Infrared-Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Guidance and Visual Perception
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose SGVPGAN, an adversarial framework for IR-visible image fusion, which has a visible-like and target-highlighted appearance.
- We develop the ASG and AVP for global and local enhancement during the training phase.
- The proposed SGVPGAN achieves significant improvements in terms of both visual appearance and quantification results.
2. Related Work
2.1. Generative Adversarial Network
2.2. Semantic Segmentation
2.3. Deep-Learning-Based Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
3. Method
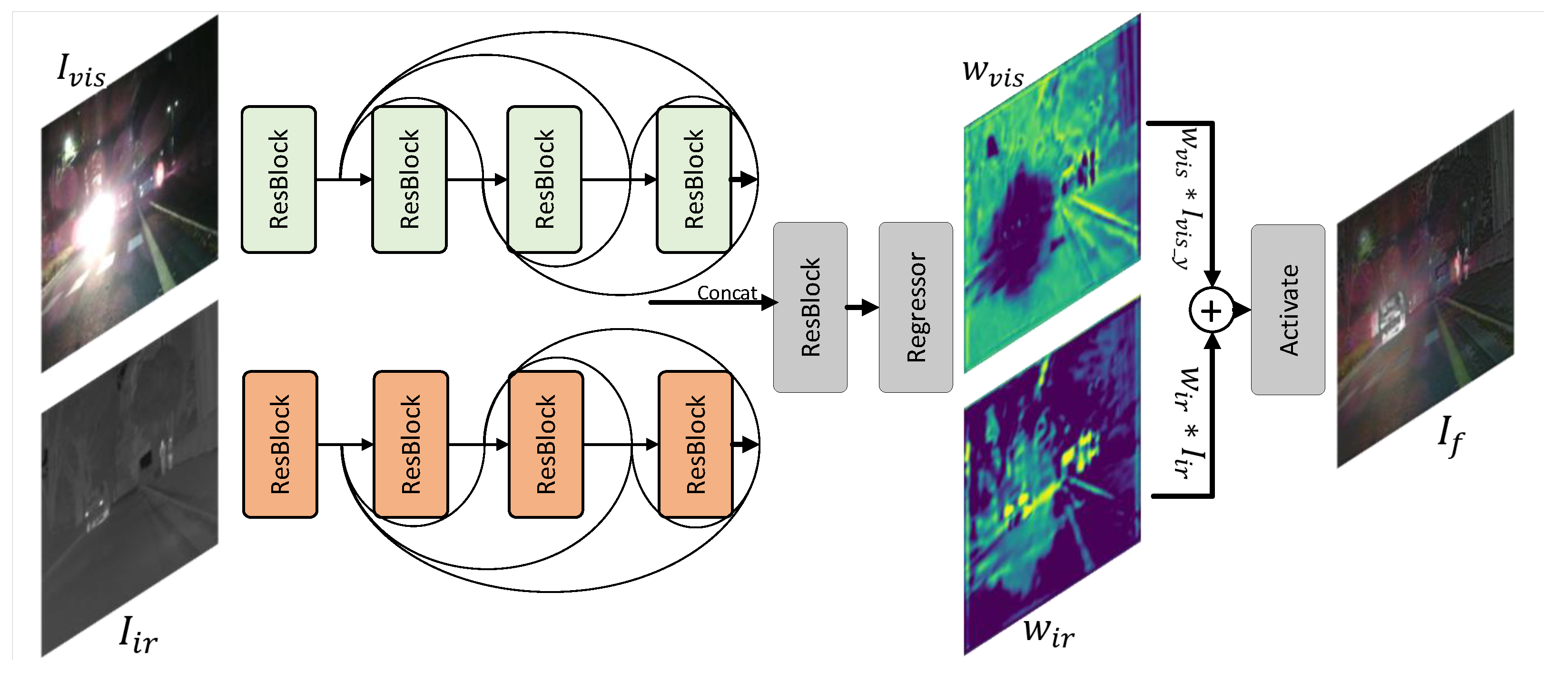
3.1. Overall Network Architecture
3.1.1. Generator Network Architecture
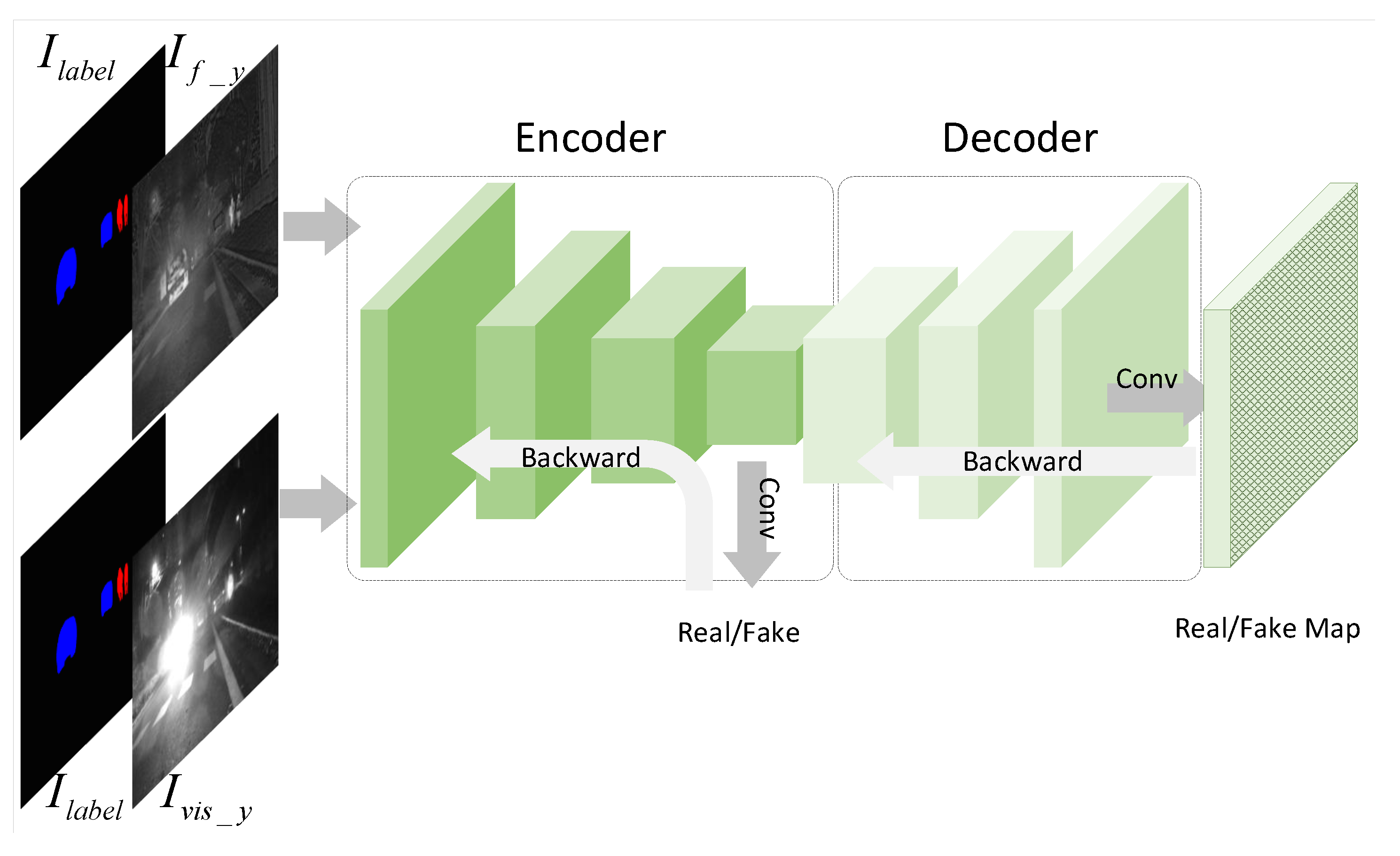
3.1.2. Perceptual Discriminator
3.1.3. Semantic Auxiliary Module
3.2. Loss Function
3.2.1. Visual Perceptual Loss
3.2.2. Semantic Guidance Loss
3.2.3. Generator Loss
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Training and Test Details
| Algorithm 1: Training SGVPGAN. |
 |
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.3.1. Objective Evaluation
4.3.2. Subjective Evaluation
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. U-Shaped Discriminator Experiment
4.4.2. Conditional Discriminator Experiment
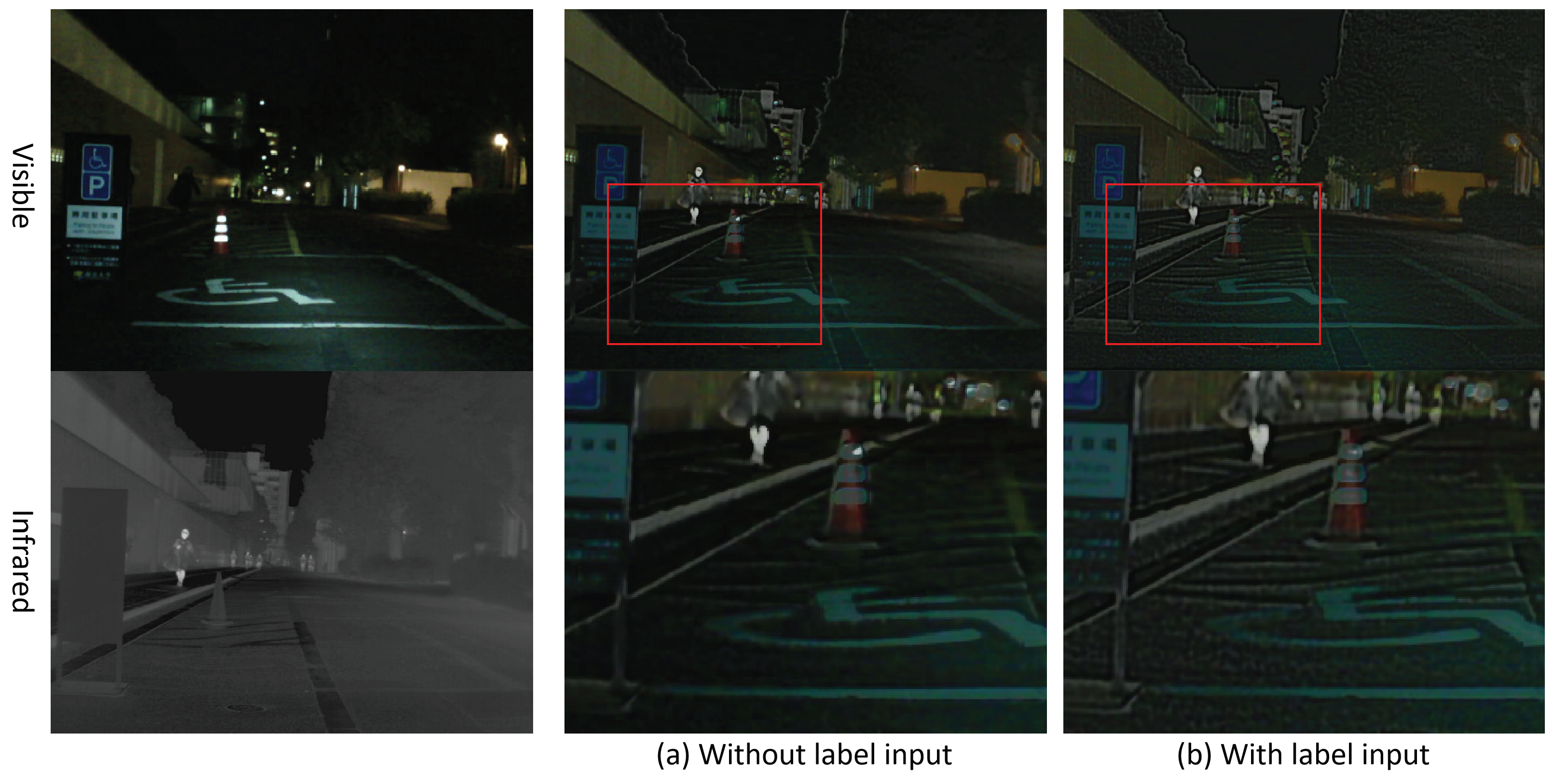
4.4.3. Semantic Auxiliary Module Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Blum, R.S.; Han, J.; Tao, D. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Xiao, G.; Liu, G. Multi-sensor image fusion based on fourth order partial differential equations. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via saliency analysis and local edge-preserving multi-scale decomposition. JOSA A 2017, 34, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. Infrared and visible image fusion using a deep learning framework. