Association Factor for Identifying Linear and Nonlinear Correlations in Noisy Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Quick Review
2.1.1. Pearson’s Correlation
2.1.2. Distance Correlation
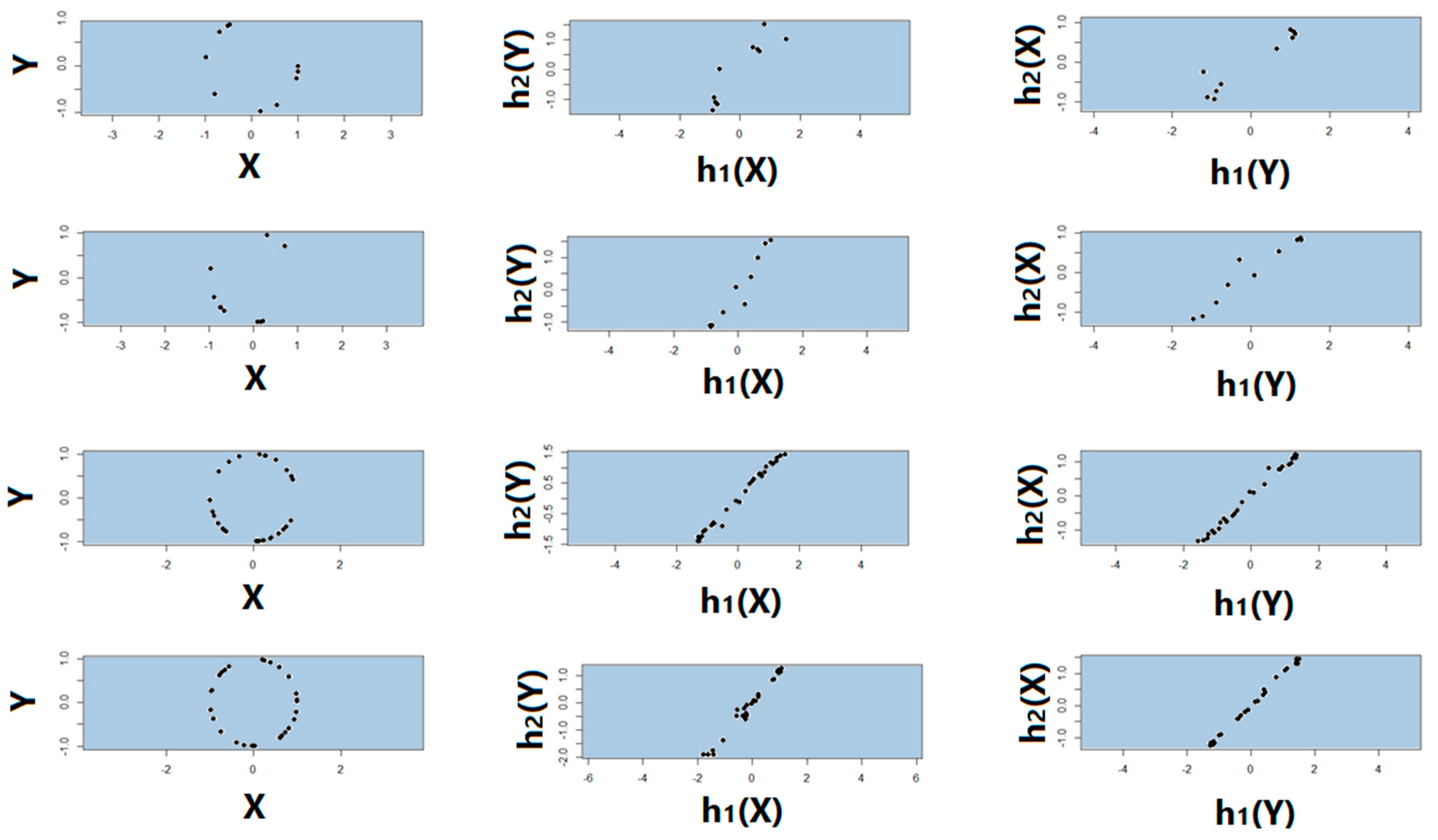
2.2. Proposed Association Factor
- Non-negativity, .
