Role of Time Scales in the Coupled Epidemic-Opinion Dynamics on Multiplex Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
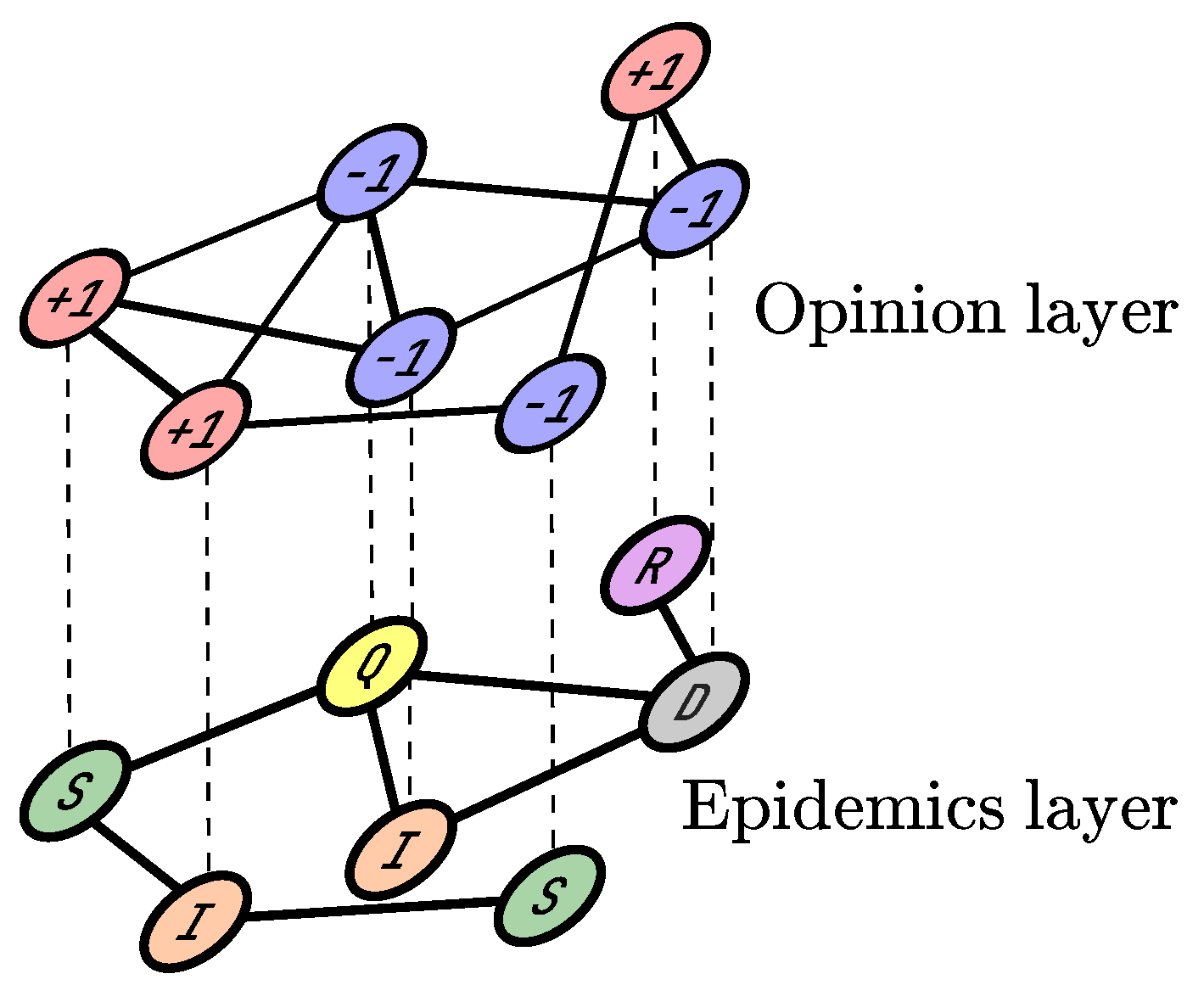
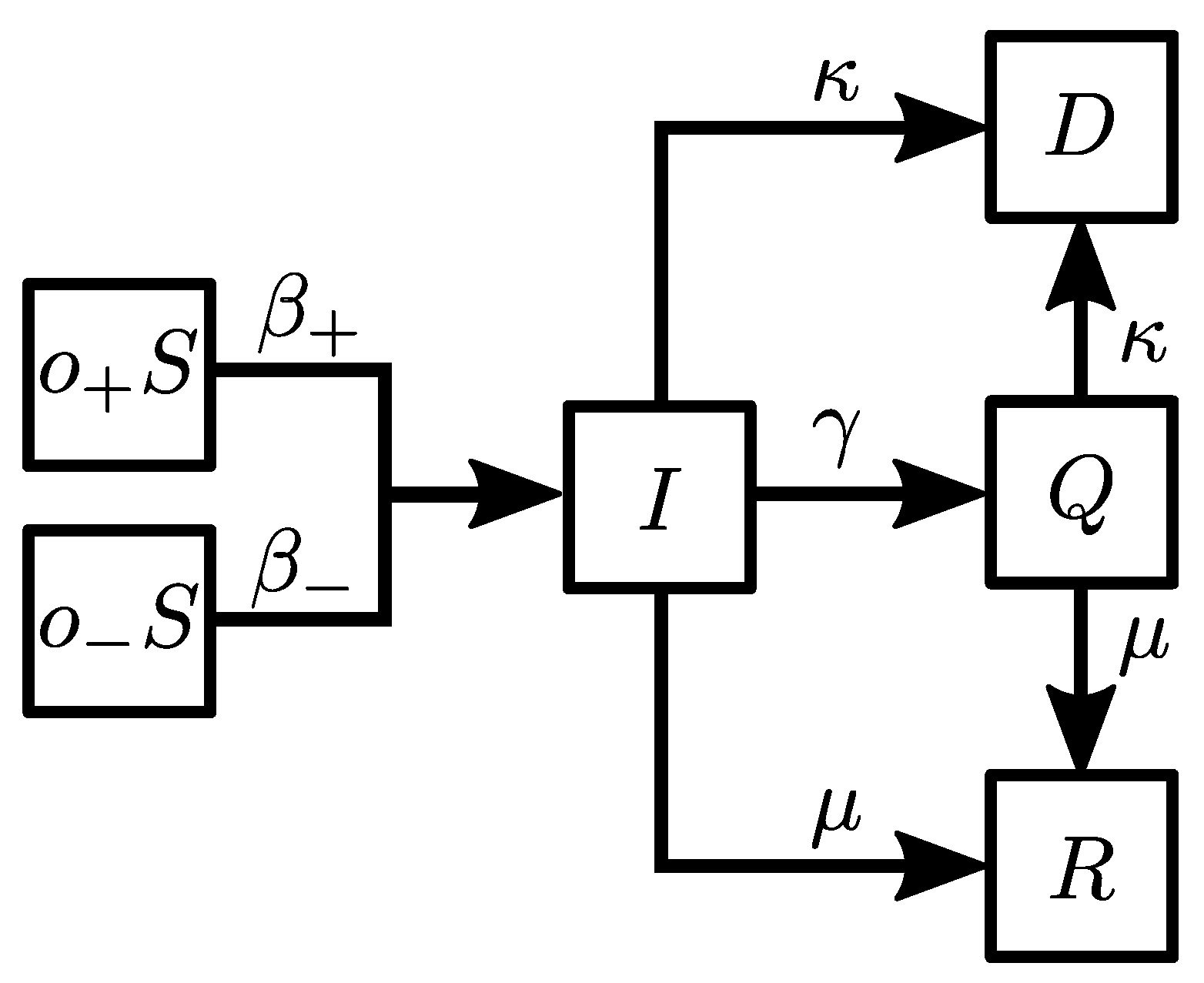
2. Materials and Methods
- (i)
- : a susceptible agent becomes infected with the probability .
- (ii)
- : an infected agent goes into quarantine with the probability .
- (iii)
- : an infected agent recovers with the probability .
- (iv)
- : an infected agent dies with the probability .
- (v)
- : an agent in quarantine recovers with the probability .
- (vi)
- : an agent in quarantine dies with the probability .
3. Results
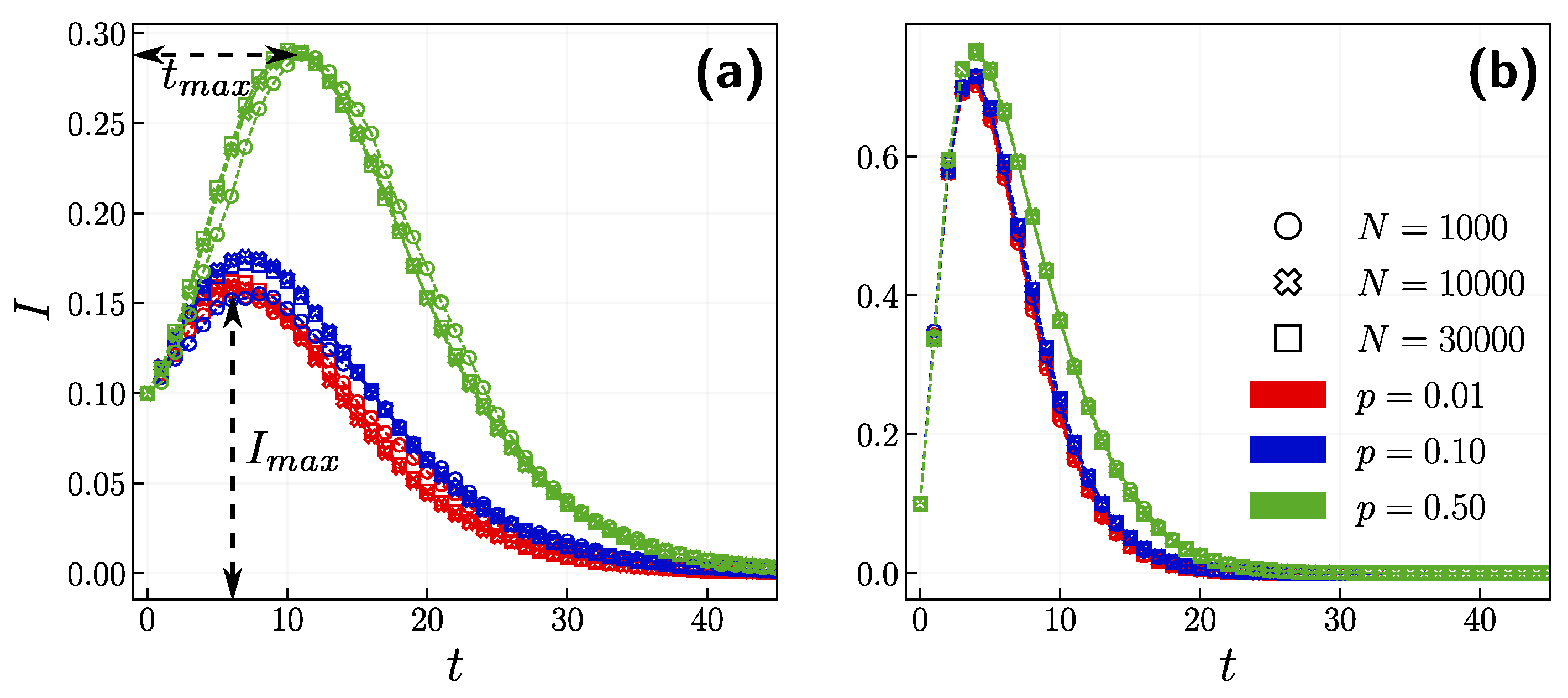
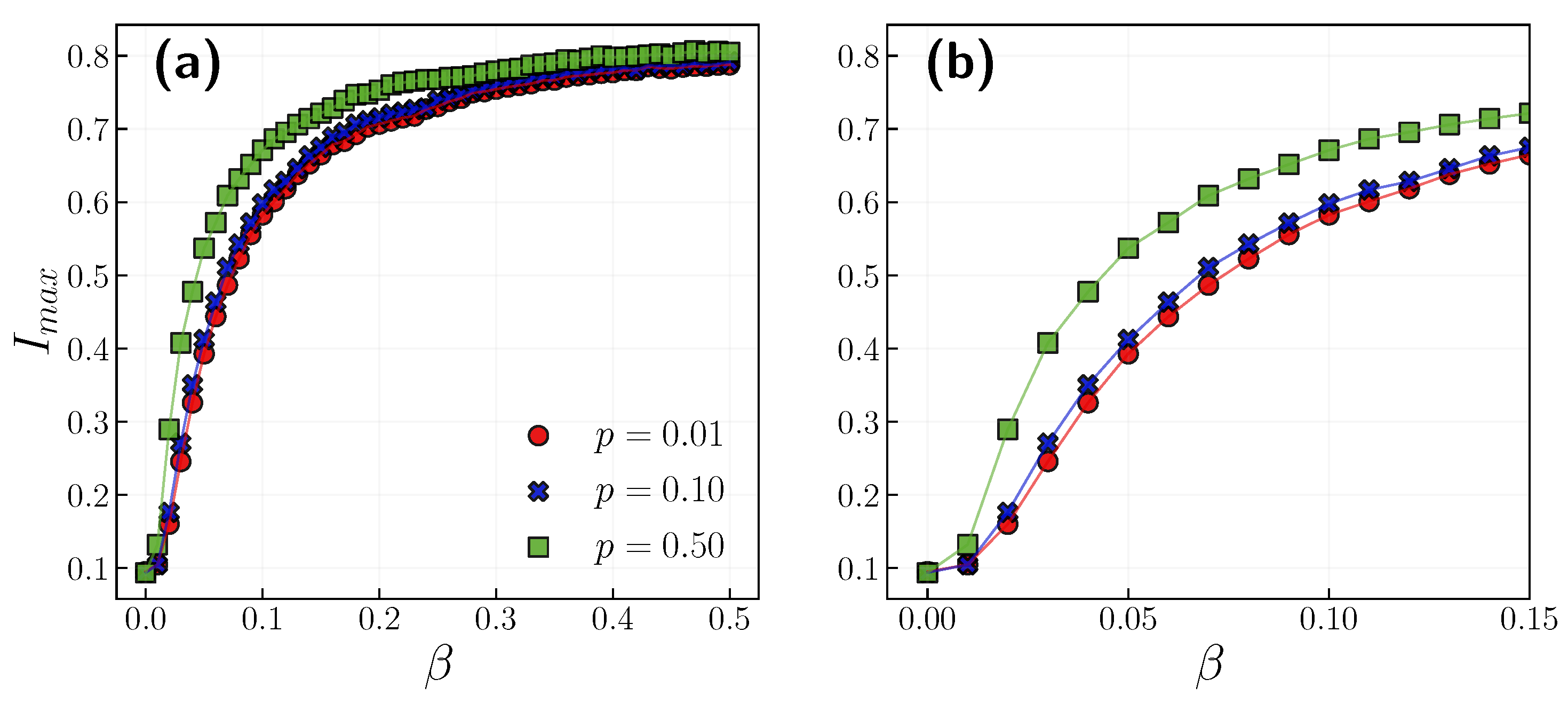
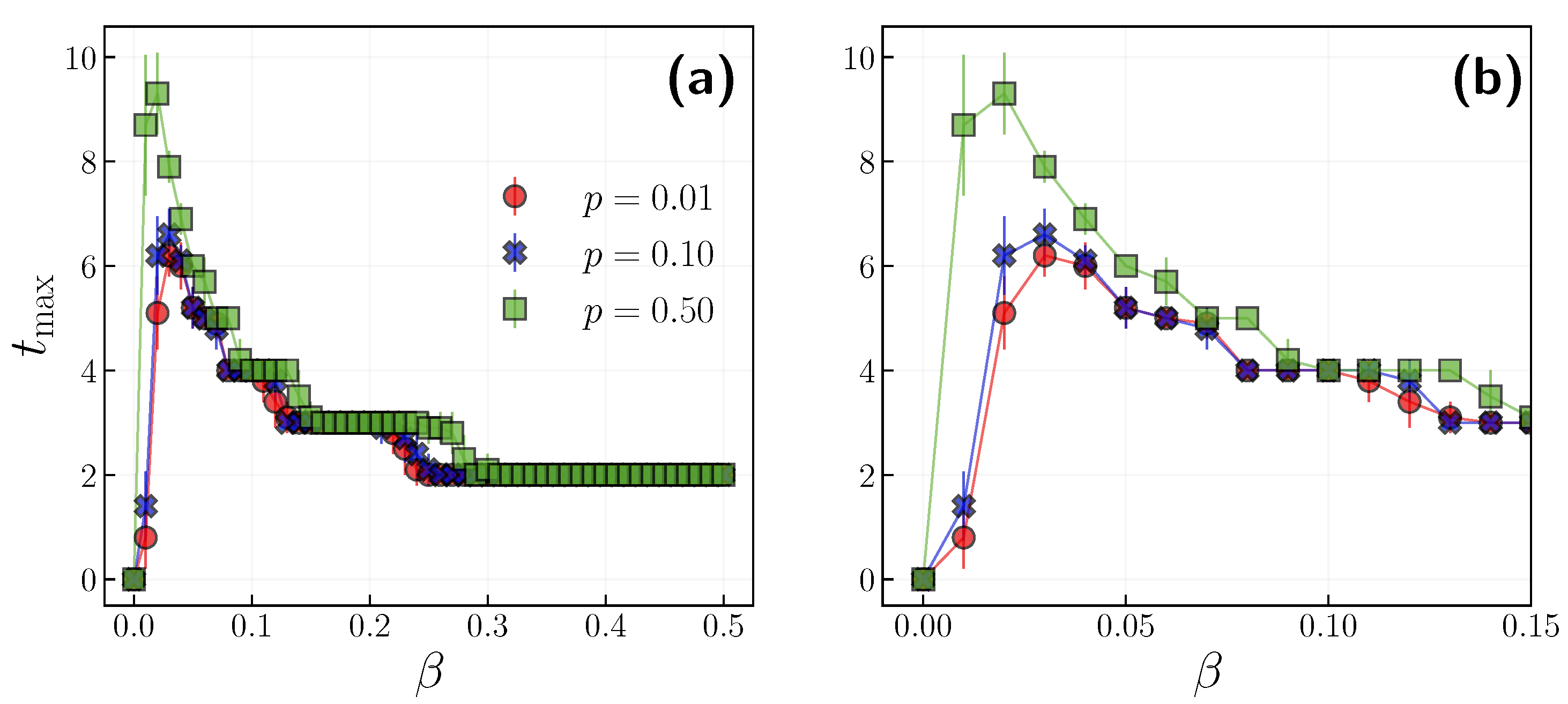
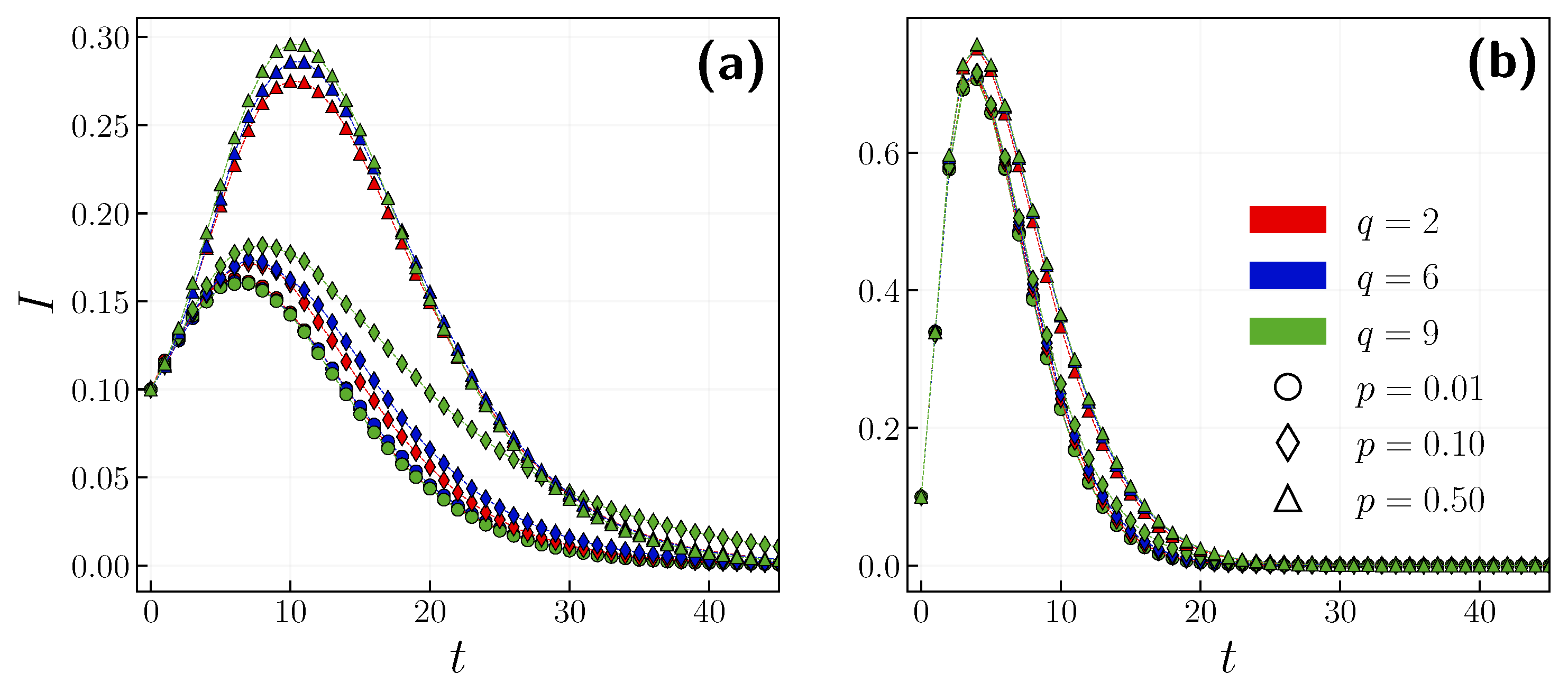
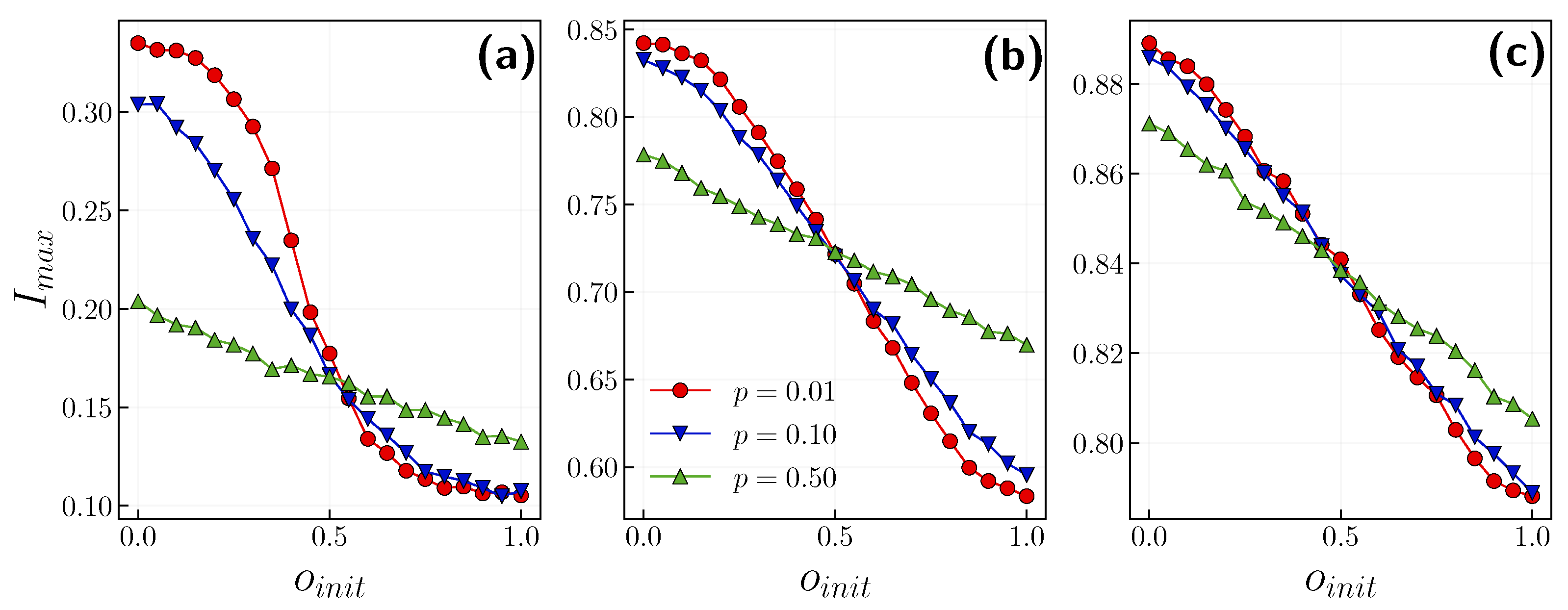
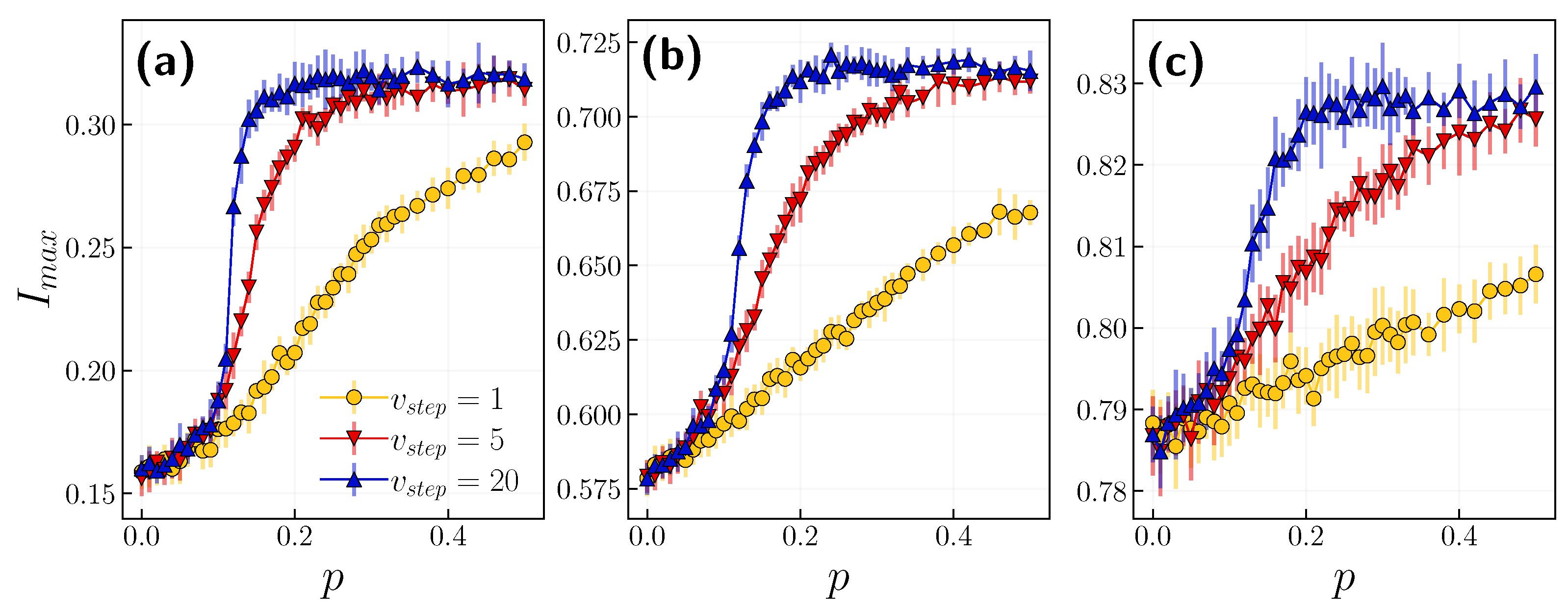
3.1. Role of the Opinion Layer
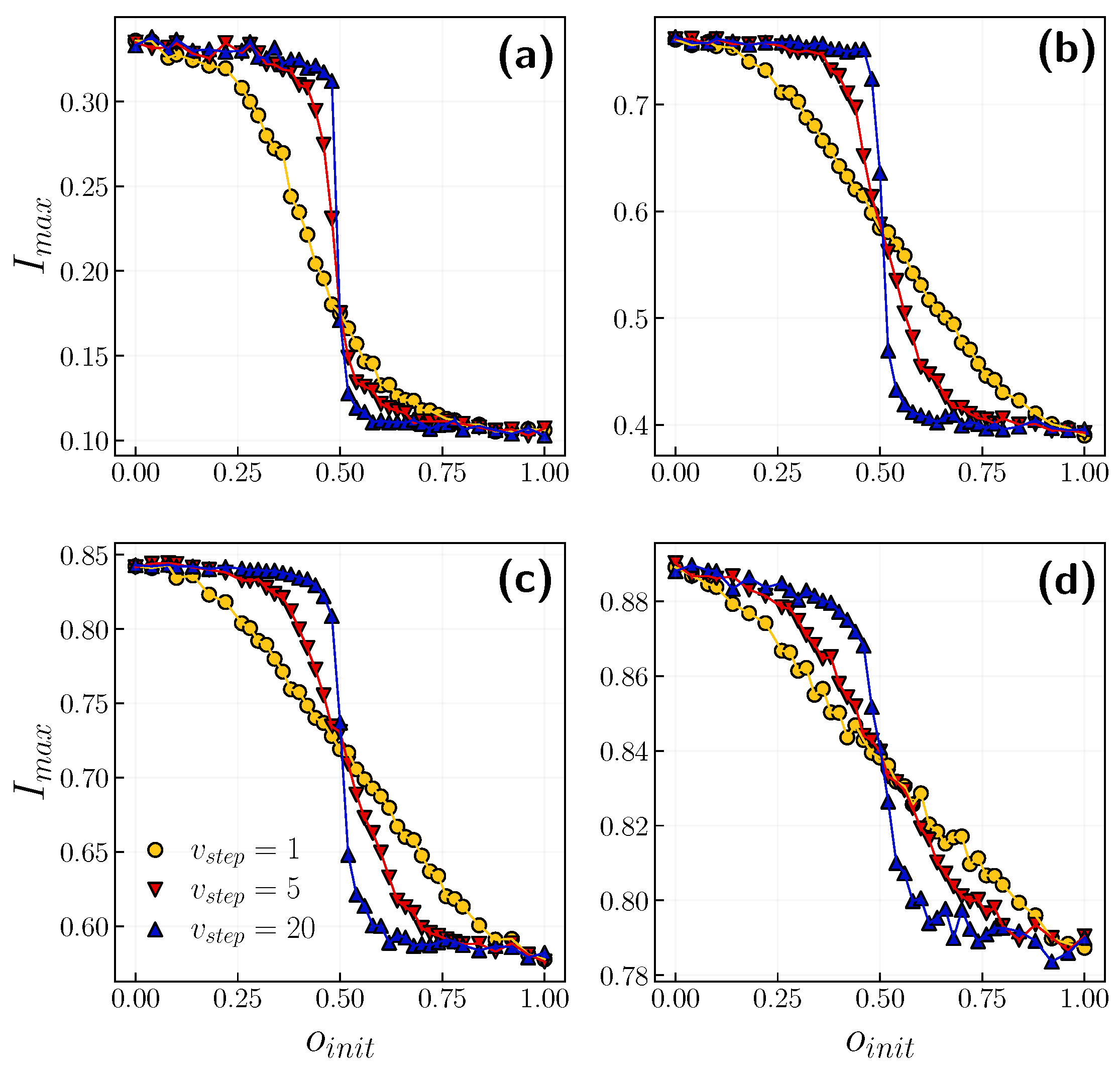
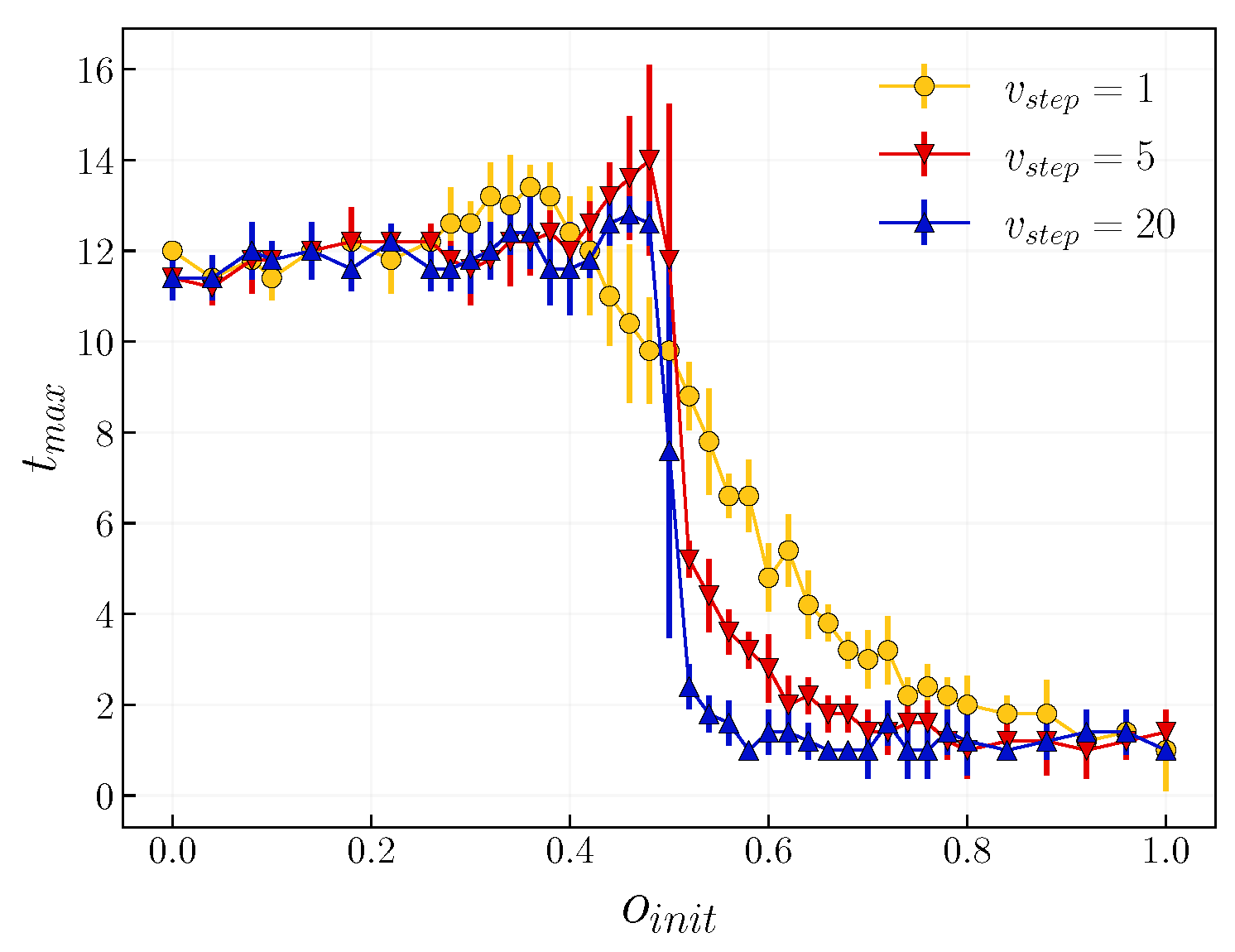
3.2. Role of Time Scales
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Glasser, J.W.; Hill, A.N. On the benefits of flattening the curve: A perspective. Math. Biosci. 2020, 326, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Castellano, C.; Van Mieghem, P.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic spreading in scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowski, A.; Kosiński, R. Epidemic spreading in a hierarchical social network. