The Flow of Information in Trading: An Entropy Approach to Market Regimes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Entropy, Information Flows and Trading
2.1.1. Entropy Measures
2.1.2. Entropy as a Causality Measure
2.1.3. Information Flow Measures
- -
- market returns → market returns ()
- -
- news sentiment → market returns ()
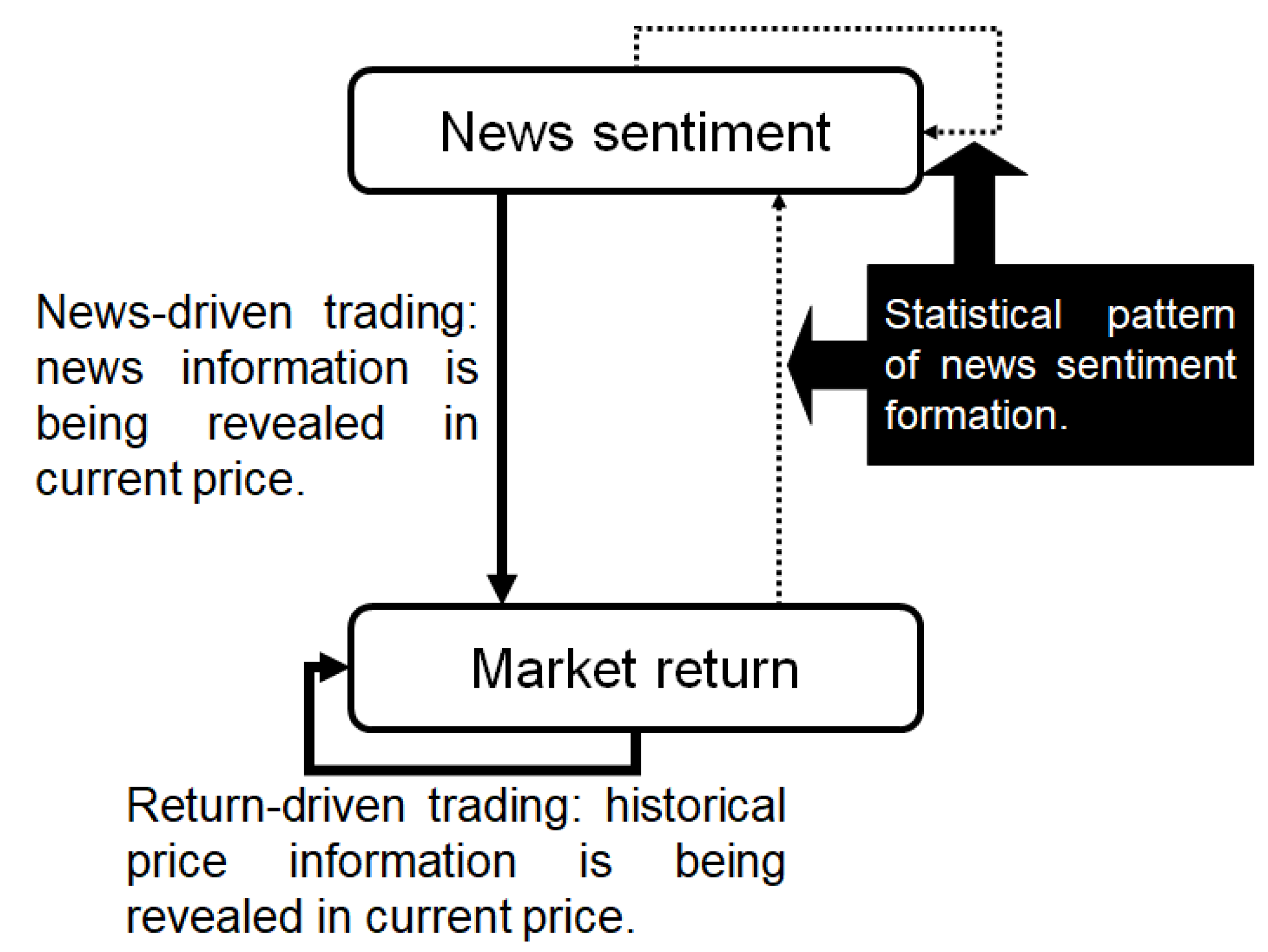
2.2. Trading Activities Identification
- -
- Return-driven trading: Investors are used to follow the market price patterns when making their trading decisions, which is called technical analysis. Such behavior can be identified through self-information flows of market returns. In other words, the memory of market return flow is the evidence of return-driven trading according to our model.
- -
- News-driven trading: This often reflects digitization of textual information that allows investors to effectively form beliefs through news and incorporate them into their trading decisions. Such trading strategies pass news sentiment to the market; hence, indicates occurrence of news-driven trading.
