Enhancing Chaos Complexity of a Plasma Model through Power Input with Desirable Random Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Mathematical Model
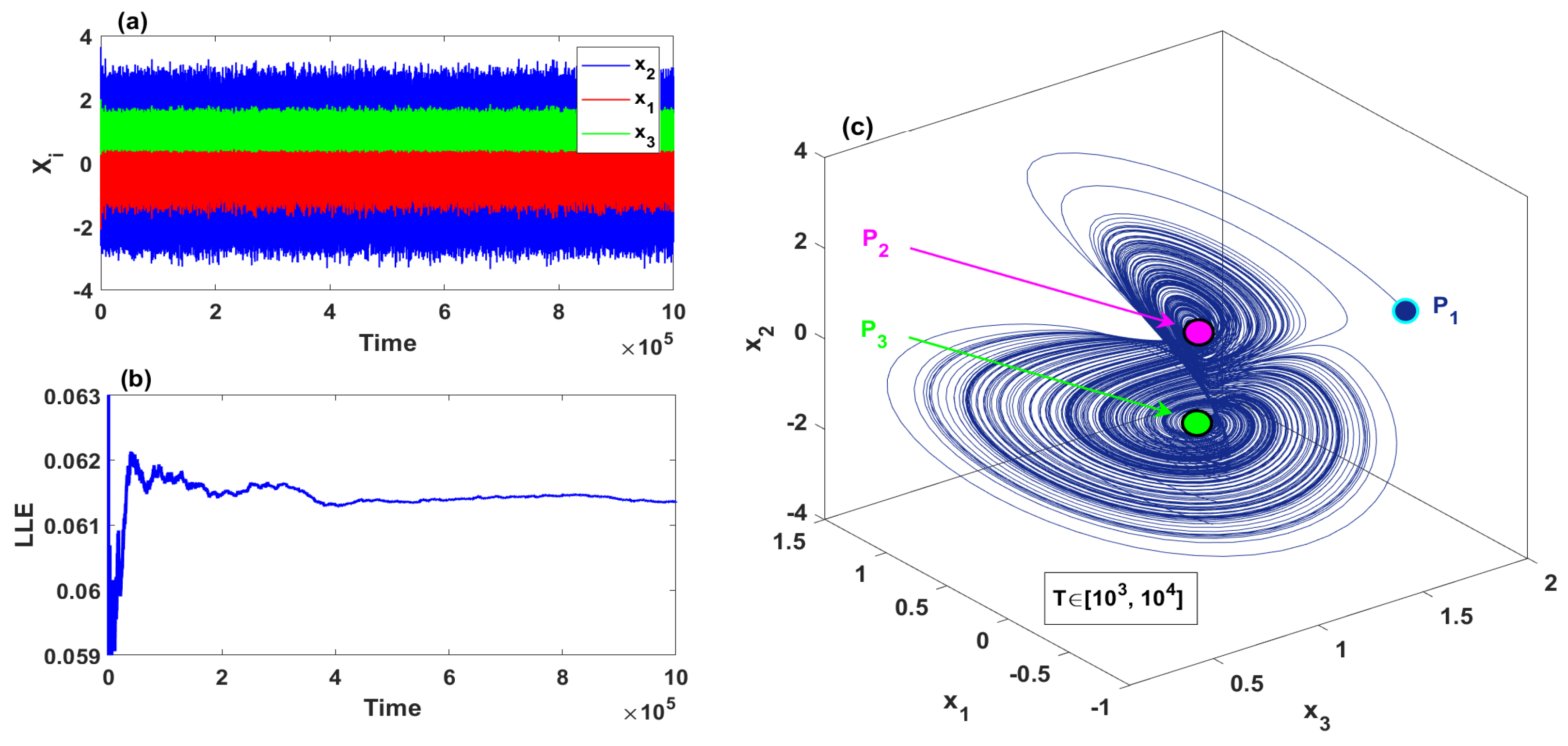
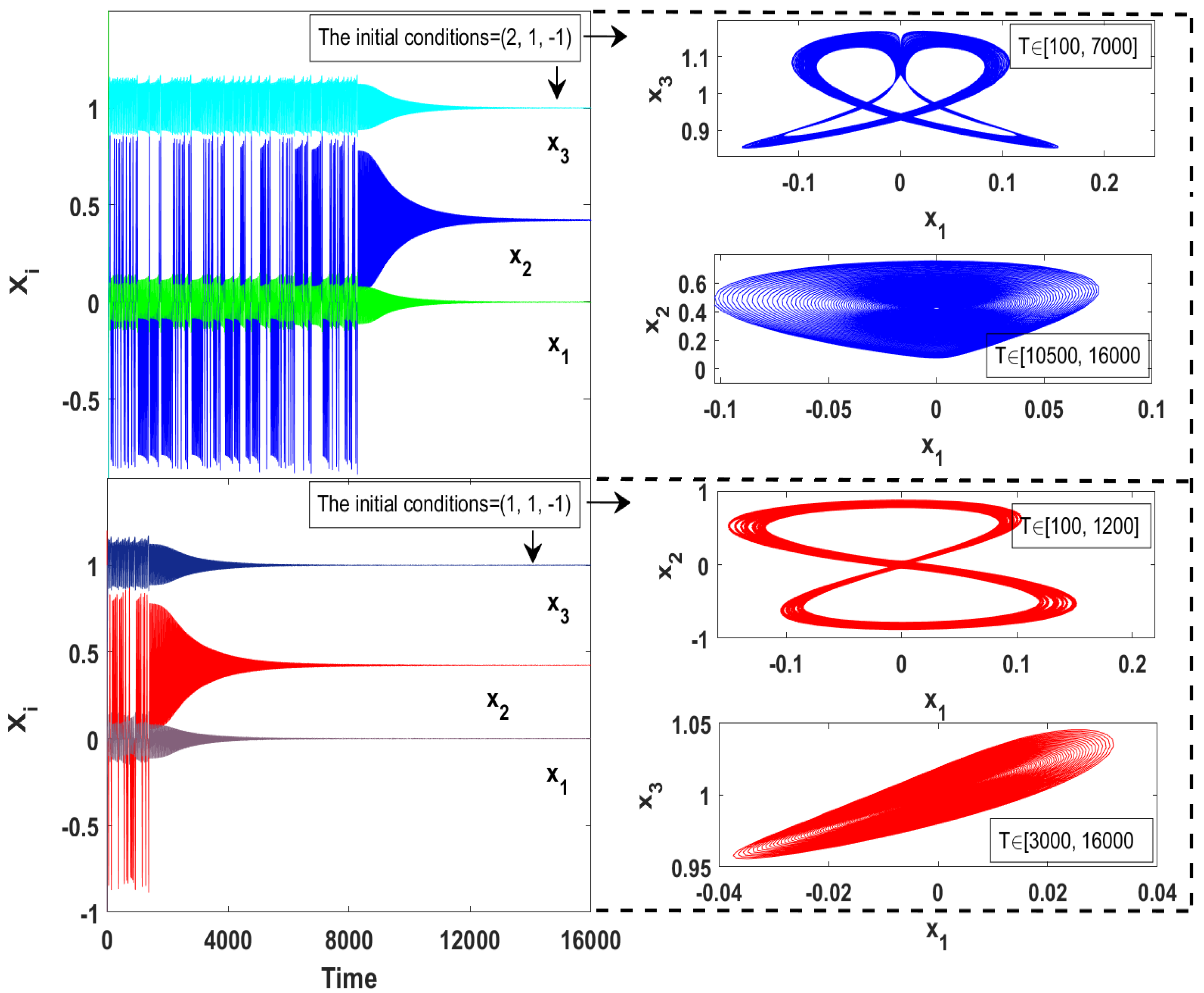