- Disappears if and only if the two vectors are not associated, for unassociated X and Y.
- Symmetry, for noiseless vectors X and Y.
- Triangular inequality, .
3. Simulation Models
3.1. Linear and Nonlinear Relationships in Noiseless Conditions
- Linear: , where is intercept and is slope.
- Fourth order polynomial: where ’s are coefficients.
- Exponential: , where is rate.
- Parabolic: , where and are coefficients.
- Let be a set of D relationship types to . Generate pairwise variables using relationships in the relationship set so that D different datasets representing the relationship types to are obtained.
- For each generated dataset , compute Pearson’s correlation (absolute value) , distance correlation , and Association Factor .
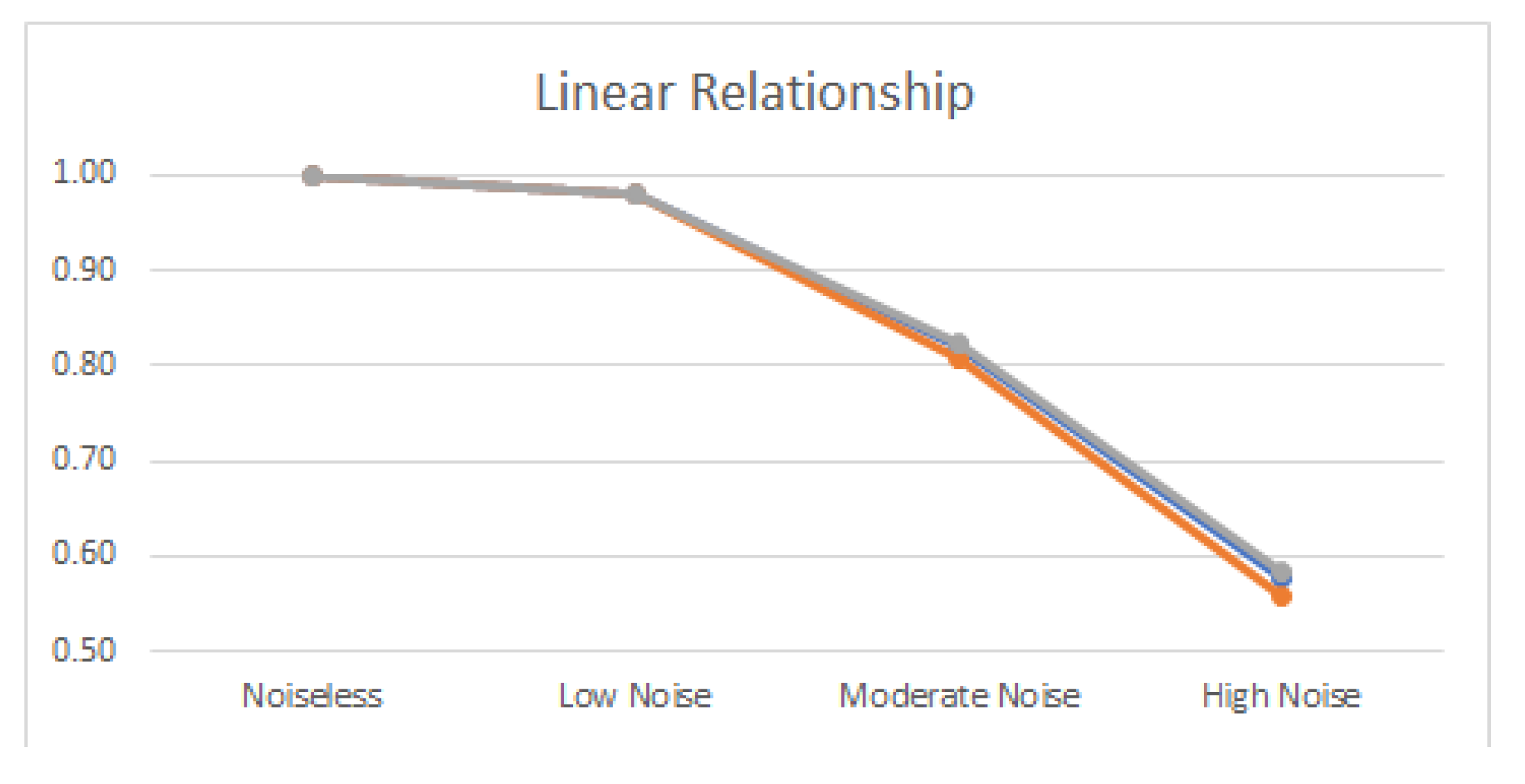
3.2. Linear and Nonlinear Relationships in Noisy Conditions
- Linear: .
