A Novel and Adaptive Angle Diversity-Based Receiver for 6G Underground Mining VLC Systems
Abstract
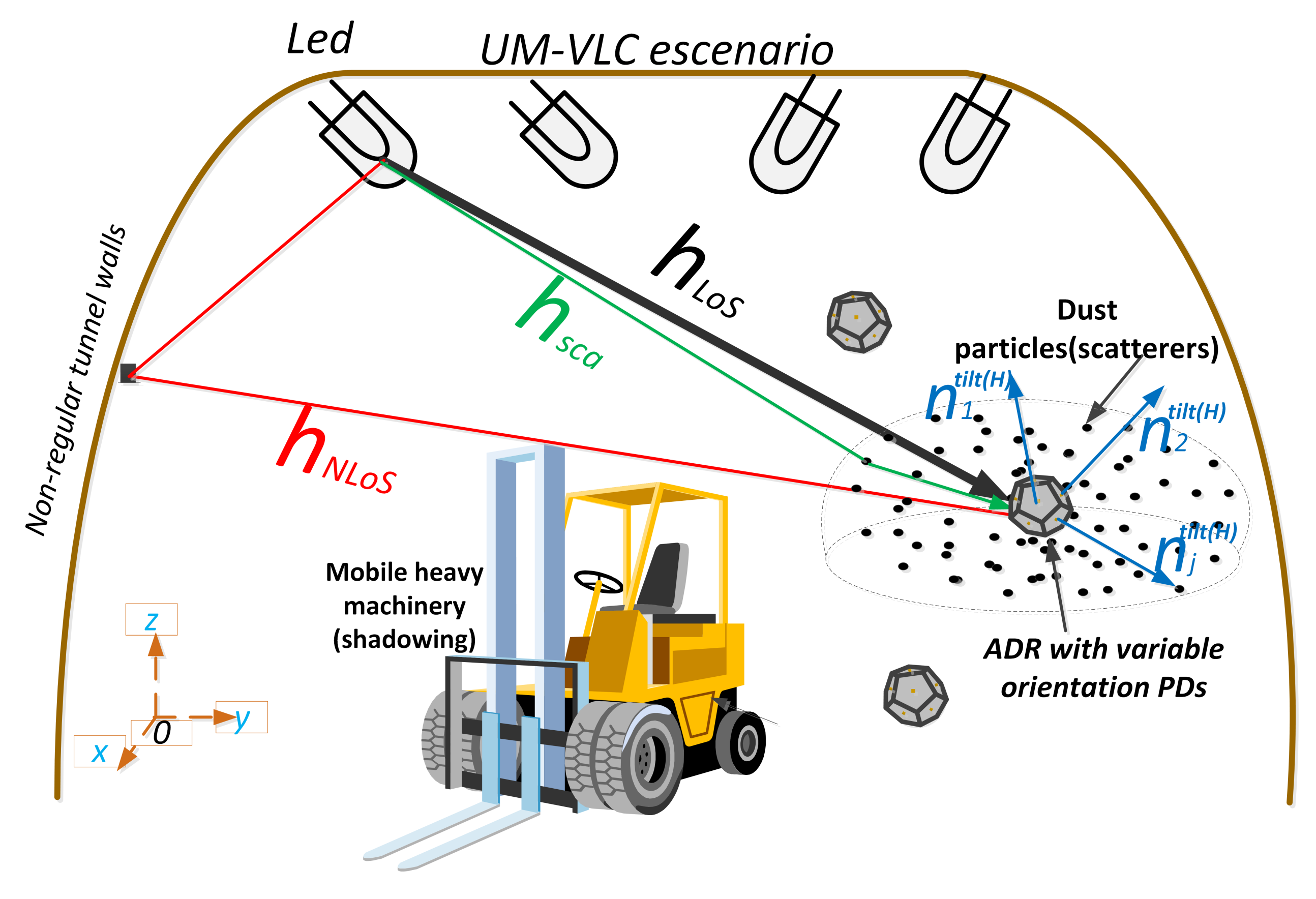
:1. Introduction
Works Related to Receiver Orientation Algorithms and Methods
- A theoretical analysis and design of an ADR structure with adaptive orientation is proposed in this work. Furthermore, the methodology to estimate the optimum angle of incidence on the receiver, along with its main mathematical expressions, is derived.
- A feasible and practical solution to improve the reception of the optical signal based on the adaptive orientation of the PDs in an ADR using an incidence angle estimation method through the RSSR tool.
- The evaluation and performance comparison of the presented solution with other typical receiver structures in an UM-VLC scenario in terms of important possible metrics for 6G technologies; such as received power, BER, and user data rate.
