Spatial Spillovers of Financial Risk and Their Dynamic Evolution: Evidence from Listed Financial Institutions in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Measurement of Risk Spillovers in Financial Submarkets
2.2. Multidimensional Economic Space
2.2.1. Economic Distance Measure
2.2.2. Gravitational Effect Spatial Weights Matrix
2.3. Multidimensional Economic Spatial Regression Model
2.4. The Tail Risk Network
2.4.1. Rules for the Tail Risk Network
2.4.2. Bonacich Key Node of the Tail Risk Network
3. Empirical Study and Results
3.1. Data Description
3.2. Dynamic Correlation Analysis and Breakpoint Detection
3.3. Multidimensional Spatial Effect Test
3.4. Spatial Spillover Effect Analysis with the Multidimensional Economic Spatial Regression Model
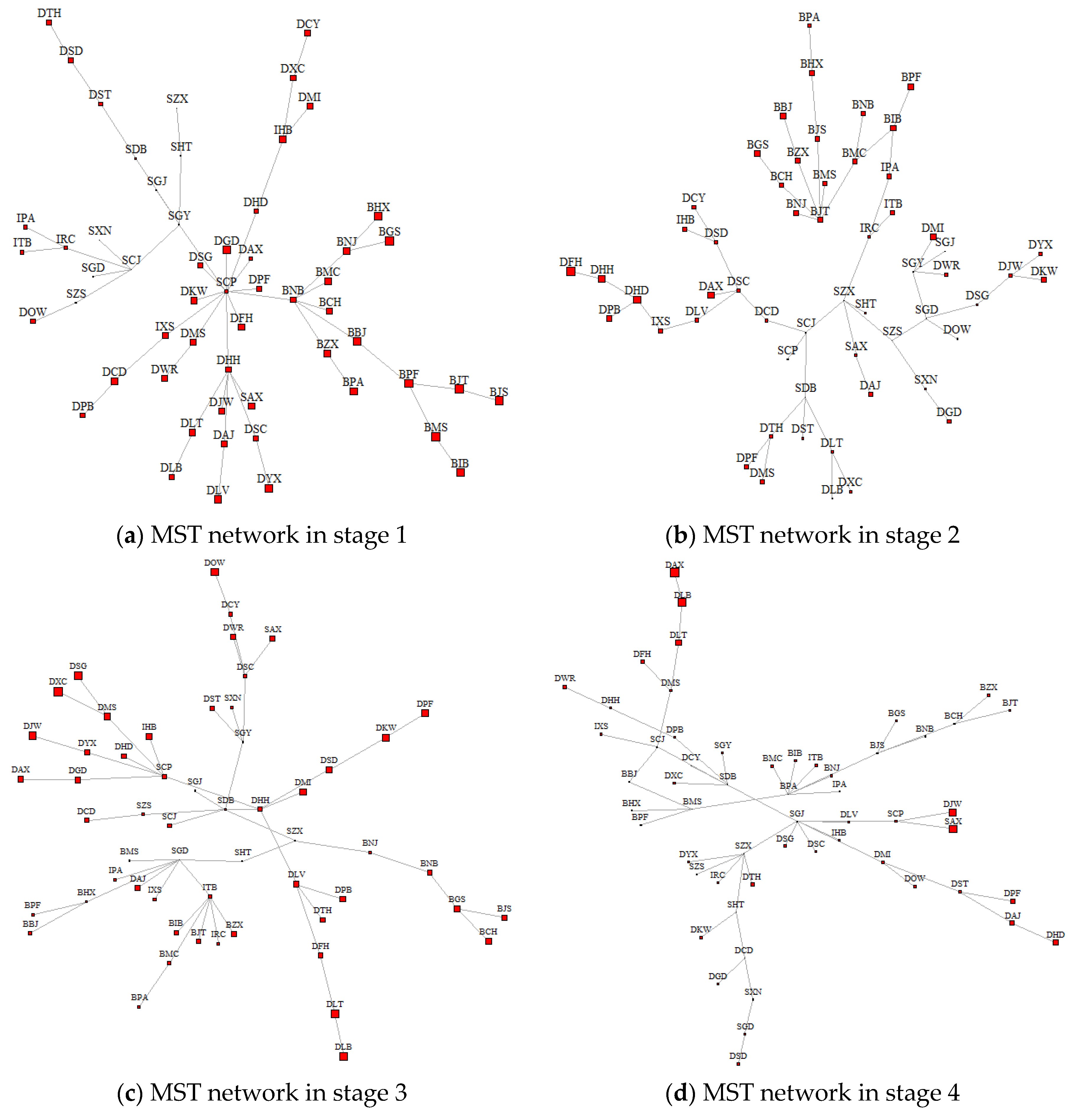
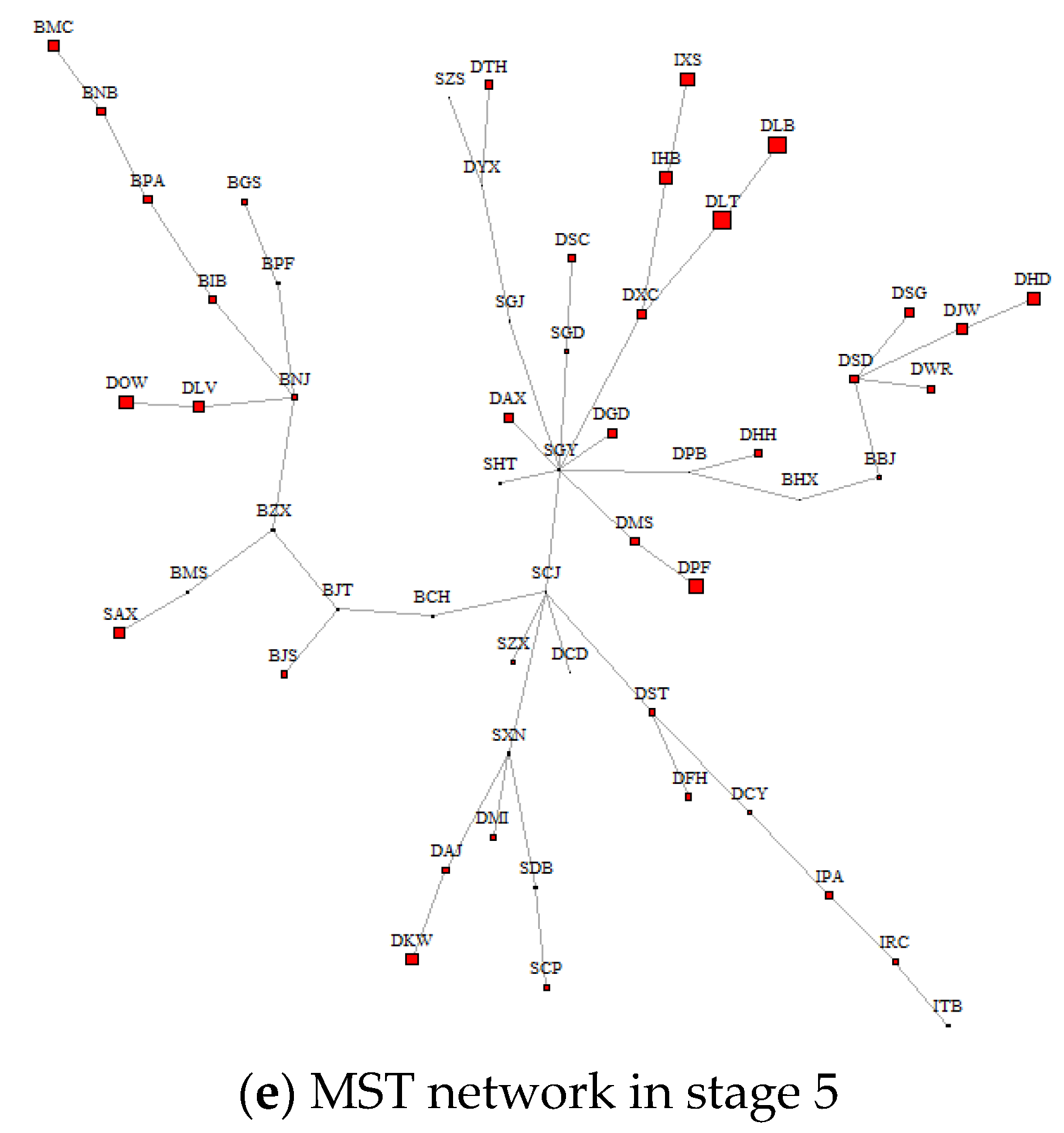
3.5. Tail Risk Network and BONACICH CEntrality
3.6. The Dynamic Evolution of the SIR Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. t-Copula-DCC-GARCH Model
Appendix B. The Bai & Perron Structural Mutation Test
Appendix C. The Economic Distance Measure
Appendix D. The Spatial Error Financial Network Panel Model
Appendix E
| ID | Company | Symbol | ID | Company | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hua Xia Bank Co., Ltd. | BHX | 29 | Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | IHB |
| 2 | China Minsheng Banking Corp., Ltd. | BMS | 30 | Xishui Strong Year Co., Ltd. Inner Mongolia | IXS |
| 3 | China Merchants Bank Co., Ltd. | BMC | 31 | Kunwu Jiuding Investment Holdings Co., Ltd. | DKW |
| 4 | Bank of Nanjing | BNJ | 32 | Luting (HongKong) Co., Ltd. | DLB |
| 5 | Industrial Bank Co., Ltd. | BIB | 33 | Sdic Capital Co., Ltd. | DCD |
| 6 | Bank of Beijing Co., Ltd. | BBJ | 34 | Xiangcai Co., Ltd. | DXC |
| 7 | Bank of Communications | BJT | 35 | Zhejiang Orient Financial Holdings Group Co., Ltd. | DFH |
| 8 | Industrial and Commercial Bank of China | BGS | 36 | Sichuan Western Resources Holding Co., Ltd. | DWR |
| 9 | China Construction Bank | BJS | 37 | Polaris Bay Group Co., Ltd. | DPB |
| 10 | Bank of China | BCH | 38 | Anhui Xinli Finance Co., Ltd. | DAX |
| 11 | China Citic Bank Co., Ltd. | BZX | 39 | Minmetals Capital Company Limited | DMI |
| 12 | Ping An Bank Co., Ltd. | BPA | 40 | State Grid Yingda Co., Ltd. | DSG |
| 13 | Bank of Ningbo | BNB | 41 | Panda Financial Holding Corp., Ltd. | DPF |
| 14 | Shanghai Pudong Development Bank Co., Ltd. | BPF | 42 | Shanghai China Fortune Co., Ltd. | DSC |