- Fourth order polynomial: .
- Exponential: .
- Parabolic: .
- Let be a set of D relationship types to . Generate pairwise variables using relationships in the relationship set so that D different datasets representing the relationship types to are obtained.
- Set (trial one).
- Generate noisy relationships by adding Gaussian noise (with noise level ) to the datasets ’s generated using the true relationships (’s).
- Compute and save Pearson’s correlation (absolute value) , distance correlation , and association factor for each noisy dataset .
- Increase t by one ().
- Repeat Steps 3 to 5 while .
- Compute the Monte Carlo average of each correlation measure as follows:
3.3. No Relationship
3.4. Symmetry Regarding Sample Size, Missing Data, and Noise Level
3.5. Entropic Distance
- ED is symmetric.
- ED is zero for comparing a distribution with itself.
- ED is positive for two different distributions.
- indicates a decrease in AF.
- indicates an increase in AF.
- indicates no change in AF.
3.6. Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (DFA)
- Integrate the time series:where is the interval and is the average interval.
- Divide the integrated time series into boxes of equal length n.
- Fit a line to the data in each box of size n separately. The y coordinate of the straight line segment in a box is denoted by .
- Remove the trend (detrend) from the integrated time series by subtracting the local trend in each box.
- Calculate the root-mean-squared fluctuation, , of the obtained detrended time series by:
- Repeat this computation over all time scales (box size n) to provide a relationship between and the box size (n).
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
- Linear: .
- Fourth order polynomial: .
- Exponential: .
- Parabolic: .
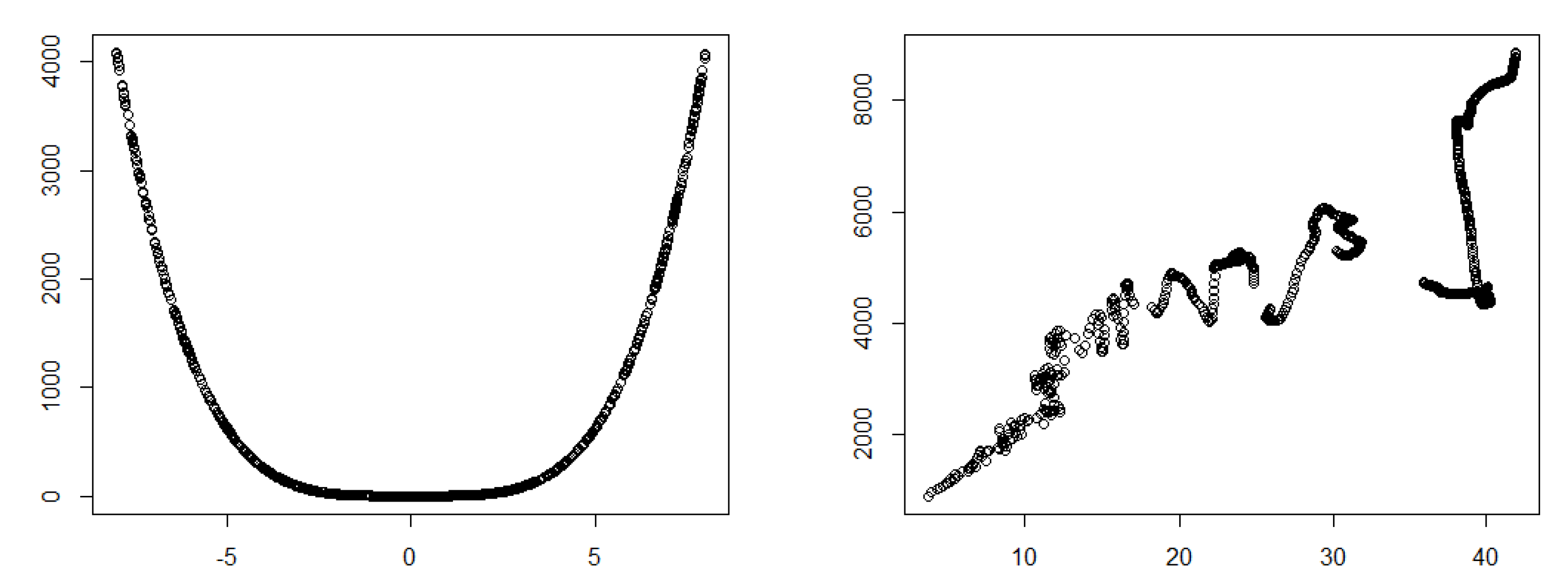
4.1. True Signal (No Noise)
4.2. Noisy Relationships
4.3. No Relationship
4.4. Test of Symmetry, Sample Size, Missing Data, and Noise Level
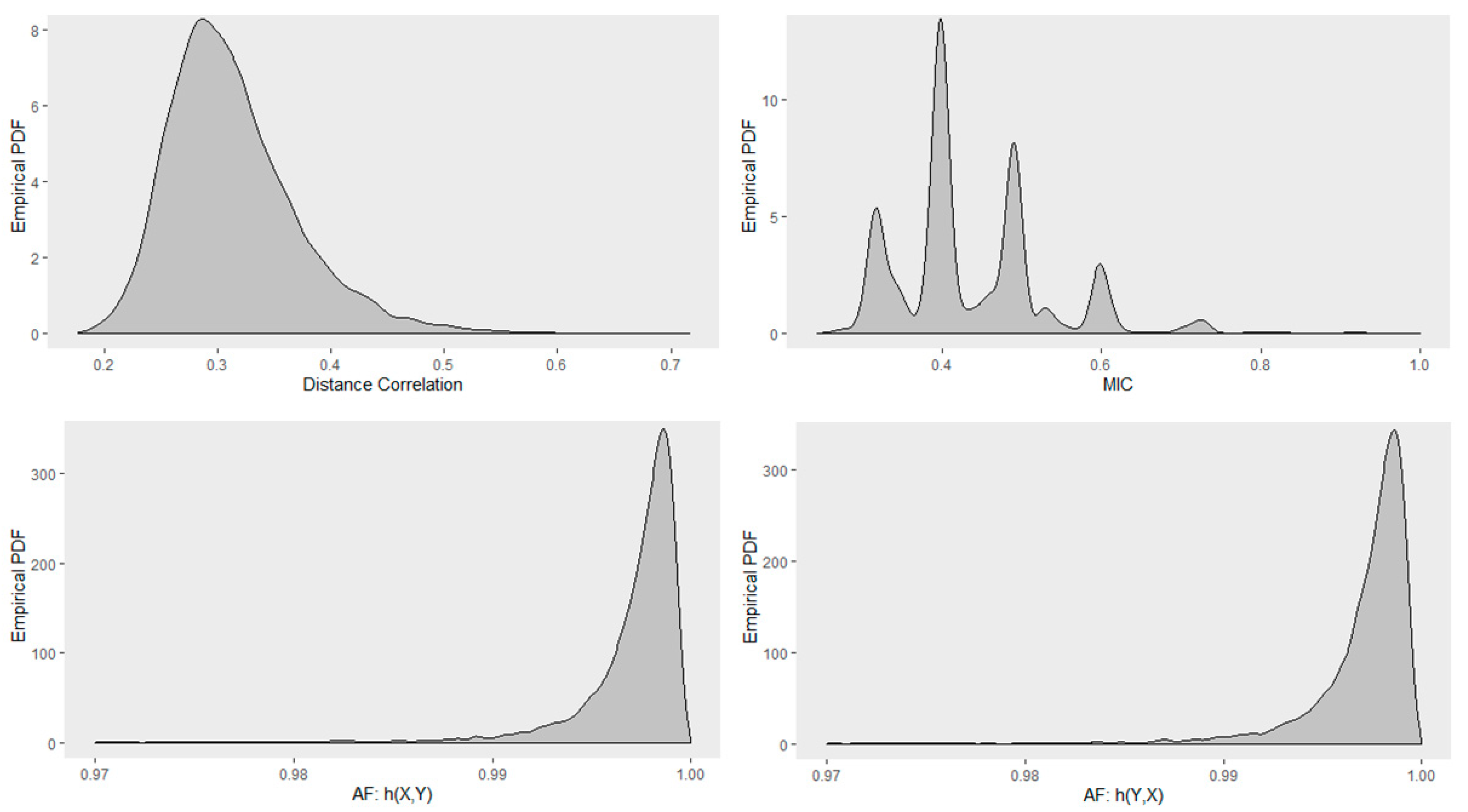
4.5. Empirical Distribution of Distance Correlation, Maximal Information Coefficient, and