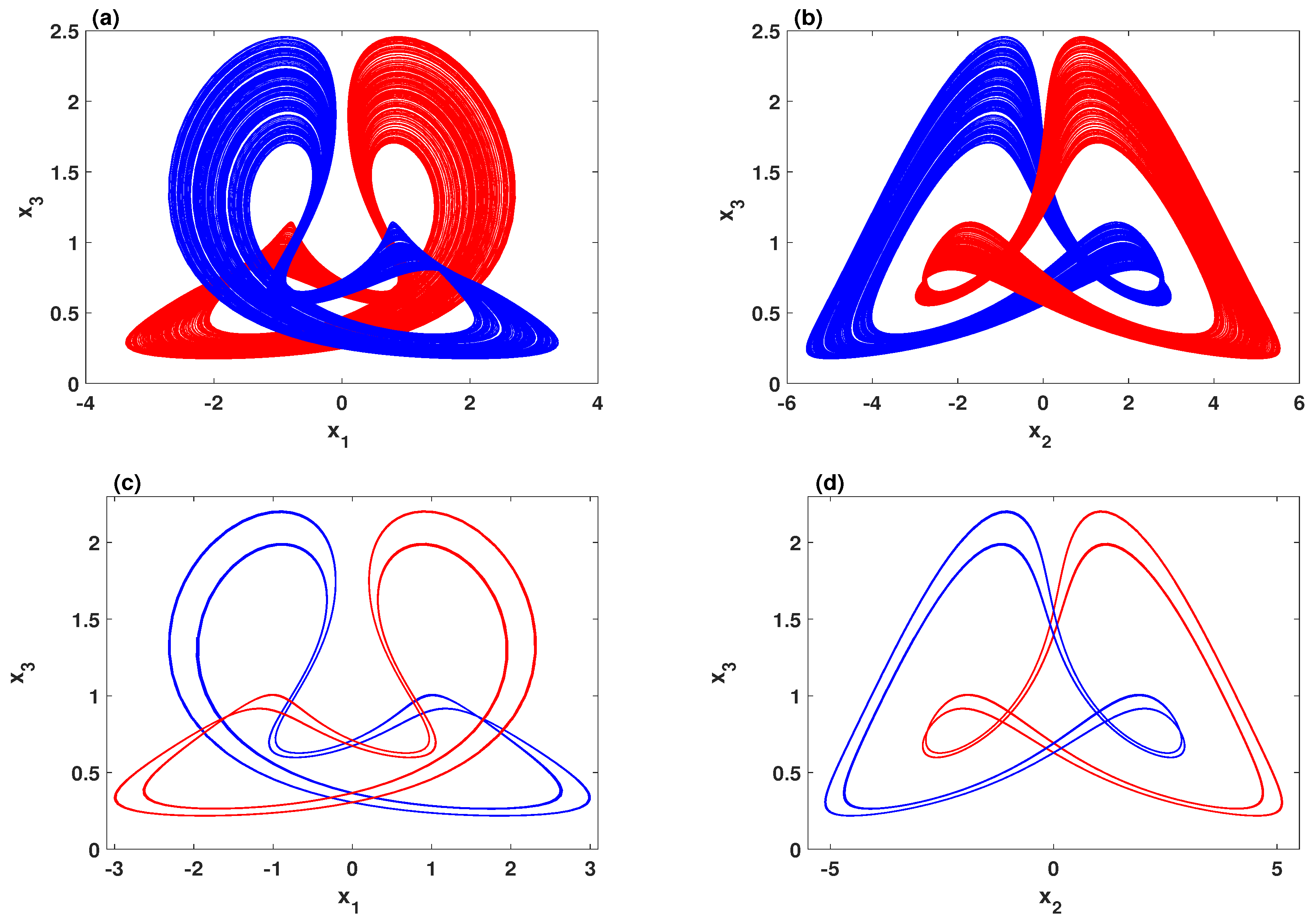
2.1. Self-Excited Chaotic Attractor and Complex Transient Chaos
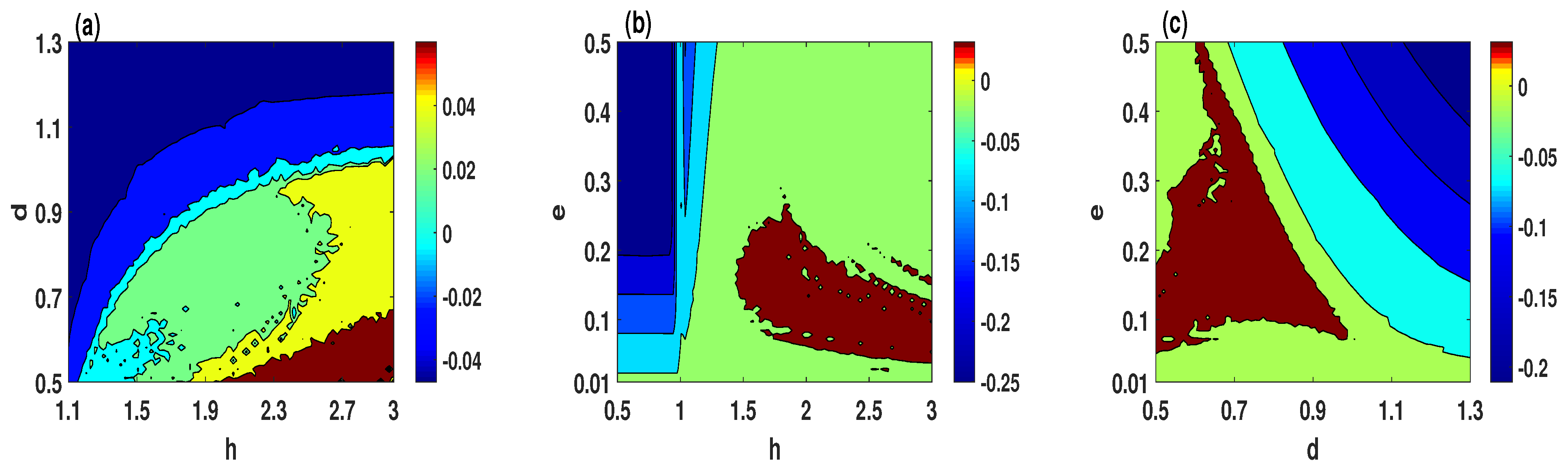
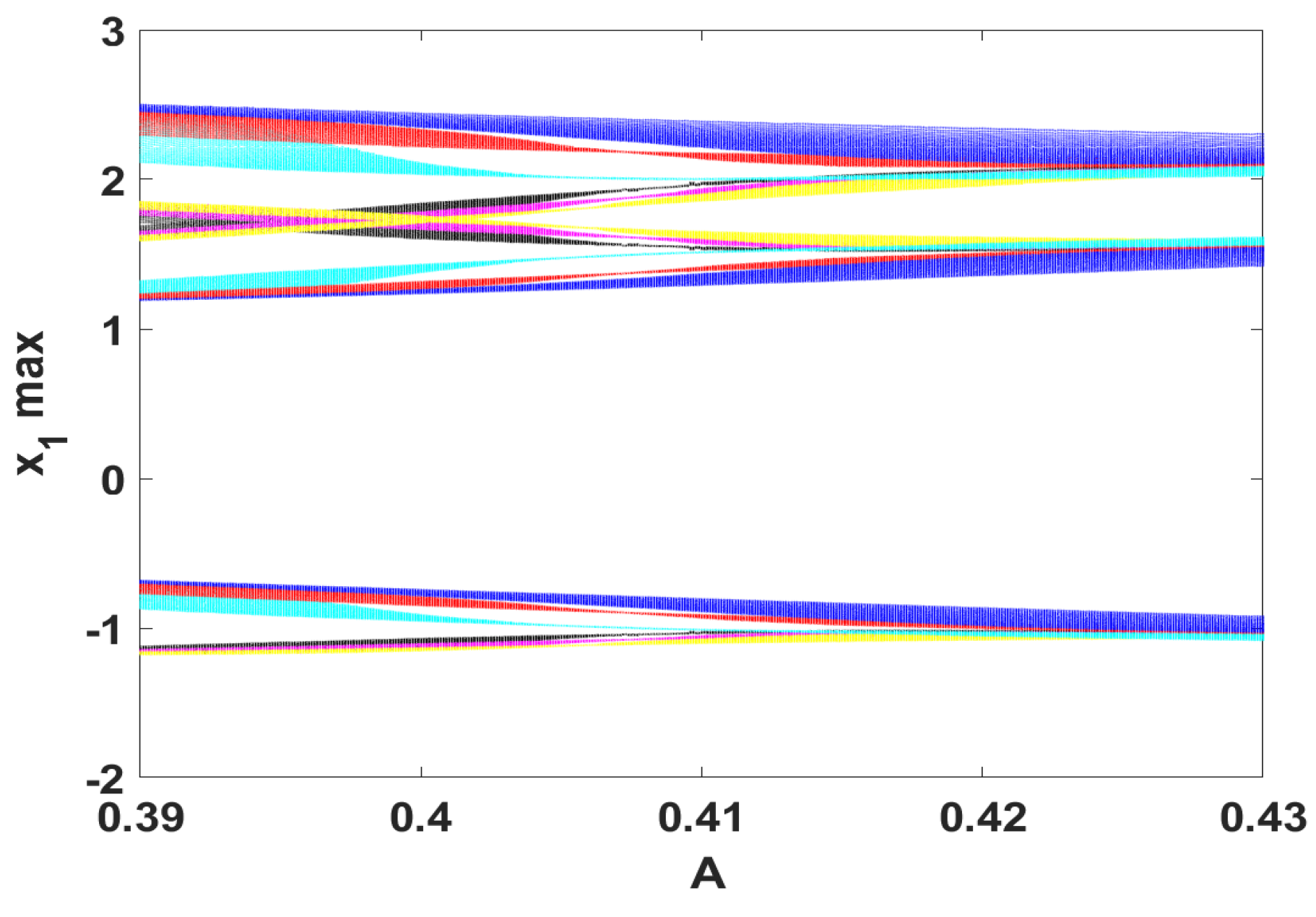
