From Boltzmann to Zipf through Shannon and Jaynes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Maximum Entropy and Pairwise Interactions
2.1. Feature Functions and Marginal Probabilities
2.2. Pairwise Constrains
3. Data and Results
3.1. Data
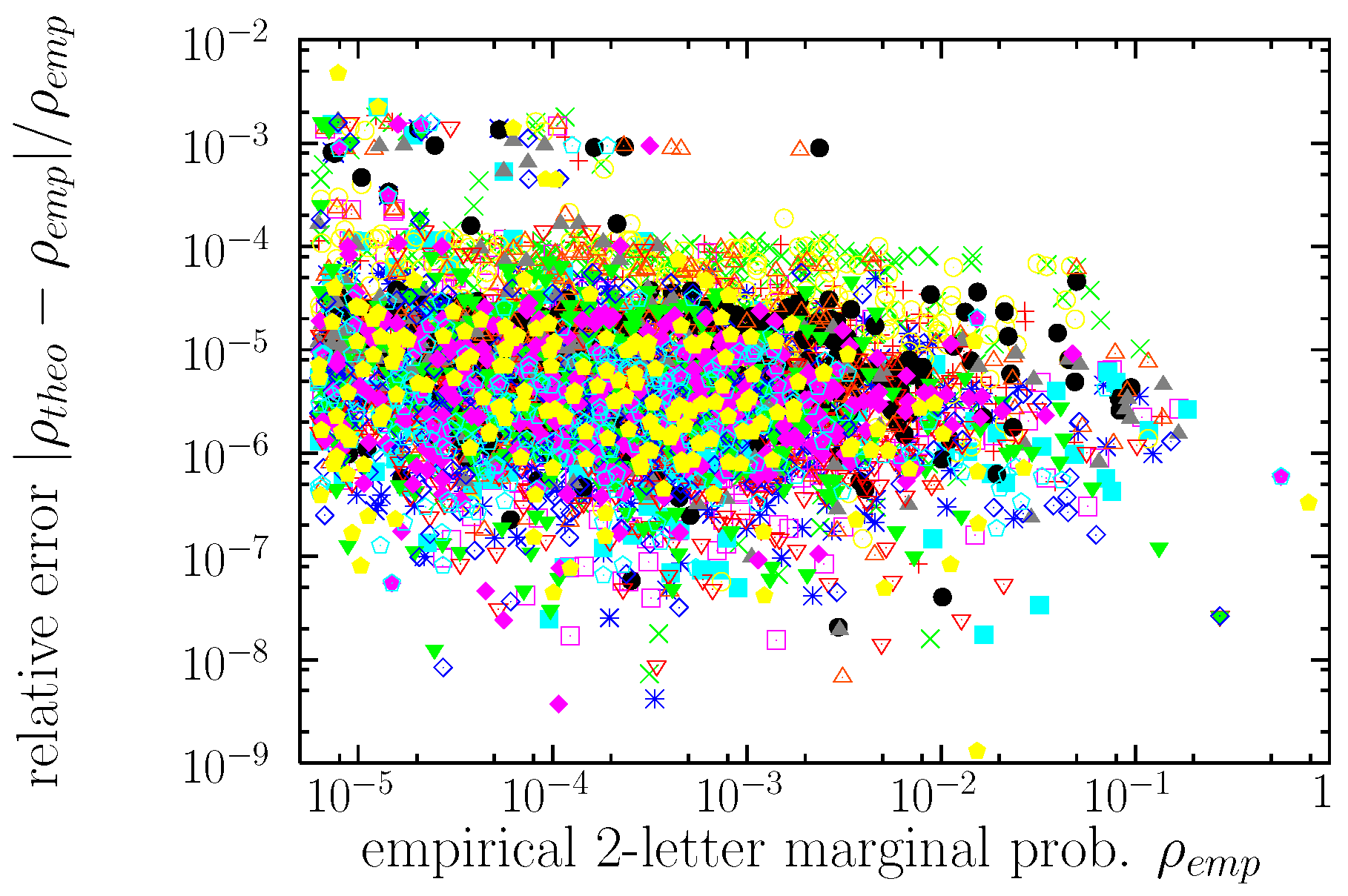
3.2. Marginal Distributions
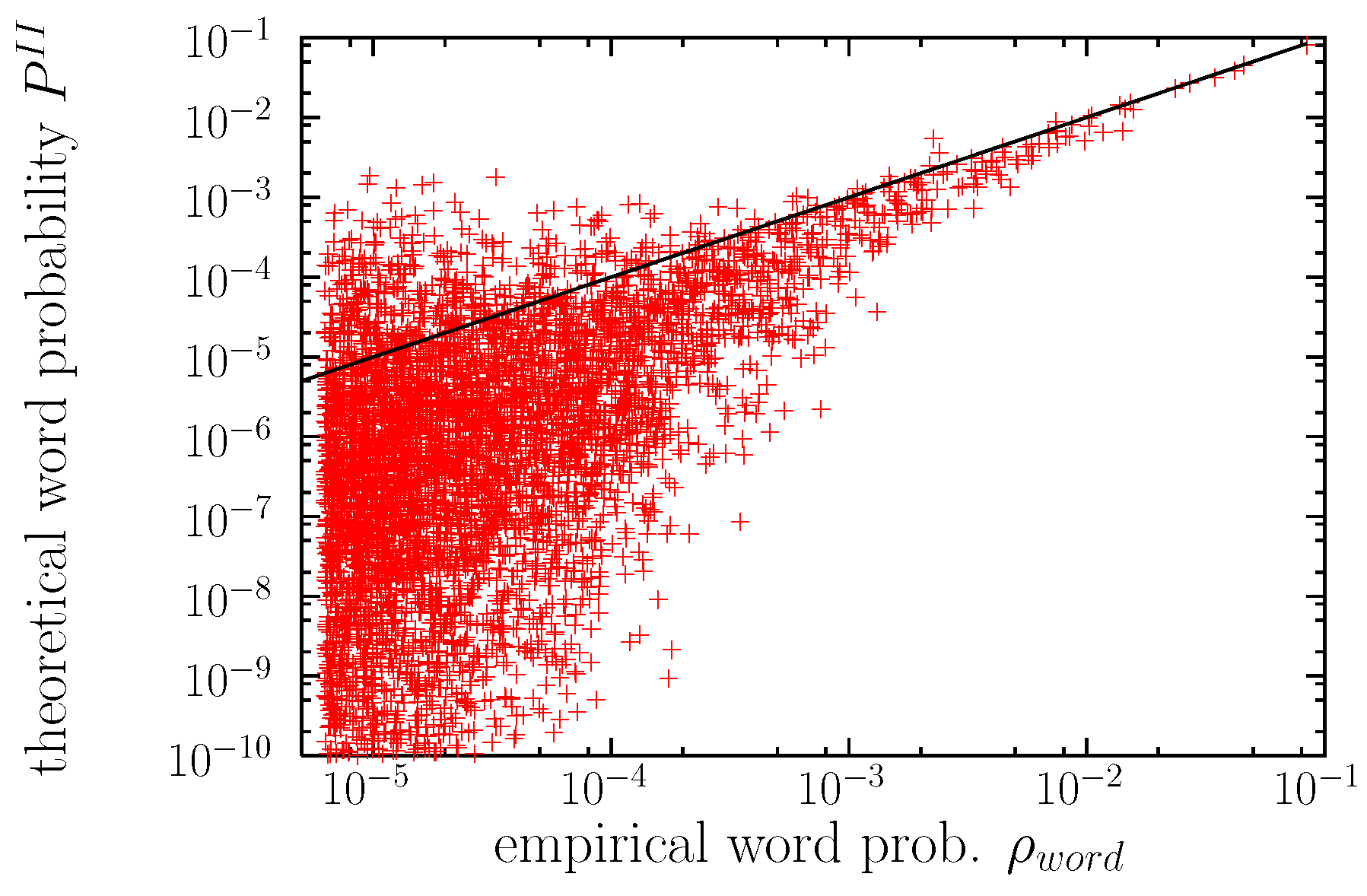
3.3. Word Distributions
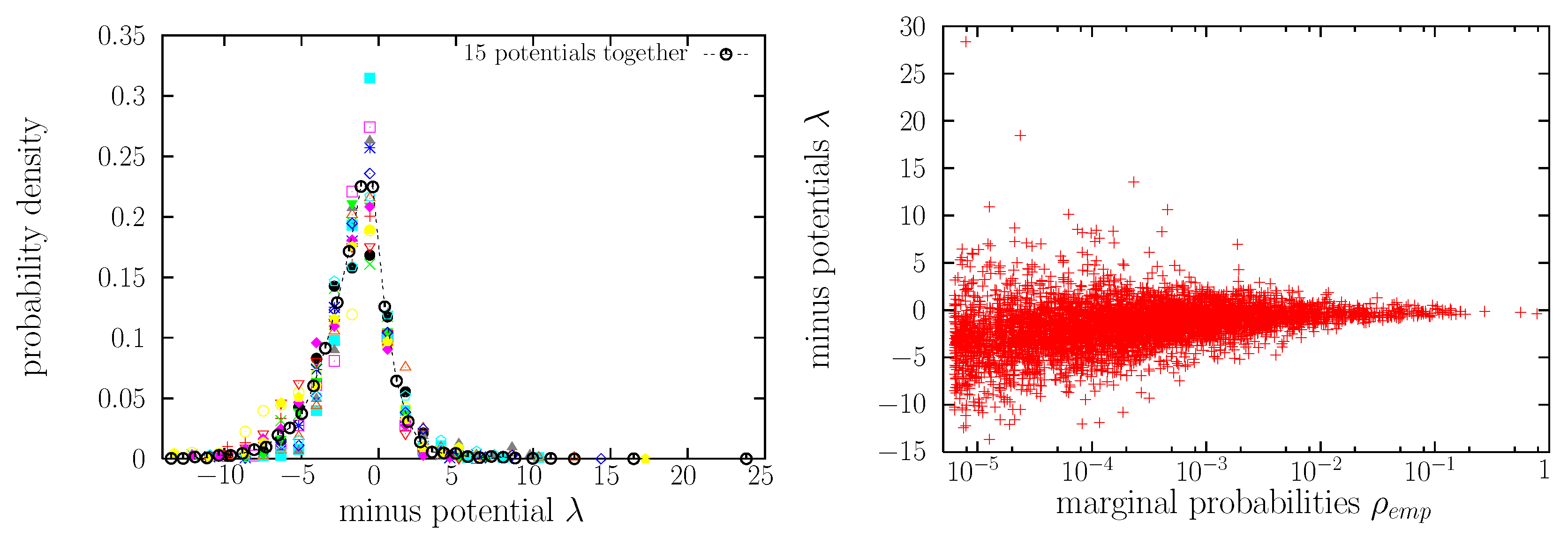
3.4. Values of Lagrange Multipliers and Potentials
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Li, W. Zipf’s law everywhere. Glottometrics 2002, 5, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Malevergne, Y.; Pisarenko, V.; Sornette, D. Testing the Pareto against the lognormal distributions with the uniformly most powerful unbiased test applied to the distribution of cities. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 036111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauset, A.; Shalizi, C.R.; Newman, M.E.J. Power-law distributions in empirical data. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 661–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axtell, R.L. Zipf distribution of U.S. firm sizes. Science 2001, 293, 1818–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pueyo, S.; Jovani, R. Comment on “A keystone mutualism drives pattern in a power function”. Science 2006, 313, 1739c–1740c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Camacho, J.; Solé, R.V. Scaling in ecological size spectra. Europhys. Lett. 2001, 55, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamic, L.A.; Huberman, B.A. Zipf’s law and the Internet. Glottometrics 2002, 3, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Furusawa, C.; Kaneko, K. Zipf’s law in gene expression. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 088102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanette, D.H. Zipf’s law and the creation of musical context. Mus. Sci. 2004, 10, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, M.; Serrà, J.; Herrera, P.; Corral, A. Zipf’s law in short-time timbral codings of speech, music, and environmental sound signals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, J.; Corral, A.; Boguñá, M.; Haro, M.; Arcos, J.L. Measuring the evolution of contemporary western popular music. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baayen, H. Word Frequency Distributions; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Baroni, M. Distributions in text. In Corpus Linguistics: An International Handbook; Lüdeling, A., Kytö, M., Eds.; Mouton de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 803–821. [Google Scholar]
- Zanette, D. Statistical patterns in written language. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3336v1. [Google Scholar]
