Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Heart Rate Measurement & Heart Rate Variability Analyses
2.3. Experimental Protocols
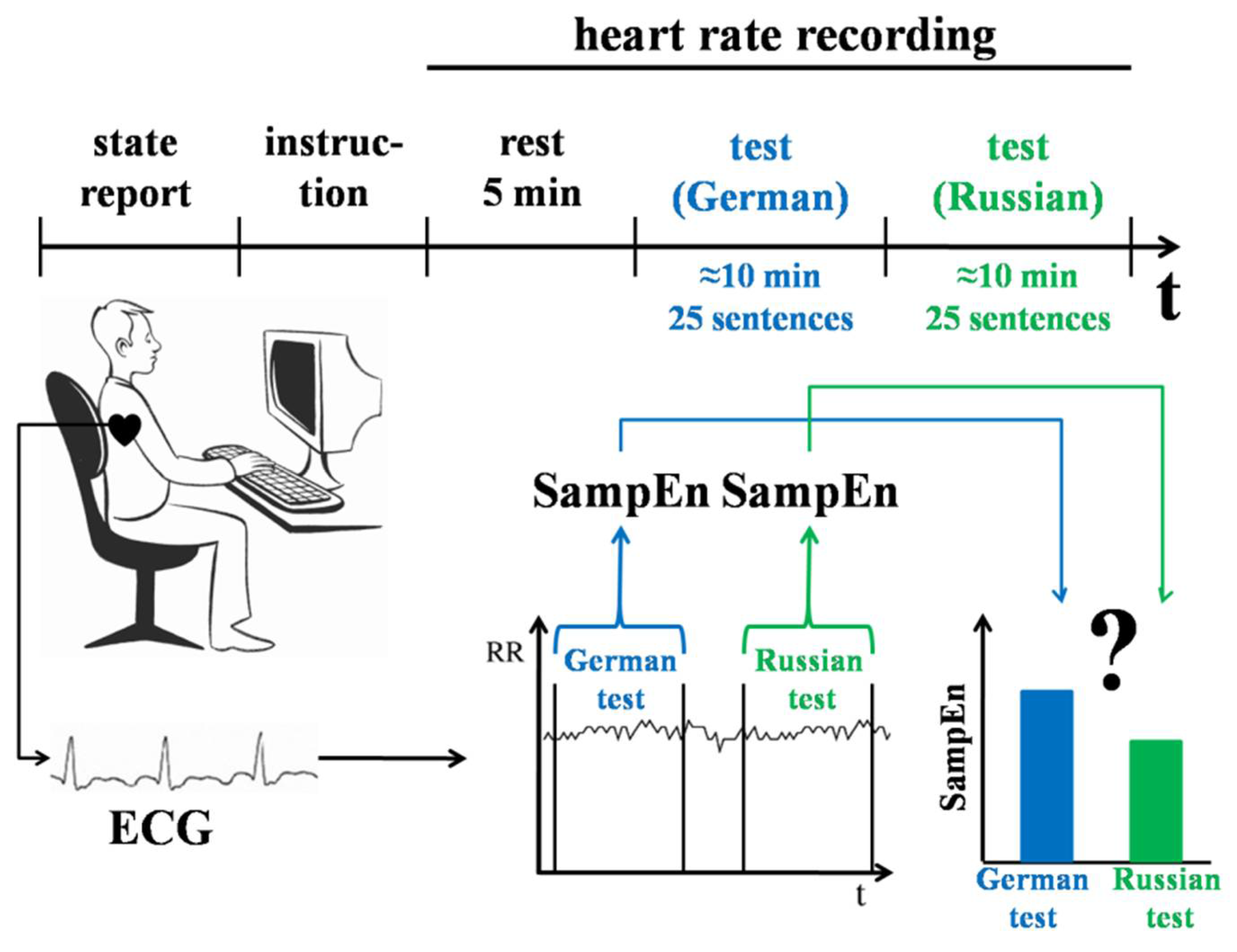
2.3.1. Experiment 1
2.3.2. Experiment 2
2.3.3. Experiment 3
2.3.4. Experiment 4
2.3.5. Experiment 5
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Dynamics of HRV During Performing a Linguistic Task Using Native and Foreign Languages (Experiment 1)
3.2. Dynamics of HRV When Using Mathematical and General Vocabulary (Experiment 2)
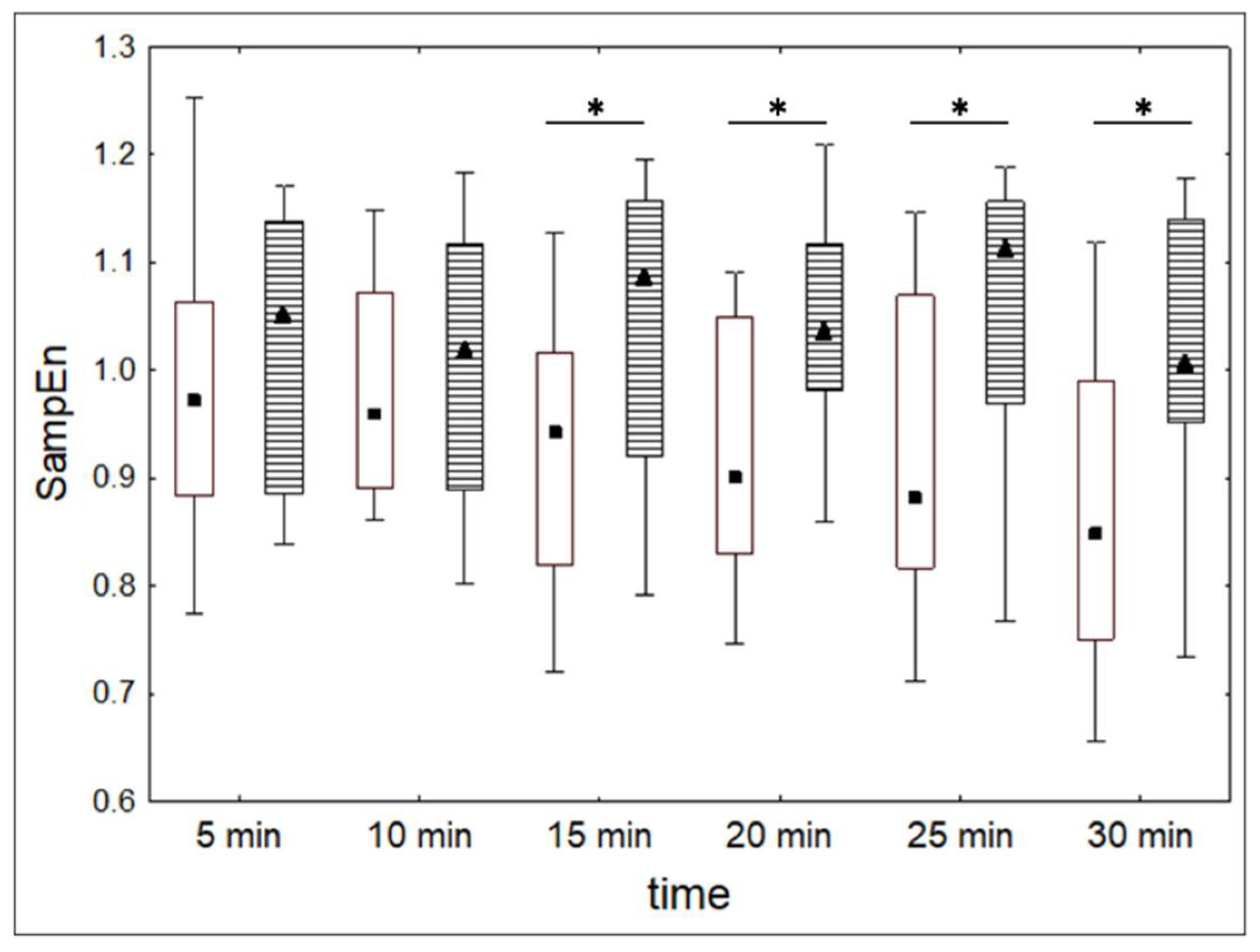
3.3. Dynamics of HRV During Alcohol Administration (Experiment 3)
3.4. Dynamics of HRV During Public Speaking (Experiment 4)
3.5. Dynamics of HRV During Learning to Play a Computer Game (Experiment 5)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matheson, H.E.; Barsalou, L.W. Embodiment and Grounding in Cognitive Neuroscience. In Stevens’ Handbook of Experimental Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience, 4th ed.; Wixted, J.T., Thompson-Schill, S.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 1–27. ISBN 978-1-119-1701-67. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, Y.I.; Grechenko, T.N.; Gavrilov, V.V.; Gorkin, A.G.; Shevchenko, D.G.; Grinchenko, Y.V.; Aleksandrov, I.O.; Maksimova, N.E.; Bezdenezhnych, B.N.; Bodunov, M.V. Formation and realization of individual experience: A psychophysiological approach. In Conceptual Advances in Brain Research. Conceptual Advances in Russian Neuroscience: Complex Brain Functions; Miller, R., Ivanitsky, A.M., Balaban, P.V., Eds.; Harwood Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 181–200. ISBN 978-9-0582-3021-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shvyrkov, V.B. Neurophysiological study of animals’ subjective experience. In Machinery of the Mind; John, R., Harmony, T., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 337–350. ISBN 978-1-4757-1085-4. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, Y.I. Comparative description of consciousness and emotions in the framework of systemic understanding of behavioural continuum and individual development. In Neuronal Bases and Psychological Aspects of Consciousness, Proceedings of the International School of Biocybernetics, Casamicciola, Napoli, Italy, 13–18 October 1997; Teddei-Ferretti, C., Musio, C., Eds.; World Scientific: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 8, pp. 220–235. ISBN 978-981-02-3597-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lasrado, R.; Boesmans, W.; Kleinjung, J.; Pin, C.; Bell, D.; Bhaw, L.; McCallum, S.; Zong, H.; Luo, L.; Clevers, H.; et al. Lineage-dependent spatial and functional organization of the mammalian enteric nervous system. Science 2017, 356, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armour, J.A. Cardiac neuronal hierarchy in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagaev, V.; Aleksandrov, V. Visceral-related area in the rat insular cortex. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 125, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, J.; Shi, T.; Apkarian, A.V. Viscero-somatic neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex (SI) of the squirrel monkey. Brain Res. 1997, 756, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, P.; Critchley, H.; van Duijvendoden, S.; Lambiase, P.D. Significance of neuro-cardiac controll mechanisms governed by higher regions of the brain. Auton. Neurosci. 