| 15 | The Pacific Securities Co., Ltd. | SCP | 43 | Shanghai Aj Group Co., Ltd. | DAJ |
| 16 | Citic Securities Company Limited | SZX | 44 | Luxin Venture Capital Group Co., Ltd. | DLV |
| 17 | Sinolink Securities Co., Ltd. | SGJ | 45 | Harbin Hatou Investment Co., Ltd. | DHH |
| 18 | Southwest Securities Co., Ltd. | SXN | 46 | Oceanwide Holdings Co., Ltd. | DOW |
| 19 | Haitong Securities Co., Ltd. | SHT | 47 | Minsheng Holdings Co., Ltd. | DMS |
| 20 | China Merchants Securities | SZS | 48 | Shaanxi International Trust Co., Ltd. | DST |
| 21 | Everbright Securities Co., Ltd. | SGD | 49 | Hainan Haide Capital Management Co., Ltd. | DHD |
| 22 | Northeast Securities Co., Ltd. | SDB | 50 | Cnpc Capital Company Limited | DCY |
| 23 | Guoyuan Securities Company Limited | SGY | 51 | Jingwei Textile Machinery Company Limited | DJW |
| 24 | Changjiang Securities Company Limited | SCJ | 52 | Guangdong Golden Dragon Development Inc. | DGD |
| 25 | Anxin Trust Co., Ltd. | SAX | 53 | Spic Dongfang Energy Corporation | DSD |
| 26 | Ping An Insurance | IPA | 54 | Guangzhou Yuexiu Financial Holdings Group Co., Ltd. | DYX |
| 27 | China Pacific Insurance (Group) Co., Ltd. | ITB | 55 | Hithink Flush Information Network Co., Ltd. | DTH |
| 28 | China Life Insurance (Group) Company | IRC | 56 | Shanghai Greencourt Investment Group Co., Ltd. | DLT |
References
- Sadorsky, P. Correlations and volatility spillovers between oil prices and the stock prices of clean energy and technology companies. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, F.X.; Yilmaz, K. Better to give than to receive: Predictive directional measurement of volatility spillovers. Int. J. Forecast. 2012, 28, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akca, K.; Ozturk, S.S. The effect of 2008 crisis on the volatility spillovers among six major markets. Int. Rev. Finance 2016, 16, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Su, Z.; Song, P. Measurement, supervision and early warning of risk contagion among global stock markets. J. Finance Res. 2020, 11, 94–112. [Google Scholar]
