Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis Based on Frequency Bands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Recruitment
4.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
4.3. Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity
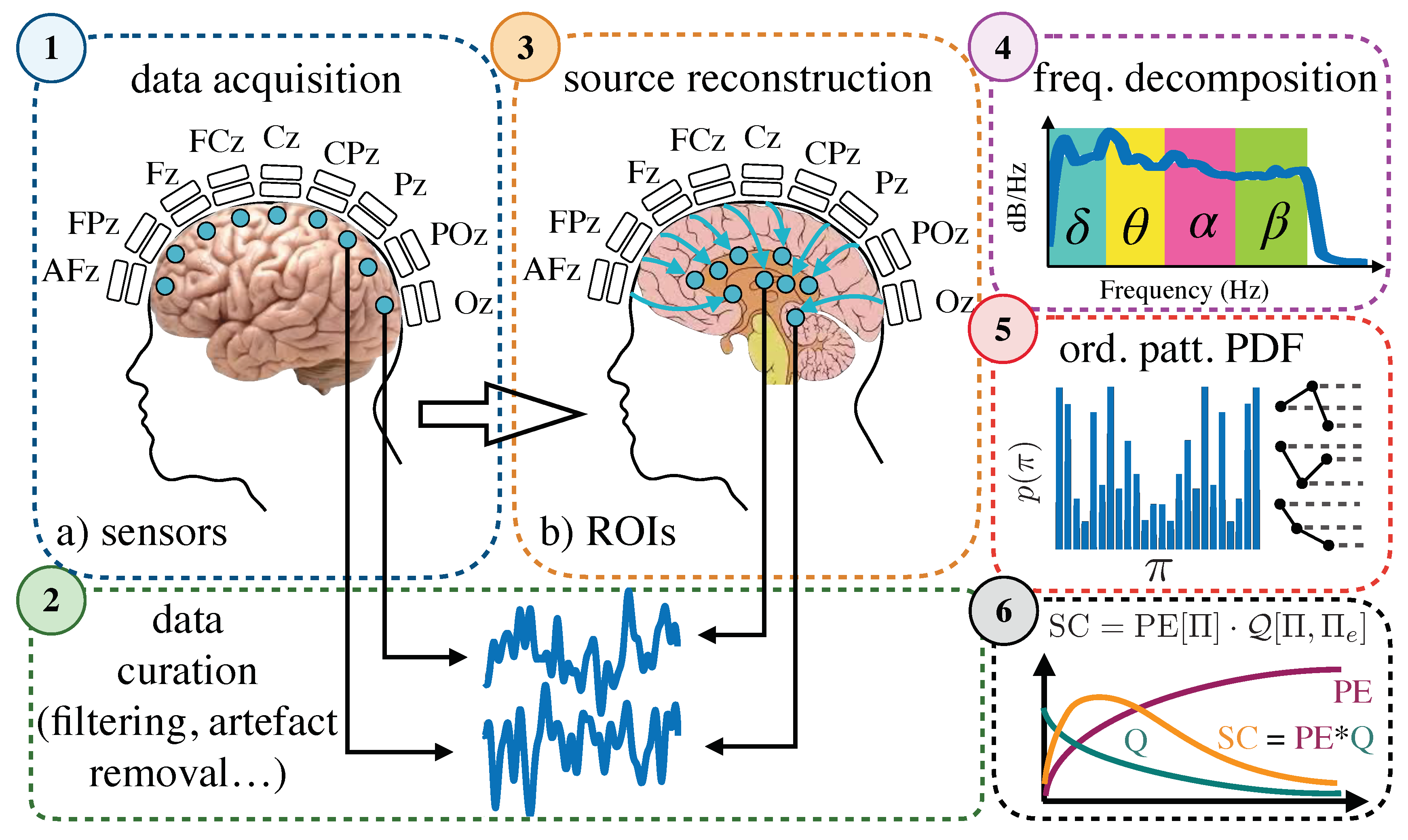
4.4. Pipeline
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.; Bateman, R.; Blennow, K.; Rowe, C.; Sperling, R.; Cummings, J. Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Doody, R.; Kurz, A.; Mohs, R.C.; Morris, J.C.; Rabins, P.V.; Ritchie, K.; Rossor, M.; Thal, L.; Winblad, B. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Marin, V.; Blazquez-Llorca, L.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Boluda, S.; Muntane, G.; Ferrer, I.; DeFelipe, J. Diminished perisomatic GABAergic terminals on cortical neurons adjacent to amyloid plaques. Front. Neuroanat. 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Demonstration of Amyloid Deposits and Neurofibrillary Changes in Whole Brain Sections. Brain Pathol. 1991, 1, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Wiste, H.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Vemuri, P.; Mielke, M.M.; Weigand, S.D.; Senjem, M.L.; Gunter, J.L.; Lowe, V.; Gregg, B.E.; et al. Rates of β-amyloid accumulation are independent of hippocampal neurodegeneration. Neurology 2014, 82, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 2002, 298, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.A.; Konnerth, A. Impairments of neural circuit function in Alzheimer’s disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palop, J.J.; Mucke, L. Amyloid-B-induced neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: From synapses toward neural networks. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Shiri-Feshki, M. Rate of progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia—Meta-analysis of 41 robust inception cohort studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2009, 119, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarci, K.; Weigand, S.D.; Przybelski, S.A.; Shiung, M.M.; Whitwell, J.L.; Negash, S.; Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; O’Brien, P.C.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Risk of dementia in MCI: Combined effect of cerebrovascular disease, volumetric MRI, and 1H MRS. Neurology 2009, 72, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagan, A.M.; Roe, C.M.; Xiong, C.; Mintun, M.A.; Morris, J.C.; Holtzman, D.M. Cerebrospinal fluid tau/β-amyloid42 ratio as a prediction of cognitive decline in nondemented older adults. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, J.B.; Xie, S.X.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Shaw, L.M. Longitudinal change in CSF Tau and Aβ biomarkers for up to 48 months in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, H.W.; Verbunt, J.P.; Scheltens, P.; Van Dijk, B.W.; Jonkman, E.J. Magnetoencephalographic analysis of cortical activity in Alzheimer’s disease: A pilot study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cappellen Van Walsum, A.