Optic Disc Segmentation Using Attention-Based U-Net and the Improved Cross-Entropy Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- In order to avoid overfitting and save model calculation, we propose using DenseNet blocks to extract features in the encoding layer. This is particularly important in the field of medical image segmentation where data sets are generally small.
- (2)
- We propose an effective semantic segmentation decoder, called the aggregation channel attention upsampling module. We use different layers of features to guide the attention mechanism, so as to fuse the information of different scales to restore pixel categories. We use squeeze excitation blocks and generalized average pooling to integrate channel information.
- (3)
- We improved the basic classification framework based on cross entropy to optimize the network. This loss function balances the contribution of dice coefficients and cross-entropy loss to the segmentation task.
- (4)
- In order to verify the effectiveness of our method, we validated our method on the Messidor [23] and RIM-ONE [24] datasets. Compared with the existing methods, the segmentation performance of our method on these fundus image datasets has been significantly improved. This further develops the application of attention mechanism and entropy in the field of image segmentation, and promotes deep learning research in the field of optic disc segmentation of fundus images.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aggregation Channel Attention Network Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation
2.2. Dense Convolutional Network for Encoding
2.3. Aggregation Channel Attention Upsampling Module
2.4. Improved Cross-Entropy Loss for Optic Disc Segmentation
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.1.1. Implementation Details
3.1.2. Data Augmentation Preprocessing
3.1.3. Dataset and Data Processing
3.2. Ablation Study
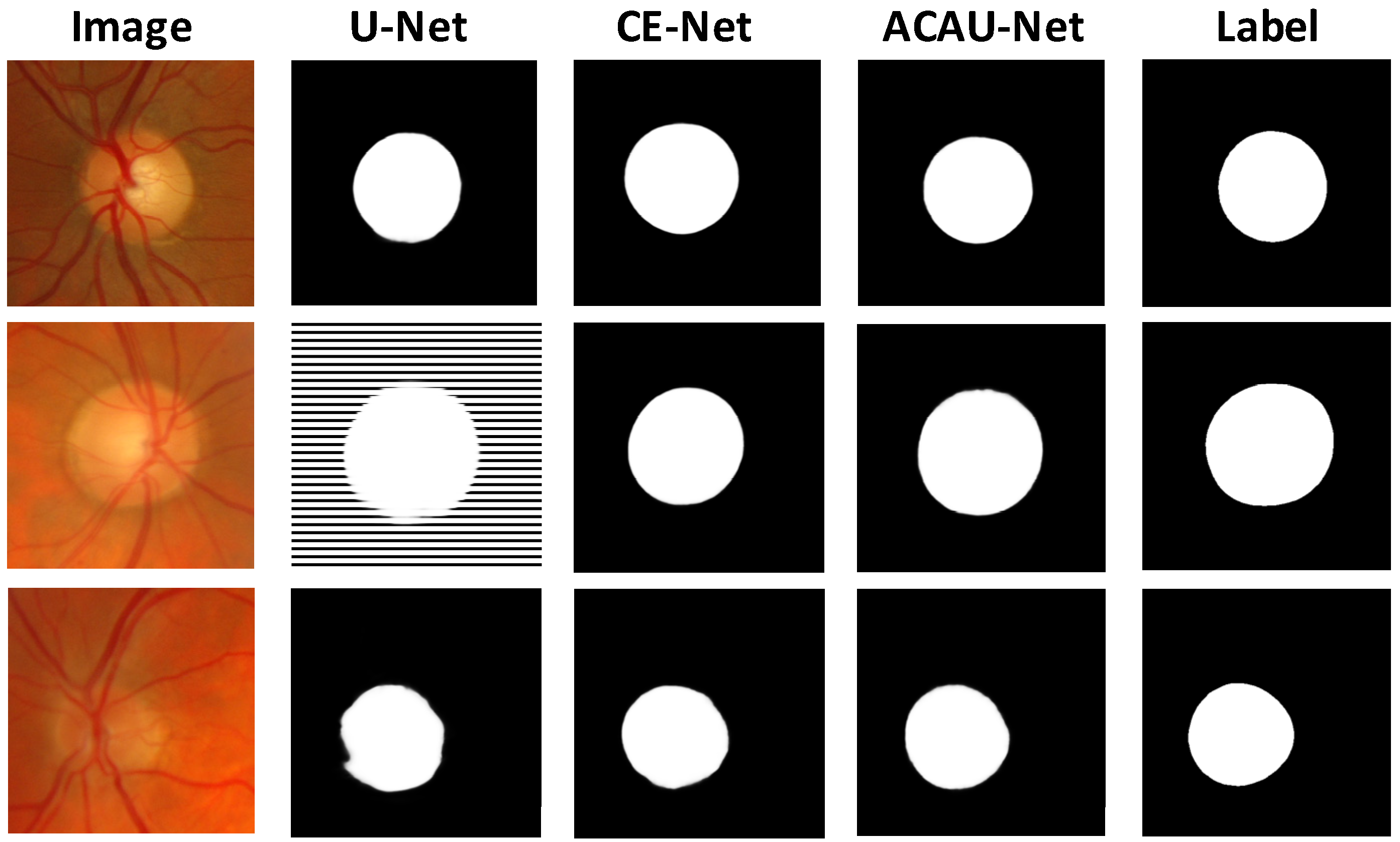
3.3. Comparison with the Baselines
3.4. Parameter Analysis
3.4.1. Hyper-Parameter Analysis
3.4.2. Loss Function Contribution Parameter
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global Prevalence of Glaucoma and Projections of Glaucoma Burden through 2040 A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonas, J.B.; Bergua, A.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, P.; Papastathopoulos, K.I.; Budde, W.M. Ranking of optic disc variables for detection of glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, G.; Sivaswamy, J.; Karan, K.; Krishnadas, S. Optic disk and cup boundary detection using regional information. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 4 April 2010; pp. 948–951. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Wong, D.; Yin, F.; Cheung, C.; Baskaran, M.; Aung, T.; Wong, T.Y. Automatic optic disc segmentation with peripapillary atrophy elimination. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 6224–6227. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, N.; Abdul Khalid, N.E.; Ariff, N. Optic cup and disc color channel multi-thresholding segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering, Penang, Malaysia, 29 November–1 December 2013; pp. 530–534. [Google Scholar]