4.6. Entropic Distance
4.7. Detrended Fluctuation Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberger, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Székely, G.J.; Rizzo, M.L.; Bakirov, N.K. Measuring and testing dependence by correlation of distances. Ann. Stat. 2007, 35, 2769–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, G.J.; Rizzo, M.L. Brownian distance covariance. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2009, 3, 1236–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueck, J.; Edelmann, D.; Gneiting, T.; Richards, D. The affinely invariant distance correlation. Bernoulli 2014, 20, 2305–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póczos, B.; Schneider, J. Conditional Distance Variance and Correlation. Figshare 2012. Available online: https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bapoczos/articles/poczos12distancecorr.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Dueck, J.; Edelmann, D.; Richards, D. Distance correlation coefficients for Lancaster distributions. J. Multivar. Anal. 2017, 154, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, D.; Richards, D.; Vogel, D. The distance standard deviation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.05777. [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch, C.; Leucht, A.; Meyer, M.; Beering, C. Empirical Characteristic Functions-Based Estimation and Distance Correlation for Locally Stationary Processes; Technical Report; University of Mannheim: Mannheim, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Górecki, T.; Krzyśko, M.; Ratajczak, W.; Wołyński, W. An Extension of the Classical Distance Correlation Coefficient for Multivariate Functional Data with Applications. Stat. Transit. New Ser. 2016, 17, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, G.J.; Rizzo, M.L. Partial distance correlation with methods for dissimilarities. Ann. Stat. 2014, 42, 2382–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, G.J.; Rizzo, M.L. The distance correlation t-test of