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 2705–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T. Image fusion based on generative adversarial network consistent with perception. Inf. Fusion 2021, 72, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, J.; Sun, Z.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Ye, J. A review on generative adversarial networks: Algorithms, theory, and applications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.06937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, A.; Donahue, J.; Simonyan, K. Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.11096. [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld, E.; Schiele, B.; Khoreva, A. A u-net based discriminator for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8207–8216. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Kim, S.; Culurciello, E. Enet: A deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02147. [Google Scholar]
- Romera, E.; Alvarez, J.M.; Bergasa, L.M.; Arroyo, R. Erfnet: Efficient residual factorized convnet for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 19, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Lou, X.; Bai, L.; Han, J. Residual pyramid learning for single-shot semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 2990–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiao, S.; Xie, C.; Shen, W.; Wang, B.; Yuille, A.L. Single-shot object detection with enriched semantics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5813–5821. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Shang, C.; Peng, T.; Shen, Q. Semantic-Aware Real-Time Correlation Tracking Framework for UAV Videos. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Ma, J.; Zhou, H. A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion based on semantic segmentation. Entropy 2021, 23, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ling, H. Semantic-supervised Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via a Dual-discriminator Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WU, W.; ZHANG, D.; HOU, J.; WANG, Y.; LU, T.; ZHOU, H. Semantic Guided Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2021, E104.A, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram Prabhakar, K.; Sai Srikar, V.; Venkatesh Babu, R. Deepfuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4714–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, J. DRF: Disentangled representation for visible and infrared image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5006713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via detail preserving adversarial learning. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A Unified Unsupervised Image Fusion Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. SwinFusion: Cross-domain Long-range Learning for General Image Fusion via Swin Transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ling, H. Unified gradient- and intensity-discriminator generative adversarial network for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2022, 88, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.; Moskewicz, M.; Karayev, S.; Girshick, R.; Darrell, T.; Keutzer, K. Densenet: Implementing efficient convnet descriptor pyramids. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.1869. [Google Scholar]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05957. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Xiao, G. VIFB: A visible and infrared image fusion benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Duanmu, Z.; Yeganeh, H.; Wang, Z. Multi-Exposure Image Fusion by Optimizing A Structural Similarity Index. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2018, 4, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Feng, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition. Opt. Commun. 2015, 341, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalingam, B.; Priya, R. Hybrid multimodality medical image fusion technique for feature enhancement in medical diagnosis. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2018, 2, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Eskicioglu, A.M.; Fisher, P.S. Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.W.; Van Aardt, J.A.; Ahmed, F.B. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, G.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zeng, K.; Wang, Z. Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3345–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and Karhunen-Loeve transform. IEEE Sensors J. 2015, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresoluti. Inf. Process. 2018, 16, 1850018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Dong, M. Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with Gaussian and bilateral filters. Inf. Fusion 2016, 30, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Xiao, G.; Zhao, J.; Dhuli, R.; Liu, G. Multi-scale guided image and video fusion: A fast and efficient approach. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 5576–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T.S. Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Zong, H. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| AG | EI | SF | EN | MI | MEF-SSIM | Inference Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADF | 0.166 | 1.77 | 2.58 | 0.378 | 1.70 | 0.919 | 0.619 |
| CNN | 0.207 | 2.22 | 3.05 | 0.382 | 2.17 | 0.904 | 6.448 |
| DLF | 0.162 | 1.74 | 2.55 | 0.377 | 1.78 | 0.932 | 6.726 |
| FPDE | 0.169 | 1.81 | 2.59 | 0.379 | 1.70 | 0.915 | 1.450 |
| GFF | 0.213 | 2.28 | 3.11 | 0.392 | 1.64 | 0.907 | 0.393 |
| Hybrid-MSD | 0.227 | 2.42 | 3.26 | 0.391 | 2.27 | 0.904 | 4.929 |
| MGFF | 0.219 | 2.34 | 3.11 | 0.385 | 1.45 | 0.902 | 1.455 |
| MST-SR | 0.209 | 2.24 | 3.05 | 0.386 | 2.14 | 0.903 | 0.709 |
| ResNet | 0.162 | 1.74 | 2.54 | 0.378 | 1.71 | 0.932 | 0.532 |
| RP-SR | 0.200 | 2.13 | 3.07 | 0.394 | 1.60 | 0.905 | 0.369 |
