Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering Based on the Maximum Correntropy Criterion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Conventional Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering
2.2. Maximum Correntropy Criterion
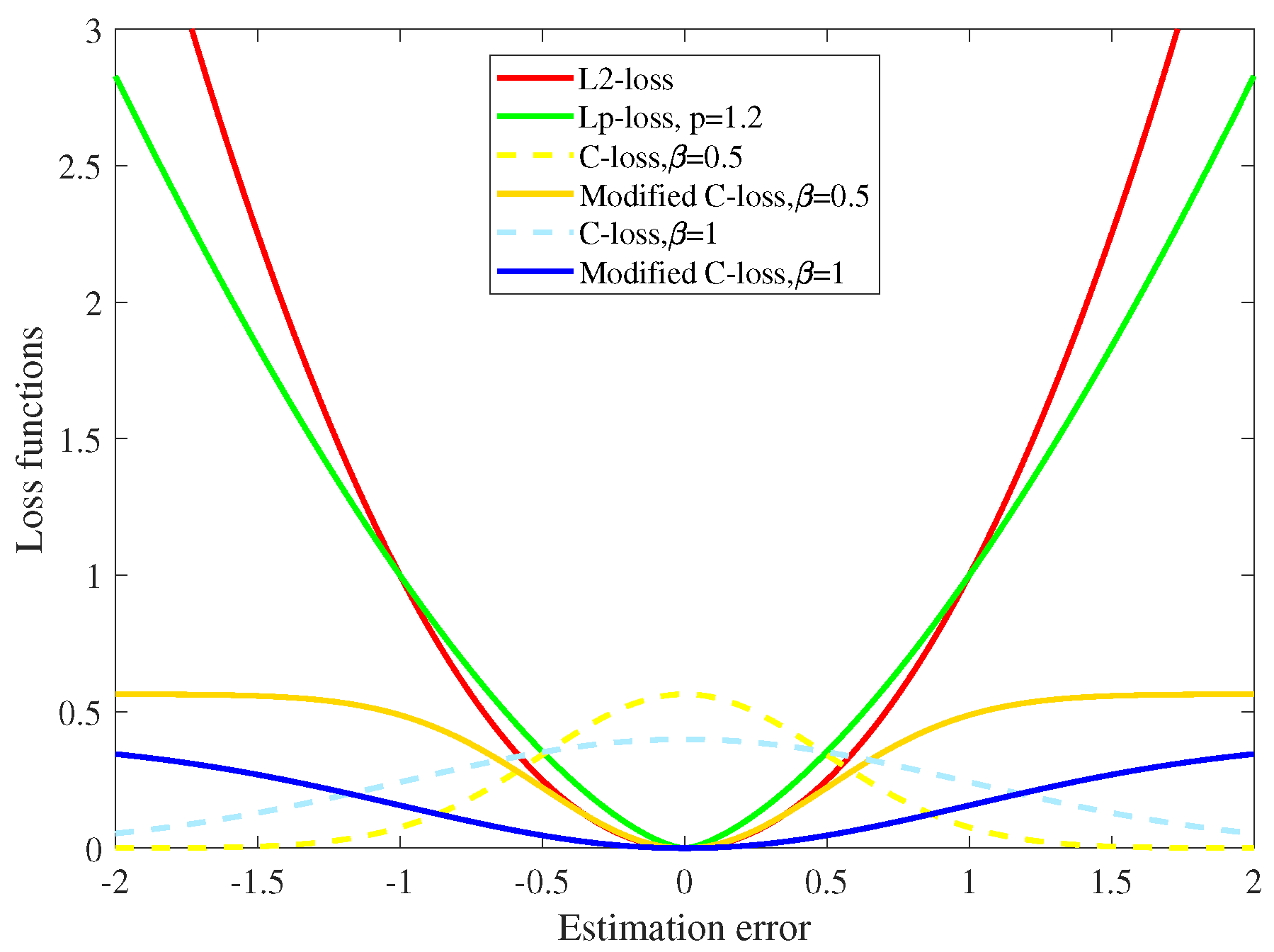
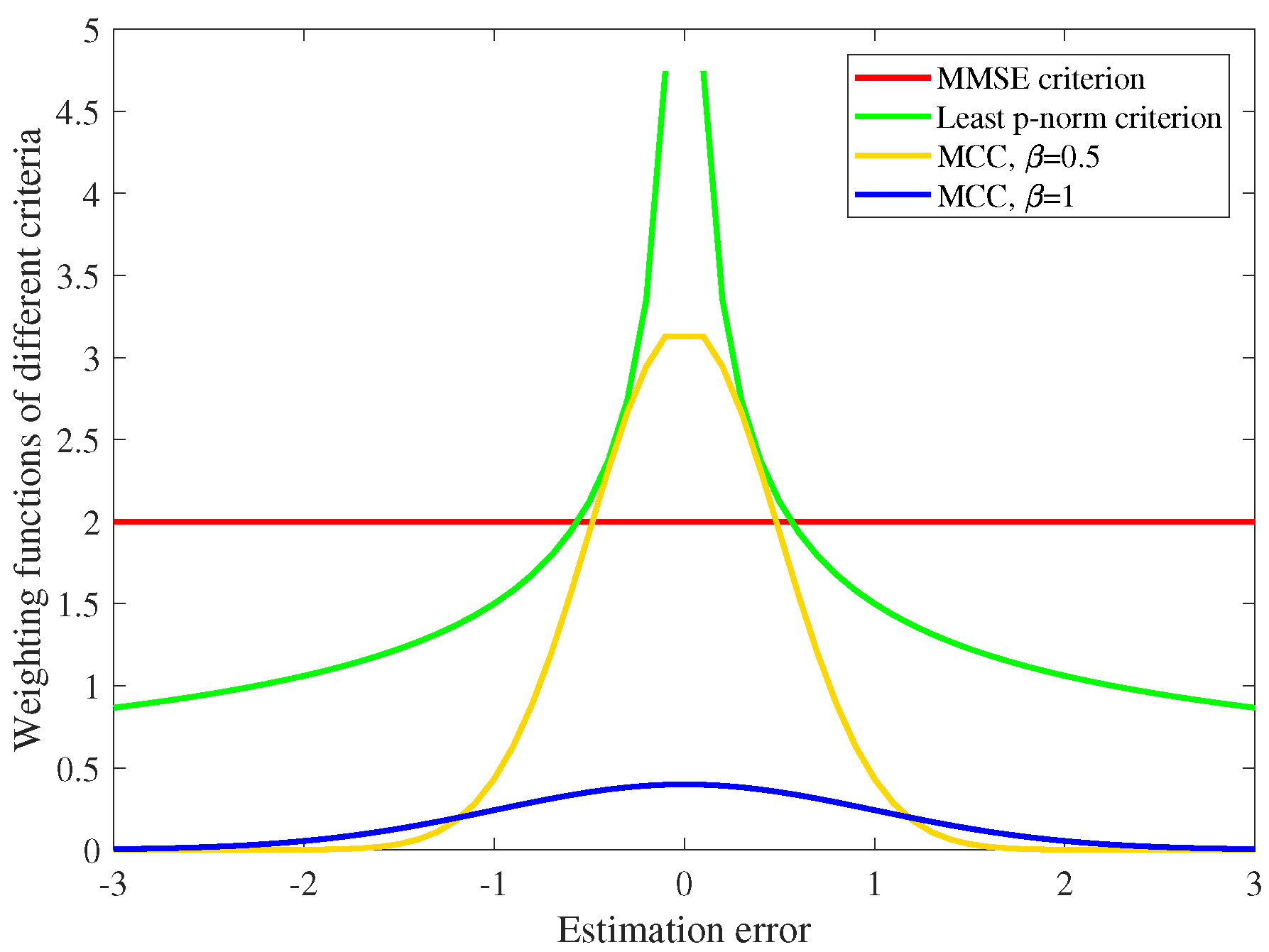
2.3. Comparison of Different Criteria
3. A Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering Based on MCC
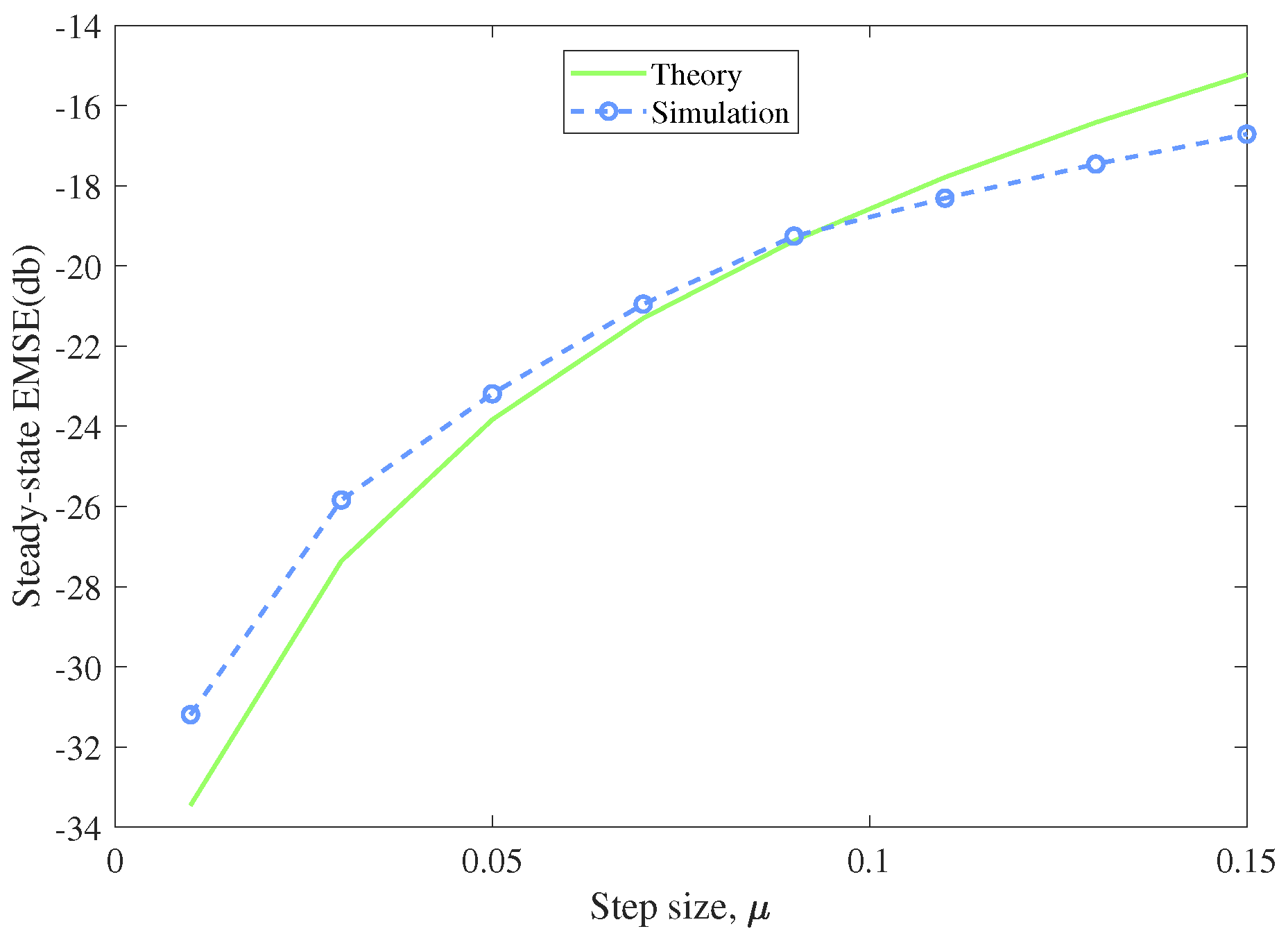
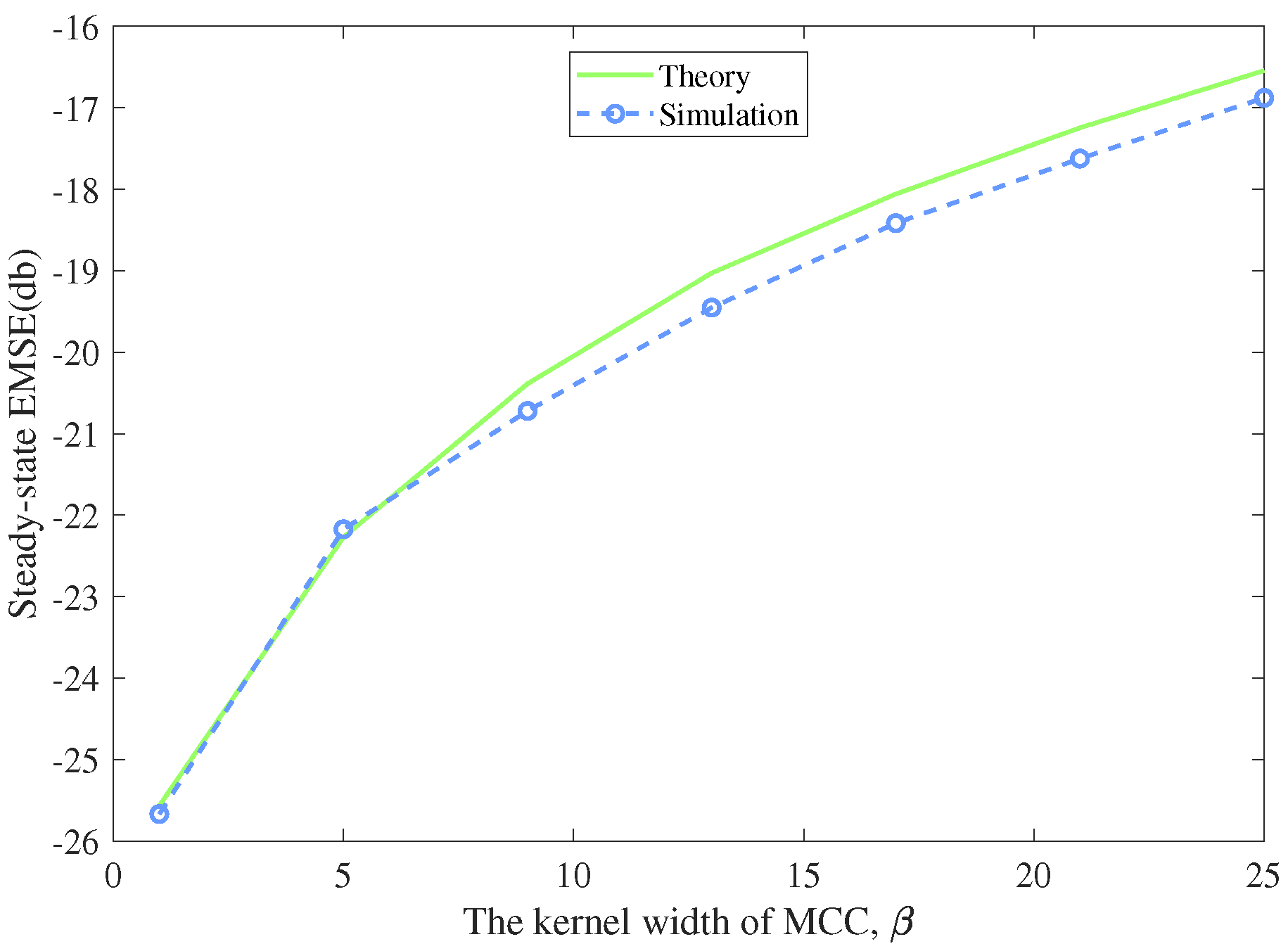
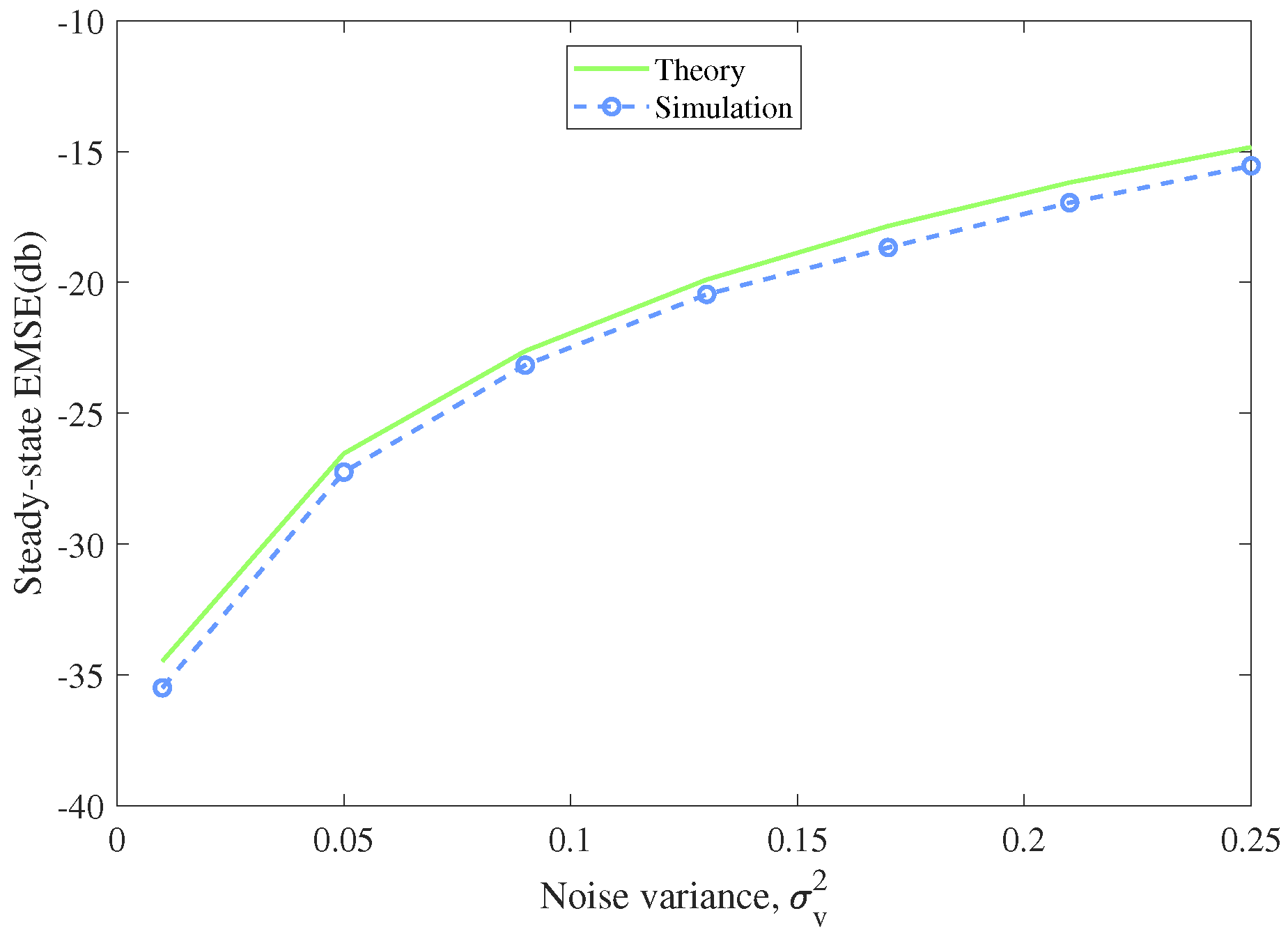
4. Steady-State Performance Analysis
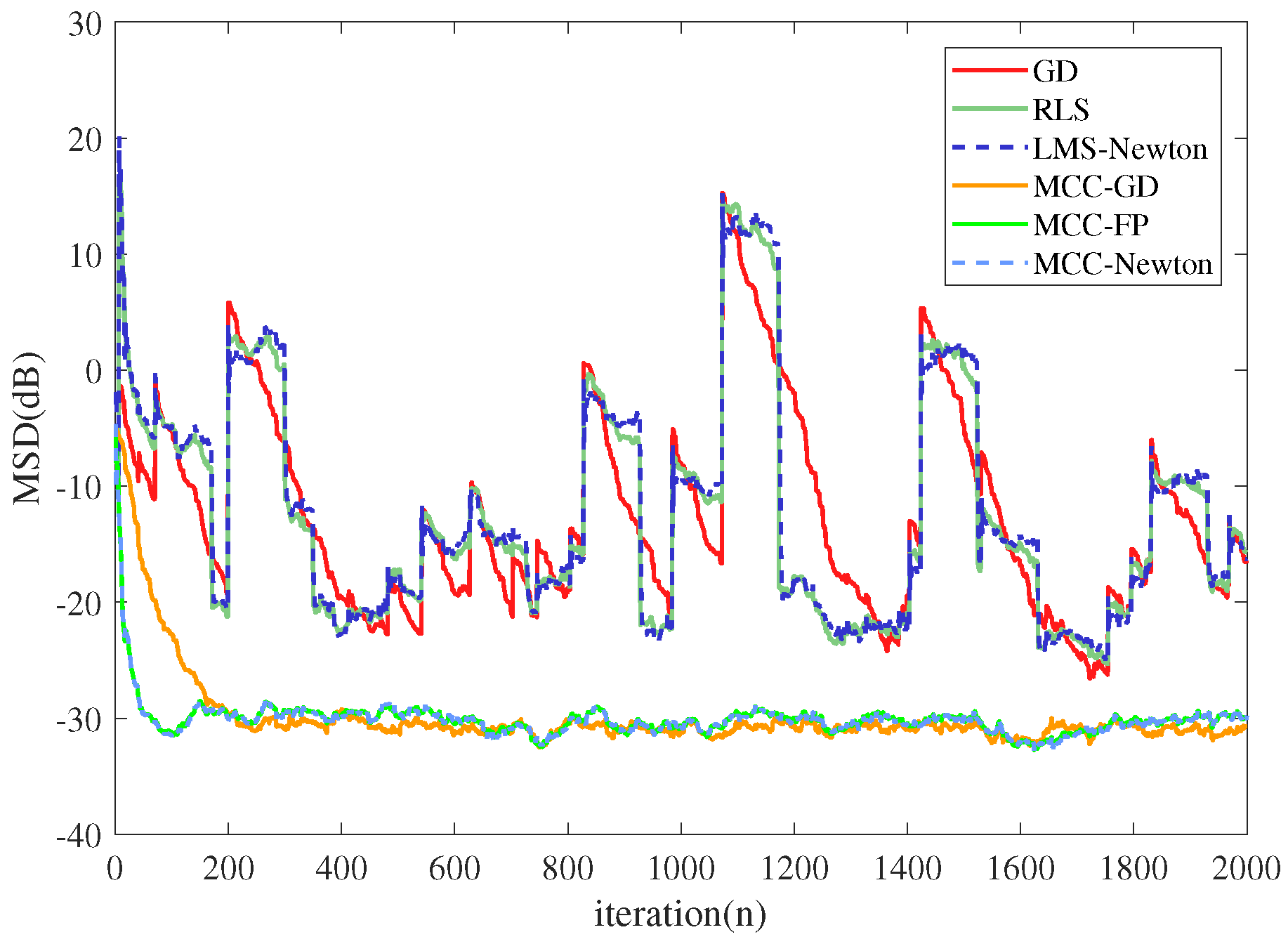
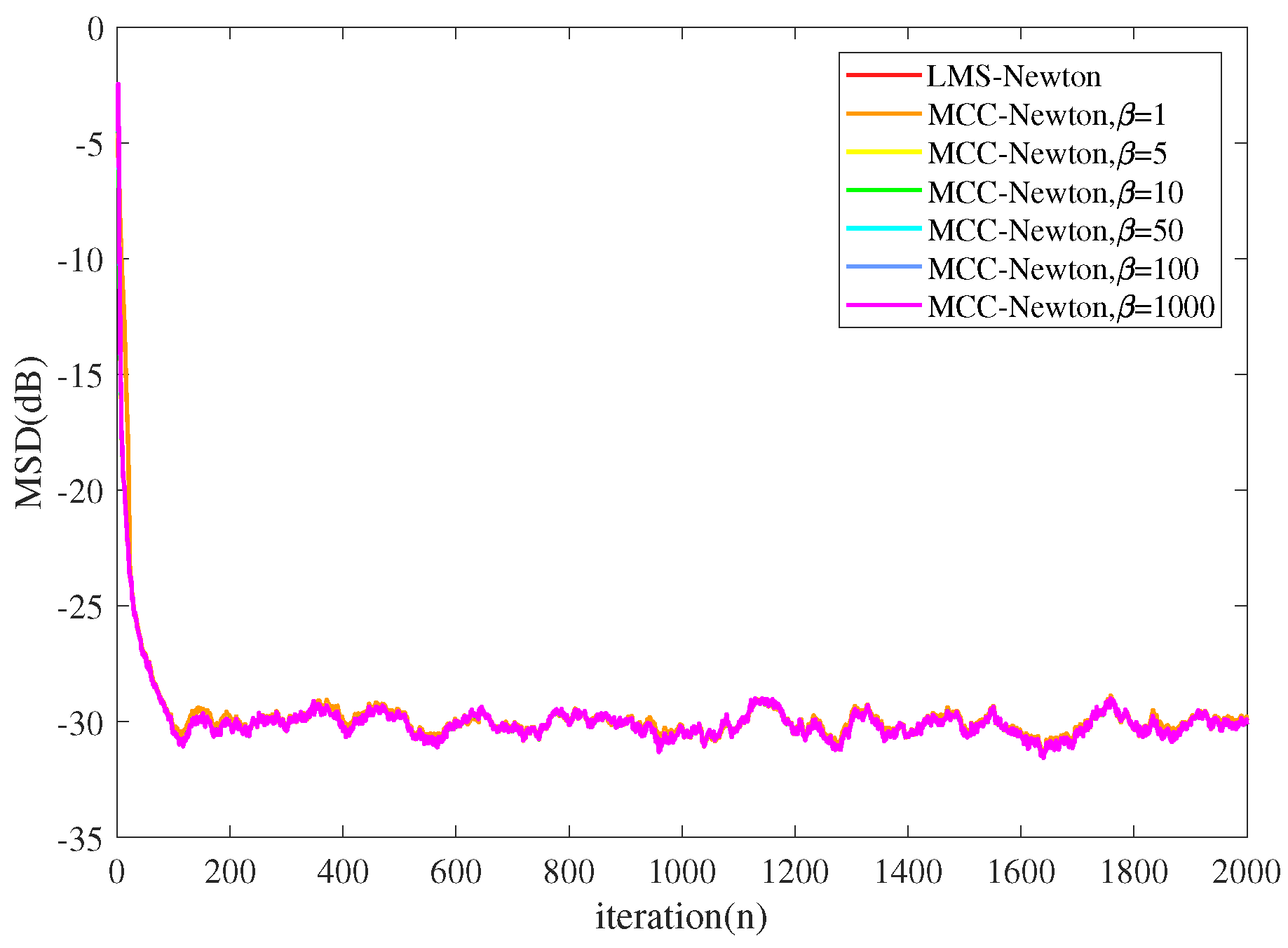
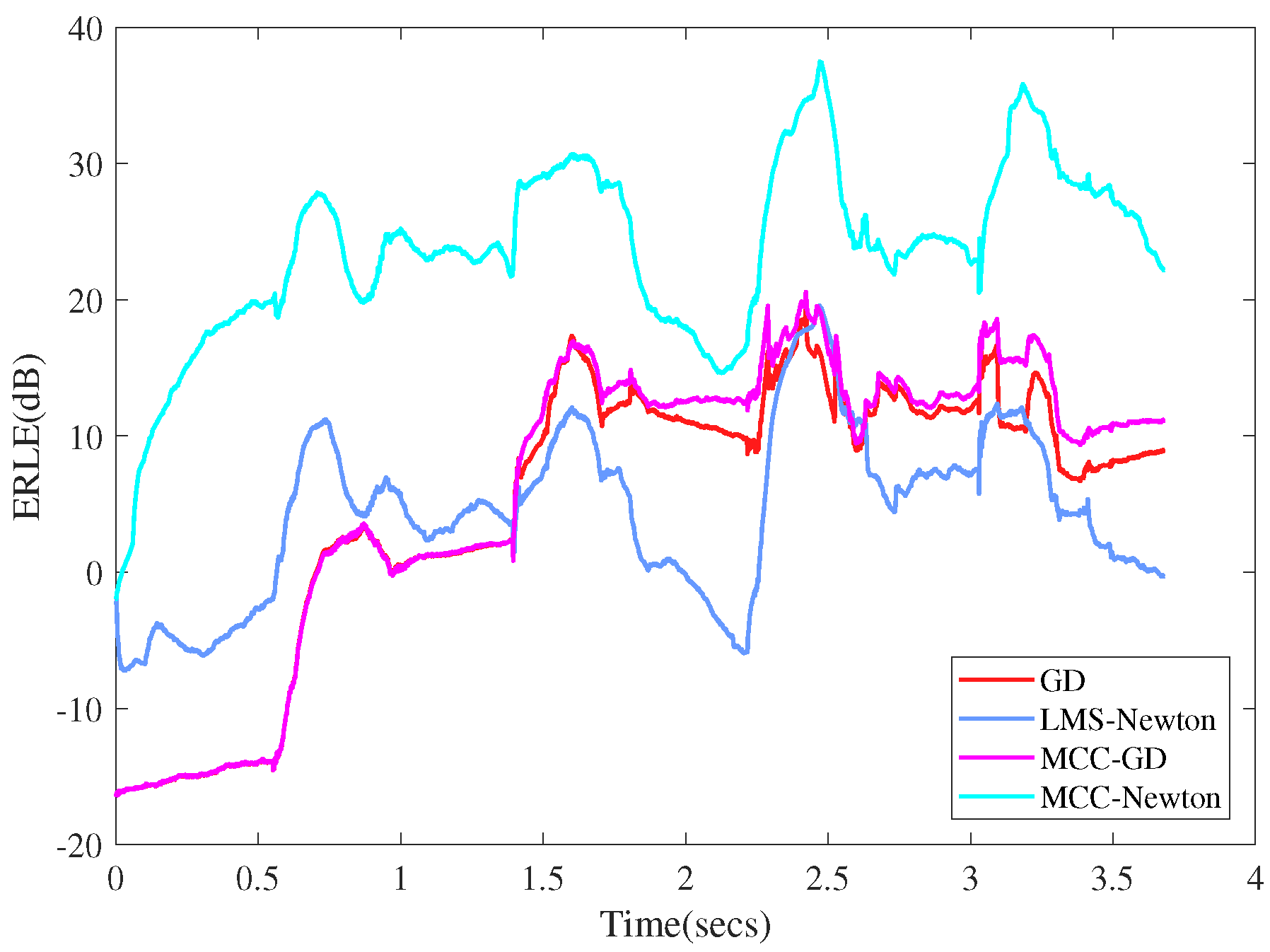
5. Experiments and Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Widrow, B.; Stearns, S.D. Adaptive Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schafhuber, D.; Matz, G.; Hlawatsch, F. Adaptive Wiener filters for time-varying channel estimation in wireless OFDM systems. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP’03), Hong Kong, China, 6–10 April 2003; Volume 4, p. IV-688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukopoulos, X.G.; Moustakides, G.V. Blind adaptive channel estimation in ofdm systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2006, 5, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Amand, F.; Gilloire, A.; Grenier, Y. Adaptive filtering algorithms for stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Detroit, MI, USA, 9–12 May 1995; Volume 5, pp. 3099–3102. [Google Scholar]
- Aung, M.T.S.; Shi, Z.; Kikuuwe, R. A new noise-reduction filter with sliding mode and low-pass filtering. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Control Applications (CCA), Juan Les Antibes, France, 8–10 October 2014; pp. 1029–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Adaptive Filter Theory; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Madisetti, V. Digital Signal Processing Fundamentals, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Petrus, P. Robust Huber adaptive filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1999, 47, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Chen, B.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J. Sparse least mean p-power algorithms for channel estimation in the presence of impulsive noise. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, J.C. Information Theoretic Learning: Renyi’s Entropy and Kernel Perspectives; Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1385–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Principe, J.C. System Parameter Identification: Information Criteria and Algorithms; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Yue, P.; Wang, M. Maximum Correntropy Unscented Kalman Filter for Spacecraft Relative State Estimation. Sensors 2016, 16, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Yue, P. Maximum correntropy square-root cubature Kalman filter with application to SINS/GPS integrated systems. ISA Trans. 2018, 80, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. A robust blind adaptive multiuser detection based on maximum correntropy criterion in satellite CDMA systems. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2019, 30, e3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Principe, J.C. Using Correntropy as a cost function in linear adaptive filters. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–19 June 2009; pp. 2950–2955. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Qu, H.; Gui, G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B. Maximum correntropy criterion based sparse adaptive filtering algorithms for robust channel estimation under non-Gaussian environments. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 2708–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, N.; Principe, J.C. Generalized Correntropy for Robust Adaptive Filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3376–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Rong, H.; Chen, B. Kernel adaptive filtering under generalized Maximum Correntropy Criterion. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1738–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M. An Adaptive Channel Estimation Based on Fixed-Point Generalized Maximum Correntropy Criterion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66281–66290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B. State space maximum correntropy filter. Signal Process. 2017, 130, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Liang, J.; Zheng, N.; Principe, J.C. Steady-State Mean-Square Error Analysis for Adaptive Filtering under the Maximum Correntropy Criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 880–884. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Qu, H.; Chen, B.; Principe, J.C. Convergence performance analysis of an adaptive kernel width MCC algorithm. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Príncipe, J.C. A closed form recursive solution for Maximum Correntropy training. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 2070–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, N.; Príncipe, J.C. Convergence of a Fixed-Point Algorithm under Maximum Correntropy Criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G. Fixed-point generalized maximum correntropy: Convergence analysis and convex combination algorithms. Signal Process. 2019, 154, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.P.; Meehan, M.; O’Regan, D. Fixed Point Theory and Applications; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Huntington, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 101, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Principe, J.C. Maximum correntropy kalman filter. Automatica 2017, 76, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.; Santos, A.; Pereira, J. State Estimation Based on Correntropy: A Proof of Concept. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 1888–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, A.R.; Hodtani, G.A. A new robust correntropy based Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 Iran Workshop on Communication and Information Theory (IWCIT), Tehran, Iran, 3–4 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Heravi, A.R.; Hodtani, G.A. Comparison of the Convergence Rates of the New Correntropy-Based Levenberg–Marquardt (CLM) Method and the Fixed-Point Maximum Correntropy (FP-MCC) Algorithm. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 37, 2884–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhotto, M.Z.A.; Antoniou, A. Robust Quasi-Newton Adaptive Filtering Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2011, 58, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.I.K.; Farhang-Boroujeny, B. Fast LMS/Newton Algorithms for Stereophonic Acoustic Echo Cancelation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang-Boroujeny, B. Fast LMS/Newton algorithms based on autoregressive modeling and their application to acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, M.L.R.; Antoniou, A. A robust quasi-Newton adaptive filtering algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems—ISCAS ’94, London, UK, 30 May–2 June 1994; Volume 2, pp. 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, P.; Krishnanand, K.; Padhee, M. Fast recursive Gauss—Newton adaptive filter for the estimation of power system frequency and harmonics in a noisy environment. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2011, 5, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chan, S.C.; Ho, K.L. A new LMS/Newton algorithm for robust adaptive filtering in impulsive noise. In Proceedings of the 2004 12th European Signal Processing Conference, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 September 2004; pp. 705–708. [Google Scholar]
- De Campos, M.L.R.; Antoniou, A. A new quasi-Newton adaptive filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog. Digit. Signal Process. 1997, 44, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshal, D.F.; Jenkins, W.K. A fast quasi-Newton adaptive filtering algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP-88), New York, NY, USA, 11–14 April 1988; Volume 3, pp. 1377–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Berberidis, K.; Rantos, S.; Palicot, J. A step-by-step quasi-Newton algorithm in the frequency domain and its application to adaptive channel equalization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 52, 3335–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B.; Principe, J.C. Efficient and robust deep learning with Correntropy-induced loss function. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-K. A channel estimation using sliding window approach and tuning algorithm for MLSE. IEEE Commun. Lett. 1999, 3, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, Z. A sliding-exponential window RLS adaptive filtering algorithm: Properties and applications. Signal Process. 1995, 45, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J. A Smoothed Algorithm with Convergence Analysis under Generalized Maximum Correntropy Criteria in Impulsive Interference. Entropy 2019, 21, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H. Steady-state performance analysis of the recursive maximum correntropy algorithm and its application in adaptive beamforming with alpha-stable noise. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.08407. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruoglu, E.E.; Fitzgerald, W.J.; Rayner, P.J.W. Near optimal detection of signals in impulsive noise modeled with a symmetric/spl alpha/-stable distribution. IEEE Commun. Lett. 1998, 2, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, P.; Qu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M. Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering Based on the Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Entropy 2020, 22, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22090922
Yue P, Qu H, Zhao J, Wang M. Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering Based on the Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Entropy. 2020; 22(9):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22090922
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Pengcheng, Hua Qu, Jihong Zhao, and Meng Wang. 2020. "Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering Based on the Maximum Correntropy Criterion" Entropy 22, no. 9: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22090922
APA StyleYue, P., Qu, H., Zhao, J., & Wang, M. (2020). Newtonian-Type Adaptive Filtering Based on the Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Entropy, 22(9), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22090922