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; Berendse, H.W.; Van Dijk, B.W.; Knol, D.L.; Scheltens, P.; Stam, C.J. A neural complexity measure applied to MEG data in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montez, T.; Poil, S.S.; Jones, B.F.; Manshanden, I.; Verbunt, J.P.; Van Dijk, B.W.; Brussaard, A.B.; Van Ooyen, A.; Stam, C.J.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Altered temporal correlations in parietal alpha and prefrontal theta oscillations in early-stage Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipova, D.; Ahveninen, J.; Jensen, O.; Ylikoski, A.; Pekkonen, E. Altered generation of spontaneous oscillations in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza, J.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A.; García, M. Extraction of spectral based measures from MEG background oscillations in Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Hornero, R.; Mayo, A.; Poza, J.; Gil-Gregorio, P.; Ortiz, T. MEG spectral profile in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza, J.; Hornero, R.; Abasolo, D.; Fernandez, A.; Escudero, J. Analysis of Spontaneous MEG Activity in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease using Spectral Entropies. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 6179–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, J.; Hornero, R.; Poza, J.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A. Assessment of classification improvement in patients with Alzheimer’s disease based on magnetoencephalogram blind source separation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero, J.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A. Blind source separation to enhance spectral and non-linear features of magnetoencephalogram recordings. Application to Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besga, A.; Ortiz, L.; Fernández, A.; Maestu, F.; Arrazola, J.; Gil-Gregorio, P.; Fuentes, M.; Ortiz, T. Structural and functional patterns in healthy aging, mild cognitive impairment, and alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2010, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.; Maestú, F.; Amo, C.; Gil, P.; Fehr, T.; Wienbruch, C.; Rockstroh, B.; Elbert, T.; Ortiz, T. Focal temporoparietal slow activity in Alzheimer’s disease revealed by magnetoencephalography. Biol. Psychiatry 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Arrazola, J.; Maestú, F.; Amo, C.; Gil-Gregorio, P.; Wienbruch, C.; Ortiz, T. Correlations of Hippocampal Atrophy and Focal Low-Frequency Magnetic Activity in Alzheimer Disease: Volumetric MR Imaging-Magnetoencephalographic Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, A.; Turrero, A.; Zuluaga, P.; Gil-Gregorio, P.; Del Pozo, F.; Maestu, F.; Moratti, S. MEG delta mapping along the healthy aging-alzheimer’s disease continuum: Diagnostic implications. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 35, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Hornero, R.; Mayo, A.; Poza, J.; Maestú, F.; Ortiz Alonso, T. Quantitative magnetoencephalography of spontaneous brain activity in alzheimer disease: An exhaustive frequency analysis. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2006, 20, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, W.; Stam, C.J.; Jones, B.F.; Zuiderwijk, I.M.; Van Dijk, B.W.; Scheltens, P. Resting-state oscillatory brain dynamics in alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 25, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza, J.