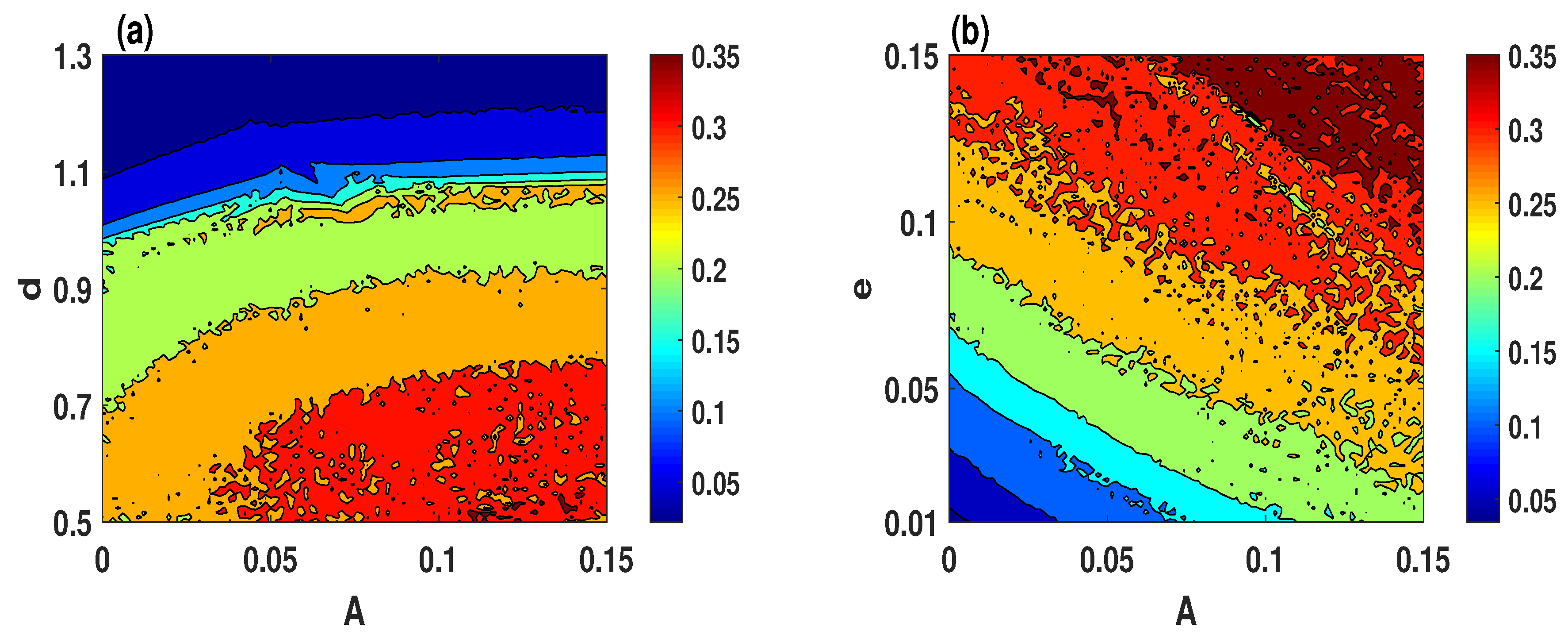
2.2. Chaotic Regions of the Plasma Model
- Figure 3a illustrates that the chaotic behavior appears in the brown, yellow, and green colors regions. Meanwhile, the quasi-periodic and periodic behaviors