Intermediate-Temperature Creep Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of an Equiatomic FCC-Structured CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Initial Microstructures
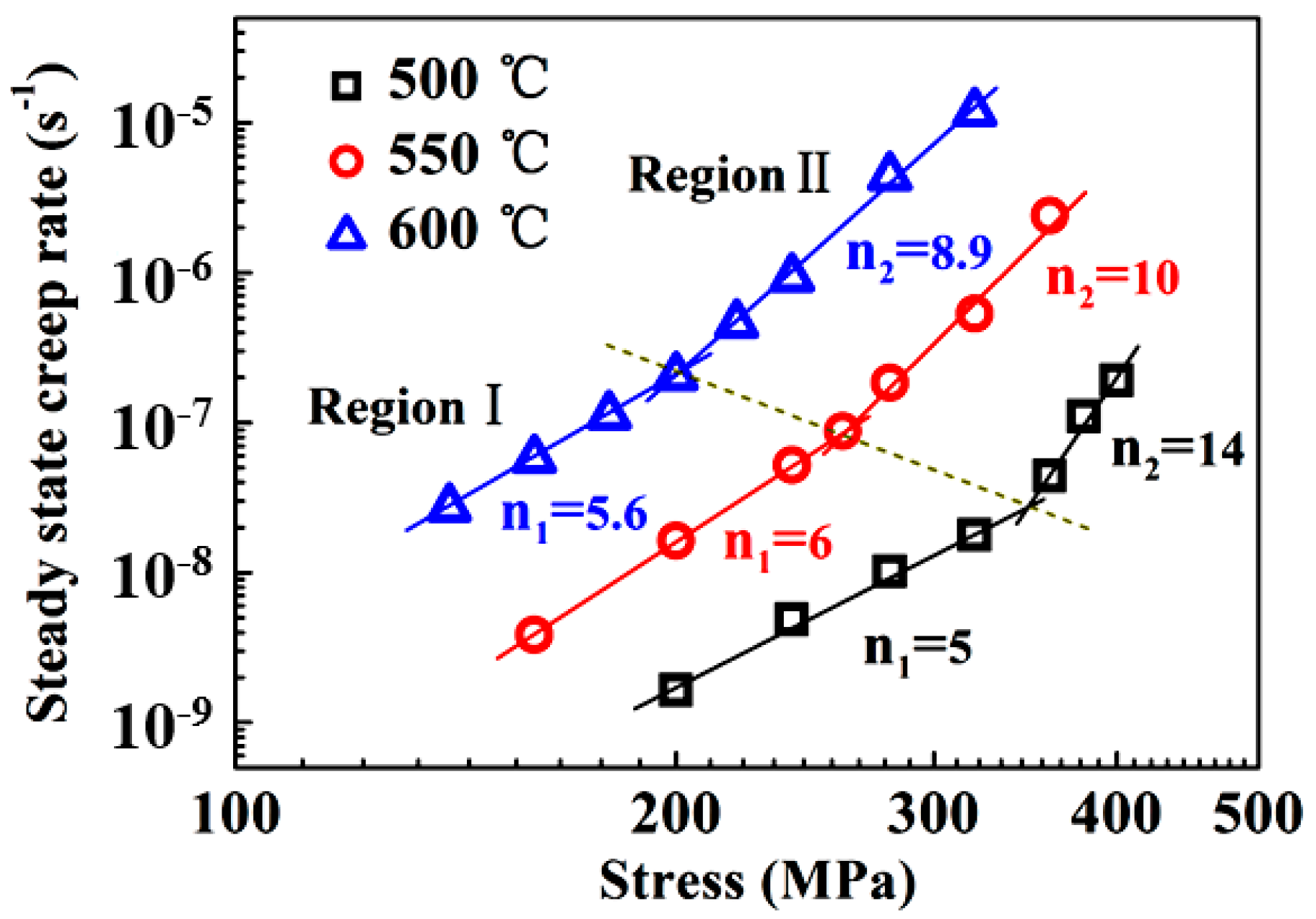
3.2. Steady-State Creep Deformation Behavior
3.3. Crept Microstructures
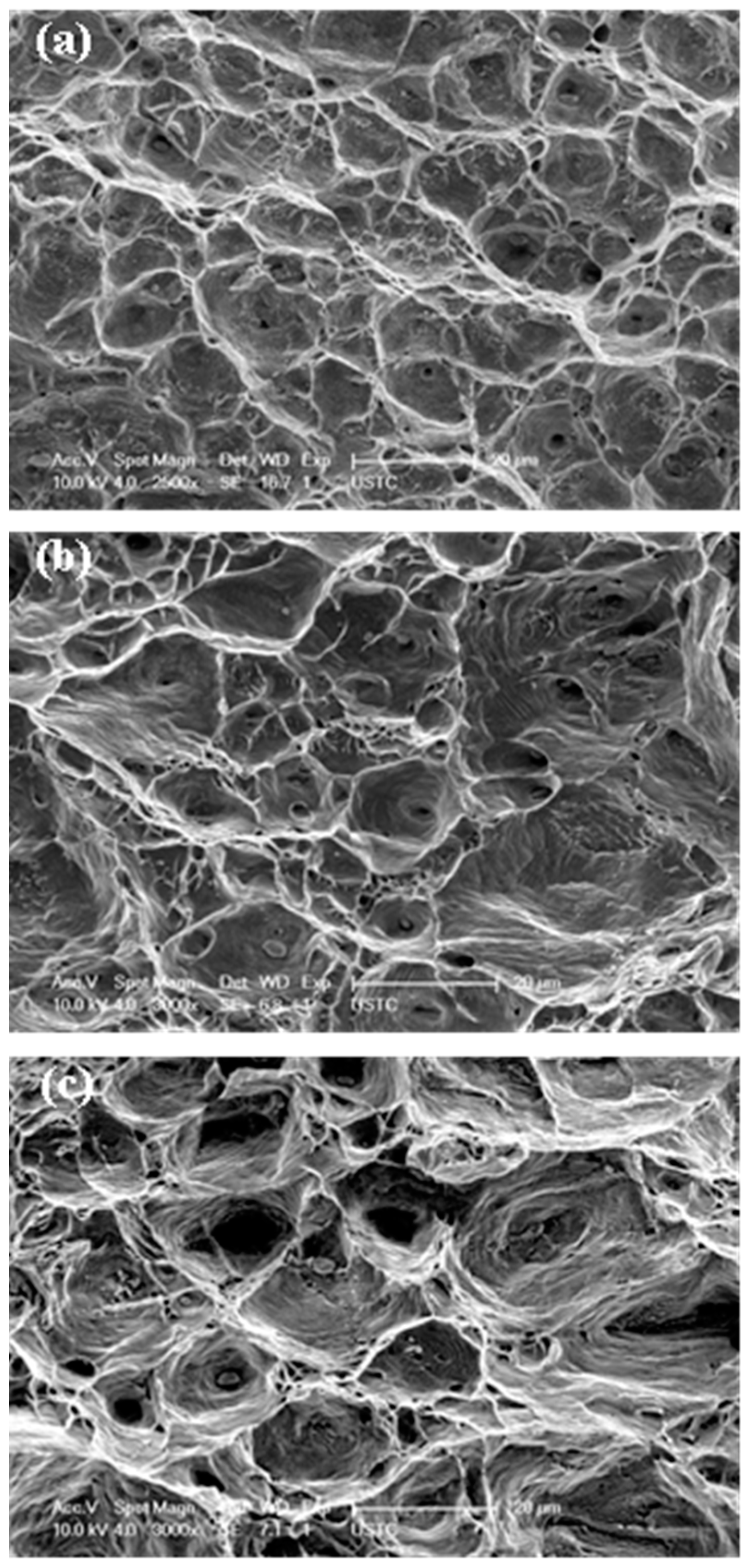
3.4. Fractographs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- An obvious transition in stress exponent and average activation energy was observed: At low stresses, the values were approximately 5 to 6 and 268 kJ/mol, whereas at high-stress regions, the corresponding values were 8.9–14 and 380 kJ/mol. Stress-assisted dislocation climb controlled by lattice diffusion is suggested as a possible rate-dominating mechanism at low stresses.
- At high stresses, obvious dynamic recrystallization occurred, leading to the refinement of average grain size. Simultaneously, nano-sized M23C6 carbides and the Cr-rich tetragonal phase were dynamically precipitated. High density of tangled and curved dislocation substructures was observed.