- Piantadosi, S.T. Zipf’s law in natural language: A critical review and future directions. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2014, 21, 1112–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, E.G.; Gerlach, M. Statistical laws in linguistics. In Creativity and Universality in Language; Lecture Notes in Morphogenesis, Esposti, M.D., Altmann, E.G., Pachet, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Sánchez, I.; Font-Clos, F.; Corral, A. Large-scale analysis of Zipf’s law in English texts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanette, D.; Montemurro, M. Dynamics of text generation with realistic Zipf’s distribution. J. Quant. Linguist. 2005, 12, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baixeries, J.; Elvevåg, B.; Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. The evolution of the exponent of Zipf’s law in language ontogeny. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Clos, F.; Boleda, G.; Corral, A. A scaling law beyond Zipf’s law and its relation with Heaps’ law. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 093033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, A.; Font-Clos, F. Dependence of exponents on text length versus finite-size scaling for word-frequency distributions. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 022318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, T.; Ferrer i Cancho, R. Lingüística Cuantitativa; El País Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Condon, E.U. Statistics of vocabulary. Science 1928, 67, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, G.K. Human Behaviour and the Principle of Least Effort. An Introduction to Human Ecology, 1st ed.; Addison-Wesley Press, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Mitzenmacher, M. A brief history of generative models for power law and lognormal distributions. Internet Math. 2004, 1, 226–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Power laws, Pareto distributions and Zipf’s law. Cont. Phys. 2005, 46, 323–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreto, V.; Servedio, V.D.P.; Strogatz, S.H.; Tria, F. Dynamics on expanding spaces: Modeling the emergence of novelties. In Creativity and Universality in Language; Degli, E.M., Altmann, E., Pachet, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 59–83. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.A. Some effects of intermittent silence. Am. J. Psychol. 1957, 70, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer i Cancho, R.; Elvevåg, B. Random texts do not exhibit the real Zipf’s law-like rank distribution. PLoS ONE 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer i Cancho, R.; Solé, R.V. Least effort and the origins of scaling in human language. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopenko, M.; Ay, N.; Obst, O.; Polani, D. Phase transitions in least-effort communications. J. Stat. Mech. 2010, 2010, P11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dickman, R.; Moloney, N.R.; Altmann, E.G. Analysis of an information-theoretic model for communication. J. Stat. Mech: Theory Exp. 2012, P12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corominas-Murtra, B.; Hanel, R.; Thurner, S. Understanding scaling through history-dependent processes with collapsing sample space. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5348–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas-Murtra, B.; Hanel, R.; Thurner, S. Extreme robustness of scaling in sample space reducing processes explains Zipf’s law in diffusion on directed networks. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 093010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. Compression and the origins of Zipf’s law for word frequencies. Complexity 2016, 21, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. On a class of skew distribution functions. Biometrika 1955, 42, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattuto, C.; Loreto, V.; Pietronero, L. Semiotic dynamics and collaborative tagging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, M.; Altmann, E.G. Stochastic model for the vocabulary growth in natural languages. Phys. Rev. X 2013, 3, 021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saichev, A.; Malevergne, Y.; Sornette, D. Theory of Zipf’s Law and of General Power Law Distributions with Gibrat’s Law of Proportional Growth; Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tria, F.; Loreto, V.; Servedio, V.D.P.; Strogatz, S.H. The dynamics of correlated novelties. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 05890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, T.J.; Foxall, E.; Glass, L.; Edwards, R. A scaling law for random walks on networks. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, P. How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organized Criticality; Copernicus: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sethna, J.P.; Dahmen, K.A.; Myers, C.R. Crackling noise. Nature 2001, 410, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornette, D. Critical Phenomena in Natural Sciences, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, N.W.; Pruessner, G.; Chapman, S.C.; Crosby, N.B.; Jensen, H.J. 25 years of self-organized criticality: Concepts and controversies. Space Sci. Rev. 2016, 198, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaynes, E.T. Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves, V.; Wang, J.; Bras, R.L.; Wood, E. Maximum entropy distributions of scale-invariant processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 118701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, I.G.; Burton, P.W. Information theory and the earthquake frequency-magnitude distribution. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1984, 74, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.; Dixit, P.D.; Dill, K.A. A maximum entropy framework for nonexponential distributions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20380–20385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrda, J.; Charvát, F. Quantification method of classification processes. Concept of structural a-entropy. Kybernetika 1967, 3, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tsallis, C. Nonextensive statistics: Theoretical, experimental and computational evidences and connections. Braz. J. Phys. 1999, 29, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, R.; Thurner, S. A comprehensive classification of complex statistical systems and an axiomatic derivation of their entropy and distribution functions. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 93, 20006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, R.; Thurner, S. When do generalized entropies apply? How phase space volume determines entropy. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 96, 50003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.J.; Bialek, W. Statistical mechanics of letters in words. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 066119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, T.; Dudík, M.; Tkacik, G.; Schapireb, R.E.; Bialek, W. Faster solutions of the inverse pairwise Ising problem. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0712.2437. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, D.; Stauffer, D. Principles of Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rossing, T. Springer Handbook of Acoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Luque, J.; Luque, B.; Lacasa, L. Scaling and universality in the human voice. J. R. Soc. Interfaces 2015, 12, 20141344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, I.G.; Luque, B.; Lacasa, L.; Luque, J.; Hernández-Fernández, A. Emergence of linguistic laws in human voice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.L.; Pietra, S.A.D.; Pietra, V.J.D. A maximum entropy approach to natural language processing. Comput. Linguist. 1996, 22, 39–71. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A. The improved iterative scaling algorithm: A gentle introduction. 1997; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, M.; Font-Clos, F. A standardized Project Gutenberg Corpus for statistical analysis of natural language and quantitative linguistics. Entropy 2020, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. On the theory of word frequencies and on related Markovian models of discourse. In Structure of Language and its Mathematical Aspects; Jakobson, R., Ed.; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1961; pp. 190–219. [Google Scholar]
- Corral, A.; Serra, I.; Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. The distinct flavors of Zipf’s law in the rank-size and in the size-distribution representations, and its maximum-likelihood fitting. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.01398. [Google Scholar]