appear in cyan and blue colors regions, respectively.
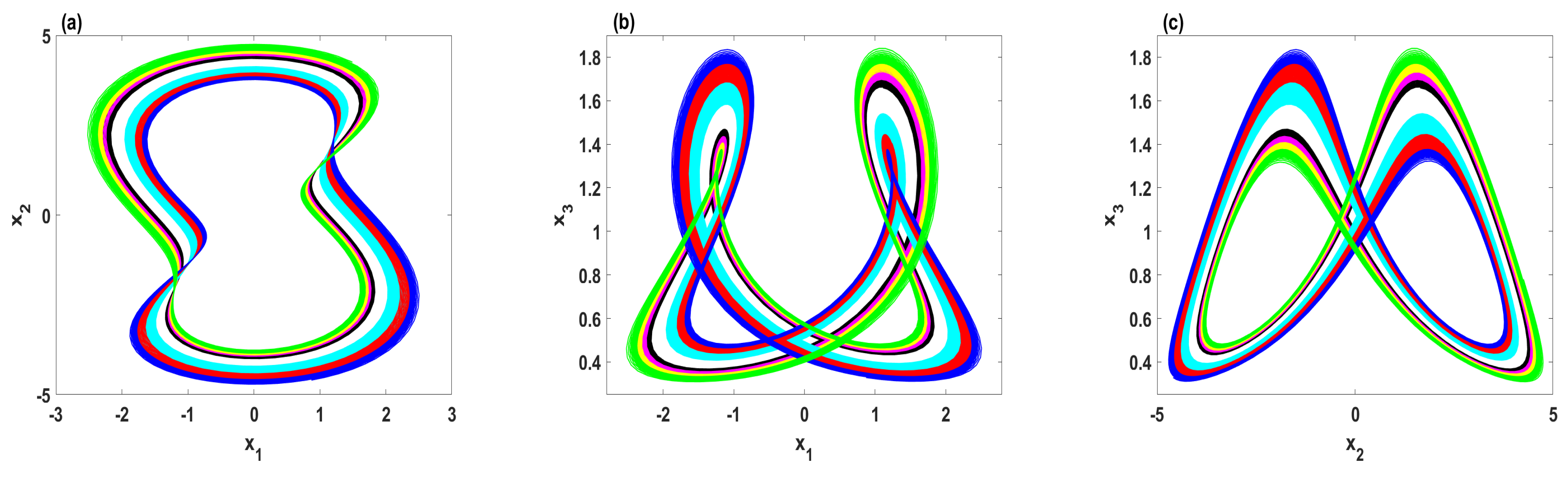
3. The Plasma Model with Coexisting Symmetric Attractors
- (1)
- is saddle point if .
- (2)
- are unstable equilibria if .