- Issac, A.; Sarathi, M.; Dutta, M. An adaptive threshold based image processing technique for improved glaucoma detection and classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 122, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Xiao, D.; Frost, S.; Kanagasingam, Y. Robust Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation with Deep Learning for Glaucoma Detection. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 74, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, G.; Sivaswamy, J.; Krishnadas, S. Optic Disk and Cup Segmentation From Monocular Color Retinal Images for Glaucoma Assessment. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Tao, D.; Yin, F.; Wong, D.; Xu, Y.; Wong, T.Y. Superpixel Classification Based Optic Cup Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Cambridge, UK, 19–22 September 1999; pp. 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, D.; Liu, J.; Lim, J.H.; Li, H.; Wong, T.Y. Automated detection of kinks from blood vessels for optic cup segmentation in retinal images. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2009, 7260, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. CE-Net: Context Encoder Network for 2D Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, H.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Wong, D.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Joint Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation Based on Multi-Label Deep Network and Polar Transformation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Fu, H.; Dai, H.; Shen, J.; Pang, Y.; Shao, L. ET-Net: A Generic Edge-aTtention Guidance Network for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Taghanaki, S.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G.; Albanie, S. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual Attention Network for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6450–6458. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–21 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 1805, 10180. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W. Channel Attention Residual U-Net for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Bangkok, Thailand, 9–11 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Gu, Z.; Hao, H.; Qi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Frangi, A.; Liu, J. CS-Net: Channel and Spatial Attention Network for Curvilinear Structure Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 721–730. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Weinberger, K. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Decencière, E.; Zhang, X.; Cazuguel, G.; Lay, B.; Cochener, B.; Trone, C.; Gain, P.; Ordonez, R.; Massin, P.; Erginay, A.; et al. Feedback on a publicly distributed image database: The Messidor database. Image Anal. Stereol. 2014, 33, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumero, F.; Alayón, S.; Sanchez, J.L.; Sigut, J.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M. RIM-ONE: An open retinal image database for optic nerve evaluation. In Proceedings of the Computer Based Medical Systems, Bristol, UK, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Targ, S.; Almeida, D.; Lyman, K. Resnet in Resnet: Generalizing Residual Architectures. Learning 2016, 1603, 08029. [Google Scholar]