independence in high dimension. J. Multivar. Anal. 2013, 117, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Matsui, M.; Mikosch, T.; Wan, P. Applications of distance correlation to time series. Bernoulli 2018, 24, 3087–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Measuring nonlinear dependence in time-series, a distance correlation approach. J. Time Ser. Anal. 2012, 33, 438–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A. Distance correlation coefficient: An application with bayesian approach in clinical data analysis. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2014, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskowiak, P.A.; Campello, R.J.; Costa, I.G. On the selection of appropriate distances for gene expression data clustering. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Wang, S.; Wahba, G. Using distance covariance for improved variable selection with application to learning genetic risk models. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H. Estimating optimal transformations for multiple regression and correlation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1985, 80, 580–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, H.O. Rankings and Preferences: New Results in Weighted Correlation and Weighted Principal Component Analysis With Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Biró, T.S.; Telcs, A.; Néda, Z. Entropic Distance for Nonlinear Master Equation. Universe 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, T.S.; Schram, Z. Non-Extensive Entropic Distance Based on Diffusion: Restrictions on Parameters in Entropy Formulae. Entropy 2016, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.K.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Quantification of scaling exponents and crossover phenomena in nonstationary heartbeat time series. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1995, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
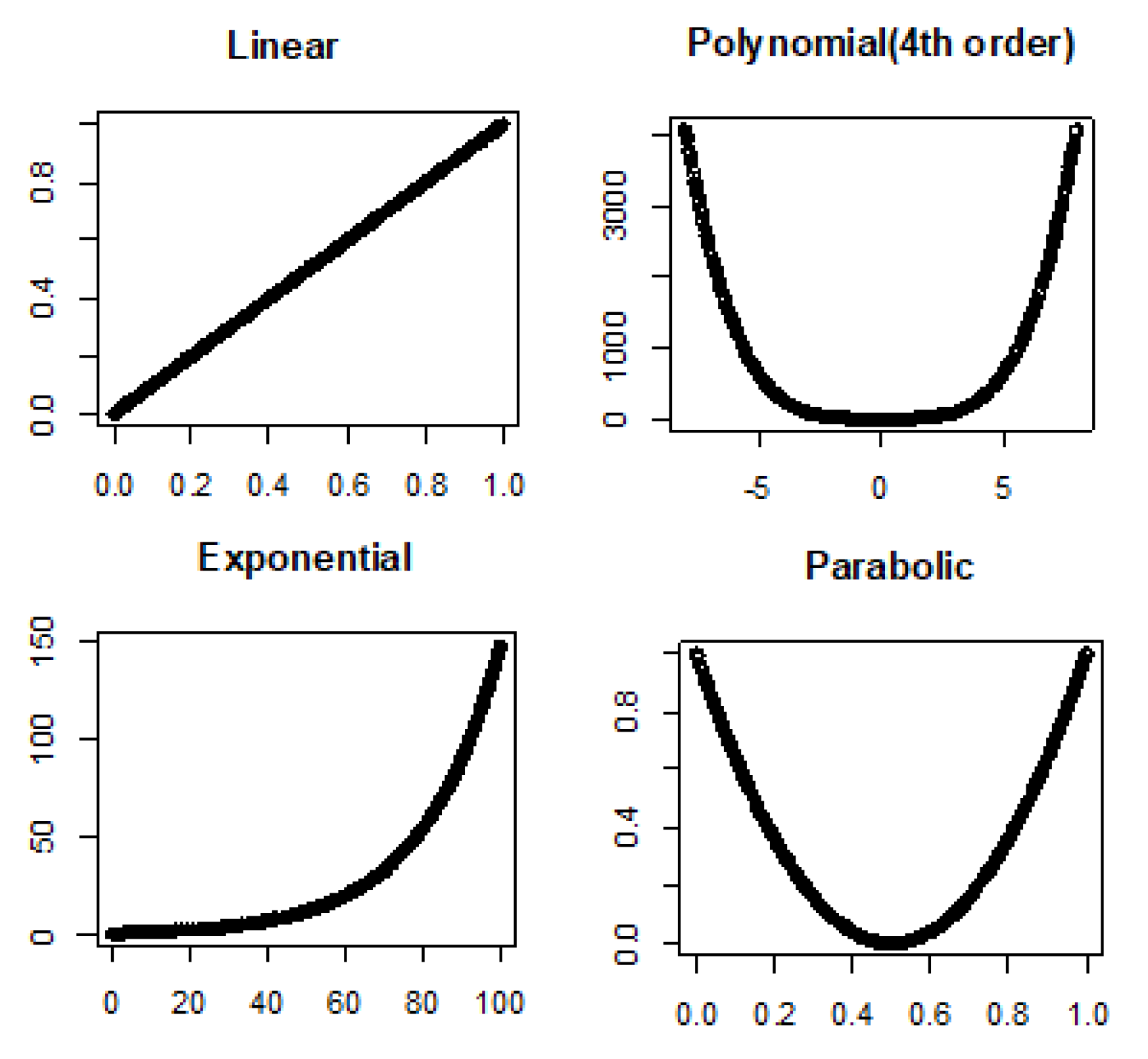