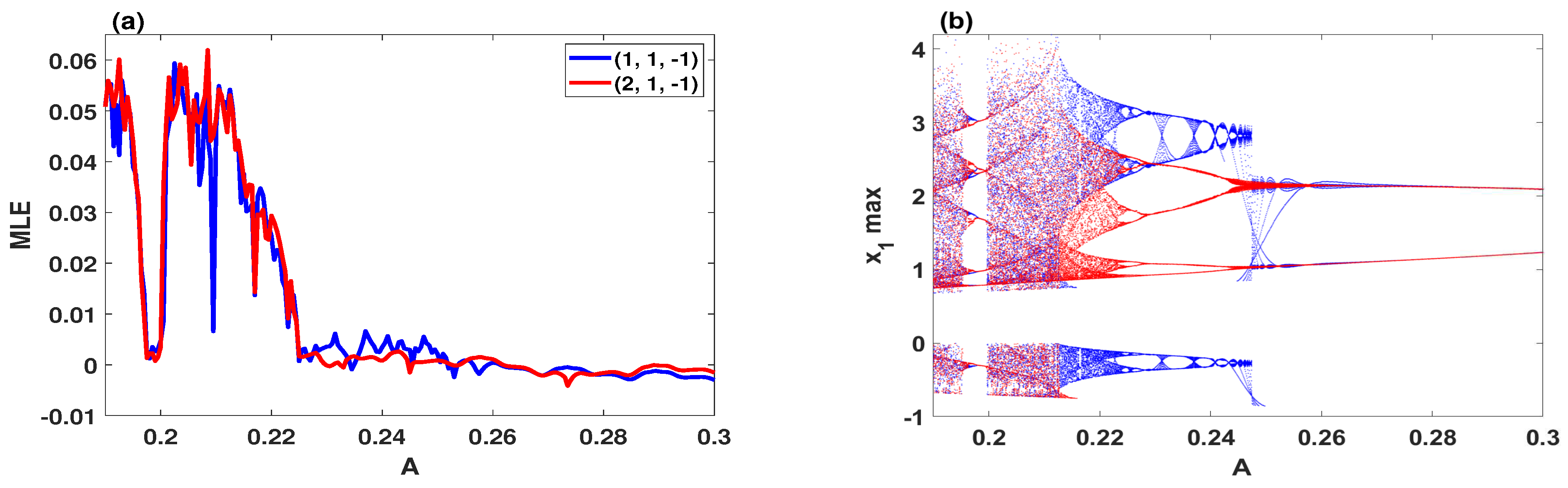
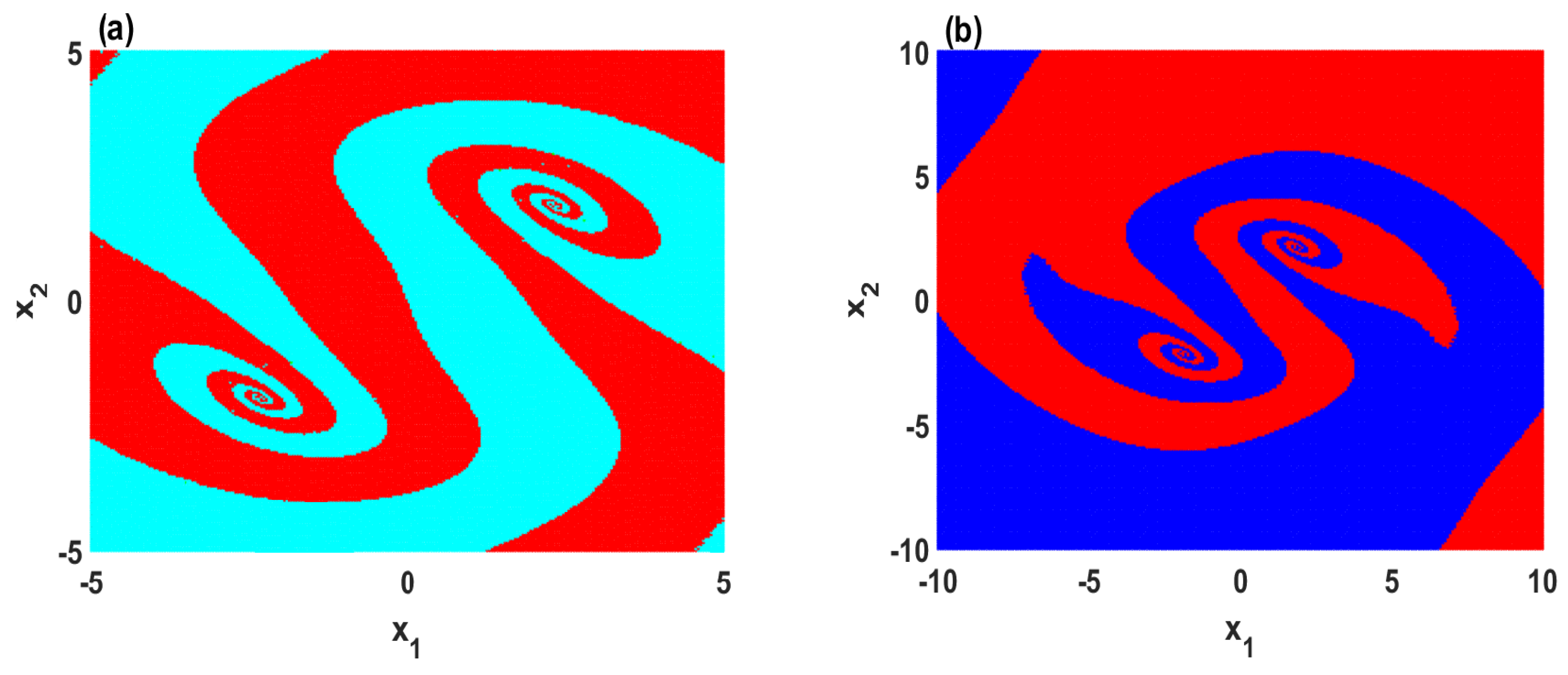
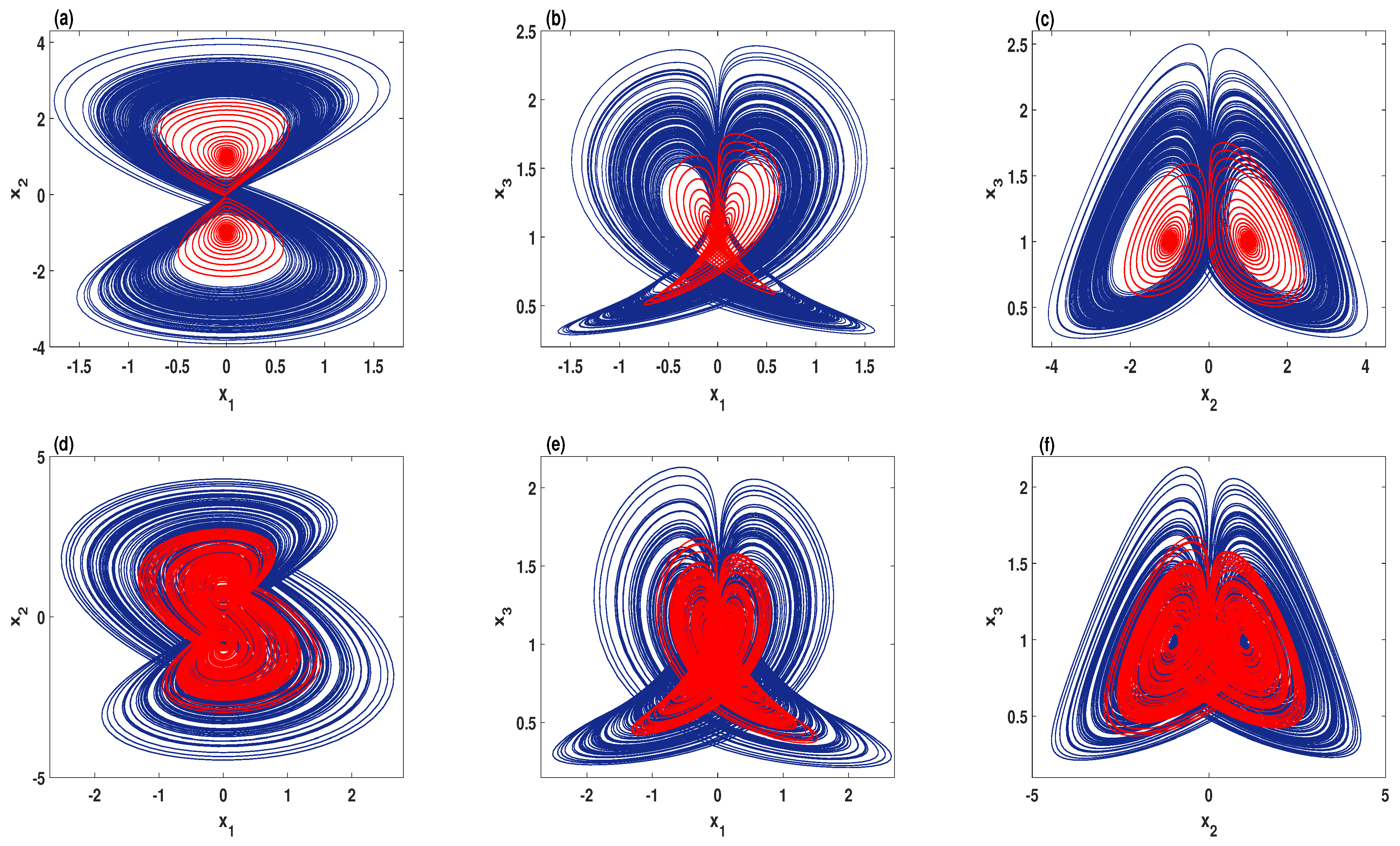
3.1. The Coexistence of a Symmetric Pair of Attractors
3.2. The Coexistence of Many Symmetric Quasi-Periodic Attractors
4. Sample Entropy Algorithm
- Reconstruction: the time series can be reconstructed as followswhere m is embedding dimension, and is time delay.
- Counting the vector pairs: For a given tolerance parameter r, let be the number of vectors such thathere, is the distance between and , which is defined as
- Calculating : According to the obtained number of vector pairs, we can getthen calculate by
- Calculating SamEn: Repeating the above steps we can get , then SamEn is given by
5. Performance Evaluations
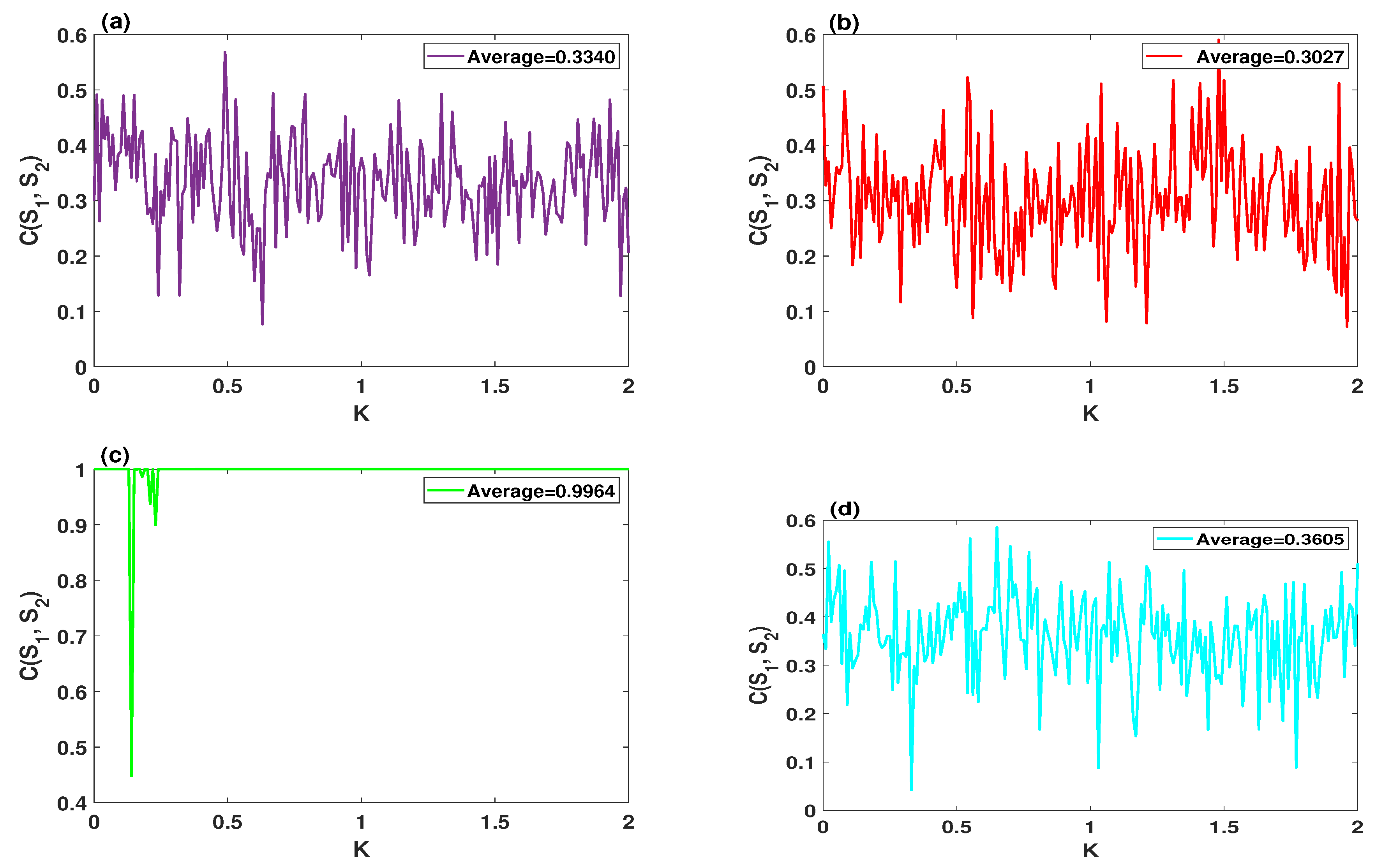
5.1. Cross-Correlation Coefficient
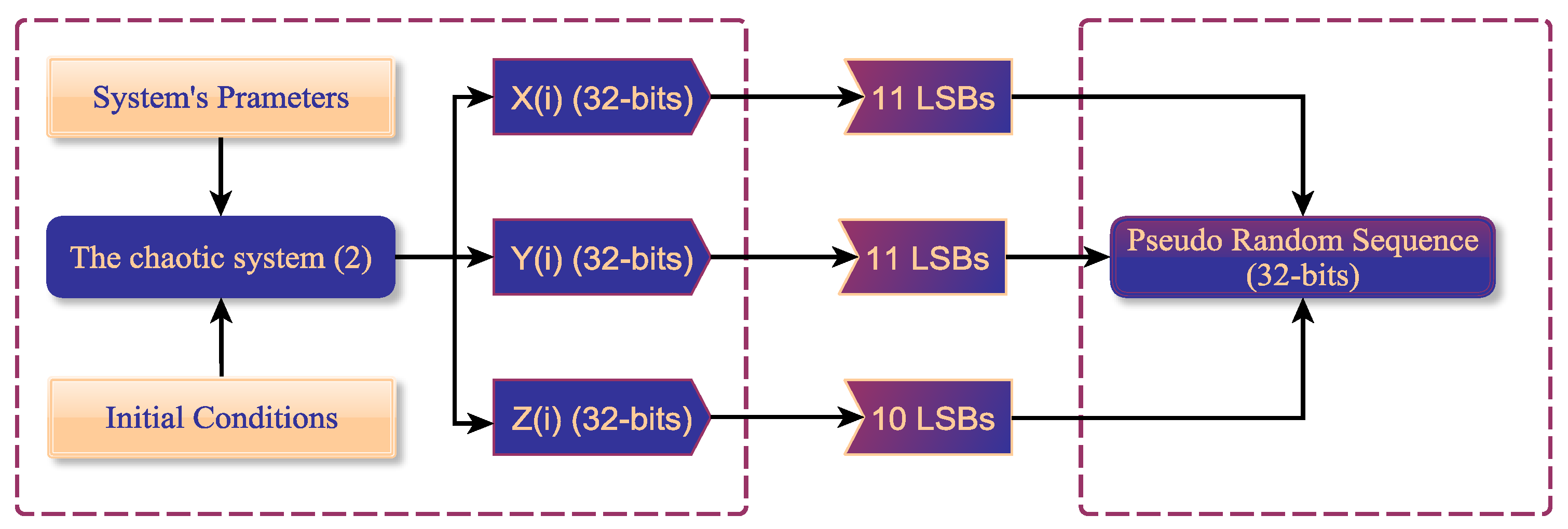
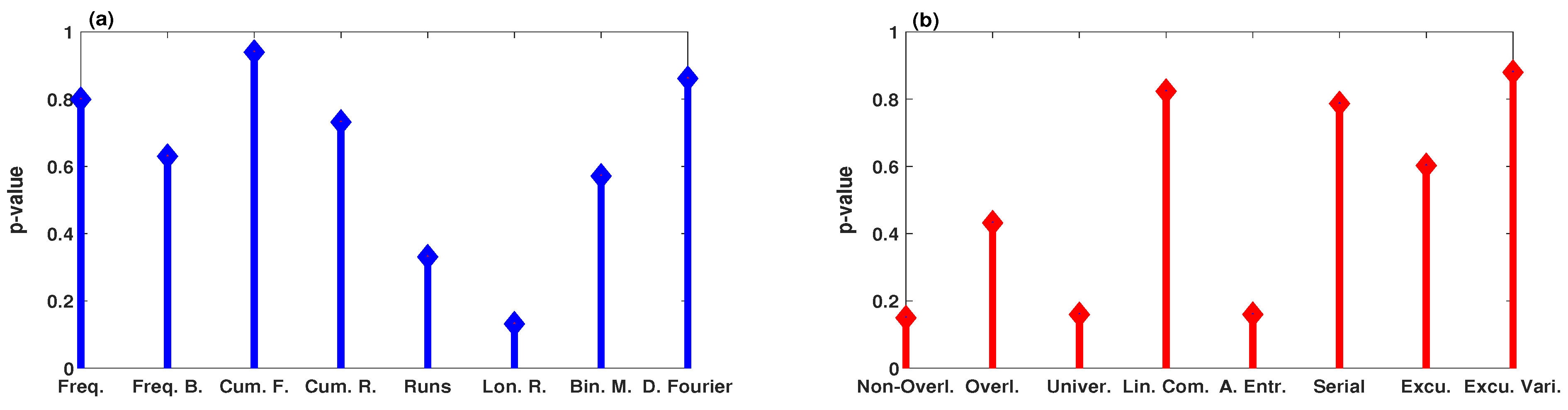
5.2. Chaos-Based Cryptographic Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, R.M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature 1976, 261, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilliers, P.; Spurrett, D. Complexity and post-modernism: Understanding complex systems. S. Afr. J. Philos. 1999, 18, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Said, M.R.M.; Banerjee, S. Enhancing the sensitivity of a chaos sensor for internet of things. Internet Things 2019, 7, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Al-Saidi, N.; Said, M.; Kilicman, A. A new hyperchaotic map and its application for image encryption. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Said, M.R.M.; Al-Saidi, N.M.; Kilicman, A. Dynamics and complexity of a new 4d chaotic laser system. Entropy 2019, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marszalek, W.; Podhaisky, H. 2D bifurcations and Newtonian properties of memristive Chua’s circuits. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2016, 113, 10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszalek, W.; Podhaisky, H.; Sadecki, J. Computing two-parameter bifurcation diagrams for oscillating circuits and systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115829–115835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, N.M.; Younus, D.; Natiq, H.; K Ariffin, M.R.; Asbullah, M.A.; Mahad, Z. A New Hyperchaotic Map for a Secure Communication Scheme with an Experimental Realization. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gao, S.; He, Z.; Zeng, X.; Jin, W.; Li, T. Identification of nonlinear dynamic system using a novel recurrent wavelet neural network based on the pipelined architecture. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 4171–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Palit, S.K.; Banerjee, S.; Ariffin, M.; Rondoni, L.; Bhattacharya, D. Can complexity decrease in congestive heart failure? Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2015, 439, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibb, B.C. Teetering towards chaos and complexity. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X. Endogenous cycles and chaos in a capitalist economy: A circuit of capital model. Metroeconomica 2015, 66, 123–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, H.-L.; Tian, B.; Xie, X.-Y.; Wu, X.-Y.; Wen, X.-Y. Solitonic and chaotic behaviors for the nonlinear dust-acoustic waves in a magnetized dusty plasma. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liao, X.; Zhang, G. Qualitative behaviors of the continuous-time chaotic dynamical systems describing the interaction of waves in plasma. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 88, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qi, G. Mechanical analysis and bound of plasma chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 108, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qi, G. Comparing mechanical analysis with generalized-competitive-mode analysis for the plasma chaotic system. Phys. Lett. A 2019, 383, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qi, G.; Hu, J.; Faradja, P. Finding method and analysis of hidden chaotic attractors for plasma chaotic system from physical and mechanistic perspectives. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 2020, 30, 2050072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; He, S.; Said, M.; Kilicman, A. Designing an m-dimensional nonlinear model for producing hyperchaos. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 114, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; Said, M.R.M. Cosine chaotification technique to enhance chaos and complexity of discrete systems. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 228, 85–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Said, M.; Ariffin, M.; He, S.; Rondoni, L.; Banerjee, S. Self-excited and hidden attractors in a novel chaotic system with complicated multistability. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudkowski, D.; Jafari, S.; Kapitaniak, T.; Kuznetsov, N.V.; Leonov, G.A.; Prasad, A. Hidden attractors in dynamical systems. Phys. Rep. 2016, 637, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Sprott, J. Simple chaotic flows with a line equilibrium. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2013, 57, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotthans, T.; Petrzela, J. New class of chaotic systems with circular equilibrium. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 81, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z. Dynamical behaviors of a chaotic system with no equilibria. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 376, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Moroz, I.; Wang, Z.; Sprott, J.C.; Kapitaniak, T. Dynamics at infinity, degenerate hopf and zero-hopf bifurcation for kingni-jafari system with hidden attractors. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2016, 2, 1650125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Feudel, U. Control of multistability. Phys. Rep. 2014, 540, 167–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Natiq, H.; Fataf, N.A.A.; Banerjee, S. Dynamics of a new hyperchaotic system and multistability. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, F.; Meucci, R.; Puccioni, G.; Tredicce, J. Experimental evidence of subharmonic bifurcations, multistability, and turbulence in a q-switched gas laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; Ariffin, M.; Said, M. Can hyperchaotic maps with high complexity produce multistability? Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2019, 29, 011103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, C.; Bao, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Generating multi-scroll Chua’s attractors via simplified piecewise-linear Chua’s diode. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 4767–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Sun, M.; Bao, H.; Hu, Y.; Bao, B. Flux–Charge Analysis of Two-Memristor-Based Chua’s Circuit: Dimensionality Decreasing Model for Detecting Extreme Multistability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, K.