2016, 199, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrist, P.A.; Webb, R.A.; Sutterer, J.R.; Howard, J.L. The cardiac-somatic relationship: Some reformulations. Psychophysiology 1970, 6, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, F.; McCraty, R.; Zerr, C.L. A healthy heart is not a metronome: An integrative review of the heart’s anatomy and heart rate variability. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Ahs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J.; Wager, T.D. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: Implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F. What the Heart Says to the Brain (and vice versa) and Why We Should Listen. Psychol. Top. 2007, 16, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.C.; Paulus, M.P.; Simmons, A.N.; Nelesen, R.A.; Dimsdale, J.E. Functional subdivisions within anterior cingulate cortex and their relationships to autonomic nervous system function. NeuroImage 2004, 22, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, M.; Thayer, J.F. How heart rate variability affects emotion regulation brain networks. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 19, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmann, T.; Thayer, J.F.; Pohlack, S.; Nees, F.; Grimm, O.; Flor, H. Structural brain correlates of heart rate variability in a healthy young adult population. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, Y.I. Psychophysiological regularities of the dynamics of individual experience and the “stream of consciousness”. In Neuronal Bases and Psychological Aspects of Consciousness, Proceedings of the International School of Biocybernetics, Casamicciola, Napoli, Italy, 13–18 October 1997; Teddei-Ferretti, C., Musio, C., Eds.; World Scientific: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 8, pp. 201–219. ISBN 978-981-02-3597-0. [Google Scholar]
- Anokhin, P.K. Biology and Neurophysiology of Conditioned Reflex and Its Role in Adaptive Behavior, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1974; pp. 190–254. ISBN 978-0-08-021516-7. [Google Scholar]
- Anokhin, P.K. Biology and Neurophysiology of Conditioned Reflex, 1st ed.; Meditzina: Moscow, Russia, 1968; pp. 406–432. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrov, Y.I. Learning and Memory: Traditional and Systems Approaches. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2006, 36, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorkin, A.G.; Shevchenko, D.G. Distinctions in the neuronal activity of the rabbit limbic cortex under different training strategies. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 1996, 26, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolbeneva, M.G.; Alexandrov, Y.I. Mental Reactivation and Pleasantness Judgment of Experience Related to Vision, Hearing, Skin Sensations, Taste and Olfaction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, Y.I.; Krylov, A.K.; Arutyunova, K.R. Activity during Learning and the Nonlinear Differentiation of Experience. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. Life Sci. 2017, 21, 391–405. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, Y.I.; Grinchenko, Y.V.; Shevchenko, D.G.; Averkin, R.G.; Matz, V.N.; Laukka, S.; Korpusova, A.V. A subset of cingulate cortical neurons is specifically activated during alcohol-acquisition behaviour. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 171, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, Y.I. How we fragment the world: The view from inside versus the view from outside. Soc. Sci. Inf. 2008, 47, 419–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, Y.I. Differentiation and development. In Development Theory: Differential-Integration Paradigm; Chuprikova, N.I., Ed.; Languages of Slavic Culture: Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 17–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Joseph, K.P.; Kannathal, N.; Lim, C.M.; Suri, J.S. Heart rate variability: A review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Vives, M.-L.; Corey, J.D. On language processing shaping decision making. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 26, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Tannenbaum, D.; Costa, A.; Corey, J.D.; Keysar, B. Thinking more or feeling less? Explaining the foreign-language effect on moral judgment. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 28, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahne, A. What’s Different in Second-Language Processing? Evidence from Event-Related Brain Potentials. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 2001, 30, 221–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscar-Berman, M. Alcohol-related ERP changes in cognition. Alcohol 1987, 4, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, A.C.; Metsala, J.L. Young children’s age-of-acquisition estimates for spoken words. Mem. Cognit. 1992, 20, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izura, C.; Ellis, A.W. Age of acquisition effects in word recognition and production in first and second languages. Psicológica 2002, 23, 245–281. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, Y.I.; Grinchenko, Y.V.; Laukka, S.; Järvilehto, T.; Maz, V.N.; Korpusova, A.V. Effect of ethanol on hippocampal neurons depends on their behavioural specialization. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 1993, 149, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, L.I.; Alexandrov, Y.I. Changes of auditory-evoked potentials in response to behaviorally meaningful tones induced by acute ethanol intake in altricial nestlings at the stage of formation of natural behavior. Alcohol 1993, 10, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, L.; Joels, M.; Roozendaal, B.; Wolf, O.T.; Oitzl, M.S. Stress effects on memory: An update and integration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 36, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, L.; Wolrf, O.T. Stress prompts habit behavior in humans. J. Neurosci. 2009, 22, 7191–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znamenskaja, I.I.; Markov, A.V.; Bahchina, A.V.; Aleksandrov, J.I. Attitude to outgroup members in stress: System dedifferentiation. Psikhol. Zh. 2016, 37, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R. Stress potentiates decision biases: A stress induced deliberation-to-intuition (SIDI) model. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 3, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parin, S.B.; Bakhchina, A.V.; Polevaya, S.A. A neurochemical framework of the theory of stress. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 94, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, Y.I.; Svarnik, O.E.; Znamenskaya, I.I.; Kolbeneva, M.G.; Arutyunova, K.R.; Krylov, A.K.; Bulava, A.I. Regression as the Stage of Development, 1st ed.; IPRAS: Moscow, Russia, 2017; pp. 10–143. ISBN 978-5-9270-0354-9. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A.P.; Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinana, T.G.; Clarke, G. Biological and psychological markers of stress in humans: Focus on the Trier Social Stress Test. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 94–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.A. Brain Systems that Mediate both Emotion and Cognition. Cognit. Emot. 1990, 4, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassum, K.M. Neurochemistry of Desire: Endogenous Opioid and Glutamate Involvement in Incentive Learning and Reward Seeking Actions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 120–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sozinov, A.A.; Bohan, A.I.; Alexandrov, Y.I. A software for assessment of new experience formation and problem solving under achievement or avoidance conditions. Exp. Psychol. 2018, 11, 75–91. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrov, Y.I. Systemic psychophysiology. In Russian Cognitive Neuroscience: Historical and Cultural Context, 1st ed.; Forsythe, C., Zotov, M.V., Radvansky, G.A., Tsvetkova, L., Eds.; CreateSpace Independent Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 65–100. [Google Scholar]
- Melillo, P.; Bracale, M.; Pecchia, L. Nonlinear heart rate variability features for real-life stress detection. Case study: Students under stress due to university examination. Biomed. Eng. Online 2011, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchinsky, A.I.; William, H.C.; Kuusela, T.; Cancio, L.C. Loss of complexity characterizes the heart response to experimental hemorrhagic shock in swine. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, R. Direct measurement of alcohol and its metabolites. Addiction 2003, 98, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newlin, D.B.; Wong, C.J.; Stapleton, J.M.; London, E.D. Intravenous cocaine decreases cardiac vagal tone, vagal index (derived in Lorenz Space), and heart period complexity (approximate entropy) in cocaine abusers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000, 23, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, G.; Allegrini, P.; Lanata, A.; Scilingo, E.P. Dominant Lyapunov exponent and approximate entropy in heart rate variability during emotional visual elicitation. Front. Neuroeng. 2012, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, I.; Balljinder, K.S.; Ciarrochi, J. A heart and a mind: Self-distancing facilitates the association between heart rate variability, and wise reasoning. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wake, E.; Brack, K. Characterization of the intrinsic cardiac nervous system. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2016, 199, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokonozi, A.K.; Michail, E.M.; Chouvarda, I.C.; Maglaveras, N.M. A Study of Heart Rate and Brain System Complexity and Their Interaction in Sleep-Deprived Subjects. Comput. Cardiol. 2008, 35, 969–971. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Angari, H.M.; Sahakian, A.V. Use of Sample Entropy Approach to Study Heart Rate Variability in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1900–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| HR Index | Group | Language | Med | Q1 | Q3 | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SampEn | 1–5 years | German | 1.30 | 1.14 | 1.36 | T = 7, Z = 3.42, p < 0.01 |