- Noori, M.; Bahri, A.; Mohammadi, K. Attention-Guided Version of 2D UNet for Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 24–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Radenović, F.; Tolias, G.; Chum, O. Fine-tuning CNN Image Retrieval with No Human Annotation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 41, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Yin, F.; Wong, D.; Yan, S.; Liu, J. Learning Supervised Descent Directions for Optic Disc Segmentation. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhou, K.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, H.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. DeepDisc: Optic Disc Segmentation Based on Atrous Convolution and Spatial Pyramid Pooling. In Proceedings of the Computational Pathology and Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis, Cham, Switzerland, 16 September 2018; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]




| Method | E |
|---|---|
| U-Net [11] | 0.055 |
| U-Net+Denseblock | 0.0532 |
| U-Net+ACAUm | 0.0519 |
| U-Net+Denseblock+ACAUm | 0.0502 |
| CE-Net [12] | 0.0518 |
| CE-Net+Denseblock | 0.0502 |
| CE-Net+ACAUm | 0.0496 |
| ACAU-Net | 0.0469 |
| Method | Messidor | R-Exp1 | R-Exp2 | R-Exp3 | R-Exp4 | R-Exp5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [11] | 0.069 | 0.137 | 0.149 | 0.156 | 0.171 | 0.149 |
| M-Net [13] | 0.113 | 0.128 | 0.135 | 0.153 | 0.142 | 0.117 |
| Faster RCNN [30] | 0.079 | 0.101 | 0.152 | 0.161 | 0.149 | 0.104 |
| DeepDisc [31] | 0.064 | 0.077 | 0.107 | 0.119 | 0.101 | 0.079 |
| CE-Net [12] | 0.051 | 0.058 | 0.112 | 0.125 | 0.080 | 0.059 |
| ACAU-Net | 0.0469 | 0.0533 | 0.0658 | 0.0674 | 0.080 | 0.066 |
| pk | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 0.0494 | 0.0495 | 0.0469 | 0.0487 | 0.0504 | 0.0543 |
| α | 0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 0.0531 | 0.0517 | 0.0485 | 0.0514 | 0.0469 | 0.0516 | 0.0515 | 0.0522 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, B.; Liu, P.; Wang, P.; Shi, L.; Zhao, J. Optic Disc Segmentation Using Attention-Based U-Net and the Improved Cross-Entropy Convolutional Neural Network. Entropy 2020, 22, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080844
Jin B, Liu P, Wang P, Shi L, Zhao J. Optic Disc Segmentation Using Attention-Based U-Net and the Improved Cross-Entropy Convolutional Neural Network. Entropy. 2020; 22(8):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080844
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Baixin, Pingping Liu, Peng Wang, Lida Shi, and Jing Zhao. 2020. "Optic Disc Segmentation Using Attention-Based U-Net and the Improved Cross-Entropy Convolutional Neural Network" Entropy 22, no. 8: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080844
APA StyleJin, B., Liu, P., Wang, P., Shi, L., & Zhao, J. (2020). Optic Disc Segmentation Using Attention-Based U-Net and the Improved Cross-Entropy Convolutional Neural Network. Entropy, 22(8), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080844