| Relationship Type | Pearson’s Correlation | Distance Correlation | Association Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Polynomial | 0.06 | 0.47 | 1.00 |
| Exponential | 0.86 | 0.91 | 1.00 |
| Parabolic | 0.05 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| Relationship Type | Pearson’s Correlation | Distance Correlation | Association Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Polynomial | −0.23 | 0.48 | 0.99 |
| Exponential | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.99 |
| Parabolic | −0.21 | 0.51 | 0.99 |
| Relationship Type | Pearson’s Correlation | Distance Correlation | Association Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.82 |
| Polynomial | −0.20 | 0.39 | 0.83 |
| Exponential | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.90 |
| Parabolic | −0.21 | 0.49 | 0.95 |
| Relationship Type | Pearson’s Correlation | Distance Correlation | Association Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.58 |
| Polynomial | −0.14 | 0.29 | 0.59 |
| Exponential | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.69 |
| Parabolic | −0.16 | 0.37 | 0.72 |
| Relationship Type | Pearson’s Correlation | Distance Correlation | Association Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Relationship | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| Sample Size | Distance Correlation | MIC | AF(X,Y) | AF(Y,X) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.221 | 0.563 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| 50 | 0.219 | 0.484 | 0.993 | 0.999 |
| 30 | 0.246 | 0.490 | 0.995 | 0.994 |
| 10 | 0.559 | 0.396 | 0.938 | 0.968 |
| Sample Size | Distance Correlation | MIC | AF(X,Y) | AF(Y,X) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.205 | 0.282 | 0.579 | 0.579 |
| 50 | 0.186 | 0.314 | 0.666 | 0.667 |
| 30 | 0.249 | 0.304 | 0.573 | 0.536 |
| 10 | 0.359 | 0.396 | 0.542 | 0.534 |
| No Noise | Low Noise | Moderate Noise | High Noise | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relationship Type | Entropic Distance | Association Factor | Entropic Distance | Association Factor | Entropic Distance | Association Factor | Entropic Distance | Association Factor |