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A.; Mayo, A. Evaluation of spectral ratio measures from spontaneous MEG recordings in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Hornero, R.; Fernandez, A.; Abasolo, D.; Escudero, J.; Lopez, M. Magnetoencephalogram background activity analysis in Alzheimer’s disease patients using auto mutual information. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 6181–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A.; Escudero, J. Analysis of the magnetoencephalogram background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients with auto-mutual information. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Escudero, J.; Gómez, C. Nonlinear analysis of electroencephalogram and magnetoencephalogram recordings in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, C.; Hornero, R.; Abasolo, D.; Fernandez, A.; Escudero, J. Analysis of MEG recordings from Alzheimer’s disease patients with sample and multiscale entropies. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 6183–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A.; Escudero, J. Analysis of MEG background activity in Alzheimer’s disease using nonlinear Methods and ANFIS. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 37, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, C.; Abásolo, D.; Poza, J.; Fernández, A.; Hornero, R. MEG analysis in Alzheimer’s disease computing approximate entropy for different frequency bands. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruña, R.; Poza, J.; Gómez, C.; García, M.; Fernández, A.; Hornero, R. Analysis of spontaneous MEG activity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using spectral entropies and statistical complexity measures. J. Neural Eng. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poza, J.; Hornero, R.; Escudero, J.; Fernández, A.; Sánchez, C.I. Regional analysis of spontaneous MEG rhythms in patients with alzheimer’s disease using spectral entropies. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.; Hornero, R.; Gómez, C.; Turrero, A.; Gil-Gregorio, P.; Matías-Santos, J.; Ortiz, T. Complexity analysis of spontaneous brain activity in alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: An MEG study. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2010, 24, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A.; López, M. Complexity analysis of the magnetoencephalogram background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Med. Eng. Phys. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumbayawonda, E.; López-Sanz, D.; Bruña, R.; Serrano, N.; Fernández, A.; Maestú, F.; Abasolo, D. Complexity changes in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: An MEG study of subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Liang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, X. Complexity extraction of electroencephalograms in Alzheimer’s disease with weighted-permutation entropy. Chaos 2015, 25, 043105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labate, D.; La Foresta, F.; Palamara, I.; Morabito, G.; Bramanti, A.; Zhang, Z.; Morabito, F.C. EEG complexity modifications and altered compressibility in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. In Recent Advances of Neural Network Models and Applications; Bassis, S., Esposito, A., Morabito, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 26, pp. 