- The anomalously high stress exponent and activation energy in HSR were attributed to the combinative effects of dynamic recrystallization and precipitation. In particular, the precipitates act as barriers for dislocation motion via producing boundary obstacle stress, resulting in high activation energy for creep deformation. However, lattice-diffusion controlled dislocation climb is still responsible for the deformation mechanism in HSR.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.F.; Gong, M.; Peng, L.M. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of an Al0.5CoCrFeCuNi high-entropy alloy in as-cast and heat-treated/quenched conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 567, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkar, T.; Gwalani, B.; Choudhuri, D.; Mikler, C.V.; Yannetta, C.J.; Chen, X.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Styles, M.J.; Gibson, M.A.; Banerjee, R. A combinatorial assessment of AlxCrCuFeNi2 (0 < x < 1.5) complex concentrated alloys: Microstructure, microhardness, and magnetic properties. Acta Mater. 2016, 116, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni, A.M.; Haas, S.; Daoud, H.; Glatzel, U.; Förster, C.; Wanderka, N. Tensile behavior and evolution of the phases in the Al10Co25Cr8Fe15Ni36Ti6 compositionally complex/high entropy alloy. Entropy 2018, 20, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.R.; Qin, G.; Zheng, H.T.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.Q.; Chiu, Y.L.; Ding, H.S.; Guo, J.J.; Fu, H.Z. Composition design of high entropy alloys using the valence electron concentration to balance strength and ductility. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.Q.; Peng, S.Y.; Wu, S.W.; Wei, Y.J.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.B.; Wang, H.T. Unconventional deformation behaviours of nanoscaled high-entropy alloys. Entropy 2018, 20, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E.P. Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, W.M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Z.Y. Alloying behavior and novel properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Intermetallics 2015, 56, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiaraj, G.D.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. Analysis of microstructure and microtexture during grain growth in low stacking fault energy equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high entropy and Ni–60 wt. % Co alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 637, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasan, C.C.; Deng, Y.; Pradeep, K.G.; Yao, M.J.; Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Composition dependence of phase stability, deformation mechanisms, and mechanical properties of the CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy system. JOM 2014, 66, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvenne, C.; Luque, A.; Curtin, W.A. Theory of strengthening in fcc high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 118, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Otto, F.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Recovery, recrystallization, grain growth and phase stability of a family of FCC-structured multi-component equiatomic solid solution alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Wu, Y.; He, J.Y.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Grain growth and the Hall–Petch relationship in a high-entropy FeCrNiCoMn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Hanold, N.L.; George, E.P. Microstructural evolution after thermomechanical processing in an equiatomic, single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with special focus on twin boundaries. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Somsen, C.; Bei, H.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gali, A.; George, E.P. Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2013, 39, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.I.; Moon, J.S.; Hong, K.; Kim, H.S. Thermally activated deformation and the rate controlling mechanism in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Bei, H. Thermal activation mechanisms and Labusch-type strengthening analysis for a family of high-entropy and equiatomic solid-solution alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 120, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, T.; Shang, J.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. The influence of Al elements on the structure and the creep behavior of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, D.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Steady state flow of the FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures. Intermetallics 2014, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. High-temperature plastic flow of a precipitation-hardened FeCoNiCr high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 686, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Gorsse, S.; Choudhuri, D.; Styles, M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Mishra, R.S.; Banerjee, R. Modifying transformation pathways in high entropy alloys or complex concentrated alloys via thermo-mechanical processing. Acta Mater. 2018, 153, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Bird, J.E.; Dorn, J.E. Experimental Correlations for High-Temperature Creep; Technical Report; California Univ., Lawrence Radiation Lab.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Kassner, M.E.; Pérez-Prado, M.T. Five-power-law creep in single phase metals and alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 1–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobolová, Z.; Čadek, J. An interpretation of steady state creep. Philos. Mag. 1972, 26, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, F.; Mahmudi, R. The microstructure and creep characteristics of cast Mg–4Zn–0.5Ca and Mg–4Zn–0.5Ca–2RE alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 610, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, P.K.; Farghalli, A.M. Creep and ductility in an Al-Cu solid-solution alloy. Metall. Trans. A 1987, 18, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Zhou, X.Z.; Yi, D.Q.; Huang, B.Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Y.F.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.C.; Gao, Q. Creep of Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–1Fe–1Cr alloy with equiaxed and lamellar microstructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.B.; Karthikeyan, S.; Hayes, R.W.; Mills, M.J. Creep behaviour of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo: II. Mechanisms of deformation. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4965–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Gadaud, P.; Horst, O.; Otto, F.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Temperature dependencies of the elastic moduli and thermal expansion coefficient of an equiatomic, single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 623, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heczko, M.; Polák, J.; Kruml, T. Microstructure and dislocation arrangements in Sanicro 25 steel fatigued at ambient and elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Stone, H.J.; Jones, N.G. Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Kuběnová, M.; Raabe, D.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Ma, K.H.; Yang, X.; Shek, C.H. Annealing effect on the phase stability and mechanical properties of (FeNiCrMn)(100−x)Cox high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 2945–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.Z.; Zhou, X.L.; Shi, T.T.; Huang, X.; Shang, Z.X.; Liu, W.W.; Ji, B.; Xu, Z.Q. Sigma phases in an 11%Cr ferritic/martensitic steel with the normalized and tempered condition. Mater. Charact. 2016, 122, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Xiao, L.; Li, J.H.; Jie, W.Q. Creep properties and creep microstructure evolution of Mg-2.49Nd-1.82Gd-0.19Zn-0.4Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 684, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, Z.F.; Tu, H.Y.; Schmauder, S.; Wu, G.X. Microstructure evolution in HR3C austenitic steel during long-term creep at 650°C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 681, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherby, O.D.; Burke, P.M. Mechanical behavior of crystalline solids at elevated temperature. Prog. Mater Sci. 1968, 13, 323–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikant, G.; Marple, B.; Charit, I.; Murty, K. Characterization of stress rupture behavior of commercial-purity-Ti via burst testing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 463, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaee, Z.; Mahmudi, R. The microstructure and creep characteristics of cast Mg–3Si and Mg–3Si–1Gd alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 673, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.V. Power-law and exponential creep in class M materials: Discrepancies in experimental observations and implications for creep modeling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 322, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allameh, S.M. High creep exponents in a nearly-lamellar γ-based titanium aluminide intermetallic. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Q.D.; Duan, Q.Q.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.M. Tensile properties and high temperature creep behavior of microalloyed Ti–Ti3Al–Nb alloys by directional solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 4484–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettberg, L.H.; Pollock, T.M. Localized recrystallization during creep in nickel-based superalloys GTD444 and René N5. Acta Mater. 2014, 73, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.L.; Liu, H.H.; Cao, F.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Sun, J.F.; Qian, M. The effect of grain size on the tensile and creep properties of Mg–2.6Nd–0.35Zn–xZr alloys at 250°C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.D.; Shaysultanov, D.G.; Yurchenko, N.Y.; Zherebtsov, S.V.; Ladygin, A.N.; Salishchev, G.A.; Tikhonovsky, M.A. High temperature deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization in CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Li, P.E.; Chen, W.X.; Jin, J.Z. Grain boundary precipitation strengthening in high temperature creep of Fe-15Cr-25Ni alloys. Scr. Metall. 1989, 23, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.E.; Zhang, J.S.; Wang, F.G.; Jin, J.Z. Influence of Intergranular carbide density and grain size on creep of Fe-15Cr-25Ni alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 23, 1379–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, C.; Fu, J.; Tong, T.; Hao, Y.; Gu, P.; Hao, H.; Peng, L. Intermediate-Temperature Creep Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of an Equiatomic FCC-Structured CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Entropy 2018, 20, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120960
Cao C, Fu J, Tong T, Hao Y, Gu P, Hao H, Peng L. Intermediate-Temperature Creep Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of an Equiatomic FCC-Structured CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Entropy. 2018; 20(12):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120960
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Chengming, Jianxin Fu, Tongwei Tong, Yuxiao Hao, Ping Gu, Hai Hao, and Liangming Peng. 2018. "Intermediate-Temperature Creep Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of an Equiatomic FCC-Structured CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy" Entropy 20, no. 12: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120960
APA StyleCao, C., Fu, J., Tong, T., Hao, Y., Gu, P., Hao, H., & Peng, L. (2018). Intermediate-Temperature Creep Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of an Equiatomic FCC-Structured CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Entropy, 20(12), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120960