| Russian | 1.12 | 1.08 | 1.17 | |||
| 6–18 years | German | 1.17 | 1.07 | 1.38 | T = 16, Z = 1.51, p = 0.13 | |
| Russian | 1.07 | 0.95 | 1.19 | |||
| av-RR (ms) | 1–5 years | German | 705 | 647 | 759 | T = 78, Z = 0.33, p = 0.74 |
| Russian | 738 | 641 | 765 | |||
| 6–18 years | German | 713 | 584 | 749 | T = 20, Z = 1.16, p = 0.25 | |
| Russian | 695 | 579 | 756 | |||
| SDNN (ms) | 1–5 years | German | 49.39 | 40.12 | 57.50 | T = 79, Z = 0.28, p = 0.78 |
| Russian | 48.81 | 42.25 | 62.55 | |||
| 6–18 years | German | 48.05 | 37.20 | 52.97 | T = 25, Z = 0.71, p = 0.48 | |
| Russian | 47.97 | 33.91 | 57.92 |
| Variables | Group | Language | Med | Q1 | Q3 | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| number of mistakes | 1–5 years | German | 12 | 6 | 13 | T = 0, Z = 3.62, p < 0.01 |
| Russian | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 6–18 years | German | 5 | 2 | 10 | T = 0, Z = 2.93, p < 0.01 | |
| Russian | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| response time (ms) | 1–5 years | German | 8166 | 6615 | 10,953 | T = 0, Z = 3.62, p < 0.01 |
| Russian | 4271 | 3787 | 5191 | |||
| 6–18 years | German | 6803 | 3565 | 8412 | T = 4, Z = 2.58, p < 0.01 | |
| Russian | 3300 | 2579 | 3835 |
| HR Index | Test | Med | Q1 | Q3 | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SampEn | mathematical terms | 1.09 | 0.98 | 1.15 | t = 7.70, p < 0.01, t-test |
| general vocabulary | 0.97 | 0.86 | 1.04 | ||
| av-RR (ms) | mathematical terms | 803 | 739 | 916 | t = −1.79, p = 0.08, t-test |
| general vocabulary | 814 | 754 | 922 | ||
| SDNN (ms) | mathematical terms | 57.30 | 45.41 | 76.68 | T = 309, Z = 0.09, p = 0.92, Wilcoxon test |
| general vocabulary | 56.66 | 44.52 | 78.32 |
| Mathematical Vocabulary | SampEn | av-RR (ms) | SDNN (ms) |
| number of mistakes | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.09 |
| response time (ms) | −0.27 | 0.13 | −0.32 |
| General vocabulary | SampEn | av-RR (ms) | SDNN (ms) |
| number of mistakes | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| response time (ms) | 0.11 | −0.28 | 0.12 |
| Statistics | Conditions | Time Period after the Start of Drinking | Friedman Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 20 min | 25 min | 30 min | |||
| Med | alcohol | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.85 | X2 = 13.62, p < 0.03 |
| control | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 1.04 | 1.11 | 1.04 | X2 = 1.60, p = 0.90 | |
| Q1 | alcohol | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.75 | |
| control | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.95 | ||
| Q3 | alcohol | 1.06 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.05 | 1.07 | 0.99 | |
| control | 1.14 | 1.13 | 1.18 | 1.12 | 1.18 | 1.15 | ||
| Wilcoxon test | T = 121 Z = 1.12 p = 0.26 | T = 127 Z = 0.96 p = 0.34 | T = 71 Z = 2.46 p < 0.05 | T = 46 Z = 3.14 p < 0.01 | T = 79 Z = 2.25 p < 0.05 | T = 73 Z = 2.41 p < 0.05 | ||
| Statistics | Conditions | Time Period after the Start of Drinking | Friedman Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 20 min | 25 min | 30 min | |||