2. VLC System Model Applied to Underground Mining Environments
2.1. Optical Transmitters and Receivers
2.2. Channel DC Gain
2.3. Receiver Optical Power
3. Adaptive Orientation Receiver
3.1. Adaptive Orientation Receiver Structure
3.2. Adaptive Receptor Orientation Scenario
3.3. Methodology Used to Estimate the Angle of Incidence
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Distribution of the Received Power
4.2. Distribution of the User Data Rate
4.3. Bit Error Rate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADR | Angle Diversity Receiver |
| AoA | Angle of Arrival |
| BER | Bit Error Rate |
| DC | Direct Current |
| FoV | Field-of-View |
| ICI | Inter-Cell Interference |
| LED | Light-Emitting Diode |
| LoS | Line-of-Sight |
| non-LoS | Non-Line of Sight |
| OOC | Optical Orthogonal Codes |
| PD | Photo-Diode |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| RSS | Received Signal Strength |
| RSSR | Received Signal Strength Ratio |
| SINR | Signal-Interference-plus-Noise-Ratio |
| TIA | Trans-Impedance Amplifier |
| ToA | Time of Arrival |
| UM | Underground Mining |
| UM-VLC | Underground Mining Visible Light Communication |
| VLC | Visible Light Communication |
References
- Ranjan, A.; Zhao, Y.; Sahu, H.B.; Misra, P. Opportunities and Challenges in Health Sensing for Extreme Industrial Environment: Perspectives From Underground Mines. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 139181–139195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkan, S.; Guzelgoz, S.; Arslan, H.; Murphy, R.R. Underground Mine Communications: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2009, 11, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, U.I.; Naqvi, I.H.; Qaisar, S.; Ali, K.; Shahid, S.; Aslam, M.A. A WSN for Monitoring and Event Reporting in Underground Mine Environments. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Niu, W.; Ha, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Chi, N. AI-Enabled Intelligent Visible Light Communications: Challenges, Progress, and Future. Photonics 2022, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miramirkhani, F.; Uysal, M. Channel modelling for indoor visible light communications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palacios Játiva, P.; Román Cañizares, M.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Dehghan Firoozabadi, A.; Seguel, F.; Montejo-Sánchez, S.; Soto, I. Interference mitigation for visible light communications in underground mines using angle diversity receivers. Sensors 2020, 20, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Játiva, P.P.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Gutiérrez, C.A.; Sánchez, I.; Castillo-Soria, F.R.; Seguel, F. Bit Error Probability of VLC Systems in Underground Mining Channels with Imperfect CSI. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 145, 154101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, D.; Hötzel, J. IoT Based information and communication system for enhancing underground mines safety and productivity: Genesis, taxonomy and open issues. Ad Hoc Networks 2018, 78, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Ha, C. Fingerprint-based indoor positioning system using visible light communication—A novel method for multipath reflections. Electronics 2019, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Hashizume, H. Time-of-arrival-based smartphone localization using visible light communication. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sapporo, Japan, 18–21 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Irshad, M.; Liu, W.; Arshad, J.; Sohail, M.N.; Murthy, A.; Khokhar, M.; Uba, M.M. A novel localization technique using luminous flux. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shi, J.; Chi, N. Reversed three-dimensional visible light indoor positioning utilizing annular receivers with multi-photodiodes. Sensors 2016, 16, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Othman, R.; Gaafar, A.; Muaaz, L.; Elsayed, M. A Hybrid RSS+AOA Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Visible Light Communication. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer, Control, Electrical, and Electronics Engineering (ICCCEEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 26 February–1 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, J.K.; Kim, J.T. Three-Dimensional VLC Positioning System Model and Method Considering Receiver Tilt. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 132205–132216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.H.; Le, H.D.; Pham, T.V.; Pham, A.T. Design and Performance Evaluation of Large-Scale VLC-Based Indoor Positioning Systems Under Impact of Receiver Orientation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 61891–61904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, C. Indoor Visible Light Localization Algorithm with Multi-Directional PD Array. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Román Cañizares, M.; Palacios Játiva, P.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Montejo-Sánchez, S.; Céspedes, S. Impact of diversity combining schemes in a multi-cell VLC system with Angle Diversity Receivers. Photonic Netw. Commun. 2022, 43, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Játiva, P.P.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Cañizares, M.R.; Céspedes, S.; Montejo-Sánchez, S. Performance Enhancement of VLC-Based Systems Using Diversity Combining Schemes in the Receiver. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Latin-American Conference on Communications (LATINCOM), Salvador, Brazil, 11–13 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Saleh, S.S.; El-Badawy, E.S.A.; Aly, M.H. A comparative analysis of localization algorithms for visible light communication. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Guo, C.; Cheng, J. A High-Coverage Camera Assisted Received Signal Strength Ratio Algorithm for Indoor Visible Light Positioning. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 5730–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Játiva, P.P.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Sánchez, I.; Seguel, F.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Firoozabadi, A.D.; Gutiérrez, C.A.; Soto, I. A VLC Channel Model for Underground Mining Environments With Scattering and Shadowing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 185445–185464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tsonev, D.; Haas, H. Improving SINR in Indoor Cellular Visible Light Communication networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 12–14 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sung, C.W.; Ho, S.W.; Wong, W.S. BER analysis for interfering visible light communication systems. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 20–22 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, F.; Wang, A.; Sana, M.U.; Husain, A.; Ashraf, I. Characteristic Study of Visible Light Communication and Influence of Coal Dust Particles in Underground Coal Mines. Electronics 2021, 10, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kinani, A.; Wang, C.; Haas, H.; Yang, Y. Characterization and Modeling of Visible Light Communication Channels. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, S.H. TOA and AOD statistics for down link Gaussian scatterer distribution model. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemlooy, Z. Optical Wireless Communications: System and Channel Modelling with MATLAB; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Játiva, P.P.; Becerra, R.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Soto, I.; Cañizares, M.R. Extreme Learning Machine Based Channel Estimator and Equalizer for Underground Mining VLC Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Latin-American Conference on Communications (LATINCOM), Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic, 17–19 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| UM Simulation Scenario | Values | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Tunnel Parameters | ||
| Dimensions (), m | () | |
| Coordinates of the , m | , | |
| Channel and element parameters | ||
| AWGN power spectral density () | [22] | |
| LED rotation angle, | 45 | [7] |
| LED tilt angle, | 45 | [7] |
| Noise bandwidth (MHz) | 100 | [23] |
| Wall reflection coefficient, | 0.6 | [7] |
| Wall rotation angle, | U[0,180] | [7] |
| Wall tilt angle, | U[0,180] | [7] |
| VLC transceiver parameters | ||
| Average transmitted power, (W) | 5 | [24] |
| Band-pass filter of transmission | 1 | [6] |
| FoV, | 70 | [24] |
| Gain of the optical filter | 1 | [24] |
| Lambertian mode number, m | 1 | [25,26] |
| LED wavelength, (nm) | 580 | [24] |
| Modulation type | OOK | [27] |
| Modulation bandwidth (MHz) | 50 | [27] |
| Modulation index | 0.3 | [27] |
| Optical filter bandwidth (nm) | 340 to 694.3 | [24] |
| Optical filter center wavelength (nm) | 580 ± 2 | [24] |
| Optical filter full width half max (nm) | 10 ± 2 | [24] |
| Physical active area, (cm2) | 1 | [6] |
| Reflective element area, | 1 | [21] |
| Refractive index, | 1.5 | [6] |
| Responsivity, (A/W) | 0.53 | [6] |
| Semi-angle at half power, | 60 | [24] |
| State-of-the-Art Solutions | Hemidodecahedral ADR with PDs with Adaptive Orientation |
|---|---|
| Hemidodecahedral ADR with PDs fixed | 61.1% |
| Hemidodecahedral ADR with the ToA method | 50.4% |
| Pyramid ADR with the ToA method | 101.3% |
| Pyramid ADR with the PDs fixed | 160.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palacios Játiva, P.; Sánchez, I.; Soto, I.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Ijaz, M.; Dehghan Firoozabadi, A.; Plets, D. A Novel and Adaptive Angle Diversity-Based Receiver for 6G Underground Mining VLC Systems. Entropy 2022, 24, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111507
Palacios Játiva P, Sánchez I, Soto I, Azurdia-Meza CA, Zabala-Blanco D, Ijaz M, Dehghan Firoozabadi A, Plets D. A Novel and Adaptive Angle Diversity-Based Receiver for 6G Underground Mining VLC Systems. Entropy. 2022; 24(11):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111507
Chicago/Turabian StylePalacios Játiva, Pablo, Iván Sánchez, Ismael Soto, Cesar A. Azurdia-Meza, David Zabala-Blanco, Muhammad Ijaz, Ali Dehghan Firoozabadi, and David Plets. 2022. "A Novel and Adaptive Angle Diversity-Based Receiver for 6G Underground Mining VLC Systems" Entropy 24, no. 11: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111507
APA StylePalacios Játiva, P., Sánchez, I., Soto, I., Azurdia-Meza, C. A., Zabala-Blanco, D., Ijaz, M., Dehghan Firoozabadi, A., & Plets, D. (2022). A Novel and Adaptive Angle Diversity-Based Receiver for 6G Underground Mining VLC Systems. Entropy, 24(11), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111507










