The Conservation of Average Entropy Production Rate in a Model of Signal Transduction: Information Thermodynamics Based on the Fluctuation Theorem
Abstract
:1. Introduction
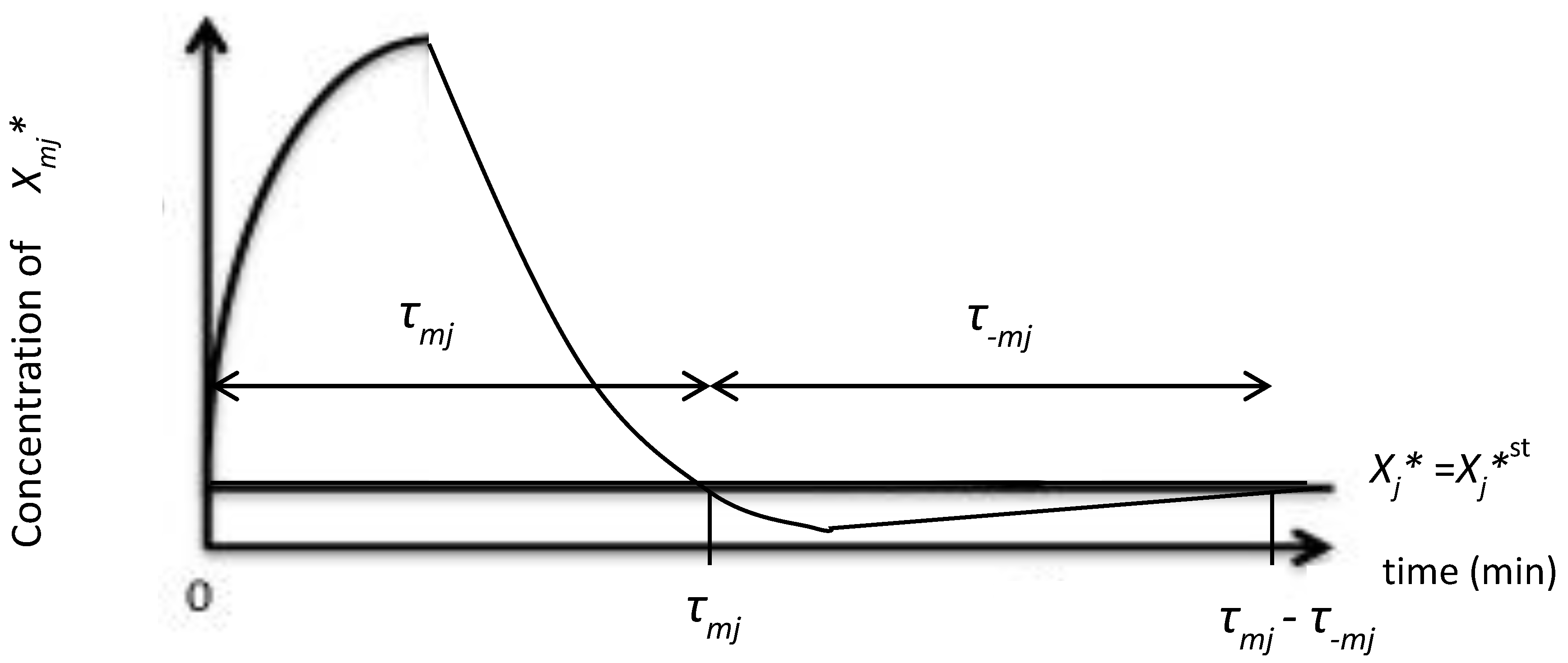
2. A Model of Signal Transduction
3. Average Entropy Production Rate in a Signal Cascade and Fluctuation Theorem (FT)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selimkhanov, J.; Taylor, B.; Yao, J.; Pilko, A.; Albeck, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Tsimring, L.; Wollman, R.; Systems biology. Accurate information transmission through dynamic biochemical signaling networks. Science 2014, 346, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, R.; Rhee, A.; Wang, C.J.; Nemenman, I.; Levchenko, A. Information transduction capacity of noisy biochemical signaling networks. Science 2011, 334, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xin, J.; Nie, Q. A critical quantity for noise attenuation in feedback systems. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govern, C.C.; ten Wolde, P.R. Energy dissipation and noise correlations in biochemical sensing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 258102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T. A model of cell biological signaling predicts a phase transition of signaling and provides mathematical formulae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T. Kinetic stability analysis of protein assembly on the center manifold around the critical point. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T. Information thermodynamics derives the entropy current of cell signal transduction as a model of a binary coding system. Entropy 2018, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Tsuruyama, T.; Nowakowski, B.; Gorecki, J.; Yoshikawa, K. Discrimination of time-dependent inflow properties with a cooperative dynamical system. Chaos 2015, 25, 103115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialek, W.; Nemenman, I.; Tishby, N. Predictability, complexity, and learning. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, 2409–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, B.C.; Nemenman, I. Automated adaptive inference of phenomenological dynamical models. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.; Wang, L.; Sorensen, P. Network-enabled gene expression analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Sollich, P.; Kuehn, R. Signalling entropy: A novel network-theoretical framework for systems analysis and interpretation of functional omic data. Methods 2014, 67, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Kawana, K.; Adachi, K.; Fujimoto, A.; Yoshida, M.; Nakamura, H.; Nishida, H.; Inoue, T.; Taguchi, A.; Ogishima, J.; et al. Intracellular signaling entropy can be a biomarker for predicting the development of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Banerji, C.R.; Severini, S.; Kuehn, R.; Sollich, P. Increased signaling entropy in cancer requires the scale-free property of protein interaction networks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Breeze, C.E.; Zheng, S.C.; Beck, S. A comparison of reference-based algorithms for correcting cell-type heterogeneity in epigenome-wide association studies. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.R.; Kejzar, N.; Tsallis, C.; Farmer, D.; White, S. Generative model for feedback networks. Phys. Rev. E Cover. Stat. Nonlinear Biol. Soft Matter Phys. 2006, 73, 016119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Liu, C.; Shen, B.; Zhao, Z. Investigating cellular network heterogeneity and modularity in cancer: A network entropy and unbalanced motif approach. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016, 10 (Suppl. 3), 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.-f. Entropy production in a cell and reversal of entropy flow as an anticancer therapy. Front. Phys. China 2009, 4, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, A.; Nemenman, I. Cellular noise and information transmission. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 28, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, D.; Mugler, A.; Brennan, M.D.; Lee, S.H.; Huebner, R.J.; Shamir, E.R.; Woo, L.A.; Kim, J.; Amar, P.; Nemenman, I.; et al. Cell-cell communication enhances the capacity of cell ensembles to sense shallow gradients during morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, T.; Youk, H. Molecular-level tuning of cellular autonomy controls the collective behaviors of cell populations. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofts, A.R. Life, information, entropy, and time: Vehicles for semantic inheritance. Complexity 2007, 13, 14–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Enver, T. Single-cell entropy for accurate estimation of differentiation potency from a cell’s transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Bao, E.L.; Wagner, M.; Whitsett, J.A.; Xu, Y. Slice: Determining cell differentiation and lineage based on single cell entropy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Hwang, E.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, S.B.; Park, K.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis via sustained erk activation and subsequent mitf degradation. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Park, M.; Han, J.; Lee, J.H.; Bae, I.H.; Choi, H.; Son, E.D.; Park, Y.H.; Lim, K.M. Liver x receptor activation inhibits melanogenesis through the acceleration of erk-mediated mitf degradation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackeigan, J.P.; Murphy, L.O.; Dimitri, C.A.; Blenis, J. Graded mitogen-activated protein kinase activity precedes switch-like c-fos induction in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 4676–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.R.; Li, C.M.; Simmons, R.; Khosla, J.; Sannes, P.L. Heparin affects signaling pathways stimulated by fibroblast growth factor-1 and-2 in type ii cells. Am. J. Phys.-L. Cell. Mol. Phy. 2004, 287, L191–L200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropavlovskaia, M.; Daoud, J.; Zhu, J.; Moosavi, M.; Ding, J.; Makhlin, J.; Assouline-Thomas, B.; Rosenberg, L. Mechanisms of action of islet neogenesis-associated protein: Comparison of the full-length recombinant protein and a bioactive peptide. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Hoover, H.E.; Honbo, N.; Kalinowski, M.; Alano, C.C.; Karliner, J.S.; Raffai, R. High-density lipoprotein determines adult mouse cardiomyocyte fate after hypoxia-reoxygenation through lipoprotein-associated sphingosine 1-phosphate. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, M.; Magi, S.; Jurman, G.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; Lassmann, T.; Arner, E.; Forrest, A.R.; Carninci, P.; Hayashizaki, Y.; et al. Promoter-level expression clustering identifies time development of transcriptional regulatory cascades initiated by erbb receptors in breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ubl, J.J.; Stricker, R.; Reiser, G. Thrombin (par-1)-induced proliferation in astrocytes via mapk involves multiple signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 283, C1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ni, X.Y.; Bai, Z.H.; Chen, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.G. Nicotine promotes cell proliferation and induces resistance to cisplatin by alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptormediated activation in raw264.7 and el4 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, K.; Seitz, T.; Li, S.; Janosch, P.; McFerran, B.; Kaiser, C.; Fee, F.; Katsanakis, K.D.; Rose, D.W.; Mischak, H.; et al. Suppression of raf-1 kinase activity and map kinase signalling by rkip. Nature 1999, 401, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Yano, N.; Deng, M.Z.; Mao, Q.F.; Shaw, S.K.; Tseng, Y.T. Beta-adrenergic receptor-pi3k signaling crosstalk in mouse heart: Elucidation of immediate downstream signaling cascades. PloS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruyama, T.; Hiratsuka, T.; Aini, W.; Nakamura, T. Stat5a modulates chemokine receptor ccr6 expression and enhances pre-b cell growth in a ccl20-dependent manner. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 2630–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T.; Hiratsuka, T.; Jin, G.; Imai, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Maruyama, Y.; Kanaya, K.; Ozeki, M.; Takakuwa, T.; Haga, H.; et al. Murine leukemia retrovirus integration induces the formation of transcription factor complexes on palindromic sequences in the signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 5a gene during the development of pre-b lymphomagenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T.; Imai, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Hiratsuka, T.; Maruyama, Y.; Kanaya, K.; Kaszynski, R.; Jin, G.; Okuno, T.; Ozeki, M.; et al. Dual retrovirus integration tagging: Identification of new signaling molecules fiz1 and hipk2 that are involved in the il-7 signaling pathway in b lymphoblastic lymphomas. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T.; Nakamura, T.; Jin, G.; Ozeki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Hiai, H. Constitutive activation of stat5a by retrovirus integration in early pre-b lymphomas of sl/kh strain mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8253–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uda, S.; Kuroda, S. Analysis of cellular signal transduction from an information theoretic approach. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2016, 51, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Muraoka, T.; Kinbara, K.; Ishijima, A.; Fukuoka, H. Single-cell e. Coli response to an instantaneously applied chemotactic signal. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Sagawa, T. Maxwell’s demon in biochemical signal transduction with feedback loop. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Sagawa, T. Information thermodynamics on causal networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 18063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uda, S.; Saito, T.H.; Kudo, T.; Kokaji, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kubota, H.; Komori, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Kuroda, S. Robustness and compensation of information transmission of signaling pathways. Science 2013, 341, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruyama, T. Channel capacity of coding system on tsallis entropy and q-statistics. Entropy 2017, 19, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruyama, T. Information thermodynamics of the cell signal transduction as a szilard engine. Entropy 2018, 20, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidus, S.; Han, B.; Wang, J. Intrinsic noise, dissipation cost, and robustness of cellular networks: The underlying energy landscape of mapk signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6039–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillouin, L. Science and information theory. Dover Publ. Inc. 2013, 2nd ed., 42. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On information and sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Sartori, P.; Neumann, S.; Sourjik, V.; Tu, Y. The energy-speed-accuracy tradeoff in sensory adaptation. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuruyama, T. The Conservation of Average Entropy Production Rate in a Model of Signal Transduction: Information Thermodynamics Based on the Fluctuation Theorem. Entropy 2018, 20, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040303
Tsuruyama T. The Conservation of Average Entropy Production Rate in a Model of Signal Transduction: Information Thermodynamics Based on the Fluctuation Theorem. Entropy. 2018; 20(4):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040303
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuruyama, Tatsuaki. 2018. "The Conservation of Average Entropy Production Rate in a Model of Signal Transduction: Information Thermodynamics Based on the Fluctuation Theorem" Entropy 20, no. 4: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040303
APA StyleTsuruyama, T. (2018). The Conservation of Average Entropy Production Rate in a Model of Signal Transduction: Information Thermodynamics Based on the Fluctuation Theorem. Entropy, 20(4), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20040303