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Morabito, F.C.; Labate, D.; La Foresta, F.; Bramanti, A.; Morabito, G.; Palamara, I. Multivariate Multi-Scale Permutation Entropy for Complexity Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease EEG. Entropy 2012, 14, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Niu, Y.; Miao, L.; Cao, R.; Yan, P.; Guo, H.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Yan, T.; Wu, J.; et al. Decreased Complexity in Alzheimer’s Disease: Resting-State fMRI Evidence of Brain Entropy Mapping. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Childress, A.R.; Detre, J.A. Brain entropy mapping using fMRI. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.H.; Herrera-Diestra, J.L.; Chavez, M. Detection of time reversibility in time series by ordinal patterns analysis. Chaos 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poza, J.; Gómez, C.; García, M.; Bachiller, A.; Fernández, A.; Hornero, R. Analysis of spontaneous MEG activity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using Jensen’s divergence. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Papo, D. Permutation entropy and its main biomedical and econophysics applications: A review. Entropy 2012, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baravalle, R.; Rosso, O.A.; Montani, F. Causal Shannon-Fisher characterization of motor/imagery movements in EEG. Entropy 2018, 20, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baravalle, R.; Rosso, O.A.; Montani, F. Rhythmic activities of the brain: Quantifying the high complexity of beta and gamma oscillations during visuomotor tasks. Chaos 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engels, M.M.; Van der Flier, W.M.; Stam, C.J.; Hillebrand, A.; Scheltens, P.; Van Straaten, E.C. Alzheimer’s disease: The state of the art in resting-state magnetoencephalography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sanz, D.; Serrano, N.; Maestú, F. The role of magnetoencephalography in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhus, E.; Curran, T. Functional role of gamma and theta oscillations in episodic memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stein, A.; Sarnthein, J. Different frequencies for different scales of cortical integration: from local gamma to long range alpha/theta synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 38, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. High-frequency oscillations and the neurobiology of schizophrenia. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundman, M.; Petersen, R.C.; Ferris, S.H.; Thomas, R.G.; Aisen, P.S.; Bennett, D.A.; Foster, N.L.; Jack, C.R.; Galasko, D.R.; Doody, R.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment Can Be Distinguished from Alzheimer Disease and Normal Aging for Clinical Trials. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, S.; Reisberg, B.; Zaudig, M.; Petersen, R.C.; Ritchie, K.; Broich, K.; Belleville, S.; Brodaty, H.; Bennett, D.; Chertkow, H.