| TIF | 0.216 | 2.32 | 3.14 | 0.388 | 1.52 | 0.904 | 0.061 |
| VSMWLS | 0.222 | 2.36 | 3.19 | 0.387 | 1.78 | 0.905 | 2.351 |
| FusionGAN | 0.170 | 1.83 | 2.67 | 0.377 | 1.49 | 0.914 | 0.369 |
| Ours | 0.249 | 2.69 | 3.25 | 0.394 | 1.95 | 0.922 | 0.121 |
| AG | EI | |
|---|---|---|
| Without a U-shaped discriminator | 0.236 | 2.553 |
| With a U-shaped discriminator | 0.248 | 2.689 |
| AG | EI | SF | EN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without a segmentation label | 0.217 | 2.351 | 0.389 | 3.106 |
| With a segmentation label | 0.248 | 2.689 | 0.394 | 3.246 |
| AG | EI | SF | EN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
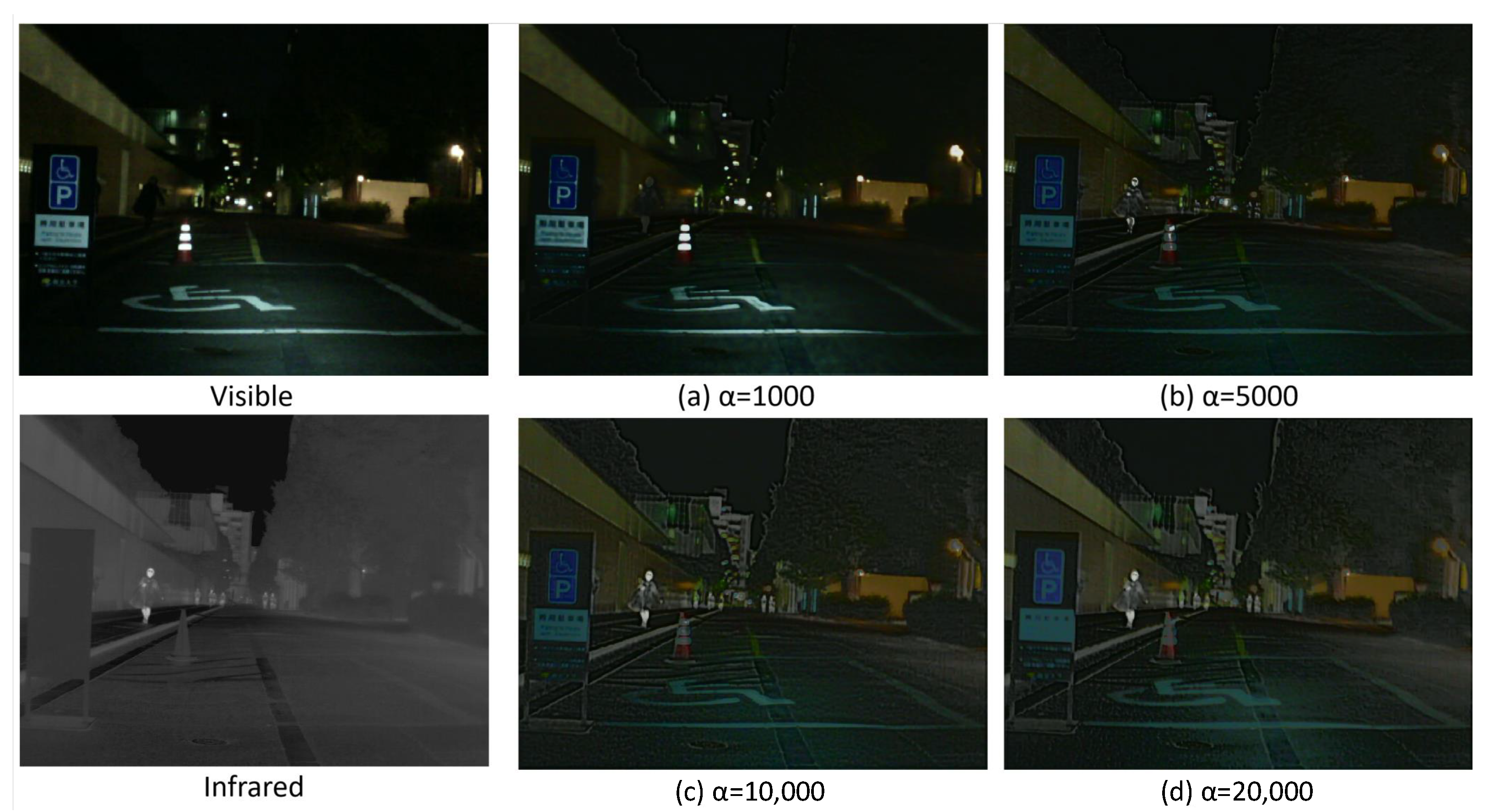
| = 1000 | 0.139 | 1.504 | 0.365 | 2.246 |
| = 5000 | 0.198 | 2.128 | 0.379 | 2.700 |
| = 10,000 | 0.248 | 2.689 | 0.394 | 3.246 |
| = 20,000 | 0.235 | 2.540 | 0.395 | 3.243 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Teng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Bai, L.; Han, J. Infrared-Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Guidance and Visual Perception. Entropy 2022, 24, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101327
Chen X, Teng Z, Liu Y, Lu J, Bai L, Han J. Infrared-Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Guidance and Visual Perception. Entropy. 2022; 24(10):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101327
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaoyu, Zhijie Teng, Yingqi Liu, Jun Lu, Lianfa Bai, and Jing Han. 2022. "Infrared-Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Guidance and Visual Perception" Entropy 24, no. 10: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101327
APA StyleChen, X., Teng, Z., Liu, Y., Lu, J., Bai, L., & Han, J. (2022). Infrared-Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Guidance and Visual Perception. Entropy, 24(10), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101327