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 031908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, B. Epidemic spreading in community networks. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2005, 72, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguná, M.; Pastor-Satorras, R. Epidemic spreading in correlated complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 047104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, Z.K. Epidemic spreading on weighted complex networks. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kivelä, M.; Arenas, A.; Barthelemy, M.; Gleeson, J.P.; Moreno, Y.; Porter, M.A. Multilayer networks. J. Complex Netw. 2014, 2, 203–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mucha, P.J.; Richardson, T.; Macon, K.; Porter, M.A.; Onnela, J.P. Community structure in time-dependent, multiscale, and multiplex networks. Science 2010, 328, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szell, M.; Lambiotte, R.; Thurner, S. Multirelational organization of large-scale social networks in an online world. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13636–13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurant, M.; Thiran, P. Layered complex networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 138701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granell, C.; Gómez, S.; Arenas, A. Dynamical interplay between awareness and epidemic spreading in multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 128701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Petkova, E.; Shaman, J. The 1918 influenza pandemic in N ew Y ork C ity: Age-specific timing, mortality, and transmission dynamics. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advice for the Public. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Rewar, S.; Mirdha, D.; Rewar, P. Treatment and prevention of pandemic H1N1 influenza. Ann. Glob. Health 2015, 81, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevention and Vaccine | Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease) | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/prevention/index.html (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Howard, J.; Huang, A.; Li, Z.; Tufekci, Z.; Zdimal, V.; van der Westhuizen, H.M.; von Delft, A.; Price, A.; Fridman, L.; Tang, L.H.; et al. An evidence review of face masks against COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2014564118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advice on the Use of Masks in the Community, during Home Care and in Healthcare Settings in the Context of the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Outbreak. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/advice-on-the-use-of-masks-in-the-community-during-home-care-and-in-healthcare-settings-in-the-context-of-the-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov)-outbreak (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Mallinas, S.R.; Maner, J.K.; Plant, E.A. What factors underlie attitudes regarding protective mask use during the COVID-19 pandemic? Personal. Individ. Differ. 