- Article
Digital Quantum Simulation of Wavepacket Correlations in a Chemical Reaction
- Shah Ishmam Mohtashim and
- Sabre Kais
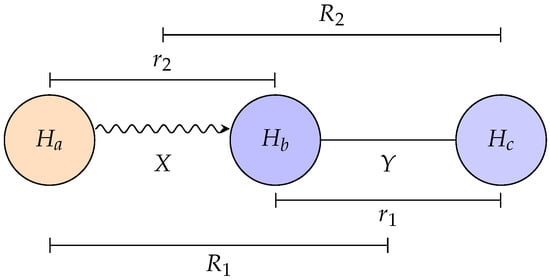
We present hybrid quantum–classical algorithms to compute time-dependent Møller wavepacket correlation functions via digital quantum simulation. Reactant and product channel wavepackets are encoded as qubit states, evolved under a discretized molecular Hamiltonian, and their correlation is reconstructed using both a modified Hadamard test and a multi-fidelity estimation (MFE) protocol. The method is applied to the collinear H + H2 exchange reaction on a London–Eyring–Polanyi–Sato potential energy surface. Quantum-estimated correlation functions show quantitative agreement with high-resolution classical wavepacket simulations across the full time domain, reproducing both short-time scattering peaks and long-time oscillatory dynamics. The ancilla-free MFE protocol achieves matching results with reduced circuit depth. These results provide a proof of principle that digital quantum circuits can be used to accurately calculate the wavepacket correlation functions for a benchmark chemical reaction system.
28 January 2026