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment. Lancet 2006, 367, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taulu, S.; Kajola, M. Presentation of electromagnetic multichannel data: The signal space separation method. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taulu, S.; Simola, J. Spatiotemporal signal space separation method for rejecting nearby interference in MEG measurements. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, P.; López-Sanz, D.; Maestú, F.; Pereda, E. Choice of magnetometers and gradiometers after signal space separation. Sensors 2017, 17, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.M. FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, B.D.; Van Drongelen, W.; Yuchtman, M.; Suzuki, A. Localization of brain electrical activity via linearly constrained minimum variance spatial filtering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 44, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Zanin, M.; Tabak, B.M.; Pérez, D.G.; Rosso, O.A. Complexity-entropy causality plane: A useful approach to quantify the stock market inefficiency. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Tabak, B.M.; Serinaldi, F.; Zanin, M.; Pérez, D.G.; Rosso, O.A. Commodity predictability analysis with a permutation information theory approach. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Fernández Bariviera, A.; Guercio, M.B.; Martinez, L.B.; Rosso, O.A. On the efficiency of sovereign bond markets. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2012, 391, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martin, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Fuentes, M.A. Distinguishing noise from chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Ruiz, R.; Mancini, H.L.; Calbet, X. A statistical measure of complexity. Phys. Lett. A 1995, 209, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation Entropy: A Natural Complexity Measure for Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunino, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Fischer, I.; Rosso, O.A.; Mirasso, C.R. Permutation-information-theory approach to unveil delay dynamics from time-series analysis. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2010, 82, 046212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, A.M.; Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A.; Casas, M. Distances in Probability Space and the Statistical Complexity Setup. Entropy 2011, 13, 1055–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, P.W.; Martin, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Intensive entropic non-triviality measure. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2004, 334, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D.P.; Crutchfield, J.P. Measures of statistical complexity: Why? Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 1998, 238, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anteneodo, C.; Plastino, A.R. Some features of the Löpez-Ruiz-Mancini-Calbet (LMC) statistical measure of complexity. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 1996, 223, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briët, J.; Harremoës, P. Properties of classical and quantum Jensen-Shannon divergence. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2009, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
