A Novel Algorithm to Improve Digital Chaotic Sequence Complexity through CCEMD and PE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Characteristic Analysis of a Chaotic System
3. A New Algorithm to Improve the Complexity of Digital Chaotic Sequences
3.1. The Basic Principles of EMD
- All the local maxima and minima of the signal are calculated to construct the upper envelopes and lower envelopes by the cubic spline interpolation. Further, represents the mean of the upper and lower envelopes and is shown as follows:where denotes a temporary signal. If satisfies the above two crucial factors, it is a first-order IMF component. Otherwise, will serve as an initial signal and the above procedures are repeated until the is an IMF and sets the as .
- Next, the first-order IMF has a high frequency, which can be extracted from byis processed as the new signal and the above procedures are repeated so that the other IMFs can be generated , .
- When the residual becomes a monotonic function or constant, EMD decomposition is terminated. The can finally be shown as follows:Thus, a non-linear signal can be decomposed into IMFs and a residual . However, there are some problems with the EMD method, and one of these is mode mixing. Generally speaking, each IMF component represents a specific physical quantity. If an IMF component contains a large number of different frequencies of signals then this phenomenon is called mode mixing, which seriously affects the performance of EMD decomposition. Aiming to resolve this issue, the complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition (CEEMD) method can effectively restrain mode mixing of EMD at a certain level. The CEEMD method was used by adding two opposite white noise signals to an original signal , and to the adopted EMD, with the purpose of restraining mode mixing.
3.2. The Implementation of the New Algorithm
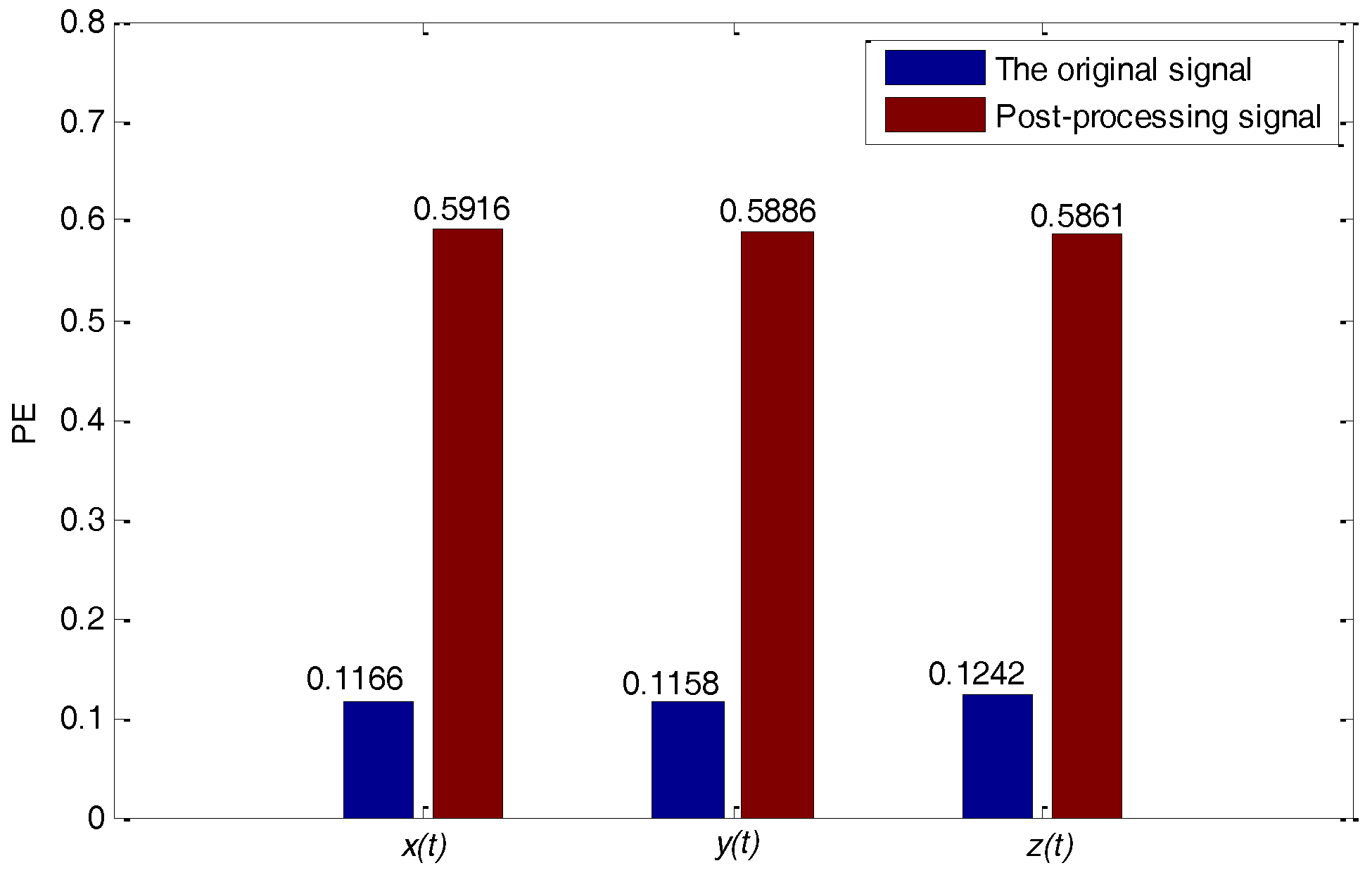
3.3. Experimental Results
3.4. The Generation and Performance Test of the Chaotic Binary Sequence
4. Image Encryption with a Chaotic Binary Sequence
4.1. Key Sensitivity
4.2. Histogram Analysis
4.3. Correlation Analysis of Adjacent Pixels
4.4. Information Entropy Analysis
5. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Tong, X.J.; Meng, X.W. An efficient chaos pseudo-random number generator applied to video encryption. Optik 2016, 127, 9305–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.X.; Yu, S.M.; Li, C.Q.; Lu, J.H.; Fang, X.L.; Guyeux, C.; Bahi, J.M. Theoretical Design and FPGA-Based Implementation of Higher-Dimensional Digital Chaotic Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2016, 63, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, D.; Ganesan, K. Chaos based video encryption using maps and Ikeda time delay system. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Akgul, A.; Kacar, S.; Cavusoglu, U. A new 4-D chaotic hyperjerk system, its synchronization, circuit design and applications in RNG, image encryption and chaos-based steganography. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ding, Q.; Du, B.X. A New Improved Scheme of Chaotic Masking Secure Communication Based on Lorenz System. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2012, 22, 1250125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.L.; Panahi, S.; Rajagopal, K.; Akgul, A.; Pham, V.T.; Jafari, S. A New Chaotic Flow with Hidden Attractor: The First Hyperjerk System with No Equilibrium. Z. Naturforsch. A 2018, 73, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.K.; Varshney, V.; Shrimali, M.D.; Prasad, A.; Kuznetsov, N.V.; Leonov, G.A. Shadowing in hidden attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 91, 2429–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Pham, V.T.; Golpayegani, S.M.R.H.; Moghtadaei, M.; Kingni, S.T. The Relationship Between Chaotic Maps and Some Chaotic Systems with Hidden Attractors. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2016, 26, 1650211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudkowski, D.; Jafari, S.; Kapitaniak, T.; Kuznetsov, N.V.; Leonov, G.A.; Prasad, A. Hidden attractors in dynamical systems. Phys. Rep. 2016, 637, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Guo, X.X. Complexity-enhanced polarization-resolved chaos in a ring network of mutually coupled vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers with multiple delays. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 6728–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rontani, D.; Mercier, E.; Wolfersberger, D.; Sciamanna, M. Enhanced complexity of optical chaos in a laser diode with phase-conjugate feedback. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4637–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.X.; Geng, X.L.; Chen, F.Y.; Pan, J.; Ding, Q. Generation and Realization of Digital Chaotic Key Sequence Based on Double K-L Transform. Chin. J. Electron. 2013, 22, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Ling, X.T. Realizing Finite Precision Chaotic Systems via Perturbation of m-Sequences. Acta Electron. Sin. 1997, 25, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Cernak, J. Digital generators of chaos. Phys. Lett. A 1996, 214, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zeng, H.T.; Xiao, Z.H.; Peng, L.H.; Malik, O.P. Fault diagnosis of rotor using EMD thresholding-based de-noising combined with probabilistic neural network. J. Vibroeng. 2017, 19, 5920–5931. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Lindemann, J.; Egelhaaf, M. Local motion adaptation enhances the representation of spatial structure at EMD arrays. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, X.F. Enhancement of Weak Lidar Signal Based on Variable Frequency Resolution EMD. IEEE Photonic Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 2882–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.S.; Zhao, Q. Pseudo-fault signal assisted EMD for fault detection and isolation in rotating machines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 81, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, Z.H. A review on Hilbert-Huang transform: Method and its applications to geophysical studies. Rev. Geophys. 2008, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, D.P.; Rehman, N.U.; Wu, Z.H.; Huang, N.E. Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Time-Frequency Analysis of Multivariate Signals. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.H.; Lin, C.; Tsao, J.; Lin, P.F.; Wang, P.C.; Huang, N.E.; Lo, M.T. Empirical mode decomposition based detrended sample entropy in electroencephalography for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 210, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.W.; Miao, Q.; Wang, L. An optimized time varying filtering based empirical mode decomposition method with grey wolf optimizer for machinery fault diagnosis. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 418, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q.; He, Y. An improved multi-kernel RVM integrated with CEEMD for high-quality intervals prediction construction and its intelligent modeling application. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 171, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrochidou, E.; Alvanitopoulos, P.; Andreadis, I.; Elenas, A. Artificial accelerograms composition based on the CEEMD. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2016, 40, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Goparaju, B.; Song, J.L.; Zhang, R.; Westover, M.B. Automated identification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals based on phase space representation and statistical features in the CEEMD domain. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 38, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation Entropy: A Natural Complexity Measure for Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, X.W. Extreme multistability in a memristor-based multi-scroll hyper-chaotic system. Chaos 2016, 26, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonov, G.A.; Kuznetsov, N.V.; Mokaev, T.N. Homoclinic orbits, and self-excited and hidden attractors in a Lorenz-like system describing convective fluid motion. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2015, 224, 1421–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.V.; Leonov, G.A.; Mokaev, T.N.; Prasad, A.; Shrimali, M.D. Finite-time Lyapunov dimension and hidden attractor of the Rabinovich system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 92, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, G.A.; Kuznetsov, N.V. Hidden Attractors in Dynamical Systems from Hidden Oscillations in Hilbert–Kolmogorov, Aizerman, and Kalman Problems to Hidden Chaotic Attractor in Chua Circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2014, 23, 1330002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Wei, Y.; Huang, W. An improvement EMD method based on the optimized rational Hermite interpolation approach and its application to gear fault diagnosis. Measurement 2015, 63, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.F.; Miao, S.X. The complexity of binary sequences using logistic chaotic maps. Complexity 2016, 21, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian-Sheng, L. Pseudo-randomness and complexity of binary sequences generated by the chaotic system. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2011, 16, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Escobar, M.A.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Abundiz-Perez, F.; Lopez-Gutierrez, R.M.; Del Campo, O.R.A. A RGB image encryption algorithm based on total plain image characteristics and chaos. Signal Process. 2015, 109, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, P.; Yang, H.Q.; Cao, H.Y. Security analysis on a color image encryption based on DNA encoding and chaos map. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 46, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Pan, C.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z.; He, J. A Chaotic Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Information Entropy. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2018, 28, 1850010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Kadir, A.; Sun, X.B. Chaos-based fast colour image encryption scheme with true random number keys from environmental noise. IET Image Process. 2017, 11, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Wang, X.Y. Color image encryption based on one-time keys and robust chaotic maps. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 59, 3320–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| IMF Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 0.1181 | 0.1959 | 0.1658 |
| IMF2 | 0.1116 | 0.1153 | 0.1198 |
| IMF3 | 0.1096 | 0.1113 | 0.1102 |
| IMF4 | 0.1069 | 0.1076 | 0.1072 |
| RS5 | 0.0542 | 0.0997 | 0.1066 |
| Test Item | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approximate Entropy | 0.28711 | 0.01063 | 0.41042 | Success |
| Block Frequency | 0.02501 | 0.43924 | 0.64085 | Success |
| Cumulative Sums | 0.14372 | 0.56658 | 0.64761 | Success |
| FFT | 0.52063 | 0.37221 | 0.11875 | Success |
| Frequency | 0.28014 | 0.48392 | 0.87461 | Success |
| Linear Complexity | 0.22374 | 0.46932 | 0.78321 | Success |
| Longest Run | 0.70665 | 0.51078 | 0.26541 | Success |
| Non-Overlapping Template | 0.32974 | 0.75331 | 0.11253 | Success |
| Overlapping Template | 0.24088 | 0.70399 | 0.32227 | Success |
| Random Excursions | 0.43747 | 0.51791 | 0.82733 | Success |
| Random Excursions Variant | 0.64578 | 0.11253 | 0.66691 | Success |
| Binary Matrix Rank | 0.15319 | 0.58700 | 0.44130 | Success |
| Runs | 0.88206 | 0.84530 | 0.71884 | Success |
| Serial Test-1 | 0.10056 | 0.17826 | 0.81473 | Success |
| Serial Test-2 | 0.15538 | 0.15538 | 0.69926 | Success |
| Maurer’s Universal | 0.75331 | 0.14268 | 0.56553 | Success |
| Direction | Plain-Image for Lena | Cipher-Image for Lena | Plain-Image for Baboon | Cipher-Image for Baboon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | 0.9712 | 0.0392 | 0.9287 | 0.0133 |
| Vertical | 0.9655 | 0.0091 | 0.9004 | 0.0522 |
| Diagonal | 0.9401 | 0.0215 | 0.8711 | 0.0093 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, C.; Xie, Z.; Ding, Q. A Novel Algorithm to Improve Digital Chaotic Sequence Complexity through CCEMD and PE. Entropy 2018, 20, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040295
Fan C, Xie Z, Ding Q. A Novel Algorithm to Improve Digital Chaotic Sequence Complexity through CCEMD and PE. Entropy. 2018; 20(4):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040295
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Chunlei, Zhigang Xie, and Qun Ding. 2018. "A Novel Algorithm to Improve Digital Chaotic Sequence Complexity through CCEMD and PE" Entropy 20, no. 4: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040295
APA StyleFan, C., Xie, Z., & Ding, Q. (2018). A Novel Algorithm to Improve Digital Chaotic Sequence Complexity through CCEMD and PE. Entropy, 20(4), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040295




