Quantum Discord, Thermal Discord, and Entropy Generation in the Minimum Error Discrimination Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
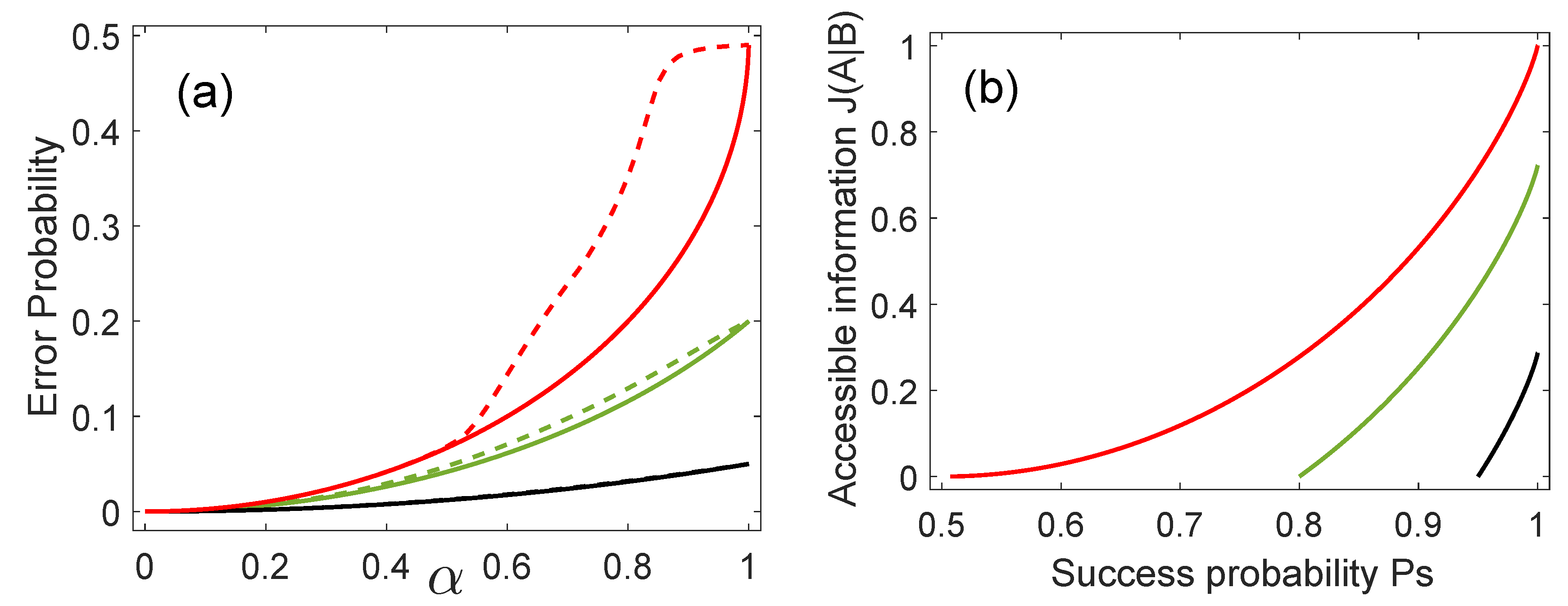
2. Minimum Error Discrimination
3. Channel without Entanglement
4. Correlations between Alice and Bob
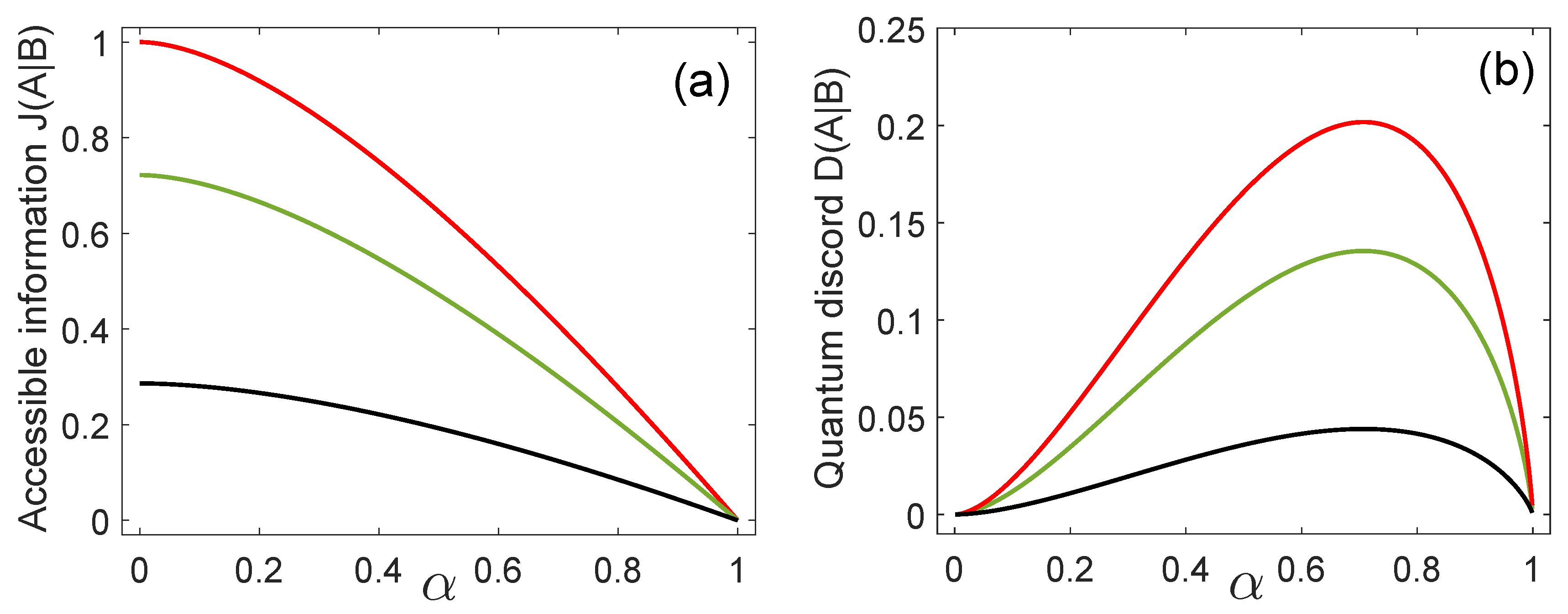
4.1. Classical Correlations and Quantum Discord
4.2. Thermal Discord
4.3. Accessible Information and Optimum Success Probability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, M.; Chrzanowski, H.M.; Assad, S.M.; Symul, T.; Modi, K.; Ralph, T.C.; Vedral, V.; Lam, P.K. Observing the operational significance of discord consumption. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwolak, M.; Zurek, W.H. Complementarity of quantum discord and classically accessible information. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-S.; Xu, X.-Y.; Li, C.-J.; Zhang, C.-J.; Zou, X.-B.; Guo, G.-C. Experimental investigation of classical and quantum correlations under decoherence. Nat. Comms. 2010, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa, L.; Retamal, J.C.; Alid-Vaccarezza, M. Dissonance is Required for assited optimal state discrimination. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 080401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Fei, S.M.; Wang, Z.-X.; Fan, H. Assisted state discrimination without entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 022328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-L.; Chen, J.-L.; Kwek, L.C.; Vedral, V. Requirement of Dissonance in Assisted Optimal State Discrimination. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horodecki, M.; Horodecki, P.; Horodecki, R.; Oppenheim, J.; Sen, A.; Sen, U.; Synak-Radtke, B. Local versus nonlocal information in quantum-information theory: Formalism and phenomena. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 71, 062307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodecki, R.; Horodecki, P.; Horodecki, M.; Horodecki, K. Quantum entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, H.; Zurek, W.H. Quantum Discord: A Measure of the Quantumness of Correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 88, 017901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herderson, L.; Vedral, V. Classical, quantum and total correlations. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2001, 34, 6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, K.; Brodutch, A.; Cable, H.; Paterek, T.; Vedral, V. The classical-quantum boundary for correlations: Discord and related measures. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Quantum discord and Maxwell’s demons. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 67, 012320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulli, C.C.; Sarandy, M.S. Global quantum discord in multipartite systems. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 042109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto, R.; Orszag, M. Determination of the maximum global quantum discord via measurements of excitations in a cavity QED network. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2014, 47, 095501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groisman, B.; Popescu, S.; Winter, A. Quantum, classical, and total amount of correlations in a quantum state. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 032317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landauer, R. Irreversibility and Heat Generation in the Computing Process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1961, 5, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Nori, F.; Vedral, V. Colloquium: The physics of Maxwell’s demon and information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, A. Complexity, Entropy and the Physics of Information; Zurek, W.H., Ed.; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; 345p. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, A. Quantum Theory: The Concepts and Methods; Kluwer Academic: Boston, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bergou, J.; Hillery, M. Introduction to the Theory of Quantum Information Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Holevo, A.S. Statistical Decision Theory for Quantum Systems. J. Multivar. Anal. 1973, 3, 337–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helstrom, C.W. Quantum Detection and Estimation Theory; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Roa, L.; Delgado, A.; Fuentes-Guridi, I. Optimal conclusive teleportation of quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 68, 022310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.; Solís-Prosser, M.A.; Delgado, A.; Jiménez, O. Quantum teleportation via maximum-confidence quantum measurements. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 062322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; Roa, L.; Retamal, J.C.; Saavedra, C. Entanglement swapping via quantum state discrimination. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 71, 012303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-Prosser, M.A.; Delgado, A.; Jiménez, O.; Neves, L. Deterministic and probabilistic entanglement swapping of nonmaximally entangled states assisted by optimal quantum state discrimination. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 012337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoenix, S.J.D.; Barnett, S.M.; Chefles, A. Three-state quantum cryptography. J. Mod. Opt. 2000, 47, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, A.K.; Parashar, P.; Agrawal, P. Probabilistic superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 012329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.M.; Riis, E. Experimental demonstration of polarization discrimination at the Helstrom bound. J. Mod. Opt. 1997, 44, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldherr, G.; Dada, A.C.; Neumann, P.; Jelezko, F.; Andersson, E.; Wrachtrup, J. Distinguishing between Nonorthogonal Quantum States of a Single Nuclear Spin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 180501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.B.M.; Kendon, V.M.; Chefles, A.; Barnett, S.M.; Riis, E.; Sasaki, M. Experimental realization of optimal detection strategies for overcomplete states. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 64, 012303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-Prosser, M.A.; Fernandes, M.F.; Jiménez, O.; Delgado, A.; Neves, L. Experimental Minimum-Error Quantum-State Discrimination in High Dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andi, S. Quantum State Discrimination and Quantum Cloning: Optimization and Implementation. Ph.D. Thesis, CUNY Academic Works, City University of New York, New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlsten, O.; Renner, R.; Rieper, E.; Vedral, V. Inadequacy of von Neumann entropy for characterizing extractable work. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 053015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Arno, M.; D’Ariano, G.M.; Sacchi, M.F. Informational power of quantum measurements. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 062304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Barnett, S.; Jozsa, R.; Osaki, M.; Hirota, O. Accessible information and optimal strategies for real symmetrical quantum sources. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 59, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, L.B. Optimal quantum measurements for two pure and mixed states. In Quantum Communications and Measurement; Belavkin, V.P., Hirota, O., Hudson, R.L., Eds.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, S.M.; Croke, S. Quantum State Discrimination. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2009, 1, 238–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streltsov, A.; Kampermann, H.; Bruss, D. Linking Quantum Discord to Entanglement in a Measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 160401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodutch, A.; Terno, D. Quantum discord, local operations, and Maxwell’s demons. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 062103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, K.; Brukner, C.; Vedral, V. Thermodynamical cost of accessing quantum information. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 2005, 38, 7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Momose, R.; Hirota, O. Optimum Measurements for Discrimination among Symmetric Quantum States and Parameter Estimation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1997, 36, 1269–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergou, J.; Feldman, E.; Hillery, M. Extracting Information from a Qubit by Multiple Observers: Toward a Theory of Sequential State Discrimination. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez, O.; Solís-Prosser, M.A.; Neves, L.; Delgado, A. Quantum Discord, Thermal Discord, and Entropy Generation in the Minimum Error Discrimination Strategy. Entropy 2019, 21, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21030263
Jiménez O, Solís-Prosser MA, Neves L, Delgado A. Quantum Discord, Thermal Discord, and Entropy Generation in the Minimum Error Discrimination Strategy. Entropy. 2019; 21(3):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21030263
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez, Omar, Miguel Angel Solís-Prosser, Leonardo Neves, and Aldo Delgado. 2019. "Quantum Discord, Thermal Discord, and Entropy Generation in the Minimum Error Discrimination Strategy" Entropy 21, no. 3: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21030263
APA StyleJiménez, O., Solís-Prosser, M. A., Neves, L., & Delgado, A. (2019). Quantum Discord, Thermal Discord, and Entropy Generation in the Minimum Error Discrimination Strategy. Entropy, 21(3), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21030263