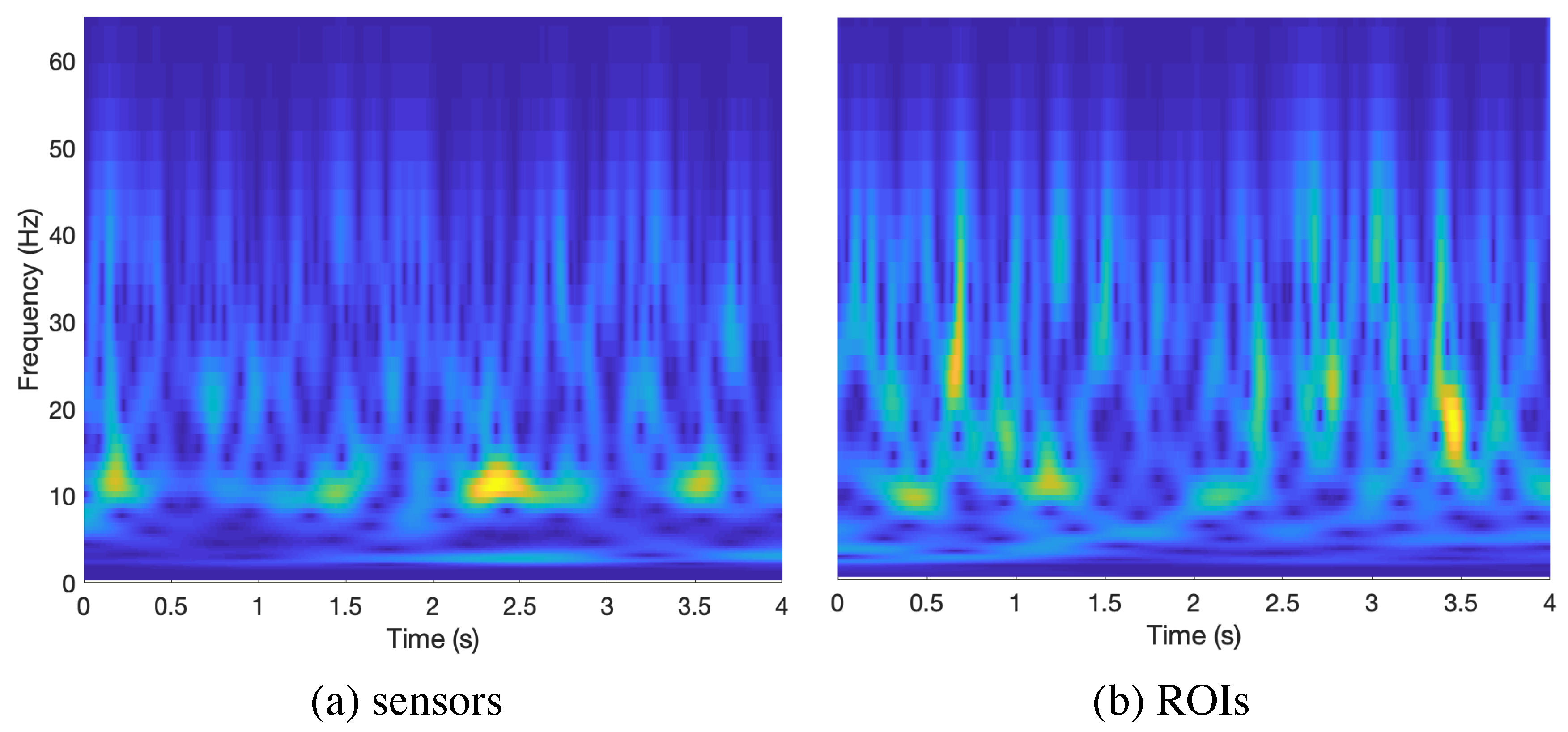




| Broadband | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 0.0046 (*** CG vs. AD) (** CG vs. MCI) | 0.0389 (** CG vs. AD) | 0.0128 (** CG vs. AD) | 0.0687 (*** CG vs. AD) | 0.0040 (*** CG vs. MCI) |
| MCI | 0.0043 (** MCI vs. AD) | 0.0396 | 0.0128 (** MCI vs. AD) | 0.0683 (*** MCI vs. AD) | 0.0046 (*** MCI vs. AD) |
| AD | 0.0034 | 0.0400 | 0.0123 | 0.0743 | 0.0040 |
| Broadband | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 0.0043 (*** CG vs. AD) (** CG vs. MCI) | 0.0380 (* CG vs. AD) | 0.0113 | 0.0648 (*** CG vs. AD) (** CG vs. MCI) | 0.0032 |
| MCI | 0.0040 (*** MCI vs. AD) | 0.0378 | 0.0114 | 0.0670 (** MCI vs. AD) | 0.0033 |
| AD | 0.0032 | 0.0372 | 0.0117 | 0.0687 | 0.0032 |
| (MCI − CG)/CG | (AD − CG)/CG | (AD − MCI)/CG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| broadband | MCI ≈ CG | AD < CG (frontal; parietal) AD > CG (frontal; left temporal) | AD < MCI (frontal; parietal) AD > MCI (frontal; left temporal) |
| MCI ≈ CG | AD > CG (left temporal; occipital) | AD > MCI (frontal; left temporal; occipital) | |
| MCI > CG (frontal) | AD > CG (frontal; left temporal) | AD > MCI (left temporal) | |
| MCI ≈ CG | AD ≈ CG | AD ≈ MCI | |
| MCI < CG (parietal; right temporal) | AD > CG (left frontal) | AD < MCI (parietal) AD > CG (left frontal) |
| (MCI − CG)/CG | (AD − CG)/CG | (AD − MCI)/CG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| broadband | MCI < CG MCI > CG (right premotor) | AD < CG (prefrontal; occipital; association cortex) | AD < MCI (prefrontal; occipital; association cortex) |
| MCI ≈ CG | AD > CG (occipital; premotor; prefrontal) | AD > MCI (occipital; premotor; prefrontal) | |
| MCI > CG (premotor; frontal inf. gyrus) | AD > CG (premotor; frontal inf. gyrus; ventral ant. cing. cortex) AD < CG (somatosensory ctx.; occipito-parietal gyrus) | AD > MCI (ventral ant. cing. cortex) AD < MCI (somatosensory ctx.; occipito-parietal gyrus) | |
| MCI > CG | AD > CG | ||
| MCI > CG (prefrontal; occipital; front. inf. gyrus) | AD > CG (prefrontal; anterior cingulate) AD < CG (occipital) | AD < MCI (occipital) AD > MCI (left premotor; frontal inf. gyrus) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Echegoyen, I.; López-Sanz, D.; Martínez, J.H.; Maestú, F.; Buldú, J.M. Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis Based on Frequency Bands. Entropy 2020, 22, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010116
Echegoyen I, López-Sanz D, Martínez JH, Maestú F, Buldú JM. Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis Based on Frequency Bands. Entropy. 2020; 22(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleEchegoyen, Ignacio, David López-Sanz, Johann H. Martínez, Fernando Maestú, and Javier M. Buldú. 2020. "Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis Based on Frequency Bands" Entropy 22, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010116
APA StyleEchegoyen, I., López-Sanz, D., Martínez, J. H., Maestú, F., & Buldú, J. M. (2020). Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis Based on Frequency Bands. Entropy, 22(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010116






