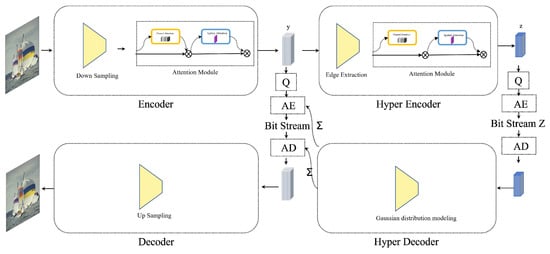
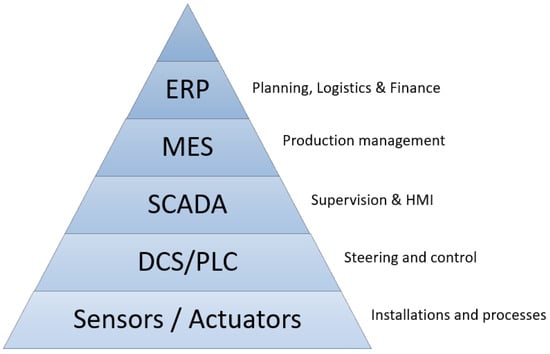
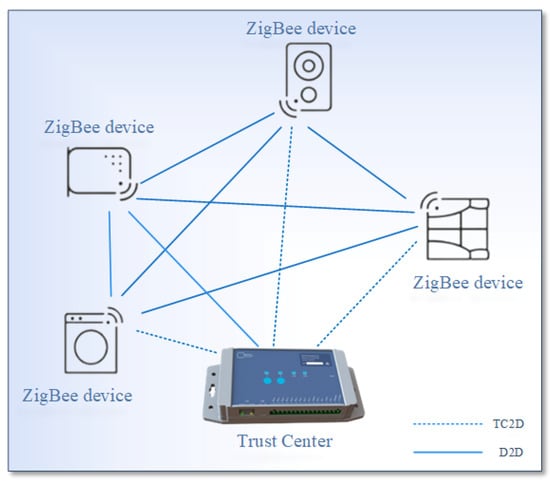
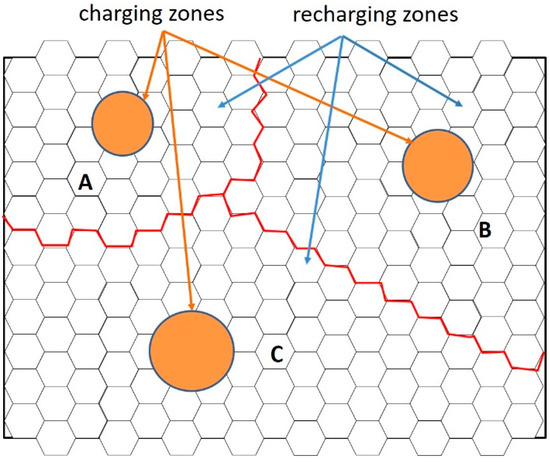
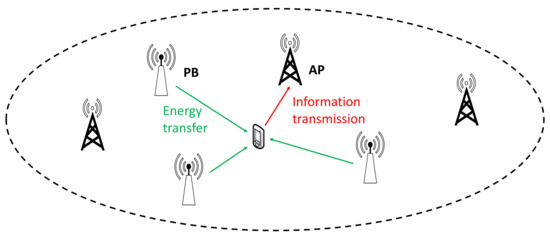
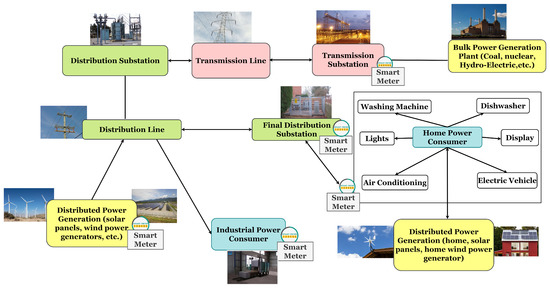
Wireless Sensor Networks towards the Internet of Things
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Sensor Networks".
Viewed by 66291
Editors
Interests: smart cities; 5G/6G; intelligent transport systems; QoE and QoS
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: smart cities and ICT for mobility; fixed/mobile communication systems and networks; professional communication systems and network design; digital media and image/video processing; smart living and build automation; industrial vision; NDT and video-surveillance systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
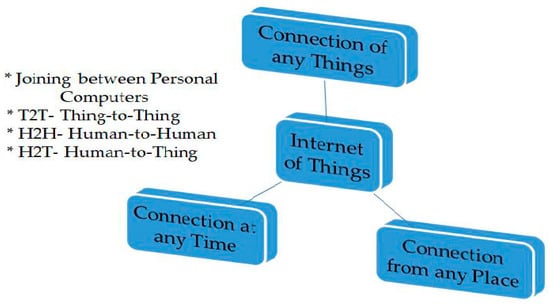
Today, wireless sensor networks continue to be highly regarded by both academia and industry, involving a wide range of stakeholders such as researchers, industrialists, hardware manufacturers, and related IT services. The areas of application of WSNs are also increasing, ranging from simple monitoring to the medical, military, and welfare fields. Among the directions in which WSNs are moving, we cannot fail to mention the interactions between people and the nodes’ environment, the use of artificial intelligence traffic management, and the use of the IoT as an industrial tool. The integration and development of low-power WSN sensors in the IoT system will be a major evolution of WSN, and several research areas are still emerging from new needs and challenges.
The purpose of this Topical Collection is to assess WSN technology and characteristics, review WSN applications, and provide information on the challenges and future of WSNs with particular emphasis on their use from an Internet of Things perspective.
A wide range of documents will be considered that present innovative approaches to the state-of-the-art, monitoring, and control of WSN with the introduction of the IoT, which allows a great variety of applications.
The topics of interest for publication include but are not limited to:
- WSN standards and specifications;
- WSN architectures and protocol stack;
- WSN IoT development platforms;
- WSN IoT data management;
- Sensor node and energy optimization;
- WSN and artificial intelligence;
- WSN for smart cities applications;
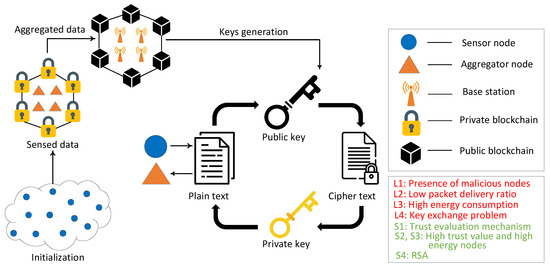
- WSN data privacy and security;
- WSN and Industry 4.0;
- Multihop routing and WSN energy efficiency.
Dr. Matteo Anedda
Prof. Dr. Daniele Giusto
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- wireless sensor networks
- sensor node
- WSN security
- ad-hoc networks
- Internet of Things