Spreading Control in Two-Layer Multiplex Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
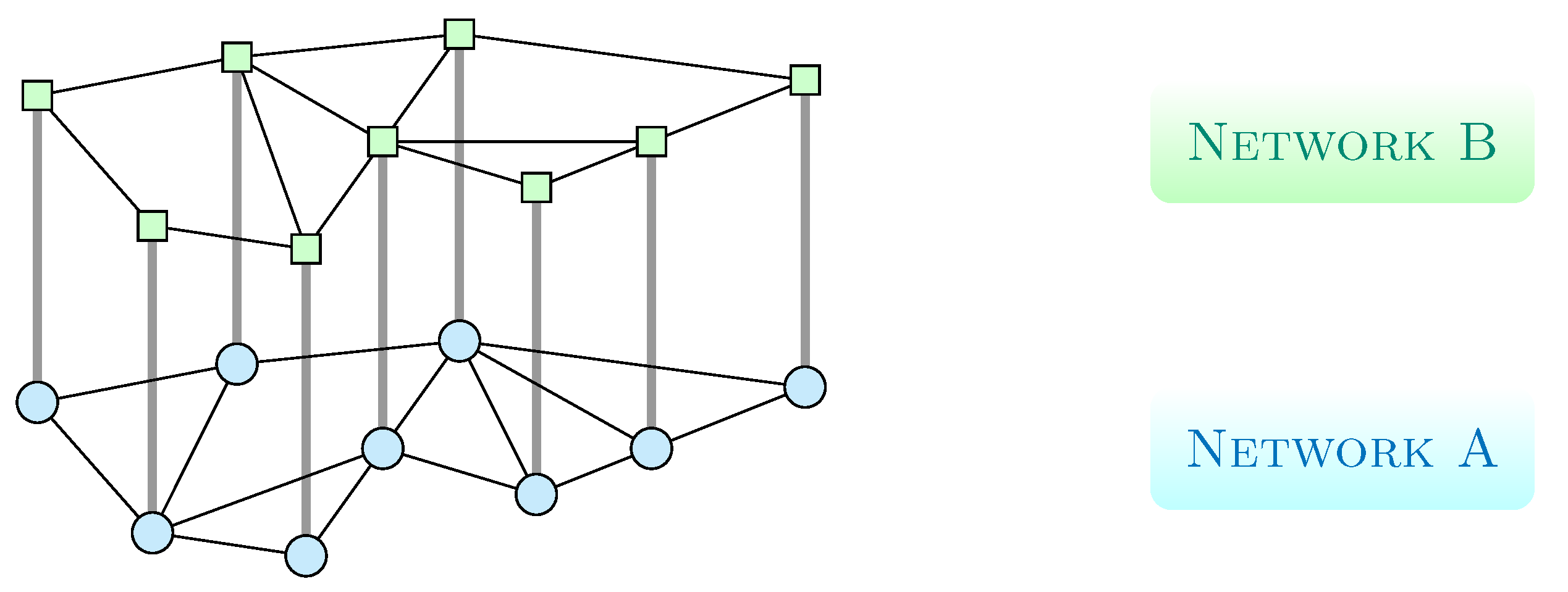
2. Problem Formulation
3. System Analysis
4. Control Design
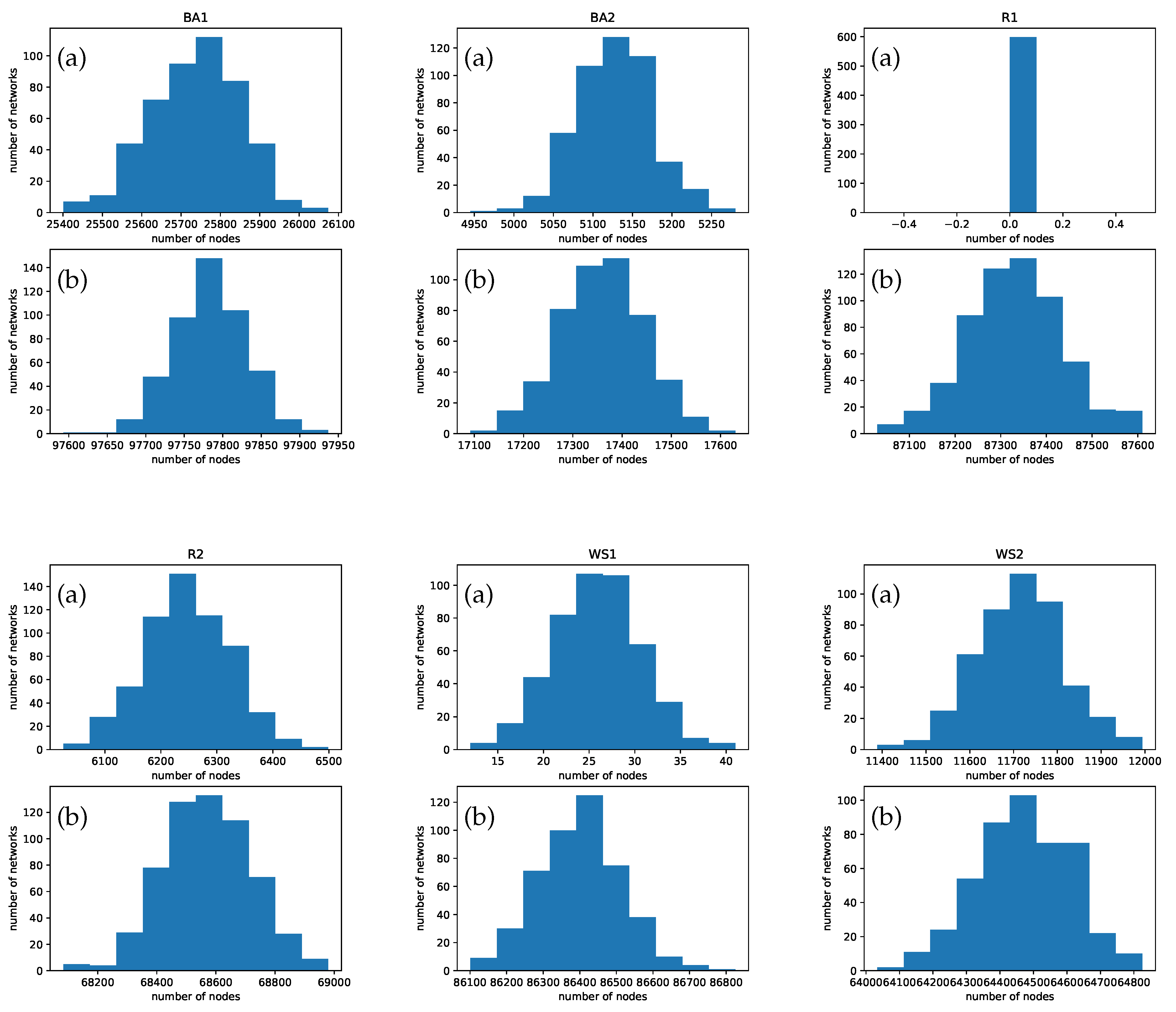
5. Simulations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BA | Barabási-Albert scale free network |
| R | Regular nearest-neighbor network |
| WS | Watts-Strogatz small-world network |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
References
- Aleta, A.; Moreno, Y. Multilayer Networks in a Nutshell. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2019, 10, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Lü, J.; Wei, X. Infection-Probability-Dependent Interlayer Interaction Propagation Processes in Multiplex Networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Feng, J.; Lu, J.-a. A unified framework of interplay between two spreading processes in multiplex networks. Europhys. Lett. 2016, 114, 26006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, A.; Longjas, A.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Georgiou, T.T.; Moreno, Y. Diffusion Dynamics and Optimal Coupling in Multiplex Networks with Directed Layers. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boccaletti, S.; Bianconi, G.; Criado, R.; del Genio, C.; nes, J.G.G.; Romance, M.; na Nadal, I.S.; Wang, Z.; Zanin, M. The structure and dynamics of multilayer networks. Phys. Rep. 2014, 544, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buldú, J.M.; Porter, M.A. Frequency-based brain networks: From a multiplex framework to a full multilayer description. Netw. Neurosci. 2018, 2, 418–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, T. Resource control of epidemic spreading through a multilayer network. