIA/CSIC Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agraria y Alimentaria, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas
Abstract: Common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) is a grain legume with dual use in animal feeding, as fodder and feed. Its rich protein content, and fatty acid and mineral composition make common vetch a very adequate food to nutritionally enrich feedstuff. In addition, relevant pharmacological properties have been reported in humans. The common vetch, like the rest of the legumes, can fix atmospheric nitrogen, an important feature that enhances sustainable agriculture systems. These properties enhance the use of vetch as a cover crop and its sowing in intercropping systems. Moreover, several studies have recently pointed out the potential of this crop in the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals, salt, or organic pollutants.
These characteristics make vetch a relevant crop in which there are different potential improvement strategies. Varieties with different yields, flowering times, shattering resistance, rhizobacteria associations, drought tolerance, nitrogen fixation capacity, and other agronomic-relevant traits have also been identified and also variations in nutritional and antinutritional factors composition are observed when different vetch accessions are compared. These data show the potential of using the variability of V. sativa genetic resources from genebanks for selecting varieties with improved traits. In the last five years, the development of genomic and transcriptomic tools in V. sativa has allowed the design of different molecular markers that have been used not only to genotype and analyze the genetic diversity of these genetic resources but also as markers for assisted breeding purposes, promoting crop improvement. Here we review and analyze all these works and present a perspective of the potential future uses and applications of different V. sativa varieties in sustainable agriculture systems.