2.3. Market Information Regime
- (1)
- The return-driven regime: The market is purely driven by chasing of return patterns. We often obtain stronger return memory in this regime.
- (2)
- The news-driven regime: The market prices moves entirely from responses to news and no self-causality in returns are detected.
- (3)
- The mixed regime: Both return-driven and news-driven trading were identified and they co-exist.
- (4)
- Other types: Neither return-driven nor news-driven trading were detected. The market either react to news and market data too slow to produce significant information flows, or have too few traders using these types of information to form market-level price impacts.
2.4. Parameter Settings and Some Calibration Issues
3. Data
3.1. Financial Market Data
3.2. News Sentiment Data
- -
- : The date and time of a news article.
- -
- : Reuters Instrument Code (RIC) of a stock for which the sentiment scores apply.
- -
- , , : Positive, neutral, and negative sentiment probabilities (i.e., ).
- -
- : A real-valued number between 0 and 1 indicating the relevance of a piece of news to a stock. One news article may refer to multiple stocks. A stock with more mentions will be assigned a higher relevance.
3.3. Stationarity Test
4. Results
- -
- There are two periods within which the market regime is driven by a single type of trading activity: (1) from the Q3 of 2008 to the Q4 of 2010, the single source of market-wide trading is news sentiment (blue bars only); while (2) from the Q4 of 2011 to the Q3 of 2012, the return memory clustering indicates return-driven activities that drive the market movements (green bars only). Before and after the news-driven regime (period 1 here), we spot a swift switch from returns to sentiment. However, for the return-driven regime (period 2 here), instead, it is more of the fact that news influence disappears from a mixed-regime. These signs are important because they could be highly indicative. They show that news sentiment always requires longer time to form compared to the belief towards some fast updating changes in the market (e.g., reflected in returns).
- -
- During the rest of the time, price movements are caused by mixed types of trading. In addition, the mixed regime demonstrates strong features associated with the market crisis timeline. In the pre-crisis period (before 2008), although there exists trading of both returns and news, often return-driven trading overpowers the news-driven (apart from one exceptional spike of news event around October 2010); while in the post-crisis period (after 2013), the dominance more often resides in the power of news-driven trading, moreover, at a much higher level than the return-driven. This finding is of great interest to us because it provides strong evidence of the change in the market regimes’ dynamics before and after the double crisis period. Furthermore, the imbalance between their dominants within the mixed regime has changed dramatically and more frequently in the post-crises years. We see a few flash spikes in news-driven trading, while there was only one spike showing clear imbalance around October 2004 during the pre-crisis period. All these suggest that the complexity of the market may have increased after the crises with the growth of modern technology and big data [42].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Coefficient | T-Stat | P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Const. | |||
| Lag-1 return | |||
| Lag-1 sentiment | |||
| Lag-2 return | |||
| Lag-2 sentiment | |||
| Lag-3 return | |||
| Lag-3 sentiment | |||
| Lag-4 return | |||
| Lag-4 sentiment | |||
| Lag-5 return | |||
| Lag-5 sentiment | |||
| Lag-6 return | |||
| Lag-6 sentiment |

| Lag-1 | Lag-2 | Lag-3 | Lag-4 | Lag-5 | Lag-6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentiment → Return | ||||||
| Return → Sentiment |
Appendix C
| d | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Return | |||
| Sentiment |
References