2021, 181, 111038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Erickson, W.W.; Jing-Schmidt, Z. # MaskOn!# MaskOff! Digital polarization of mask-wearing in the United States during COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250817. [Google Scholar]
- Guillon, M.; Kergall, P. Attitudes and opinions on quarantine and support for a contact-tracing application in France during the COVID-19 outbreak. Public Health 2020, 188, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradoń, K.T.; Hołyst, J.A.; Moy, W.R.; Sienkiewicz, J.; Suchecki, K. Countering misinformation: A multidisciplinary approach. Big Data Soc. 2021, 8, 205395172110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.; Quattrociocchi, W.; Galeazzi, A.; Valensise, C.M.; Brugnoli, E.; Schmidt, A.L.; Zola, P.; Zollo, F.; Scala, A. The COVID-19 social media infodemic. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, C.; Muñoz, M.A.; Pastor-Satorras, R. Nonlinear q-voter model. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 041129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clifford, P.; Sudbury, A. A model for spatial conflict. Biometrika 1973, 60, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznajd-Weron, K.; Sznajd, J. Opinion evolution in closed community. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2000, 11, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyczka, P.; Sznajd-Weron, K.; Cisło, J. Phase transitions in the q-voter model with two types of stochastic driving. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 011105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jędrzejewski, A. Pair approximation for the q-voter model with independence on complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 012307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przybyła, P.; Sznajd-Weron, K.; Weron, R. Diffusion of innovation within an agent-based model: Spinsons, independence and advertising. Adv. Complex Syst. 2014, 17, 1450004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriasz, R.; Krueger, T.; Marcjasz, G.; Sznajd-Weron, K. The hunt opinion model—An agent based approach to recurring fashion cycles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiel, A.; Sznajd-Weron, K. Phase transitions in the q-voter model with noise on a duplex clique. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 052812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chmiel, A.; Sienkiewicz, J.; Fronczak, A.; Fronczak, P. A veritable zoology of successive phase transitions in the asymmetric q-voter model on multiplex networks. Entropy 2020, 22, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Rojas, F.; Vazquez, F. Interacting opinion and disease dynamics in multiplex networks: Discontinuous phase transition and nonmonotonic consensus times. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 052315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amato, R.; Kouvaris, N.E.; San Miguel, M.; Díaz-Guilera, A. Opinion competition dynamics on multiplex networks. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 123019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, S.; Diaz-Guilera, A.; Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Perez-Vicente, C.J.; Moreno, Y.; Arenas, A. Diffusion dynamics on multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 028701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Gardenes, J.; Reinares, I.; Arenas, A.; Floría, L.M. Evolution of cooperation in multiplex networks. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ventura, P.C.; Moreno, Y.; Rodrigues, F.A. Role of time scale in the spreading of asymmetrically interacting diseases. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 013146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.C.V.; Velásquez-Rojas, F.; Connaughton, C.; Vazquez, F.; Moreno, Y.; Rodrigues, F.A. Epidemic spreading with awareness and different timescales in multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 032313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jȩdrzejewski, A.; Sznajd-Weron, K.; Szwabiński, J. Mapping the q-voter model: From a single chain to complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 446, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramiuk, A.; Pawłowski, J.; Sznajd-Weron, K. Is independence necessary for a discontinuous phase transition within the q-voter model? Entropy 2019, 21, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mobilia, M. Does a single zealot affect an infinite group of voters? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 028701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sznajd-Weron, K.; Tabiszewski, M.; Timpanaro, A.M. Phase transition in the Sznajd model with independence. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2011, 96, 48002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Thieme, H.R. Recurrent outbreaks of childhood diseases revisited: The impact of isolation. Math. Biosci. 1995, 128, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hethcote, H.; Zhien, M.; Shengbing, L. Effects of quarantine in six endemic models for infectious diseases. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, R.; Cats, O.; Sienkiewicz, J. Modelling virus spreading in ride-pooling networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Situation Updates. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/situation-updates (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Holme, P.; Kim, B.J. Growing scale-free networks with tunable clustering. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 026107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granell, C.; Gómez, S.; Arenas, A. Competing spreading processes on multiplex networks: Awareness and epidemics. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 012808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chinazzi, M.; Davis, J.T.; Ajelli, M.; Gioannini, C.; Litvinova, M.; Merler, S.; Piontti, A.P.Y.; Mu, K.; Rossi, L.; Sun, K.; et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science 2020, 368, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N | 10,000 | number of nodes |
| m | 10 | number of links generated by newly added node in network construction |
| Nm | number of additional links in opinion layer | |
| p | 0.01 | probability of an agent to act independently in opinion layer |
| q | 6 | size of q-lobby in opinion layer |
| 1.0 | initial fraction of agents with positive opinions | |
| initial fraction of infected agents | ||
| duration of infected state for agent i | ||
| infection probability | ||
| probability of an agent to enter the quarantine | ||
| probability of recovery | ||
| probability of death | ||
| 1 | number of opinion layer updates per one epidemic layer update |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankowski, R.; Chmiel, A. Role of Time Scales in the Coupled Epidemic-Opinion Dynamics on Multiplex Networks. Entropy 2022, 24, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010105
Jankowski R, Chmiel A. Role of Time Scales in the Coupled Epidemic-Opinion Dynamics on Multiplex Networks. Entropy. 2022; 24(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankowski, Robert, and Anna Chmiel. 2022. "Role of Time Scales in the Coupled Epidemic-Opinion Dynamics on Multiplex Networks" Entropy 24, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010105
APA StyleJankowski, R., & Chmiel, A. (2022). Role of Time Scales in the Coupled Epidemic-Opinion Dynamics on Multiplex Networks. Entropy, 24(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010105