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda, G.F.; Cozzo, E.; Peixoto, T.P.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Moreno, Y. Disease Localization in Multilayer Networks. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 011014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granell, C.; Gómez, S.; Arenas, A. Dynamical Interplay between Awareness and Epidemic Spreading in Multiplex Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 128701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granell, C.; Gómez, S.; Arenas, A. Competing spreading processes on multiplex networks: Awareness and epidemics. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 012808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaum, A.; Jaquez, R.B. Estimating the state probability distribution for epidemic spreading in complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 291, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanoev, A.; Trpevski, D.; Kocarev, L. Modeling the Spread of Multiple Concurrent Contagions on Networks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Tang, M.; Cai, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Braunstein, L.A. Suppressing epidemic spreading in multiplex networks with social-support. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 013007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, C.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, K. Information transport in multiplex networks. Phys. A 2016, 447, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, C.G.S.; Aquino, A.L.L.; Ramos, H.S.; Frery, A.C.; Rosso, O.A. A detailed characterization of complex networks using Information Theory. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Valler, N.C.; Prakash, B.A.; Neamtiu, I.; Faloutsos, M.; Faloutsos, C. Competing Memes Propagation on Networks: A Network Science Perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2013, 31, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harush, U.; Barzel, B. Dynamic patterns of information flow in complex networks. Nat. Commun. 2017, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baggio, G.; Rutten, V.; Hennequin, G.; Zampieri, S. Efficient communication over complex dynamical networks: The role of matrix non-normality. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Di, Z.; Wang, W.X.; Lai, Y.C. Exact controllability of complex networks. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nozari, E.; Pasqualetti, F.; Cortés, J. Time-invariant versus time-varying actuator scheduling in complex networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 American Control Conference (ACC), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 May 2017; pp. 4995–5000. [Google Scholar]
- Lindmark, G.; Altafini, C. Minimum energy control for complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G. Pinning control and controllability of complex dynamical networks. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2017, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.P.; Wang, W.X.; Hao, F.; Lai, Y.C. Universal framework for edge controllability of complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, K.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Deng, L.; Xiao, G.; Zeng, F.; Pei, J. Target Controllability of Two-Layer Multiplex Networks Based on Network Flow Theory. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Structural Accessibility and Structural Observabilityof Nonlinear Networked Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1656–1666. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menara, T.; Baggio, G.; Bassett, D.S.; Pasqualetti, F. Conditions for Feedback Linearization of Network Systems. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2020, 4, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, G.; Dall’Asta, L.; Bianconi, G. Control of Multilayer Networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pósfai, M.; Gao, J.; Cornelius, S.P.; Barabási, A.L.; D’Souza, R.M. Controllability of multiplex, multi-time-scale networks. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 032316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Ding, J.; Wen, C.; Pei, J. Optimal control of complex networks based on matrix differentiation. Europhys. Lett. 2016, 115, 68005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, N.J.; Nowzari, C.; Preciado, V.M.; Pappas, G.J. Optimal Resource Allocation for Competitive Spreading Processes on Bilayer Networks. IEEE Trans. Control. Netw. Syst. 2018, 5, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Lv, T. Efficient target control of complex networks based on preferential matching. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, V.; Criado, R.; Romance, M.; Russo, G.; Latora, V. Controlling centrality in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nacher, J.C.; Ishitsuka, M.; Miyazaki, S.; Akutsu, T. Finding and analysing the minimum set of driver nodes required to control multilayer networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidori, A. Nonlinear Control Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Roy, S.; Saberi, A. Designing spatially heterogeneous strategies for control of virus spread. IET Syst. Biol. 2008, 2, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcón Ramos, L.A.; Bernal Jaquez, R.; Schaum, A. Output-Feedback Control for Discrete-Time Spreading Models in Complex Networks. Entropy 2018, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcón-Ramos, L.A.; Bernal Jaquez, R.; Schaum, A. Output-Feedback Control of Virus Spreading in Complex Networks With Quarantine. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 2018, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Ramos, L.A.; Schaum, A.; Lucatero, C.R.; Jaquez, R.B. Stability analysis for virus spreading in complex networks with quarantine and non-homogeneous transition rates. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 490, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowzari, C.; Preciado, V.M.; Pappas, G.J. Analysis and Control of Epidemics: A Survey of Spreading Processes on Complex Networks. IEEE Control Syst. 2016, 36, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakrabarti, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Leskovec, J.; Faloutsos, C. Epidemic Thresholds in Real Networks. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2008, 10, 1:1–1:26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.; Arenas, A.; Borge-Holthoefer, J.; Meloni, S.; Moreno, Y. Discrete-time Markov chain approach to contact-based disease spreading in complex networks. Europhys. Lett. 2010, 89, 38009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Tang, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Braunstein, L.A. Unification of theoretical approaches for epidemic spreading on complex networks. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 80, 036603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.; Arenas, A.; Borge-Holthoefer, J.; Meloni, S.; Moreno, Y. Probabilistic framework for epidemic spreading in complex networks. Int. J. Complex Syst. Sci. 2011, 1, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chakrabarti, D.; Wang, C.; Faloutsos, C. Epidemic Spreading in Real Networks: An Eigenvalue Viewpoint. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems, Florence, Italy, 6–8 October 2003; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal Jaquez, R.; Schaum, A.; Alarcón, L.; Rodríguez, C. Stability analysis for virus spreading in complex networks with quarantine. Publicaciones Matemáticas Del Urug. 2013, 14, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Achterberg, M.A.; Dubbeldam, J.L.A.; Stam, C.J.; Van Mieghem, P. Classification of link-breaking and link-creation updating rules in susceptible-infected-susceptible epidemics on adaptive networks. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 101, 052302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sontag, E.D. On the Input-to-State Stability Property. Eur. J. Control. 1995, 1, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.P.; Wang, Y. Input-to-state stability for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Automatica 2001, 37, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, T.; Bromwich, T. An Introduction to the Theory of Infinite Series; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, C.G. Matrices and Linear Transformations; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Chen, G. Complex networks: Small-world, scale-free and beyond. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2003, 3, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Scenario | Critical Parameter | Satisfied | Not Satisfied |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | |
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | and | - | |
| 5 | or | ||
| Network | Parameters |
|---|---|
| , | |
| , | |
| Every node is connected with 20 nearest neighbors. | |