| Med | alcohol | 716 | 734 | 729 | 718 | 717 | 715 | X2 = 23.52, p < 0.01 |
| control | 770 | 796 | 804 | 829 | 832 | 811 | X2 = 40.63, p < 0.01 | |
| Q1 | alcohol | 680 | 676 | 649 | 659 | 657 | 632 | |
| control | 697 | 736 | 745 | 752 | 739 | 748 | ||
| Q3 | alcohol | 782 | 797 | 785 | 792 | 794 | 764 | |
| control | 870 | 921 | 898 | 903 | 940 | 916 | ||
| Wilcoxon test | T = 87 Z = 2.25 p < 0.05 | T = 57 Z = 3.01 p < 0.01 | T = 37 Z = 3.52 p < 0.01 | T = 16 Z = 4.05 p < 0.01 | T = 25 Z = 3.82 p < 0.01 | T = 24 Z = 3.85 p < 0.01 | ||
| Statistics | Conditions | Time Period after the Start of Drinking | Friedman Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 20 min | 25 min | 30 min | |||
| Med | alcohol | 70.99 | 67.78 | 70.26 | 69.99 | 67.34 | 65.42 | X2 = 8.90, p = 0.11 |
| control | 68.99 | 80.66 | 73.62 | 78.15 | 78.09 | 74.90 | X2 = 4.69, p = 0.45 | |
| Q1 | alcohol | 54.32 | 52.34 | 46.61 | 46.03 | 48.47 | 49.35 | |
| control | 54.55 | 65.01 | 59.90 | 58.90 | 69.42 | 58.87 | ||
| Q3 | alcohol | 80.97 | 76.46 | 76.33 | 80.93 | 76.20 | 70.47 | |
| control | 100.77 | 92.83 | 97.11 | 108.10 | 96.74 | 120.74 | ||
| Wilcoxon test | T = 136 Z = 1.01 p = 0.32 | T = 68 Z = 2.73 p < 0.01 | T = 111 Z = 1.64 p = 0.101 | T = 62 Z = 2.88 p < 0.01 | T = 64 Z = 2.83 p < 0.01 | T = 59 Z = 2.96 p < 0.01 | ||
| HR Index | Period | Med | Q1 | Q3 | Wilcoxon Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SampEn | rest | 0.77 | 0.64 | 1.07 | T = 16, Z = 2.06, p < 0.05 |
| stress | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.67 | ||
| av-RR (ms) | rest | 585 | 505 | 686 | T = 8, Z = 2.62, p < 0.05 |
| stress | 470 | 411 | 531 | ||
| SDNN (ms) | rest | 56.14 | 47.99 | 69.28 | T = 0, Z = 3.18, p < 0.01 |
| stress | 43.26 | 27.19 | 54.11 |
| HR Index | Point of Time from the Start of Playing the Game | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | 140 | 150 | |
| SampEn | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.73 ± 0.02 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 0.74 ± 0.02 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 0.76 ± 0.02 |
| av-RR (ms) | 789 ± 19.02 | 793 ± 19.73 | 792 ± 20.12 | 792 ± 20.24 | 791 ± 20.21 | 791 ± 20.06 |
| SDNN (ms) | 58.91 ± 4.66 | 52.19 ± 4.01 | 50.79 ± 3.84 | 50.04 ± 3.71 | 49.88 ± 3.81 | 49.93 ± 3.52 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakhchina, A.V.; Arutyunova, K.R.; Sozinov, A.A.; Demidovsky, A.V.; Alexandrov, Y.I. Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour. Entropy 2018, 20, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20060449
Bakhchina AV, Arutyunova KR, Sozinov AA, Demidovsky AV, Alexandrov YI. Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour. Entropy. 2018; 20(6):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20060449
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakhchina, Anastasiia V., Karina R. Arutyunova, Alexey A. Sozinov, Alexander V. Demidovsky, and Yurii I. Alexandrov. 2018. "Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour" Entropy 20, no. 6: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20060449
APA StyleBakhchina, A. V., Arutyunova, K. R., Sozinov, A. A., Demidovsky, A. V., & Alexandrov, Y. I. (2018). Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour. Entropy, 20(6), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20060449