- Copeland, T.E. A Model of Asset Trading Under the Assumption of Sequential Information Arrival. J. Financ. 1976, 31, 1149–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merton, R.C. A Simple Model of Capital Market Equilibrium with Incomplete Information. J. Financ. 1986, 42, 483–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.C.; Hsieh, W.l.G.; Tse, Y. Price discovery on the S&P 500 index markets: An analysis of spot index, index futures, and SPDRs. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 1999, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hasbrouck, J. Intraday price formation in US equity index markets. J. Financ. 2003, 58, 2375–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, Y.; Erenburg, G. Competition for order flow, market quality, and price discovery in the Nasdaq 100 index tracking stock. J. Financ. Res. 2003, 26, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendershott, T.; Jones, C.M.; Menkveld, A.J. Does algorithmic trading improve liquidity? J. Financ. 2011, 66, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, E.; Sagade, S. Price discovery and the cross-section of high-frequency trading. J. Financ. Mark. 2016, 30, 54–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, E.; Li, D.; Saar, G. The competitive landscape of high-frequency trading firms. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2018, 31, 2227–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M. Rational markets: Yes or no? The affirmative case. Financ. Anal. J. 2001, 57, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkiel, B.G. The efficient market hypothesis and its critics. J. Econ. Perspect. 2003, 17, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramov, D.; Chordia, T.; Goyal, A. Liquidity and autocorrelations in individual stock returns. J. Financ. 2006, 61, 2365–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschinski, R.; Kantz, H. Analysing the information flow between financial time series. Eur. Phys. J. B 2002, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfl, T.; Peter, F.J. Using transfer entropy to measure information flows between financial markets. Stud. Nonlinear Dyn. Econom. 2013, 17, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jizba, P.; Kleinert, H.; Shefaat, M. Rényi’s information transfer between financial time series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2012, 391, 2971–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfl, T.; Peter, F.J. Analyzing volatility transmission using group transfer entropy. Energy Econ. 2018, 75, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.; Mastroeni, L.; Vellucci, P. Modeling the flow of information between financial time-series by an entropy-based approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.; Mastroenim, L.; Quaresima, G.; Vellucci, P. Does OVX affect WTI and Brent oil spot variance? Evidence from an entropy analysis. Energy Econ. 2020, 89, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsoni, B. Algorithmic Trading and DMA: An Introduction to Direct Access Trading Strategies; 4Myeloma Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.; Wurgler, J. Investor sentiment in the stock market. J. Econ. Perspect. 2007, 21, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlock, P.C.; Saar-Tsechansky, M.; MacSkassy, S. More than words: Quantifying language to measure firms’ fundamentals. J. Financ. 2008, 63, 1437–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranco, G.; Aleksovski, D.; Caldarelli, G.; Grčar, M.; Mozetič, I. The effects of Twitter sentiment on stock price returns. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ver Steeg, G.; Galstyan, A. Information transfer in social media. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on World Wide Web, Lyon, France, 16–20 April 2012; pp. 509–518. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, L.J. Cluster formation and evolution in networks of financial market indices. Algorithmic Financ. 2013, 2, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.J. Structure of a global network of financial companies based on transfer entropy. Entropy 2014, 16, 4443–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekiros, S.; Nguyen, D.K.; Sandoval, L.J.; Uddin, G.S. Information diffusion, cluster formation and entropy-based network dynamics in equity and commodity markets. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 256, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amblard, P.O.; Michel, O.J. The relation between Granger causality and directed information theory: A review. Entropy 2012, 15, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.; Barrett, A.B.; Seth, A.K. Granger causality and transfer entropy are equivalent for Gaussian variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.F.; Hu, H.P.; Deng, Y.S.; Ding, N.D. An entropy measure of non-stationary processes. Entropy 2014, 16, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.M.; Bucholtz, F.; Michalowicz, J.V. Linearized transfer entropy for continuous second order systems. Entropy 2013, 15, 3186–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopenko, M.; Lizier, J.T.; Price, D.C. On thermodynamic interpretation of transfer entropy. Entropy 2013, 15, 524–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Chen, J.; Hawkes, A.G.; Yang, S.Y. Information Transition in Trading and its Effect on Market Efficiency: An Entropy Approach. In Proceedings of the First International Forum on Financial Mathematics and Financial Technology; Zheng, Z., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Yuan, Y. Investor sentiment and the mean–variance relation. J. Financ. Econ. 2011, 100, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.M.; Toh, B. Investor sentiment and the MAX effect. J. Bank. Financ. 2014, 46, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Liu, A.; Chen, J.; Hawkes, A. Applications of a multivariate Hawkes process to joint modeling of sentiment and market return events. Quant. Financ. 2018, 18, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkelmann, K.; Kempthorne, O. Design and Analysis of Experiments, Introduction to Experimental Design, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, T. Measuring Information Transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Ferrer, J.; Mateo-Sanz, J.M. Practical data-oriented microaggregation for statistical disclosure control. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2002, 14, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokolakis, G.; Nanopoulos, P.; Fouskakis, D. Bregman divergences in the (m × k)-partitioning problem. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2006, 51, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokolakis, G.; Fouskakis, D. On the discrepancy measures for the optimal equal probability partitioning in bayesian multivariate micro-aggregation. J. Classif. 2008, 25, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöschel, T.; Ebeling, W.; Rosé, H. Guessing probablity distributions from small samples. J. Stat. Phys. 1995, 80, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, S.Y.; Song, Q.; Mo, S.Y.K.; Datta, K.; Deane, A. The Impact of Abnormal News Sentiment on Financial Markets. J. Bus. Econ. 2015, 6, 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, J. Structural causes of the global financial crisis: A critical assessment of the ’new financial architecture’. Camb. J. Econ. 2009, 33, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shleifer, A. Inefficient Markets: An Introduction to Behavioral Finance; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Loughran, T.; McDonald, B. Textual analysis in accounting and finance: A survey. J. Account. Res. 2016, 54, 1187–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, M.; Petracco-Giudici, M.; Naltsidis, M. Walking down wall street with a tablet: A survey of stock market predictions using the web. J. Econ. Surv. 2016, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
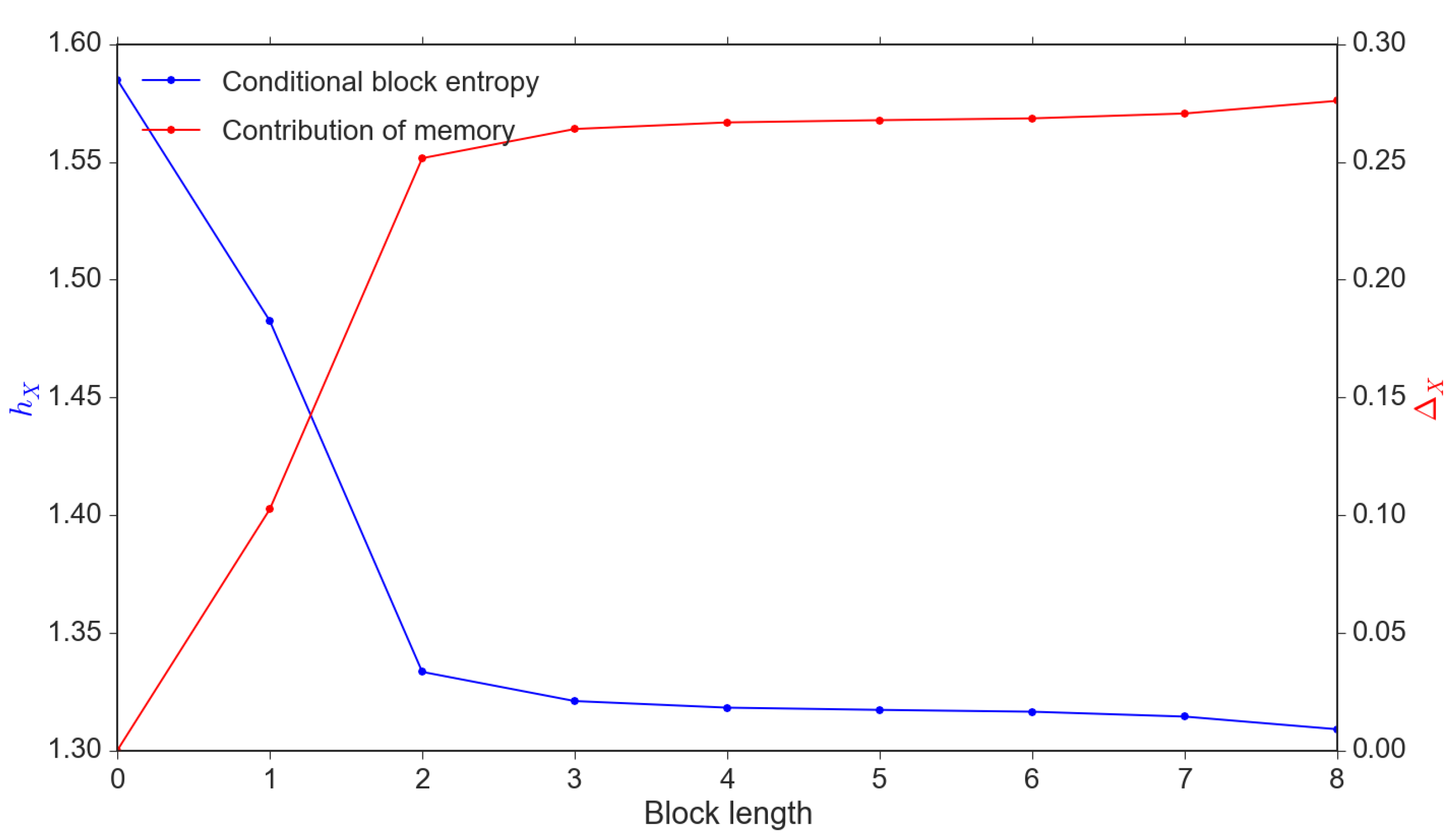





| t-Statistic | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Price level | ||
| Log-return | ||
| News sentiment |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, A.; Chen, J.; Yang, S.Y.; Hawkes, A.G. The Flow of Information in Trading: An Entropy Approach to Market Regimes. Entropy 2020, 22, 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091064
Liu A, Chen J, Yang SY, Hawkes AG. The Flow of Information in Trading: An Entropy Approach to Market Regimes. Entropy. 2020; 22(9):1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091064
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Anqi, Jing Chen, Steve Y. Yang, and Alan G. Hawkes. 2020. "The Flow of Information in Trading: An Entropy Approach to Market Regimes" Entropy 22, no. 9: 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091064
APA StyleLiu, A., Chen, J., Yang, S. Y., & Hawkes, A. G. (2020). The Flow of Information in Trading: An Entropy Approach to Market Regimes. Entropy, 22(9), 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22091064