| Every node is connected with 10 nearest neighbors. | |
| Every node in network was randomly rewired with probability . | |
| Every node in network was randomly rewired with probability . |
| Network | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| , , | |||
| , , |
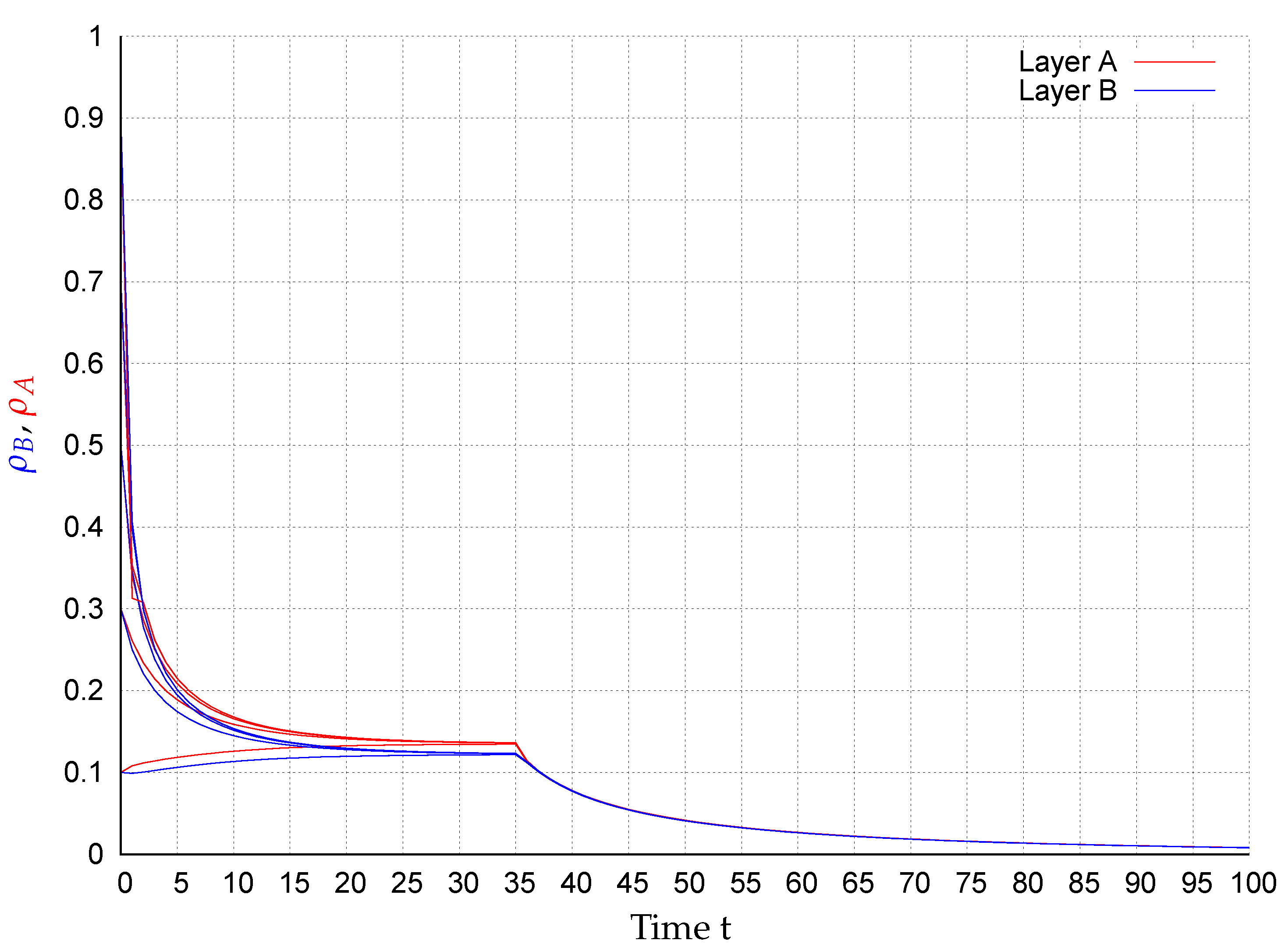
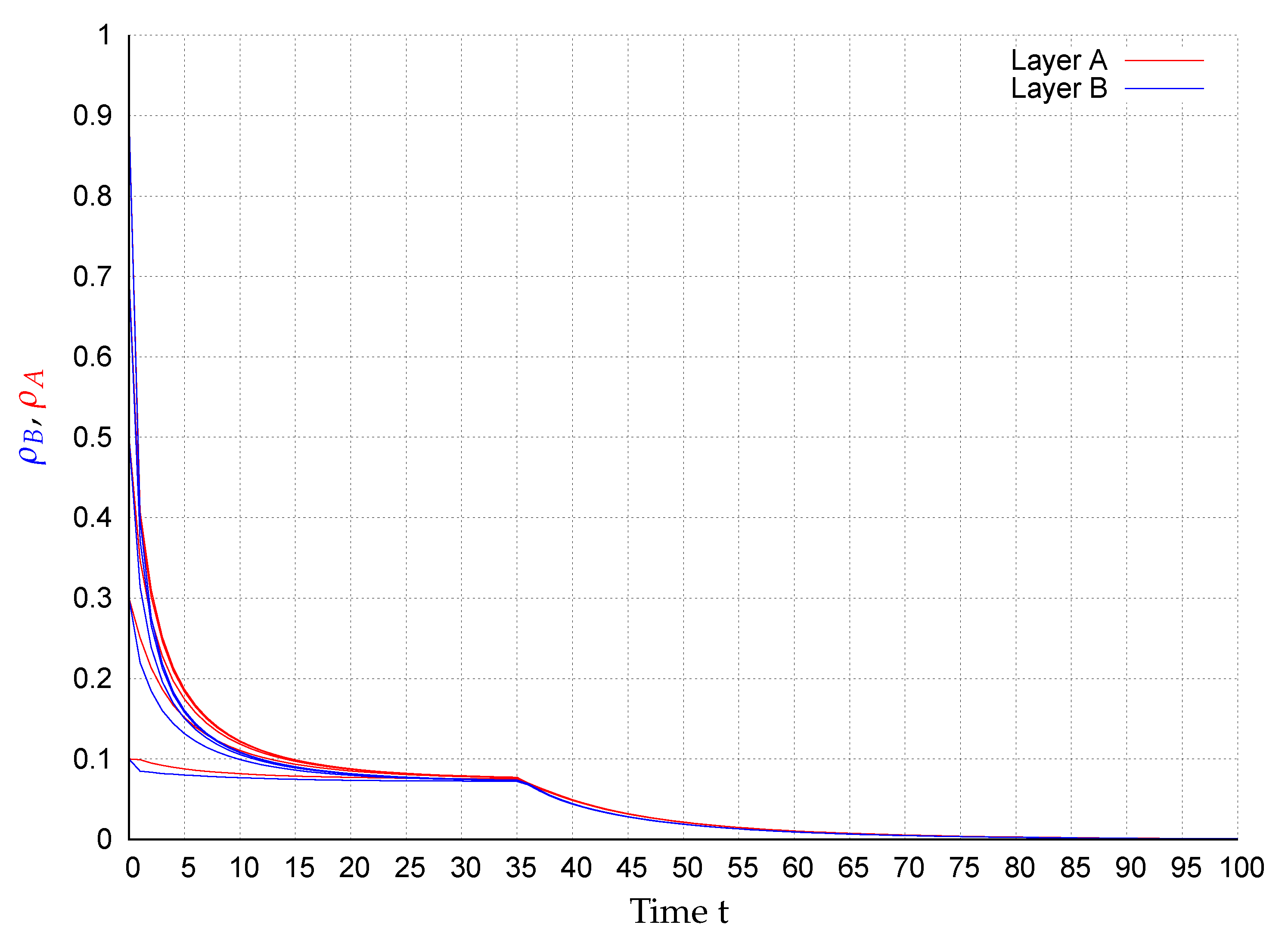
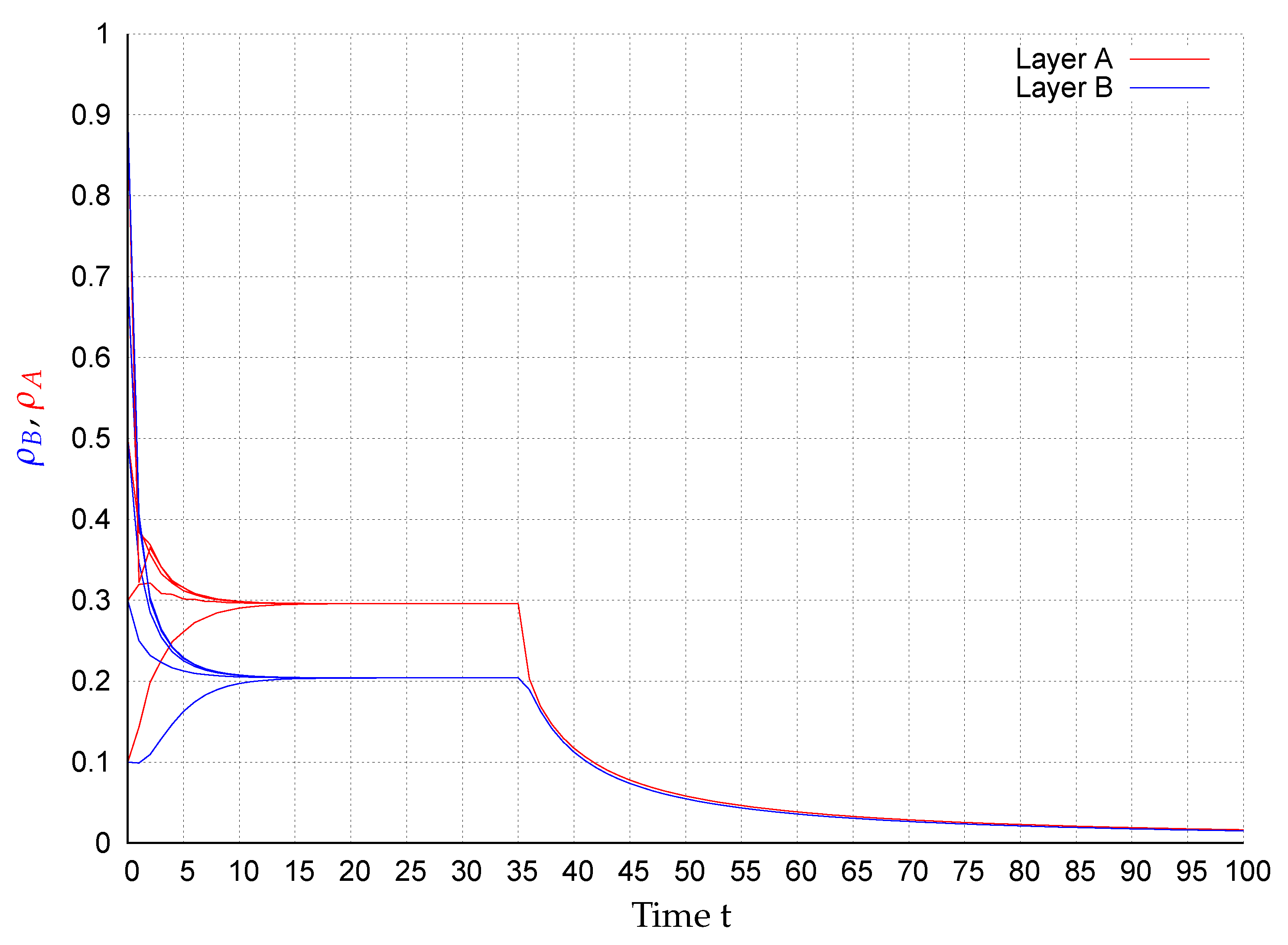
| No. | Layer A | Layer B | Amenable Parameters Chosen | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | and | 2 | ||
| 2 | , and | 3 | ||
| 3 | , and | 4 | ||
| 4 | and | 5 | ||
| 5 | , and | 6 | ||
| 6 | and | 7 |
| Network | or | and | Nodes to Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12,178 | 25,716 | 52,080 | 7761 | 97,735 | |
| 0 | 5082 | 12,191 | 0 | 17,273 | |
| 19,939 | 0 | 67,448 | 0 | 87,387 | |
| 0 | 6138 | 62,286 | 0 | 68,424 | |
| 19,915 | 30 | 66,501 | 24 | 86,470 | |
| 0 | 11,697 | 52,678 | 0 | 64,375 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernal Jaquez, R.; Alarcón Ramos, L.A.; Schaum, A. Spreading Control in Two-Layer Multiplex Networks. Entropy 2020, 22, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101157
Bernal Jaquez R, Alarcón Ramos LA, Schaum A. Spreading Control in Two-Layer Multiplex Networks. Entropy. 2020; 22(10):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101157
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernal Jaquez, Roberto, Luis Angel Alarcón Ramos, and Alexander Schaum. 2020. "Spreading Control in Two-Layer Multiplex Networks" Entropy 22, no. 10: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101157
APA StyleBernal Jaquez, R., Alarcón Ramos, L. A., & Schaum, A. (2020). Spreading Control in Two-Layer Multiplex Networks. Entropy, 22(10), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101157





