Exploring the Phase Space of Multi-Principal-Element Alloys and Predicting the Formation of Bulk Metallic Glasses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- A composition range of already known elements with best glass-forming ability;
- -
- Additional alloying elements for a known basic alloy to form a glass;
- -
- Any glass-forming alloy (limited by the database of elements).
3. Results
3.1. Run-Time
3.2. Glass-Formation
3.3. Micro-Alloying
3.4. Search for New Glasses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.D.; Johnson, W.L. Shear flow characteristics and crystallization kinetics during steady non-isothermal flow of Vitreloy-1. Acta. Materialia. 2004, 52, 3403–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.L.; Buchanan, R.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Green, B.A.; Wang, G.Y.; Liu, C.T.; Horton, J.A. Four-point-bending-fatigue behavior of the Zr-based Vitreloy 105 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 467, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Chen, N.; Wada, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kato, H.; Inoue, A.; Yeh, J.W. Pd20Pt20Cu20Ni20P20 high-entropy alloy as a bulk metallic glass in the centimeter. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C.T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2011, 21, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Quantitative evaluation of critical cooling rate for metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 304, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battezzati, L.; Greer, A.L. The viscosity of liquid metals and alloys. Acta Metall. 1989, 37, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, A.L.; Walls, H.A.; Jethani, K.R. Determination of the coordination number of liquid metals near the melting point. Metall. Trans. A 1985, 16, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębski, A.; Dębski, R.; Gasior, W. New features of Entall database: Comparison of experimental and model formation enthalpies. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 59, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayah, M. Ptable: The Interactive Periodic Table. Available online: https://www.ptable.com (accessed on 11 June 2019).
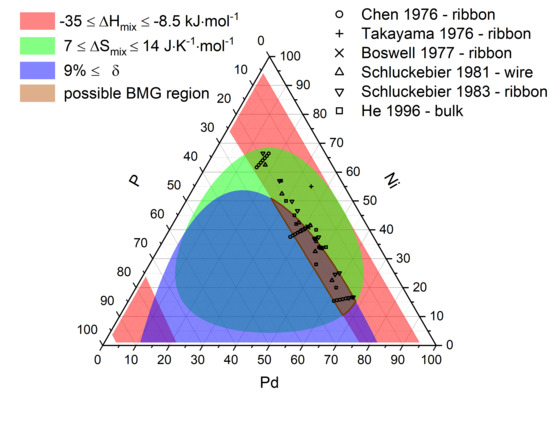
- Chen, H.S. Glass temperature, formation and stability of Fe, Co, Ni, Pd and Pt based glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1976, 23, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, S.; Maddin, R. Microscopic observations of fracture behavior in a Ni55Pd35P10 metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1976, 23, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, P.G. Crystallisation of A (Ni5Pd5)82P18 amorphous alloy. Scr. Metall. 1977, 11, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluckebier, G.; Predel, B. Verhalten von Nickel-Palladium-Phosphor-Glaesern in der Naehe der Glastemperatur. Z. Für Met. 1981, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Schluckebier, G.; Predel, B. Investigations on Demixing and Crystallization Behavior of Metallic Glasses of the System Palladium-Nickel-Phosphorus. Z. Für Met. 1983, 74, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Schwarz, R.B.; Archuleta, J.I. Bulk glass formation in the Pd–Ni–P system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1861–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiminami, C.S.; Sahm, P.R. The Formation Kinetics of PdCuSi-and PdNiP-Metallic Glasses. In Science and Technology of the Undercooled Melt: Rapid Solidification Materials and Technologies; Sahm, P.R., Jones, H., Adam, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberger, Germany, 1986; pp. 246–248. [Google Scholar]
- Drehman, A.J.; Greer, A.L.; Turnbull, D. Bulk formation of a metallic glass: Pd40Ni40P20. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1982, 41, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kui, H.W.; Greer, A.L.; Turnbull, D. Formation of bulk metallic glass by fluxing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 45, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, G.; Görler, G.P.; Willnecker, R.; Dietz, G. Thermodynamic properties of Pd40Ni40P20 in the glassy, liquid, and crystalline states. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 65, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Miller, C.E. Centrifugal spinning of metallic glass filaments. Mater. Res. Bull. 1976, 11, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.M.; Eckert, J.; Löser, W.; Dhindaw, B.K.; Schultz, L. Cooling Rate Evaluation for Bulk Amorphous Alloys from Eutectic Microstructures in Casting Processes. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laws, K.J.; Shamlaye, K.F.; Gun, B.; Ferry, M. Synthesis of copper-based bulk metallic glasses in the ternary Cu–Mg–Ca system. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 486, L27–L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xia, J.; Dong, C. Bulk metallic glass formation in Cu–Zr–Ti ternary system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 3425–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Woychik, C.G.; Dutkiewicz, J. Solidification structures in rapidly quenched Cu-Ti-Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans A 1988, 19, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollmann, N.; Binkowski, I.; Schmidt, V.; Rösner, H.; Wilde, G. Impact of micro-alloying on the plasticity of Pd-based bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2016, 111, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubek, R.; Seleznev, M.; Binkowski, I.; Peterlechner, M.; Divinski, S.V.; Wilde, G. The impact of micro-alloying on relaxation dynamics in Pd40Ni40P20 bulk metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.H.; Johnson, W.L. Formation of Ti–Zr–Cu–Ni bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 6514–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Men, H.; Pang, S.; Inoue, A.; Zhang, T. New Ti-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses with Significant Plasticity. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2218–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Xu, J. Ti (Zr)-Cu-Ni Bulk Metallic Glasses with Optimal Glass-Forming Ability and Their Compressive Properties. Metall. Mater. Trans A 2008, 39, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.-C. Formation of Ductile Cu-Based Bulk Metallic Glass Matrix Composite by Ta Addition. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 2224–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.Y.; Shek, C.H. Abrasive wear of Cu60Zr30Ti10 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 384, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, D.; Ohkubo, T.; Mukai, T.; Hono, K. Characterization of Nanocrystal Dispersed Cu60Zr 30Ti10 Metallic Glass. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tam, C.Y.; Shek, C.H. Oxidation-induced copper segregation in Cu60Zr30Ti10 bulk metallic glass. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarumi, R.; Hirao, M.; Ichitsubo, T.; Matsubara, E.; Saida, J.; Kato, H. Low Temperature Elastic Properties of CuZrTi Bulk Metallic Glass. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 1842–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, J.; Kumar, S.; Dong, C.; Murty, B.S. Tribological behaviour of Cu60Zr30Ti10 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 458, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, U.; Jastrow, L.; Meuris, M. Oxidation of Cu60Zr30Ti10 metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.J.; Fu, L.F.; Qiao, D.C.; Choo, H.; Liaw, P.K.; Browning, N.D.; Löffler, J.F. Effect of microalloying on the glass-forming ability of Cu60Zr30Ti10 bulk metallic glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 4218–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabski, M.; Peterlechner, M.; Wilde, G. Exploring the Phase Space of Multi-Principal-Element Alloys and Predicting the Formation of Bulk Metallic Glasses. Entropy 2020, 22, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030292
Gabski M, Peterlechner M, Wilde G. Exploring the Phase Space of Multi-Principal-Element Alloys and Predicting the Formation of Bulk Metallic Glasses. Entropy. 2020; 22(3):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030292
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabski, Mirko, Martin Peterlechner, and Gerhard Wilde. 2020. "Exploring the Phase Space of Multi-Principal-Element Alloys and Predicting the Formation of Bulk Metallic Glasses" Entropy 22, no. 3: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030292
APA StyleGabski, M., Peterlechner, M., & Wilde, G. (2020). Exploring the Phase Space of Multi-Principal-Element Alloys and Predicting the Formation of Bulk Metallic Glasses. Entropy, 22(3), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030292