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Coexisting Infinite Orbits in an Area-Preserving Lozi Map. Entropy 2020, 22, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leutcho, G.D.; Jafari, S.; Hamarash, I.I.; Kengne, J.; Njitacke, Z.T.; Hussain, I. A new megastable nonlinear oscillator with infinite attractors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 134, 109703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedűs, F.; Krähling, P.; Aron, M.; Lauterborn, W.; Mettin, R.; Parlitz, U. Feedforward attractor targeting for non-linear oscillators using a dual-frequency driving technique. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2020, 30, 073123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedűs, F.; Krähling, P.; Lauterborn, W.; Mettin, R.; Parlitz, U. High-performance GPU computations in nonlinear dynamics: An efficient tool for new discoveries. Meccanica 2020, 55, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Kuntsevich, B.F. Control of multistability in a directly modulated diode laser. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2002, 38, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, D.; Dumbrajs, O.; Igochine, V.; Lackner, K.; Meyer-Spasche, R.; Zohm, H.; Team, A.U. A low-dimensional model system for quasi-periodic plasma perturbations. Phys. Plasmas 2011, 18, 062307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Tech. Rep. SP 800-22; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2001.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natiq, H.; Kamel Ariffin, M.R.; Asbullah, M.A.; Mahad, Z.; Najah, M. Enhancing Chaos Complexity of a Plasma Model through Power Input with Desirable Random Features. Entropy 2021, 23, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010048
Natiq H, Kamel Ariffin MR, Asbullah MA, Mahad Z, Najah M. Enhancing Chaos Complexity of a Plasma Model through Power Input with Desirable Random Features. Entropy. 2021; 23(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatiq, Hayder, Muhammad Rezal Kamel Ariffin, Muhammad Asyraf Asbullah, Zahari Mahad, and Mohammed Najah. 2021. "Enhancing Chaos Complexity of a Plasma Model through Power Input with Desirable Random Features" Entropy 23, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010048
APA StyleNatiq, H., Kamel Ariffin, M. R., Asbullah, M. A., Mahad, Z., & Najah, M. (2021). Enhancing Chaos Complexity of a Plasma Model through Power Input with Desirable Random Features. Entropy, 23(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010048





