Understanding of Collective Atom Phase Control in Modified Photon Echoes for a Near-Perfect Storage Time-Extended Quantum Memory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Theory: Maxwell–Bloch Equations
1.1.1. A. Conventional Two-Pulse Photon Echo
1.1.2. B. DR Echo
2. Discussion
2.1. A. CDR Echo
2.2. A. Single Rephased Photon Echo
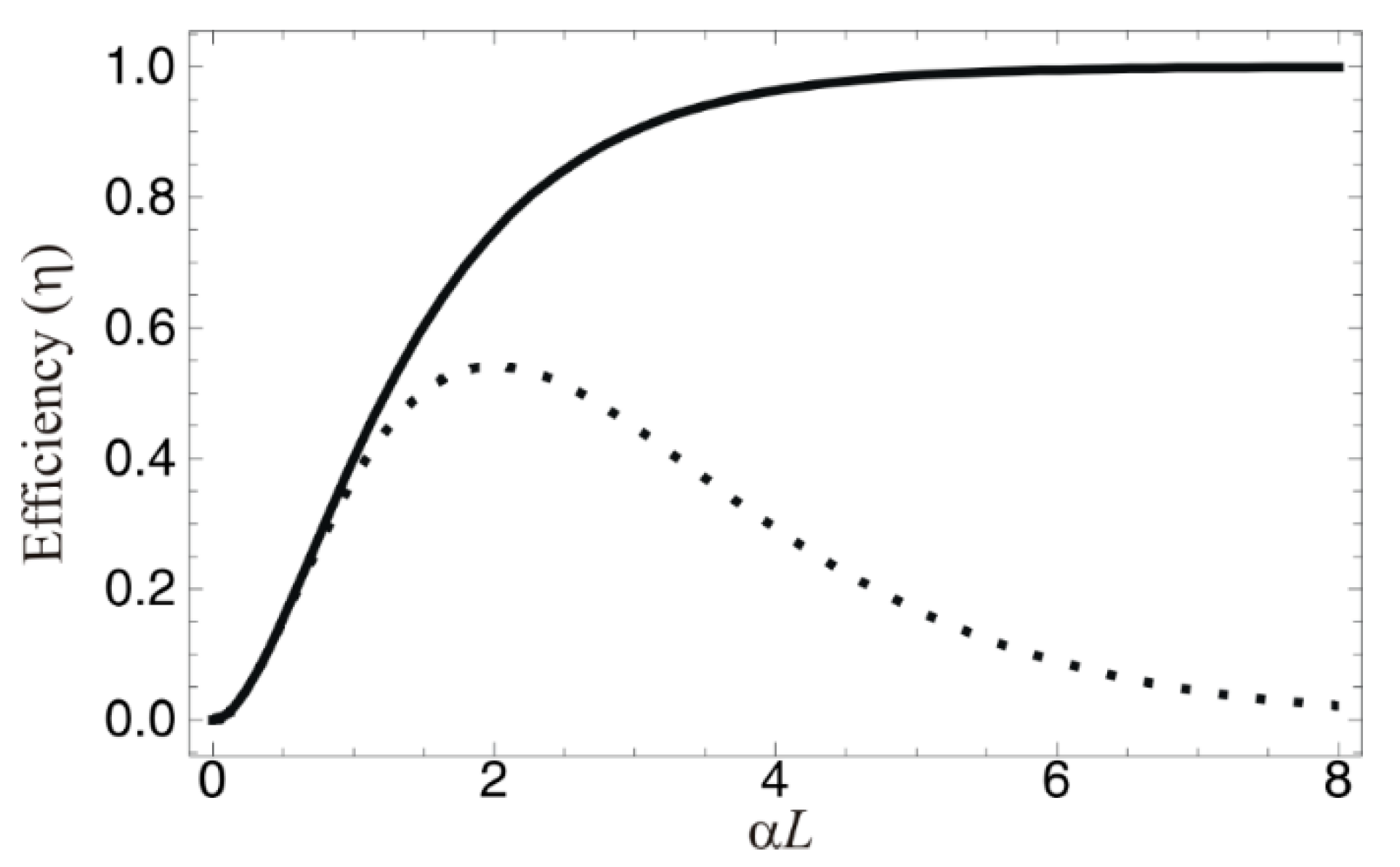
2.3. A. Near Perfect Retrieval Efficiency in CDR
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moiseev, S.A.; Kröll, S. Complete reconstruction of the quantum state of a single-photon wave packet absorbed by a Doppler-broadened transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 173601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseev, S.A.; Tarasov, V.F.; Ham, B.S. Quantum memory photon echo-like techniques in solids. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclass Opt. 2003, 5, S497–S502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, B.; Tittel, W.; Gisin, N.; Nilsson, M.; Kröll, S.; Cirac, J.I. Quantum memory for nonstationary light fields based on controlled reversible inhomogeneous broadening. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 020302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, A.L.; Longdell, J.J.; Sellars, M.J.; Manson, N.B. Photon echoes produced by switching electric fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 043602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedges, M.P.; Longdell, J.J.; Li, Y.; Sellars, M.J. Efficient quantum memory for light. Nature 2010, 465, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Riedmatten, H.; Afzelius, M.; Staudt, M.U.; Simon, C.; Gisin, N. A solid-state light-matter interface at the single-photon level. Nature 2008, 456, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglamyurek, E.; Sinclair, N.; Jin, J.; Slater, J.A.; Oblak, D.; Bussieres, F.; George, M.; Ricken, R.; Sohler, W.; Tittel, W. Broadband waveguide quantum memory for entangled photons. Nature 2011, 469, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afzelius, M.; Usmani, I.; Amari, A.; Lauritzen, B.; Walther, A.; Simon, C.; Sangouard, N.; Minář, J.; de Riedmatten, H.; Gisin, N.; et al. Demonstration of atomic frequency comb memory for light with spin-wave storage. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 040503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gündoğan, M.; Mazzera, M.; Ledingham, P.M.; Cristiani, M.; de Riedmatten, H. Coherent storage of temporally multimode light using a spin-wave atomic frequency comb memory. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 045012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damon, V.; Bonarota, M.; Louchet-Chauvet, A.; Chanelière, T.; Le Gouët, J.-L. Revival of silenced echo and quantum memory for light. New. J. Phys. 2011, 13, 093031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajczgewand, J.; Ahlefeldt, R.; Böttger, T.; Louchet-Chauvet, A.; Le Gouët, J.-L.; Chanelière, T. Optical memory bandwidth and multiplexing capacity in the erbium telecommunication window. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 023031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arcangeli, A.; Ferrier, A.; Goldner, P. Stark echo modulation for quantum memories. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 062303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAuslan, D.L.; Ledingham, P.M.; Naylor, W.R.; Beavan, S.E.; Hedges, M.P.; Sellars, M.J.; Longdell, J.J. Photon-echo quantum memories in inhomogeneously broadened two-level atoms. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 022309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, B.S. Atom phase controlled noise-free photon echoes. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1101.5480v2. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, B.S. Coherent control of collective atom phase for ultralong, inversion-free photon echoes. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 031402(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, B.S. A controlled ac Stark echo for quantum memories. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, R.; Ham, B.S. Analysis of Controlled Coherence Conversion in a Double Rephasing Scheme of Photon Echoes for Quantum Memories. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.02167v2. [Google Scholar]
- Kalachev, A.A.; Karimullin, K.; Samartsev, V.; Zuikov, V. Optical echo-spectroscopy of highly doped Tm:YAG. Laser Phys. Lett. 2008, 5, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samartsev, V.V.; Shegeda, A.M.; Shkalikov, A.V.; Karimullin, K.R.; Mitrofanova, T.G.; A Zuikov, V. Incoherent backward photon echo in ruby upon excitation through an optical fiber. Laser Phys. Lett. 2007, 4, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, B.S. Control of photon storage time using phase locking. Opt. Exp. 2010, 18, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Ham, B.S. Rephasing halted photon echoes using controlled optical deshelving. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 093011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, B.S. Gaussian beam profile effectiveness on double rephasing photon echoes. arXiv 2017, Entropy (to be published). arXiv:1701.04291. [Google Scholar]
- Steane, A.M. Efficient fault-tolerant quantum computing. Nature 1999, 399, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, B.S. Collective atom phase controls in photon echoes for quantum memory applications I: Population inversion removal. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, B.S.; Shahriar, M.S.; Kim, M.K.; Hemmer, P.R. Spin coherence excitation and rephasing with optically shelved atoms. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, R11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangouard, N.; Simon, C.; Afzelius, M.; Gisin, N. Analysis of a quantum memory for photons based on controlled reversible inhomogeneous broadening. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 75, 032327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, M.; Hedges, M.; Ahlefeldt, R.; Bartholomew, J.G.; Beavan, S.E.; Wittig, S.M.; Longdell, J.J.; Sellars, M.J. Optical addressable nuclear spin in a solid with a six-hour coherence time. Nature 2015, 517, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, R.; Ham, B.S. Understanding of Collective Atom Phase Control in Modified Photon Echoes for a Near-Perfect Storage Time-Extended Quantum Memory. Entropy 2020, 22, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080900
Ullah R, Ham BS. Understanding of Collective Atom Phase Control in Modified Photon Echoes for a Near-Perfect Storage Time-Extended Quantum Memory. Entropy. 2020; 22(8):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080900
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Rahmat, and Byoung S. Ham. 2020. "Understanding of Collective Atom Phase Control in Modified Photon Echoes for a Near-Perfect Storage Time-Extended Quantum Memory" Entropy 22, no. 8: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080900
APA StyleUllah, R., & Ham, B. S. (2020). Understanding of Collective Atom Phase Control in Modified Photon Echoes for a Near-Perfect Storage Time-Extended Quantum Memory. Entropy, 22(8), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22080900