| Linear | 1.989 | 1.000 | 1.993 | 0.980 | 1.796 | 0.820 | 1.539 | 0.580 |
| Polynomial | 1.203 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.953 | 0.830 | 0.931 | 0.590 |
| Exponential | 1.845 | 1.000 | 1.847 | 0.990 | 1.749 | 0.900 | 1.512 | 0.690 |
| Parabolic | 1.106 | 1.000 | 0.848 | 0.990 | 0.825 | 0.950 | 0.812 | 0.720 |
| Noiseless to Low Noise | Low Noise to Moderate Noise | Moderate Noise to High Noise | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relationship Types | Entropic Distance | Association Factor | Entropic Distance | Association | Entropic Distance | Association Factor |
| Linear | 100% | 98% | 90% | 84% | 86% | 71% |
| Polynomial | 83% | 99% | 95% | 84% | 98% | 71% |
| Exponential | 100% | 99% | 95% | 91% | 86% | 77% |
| Parabolic | 77% | 99% | 97% | 96% | 98% | 76% |
| Relationship Type | Pearson’s Correlation Original Data | Pearson’s Correlation Detrended Data | DFA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Polynomial | 0.06 | 0.77 | 0.76 |
| Exponential | 0.86 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Parabolic | 0.05 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kachouie, N.N.; Deebani, W. Association Factor for Identifying Linear and Nonlinear Correlations in Noisy Conditions. Entropy 2020, 22, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040440
Kachouie NN, Deebani W. Association Factor for Identifying Linear and Nonlinear Correlations in Noisy Conditions. Entropy. 2020; 22(4):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040440
Chicago/Turabian StyleKachouie, Nezamoddin N., and Wejdan Deebani. 2020. "Association Factor for Identifying Linear and Nonlinear Correlations in Noisy Conditions" Entropy 22, no. 4: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040440
APA StyleKachouie, N. N., & Deebani, W. (2020). Association Factor for Identifying Linear and Nonlinear Correlations in Noisy Conditions. Entropy, 22(4), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040440