- Deluca, A.; Corral, A. Fitting and goodness-of-fit test of non-truncated and truncated power-law distributions. Acta Geophys. 2013, 61, 1351–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, A.; González, A. Power law distributions in geoscience revisited. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, A.; Font, F.; Camacho, J. Non-characteristic half-lives in radioactive decay. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 066103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voitalov, I.; van der Hoorn, P.; van der Hofstad, R.; Krioukov, D. Scale-free networks well done. Phys. Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 033034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, A. Scaling in the timing of extreme events. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2015, 74, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, S.M.; Tebbens, S.F. Upper-truncated power laws in natural systems. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2001, 158, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramwell, S.T.; Christensen, K.; Fortin, J.-Y.; Holdsworth, P.C.W.; Jensen, H.J.; Lise, S.; López, J.M.; Nicodemi, M.; Pinton, J.-F.; Sellitto, M. Universal fluctuations in correlated systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 3744–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Clos, F.; Moloney, N.R. Percolation on trees as a Brownian excursion: From Gaussian to Kolmogorov-Smirnov to exponential statistics. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 030102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, A.; Garcia-Millan, R.; Moloney, N.R.; Font-Clos, F. Phase transition, scaling of moments, and order-parameter distributions in Brownian particles and branching processes with finite-size effects. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 062156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, I.G.; Luque, B.; Lacasa, L.; Kello, C.T.; Hernández-Fernández, A. On the physical origin of linguistic laws and lognormality in speech. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 191023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral, A.; Serra, I. The brevity law as a scaling law, and a possible origin of Zipf’s law for word frequencies. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.13467. [Google Scholar]
- Bentz, C.; Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. Zipf’s law of abbreviation as a language universal. In Proceedings of the Leiden Workshop on Capturing Phylogenetic Algorithms for Linguistics, Leiden, The Netherlands, 26–30 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sakellariou, J.; Tria, F.; Loreto, V.; Pachet, F. Maximum entropy models capture melodic styles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Distribution | V | a | b | o.m. | v | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 223 | 0.143 | th (an, of, to, he) | 63.1 | ∞ | 1.36 | 40 | 1.282 ± 0.213 | 0.21 | |
| 471 | 0.146 | te (i□, o□, a□, ad) | 16.6 | ∞ | 1.94 | 133 | 1.138 ± 0.097 | 0.24 | |
