Soft Interference Cancellation for Random Coding in Massive Gaussian Multiple-Access †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Improve the theoretical bounds in [8].
- (2)
- Propose coding and decoding schemes with polynomial complexity that closely approach the performances promised by these bounds.
- (3)
- Investigate in which way these results for static channels carry over to fading channels.
- (A)
- (B)
- Treating residual interference as independent additive white Gaussian noise.
- (C)
- Recent calculations of the exact ensemble-averaged block-error probability of independent identically distributed (iid) Gaussian random codes in [11].
- (D)
- Orthogonal constellations as efficient block codes with low rate.
- (E)
- Finding the fixed-point of the iterations by tracking the evolution of the multiuser efficiency of all devices as pioneered in [12].
- (F)
2. System Model
3. Large-System Analysis
3.1. Asymptotic Block Error Probability
- an orthonormal transformation such that , denoting the codeword of the codebook of the device of interest, is a positive multiple of the unit vector, for all .
- the removal of all coordinates with indices greater than .
3.2. Evolution of Residual Interference
3.3. Improving Convergence
4. The Near-Far Gain
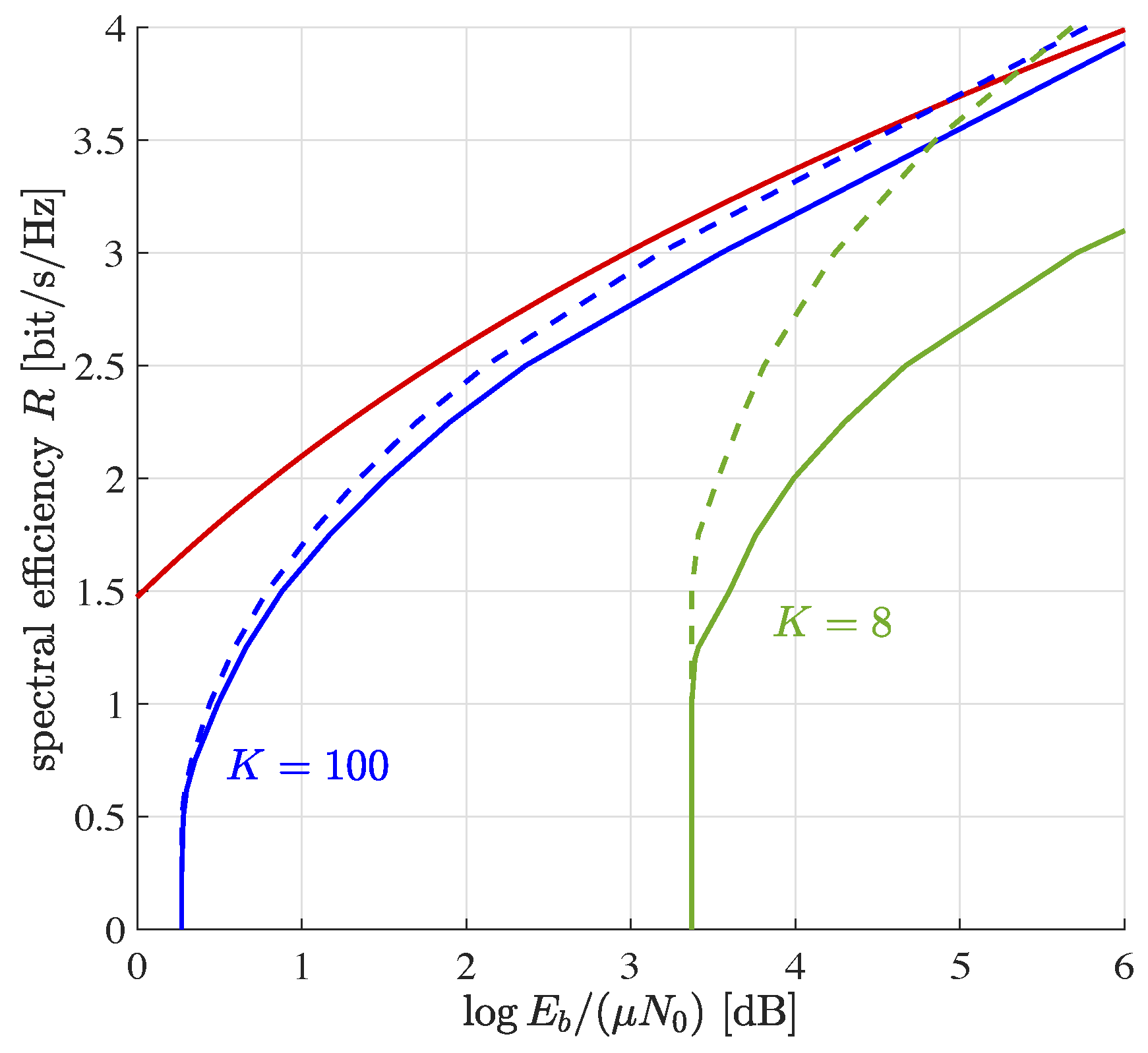
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Equal Path Loss for All Devices
5.1.1. Equal Power Regime
5.1.2. Distributed Power Regime
5.1.3. Finite Number of Devices
5.1.4. Minimum Signal-to-Noise Ratio
5.2. Discretized Path Loss Model
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Unconditional Block Error Probability
Appendix B. Limit of the Generalized Marcum Q-Function
References
- Chen, X.; Chen, T.Y.; Guo, D. Capacity of Gaussian Many-Access Channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 3516–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyanskiy, Y. A perspective on massive random-access. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Aachen, Germany, 25–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Caire, G.; Müller, R.R. The Optimal Received Power Distribution for IC-based Iterative Multiuser Joint Decoders. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Allerton Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing, Monticello, IL, USA, 3–5 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Caire, G.; Müller, R.R.; Tanaka, T. Iterative Multiuser Joint Decoding: Optimal Power Allocation and Low-Complexity Implementation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2004, 50, 1950–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Barron, A.R. Least Squares Superposition Codes of Moderate Dictionary Size Are Reliable at Rates up to Capacity. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2012, 58, 2541–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, C.; Greig, A.; Venkataramanan, R. Capacity-Achieving Sparse Superposition Codes via Approximate Message Passing Decoding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 1476–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, J.; Krzakala, F. Approximate Message-Passing Decoder and Capacity Achieving Sparse Superposition Codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 4894–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadik, I.; Polyanskiy, Y.; Thrampoulidis, C. Improved bounds on Gaussian MAC and sparse regression via Gaussian inequalities. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Paris, France, 7–12 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, L.B.; Poor, H.V. Soft-Decision Interference Cancellation for AWGN Multi-User Channels. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Cambridge, MA, USA, 27 June–1 July 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Poor, H.V. Iterative (Turbo) Soft Interference Cancellation and Decoding for Coded CDMA. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1999, 47, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R. On Approximation, Bounding & Exact Calculation of Block Error Probability for Random Code Ensembles. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021. early access. [Google Scholar]
- Boutros, J.; Caire, G. Iterative Multiuser Joint Decoding: Unified Framework and Asymptotic Analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2002, 48, 1772–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdú, S. Multiuser Detection; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, A.V.; Taber, J.E. Error Rates in Coherent Communication Systems. IRE Trans. Commun. Syst. 1962, 10, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J.G. Digital Communications, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T. The asymptotic distribution of the largest entries of sample correlation matrices. Ann. Appl. Probab. 2004, 14, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, T.; Urbanke, R. Modern Coding Theory; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Opper, M.; Winther, O. Expectation Consistent Approximate Inference. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 2177–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L.; Maleki, A.; Montanari, A. Message Passing Algorithms for Compressed Sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18914–18919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ping, L. Orthogonal AMP. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2020–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangan, S.; Schniter, P.; Fletcher, A.K. Vector Approximate Message Passing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2019, 65, 6664–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K. Convolutional Approximate Massage-Passing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimori, H. Statistical Physics of Spin Glasses and Information Processing; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, D.J. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Caire, G.; Müller, R.R.; Knopp, R. Hard Fairness versus Proportional Fairness in Wireless Communications: The Single Cell Case. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 1366–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.R. Power and Bandwidth Efficiency of Multiuser Systems with Random Spreading; Shaker-Verlag: Aachen, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, D.N.; Hanly, S.V. Multi-access Fading Channels: Part I: Polymatroid Structure, Optimal Resource Allocation and Throughput Capacities. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1998, 44, 2796–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.R.; Caire, G.; Knopp, R. Multiuser Diversity in Delay-Limited Cellular Wideband Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Rotorua, New Zealand, 28 August–2 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Lei, X.; Karagiannidis, G.K.; Schober, R.; Yuan, J.; Bhargava, V.K. A Survey on Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access for 5G Networks: Research Challenges and Future Trends. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2181–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkarimi, M.; Müller, R.R. Machine Type Communications Close to Channel Capacity by AMP. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Melbourne, Australia, 12–20 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, K.; Rush, C.; Venkataramanan, R. Near-Optimal Coding for Massive Multiple Access. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04730v1. [Google Scholar]
- Polyanskiy, Y.; Poor, H.V.; Verdú, S. Minimum Energy to Send k Bits With and Without Feedback. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 4880–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 100% | average | |||
| 3.82 dB | 3.82 dB | |||
| 81.6% | 18.4% | average | ||
| 3.76 dB | 6.53 dB | 4.42 dB | ||
| 69.0% | 31.0% | average | ||
| 3.67 dB | 7.56 dB | 5.28 dB | ||
| 63.3% | 36.7% | average | ||
| 3.64 dB | 8.38 dB | 6.01 dB | ||
| 58.4% | 41.6% | average | ||
| 3.60 dB | 9.10 dB | 6.73 dB | ||
| 50.9% | 23.1% | 26.0% | average | |
| 3.53 dB | 8.15 dB | 10.9 dB | 7.68 dB |
| 100% | average | ||||||
| 0.30 dB | 0.30 dB | ||||||
| 68.3% | 31.7% | average | |||||
| 0.23 dB | 1.73 dB | 0.76 dB | |||||
| 52.8% | 22.3% | 24.9% | average | ||||
| 0.19 dB | 1.86 dB | 2.81 dB | 1.36 dB | ||||
| 41.7% | 23.3% | 10.6% | 24.2% | average | |||
| 0.13 dB | 1.93 dB | 2.87 dB | 3.92 dB | 2.04 dB | |||
| 34.5% | 22.0% | 3.16% | 7.61% | 11.3% | 21.4% | average | |
| 0.10 dB | 1.96 dB | 3.24 dB | 3.36 dB | 3.74 dB | 5.11 dB | 2.76 dB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, R.R. Soft Interference Cancellation for Random Coding in Massive Gaussian Multiple-Access. Entropy 2021, 23, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23050539
Müller RR. Soft Interference Cancellation for Random Coding in Massive Gaussian Multiple-Access. Entropy. 2021; 23(5):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23050539
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Ralf R. 2021. "Soft Interference Cancellation for Random Coding in Massive Gaussian Multiple-Access" Entropy 23, no. 5: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23050539
APA StyleMüller, R. R. (2021). Soft Interference Cancellation for Random Coding in Massive Gaussian Multiple-Access. Entropy, 23(5), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23050539