| 455 | 0.038 | t□ (a□, o□, i□, h□) | 34.7 | ∞ | 1.04 | 81 | 1.391 ± 0.156 | 0.23 | |
| 391 | 0.043 | t□ (a□, o□, i□, h□) | 36.3 | ∞ | 1.07 | 78 | 1.433 ± 0.175 | 0.28 | |
| 285 | 0.042 | t□ (a□, o□, w□, i□) | 69.2 | ∞ | 0.78 | 45 | 2.110 ± 0.324 | 0.23 | |
| 309 | 0.160 | he (f□, o□, □□, nd) | 57.5 | ∞ | 1.44 | 42 | 1.207 ± 0.197 | 0.29 | |
| 361 | 0.049 | h□ (n□, o□, f□, e□) | 60.3 | ∞ | 0.91 | 50 | 1.466 ± 0.210 | 0.24 | |
| 334 | 0.057 | h□ (o□, n□, e□, a□) | 52.5 | ∞ | 1.04 | 53 | 1.309 ± 0.183 | 0.29 | |
| 240 | 0.055 | h□ (o□, n□, e□, a□) | 145.0 | ∞ | 0.58 | 21 | 2.576 ± 0.627 | 0.22 | |
| 330 | 0.048 | □□ (e□, d□, s□, t□) | 83.2 | ∞ | 0.76 | 36 | 1.764 ± 0.340 | 0.41 | |
| 371 | 0.039 | □□ (e□, d□, s□, r□) | 50.1 | ∞ | 0.89 | 57 | 1.359 ± 0.190 | 0.28 | |
| 273 | 0.045 | □□ (e□, d□, r□, t□) | 75.9 | ∞ | 0.78 | 44 | 1.935 ± 0.298 | 0.32 | |
| 278 | 0.051 | □□ (e□, t□, n□, h□) | 87.1 | ∞ | 0.77 | 35 | 1.579 ± 0.270 | 0.33 | |
| 244 | 0.044 | □□ (e□, t□, n□, l□) | 100.0 | ∞ | 0.64 | 31 | 1.946 ± 0.378 | 0.28 | |
| 154 | 0.115 | □□ (e□, s□, d□, t□) | 72.4 | ∞ | 1.20 | 34 | 1.140 ± 0.201 | 0.58 | |
| 11042 | 0.071 | the (of, and, to, a) | 1.0 | 0.073 | 2.85 | 925 | 0.925 ± 0.030 | 0.25 | |
| 5081 | 0.084 | the (of, and, to, a) | 0.5 | 0.087 | 3.20 | 1426 | 0.811 ± 0.023 | 0.31 | |
| 2174013 | 0.081 | the (of, and, to, a) | 0.2 | 0.083 | 3.53 | 2947 | 0.886 ± 0.017 | 0.38 |
| r | Word | Case | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 2.88 | whe | ∄ |
| 48 | 2.20 | wis | abbrev. |
| 52 | 1.95 | mo | abbrev. |
| 61 | 1.74 | wast | arch. |
| 64 | 1.69 | ond | ∄ |
| 71 | 1.52 | ar | abbrev. |
| 77 | 1.40 | ane | ∃ |
| 87 | 1.24 | ald | abbrev. |
| 89 | 1.21 | bo | ∃ |
| 92 | 1.16 | thes | ∄ |
| 94 | 1.10 | hime | ∄ |
| 98 | 9.83 | hive | ∃ |
| 102 | 9.45 | thise | ∄ |
| 103 | 9.39 | af | abbrev. |
| 110 | 8.80 | wer | ∄ |
| 117 | 8.16 | thay | ∄ |
| 118 | 8.16 | hes | ∄ |
| 123 | 7.88 | wath | ∃ |
| 125 | 7.82 | hor | abbrev. |
| 127 | 7.60 | sime | ∄ |
| 134 | 7.22 | tome | ∃ |
| 135 | 7.21 | har | ∃ |
| 141 | 6.94 | thit | ∄ |
| 143 | 6.86 | mas | abbrev. |
| 146 | 6.77 | hew | ∃ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corral, Á.; García del Muro, M. From Boltzmann to Zipf through Shannon and Jaynes. Entropy 2020, 22, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020179
Corral Á, García del Muro M. From Boltzmann to Zipf through Shannon and Jaynes. Entropy. 2020; 22(2):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020179
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorral, Álvaro, and Montserrat García del Muro. 2020. "From Boltzmann to Zipf through Shannon and Jaynes" Entropy 22, no. 2: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020179
APA StyleCorral, Á., & García del Muro, M. (2020). From Boltzmann to Zipf through Shannon and Jaynes. Entropy, 22(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020179