- Croitorov, O.; Giovannini, M.; Hohberger, S.; Ratto, M.; Vogel, L. Financial spillover and global risk in a multi-region model of the world economy. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2020, 177, 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Nimmo, M.; Nguyen, V.H.; Wu, E. On the international spillover effects of country-specific financial sector bailouts and sovereign risk shocks. Econ. Rec. 2021, 97, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Zhuang, X.T.; Wang, J.; Gong, X.L. Impacts of the Sino-US trade friction on China’s Shanghai and Shenzhen stock sectors. J. Manag. Sci. China 2021, 24, 34–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.J.; Xie, C.; He, K.J.; Stanley, H.E. Extreme risk spillover network: Application to financial institutions. Quant. Finance 2017, 17, 1417–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, S.; Hoang, T.V.; Arreola-Hernandez, J. Risk spillovers between large banks and the financial sector: Asymmetric evidence from Europe. Finance Res. Lett. 2019, 28, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, R.; Olmo, J. Volatility spillover between economic sectors in financial crisis prediction: Evidence spanning the great financial crisis and COVID-19 pandemic. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2021, 57, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jondeau, E.; Rockinger, M. The Copula-GARCH model of conditional dependencies: An international stock market application. J. Int. Money Finance 2006, 25, 827–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkowska, A.; Wanat, S. Dependencies and systemic risk in the European insurance sector: New evidence based on Copula-DCC-GARCH model and selected clustering methods. Entrep. Bus. Econ. Rev. 2021, 8, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J. What is systemic risk? Moral hazard, initial shocks, and propagation. Monet. Econ. Stud. 2000, 18, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.; Diybvig, P. Bank runs, deposit insurance, and liquidity. J. Political Econ. 2010, 91, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhao, X.J.; Zheng, Z.G. Why did investment banks take more risk than optimal? A theoretical analysis of reasons for subprime crisis. Actual Probl. Econ. 2012, 127, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.; Bali, T.G.; Tang, Y. Does systemic risk in the financial sector predict future economic downturns? Rev. Financ. Stud. 2012, 25, 3000–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzan, S. Loss aversion and market crashes. Econ. Model. 2020, 92, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.A.; Du, F.Z. Financial innovation, systematic risk and commercial banks’ stability in China: Theory and evidence. Appl. Econ. 2016, 48, 3887–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.B.; Fareed, M.; Salameh, A.A.; Hussain, H. Financial innovation, sustainable economic growth, and credit risk: A case of the ASEAN banking sector. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 729922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Y.; Wang, D.P.; Fang, Y. Measuring and supervising financial institutions’ marginal contribution to systemic risk in China: A research based on ME and leverage. Nankai Econ. Stud. 2011, 4, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Upper, C. Simulation methods to assess the danger of contagion in interbank markets. J. Financ. Stab. 2011, 7, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzubas, T.U.; Saltoglu, B.; Sever, C. Systemic risk and heterogeneous leverage in banking networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. ITS Appl. 2016, 462, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, B. Systemic risk, bank’s capital buffer, and leverage. Econ. J. Emerg. Mark. 2017, 9, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cincinelli, P.; Pellini, E.; Urga, G. Leverage and systemic risk pro-cyclicality in the Chinese financial system. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 78, 101–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, J.H.; Shin, H.S.; Shin, K. Noncore bank liabilities and financial vulnerability. J. Money Credit Bank. 2013, 45, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, F.; Marmi, S.; Lillo, F. When micro prudence increases macro risk: The destabilizing effects of financial innovation, leverage, and diversification. Oper. Res. 2016, 64, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ji, Q. Identifying systemically important financial institutions in China: New evidence from a dynamic copula-CoVaR approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banulescu, G.D.; Dumitrescu, E.I. Which are the SIFIs? A component expected shortfall approach to systemic risk. J. Bank. Financ. 2015, 50, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmissi, B.; Bejaoui, A.; Snoussi, W. On identifying the domestic systemically important banks: The case of Tunisia. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2017, 42, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, H.; Cevik, E.I.; Cevik, N.K.; Dibooglu, S. Identifying systemically important financial institutions in Turkey. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2021, 56, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.G. Global systemic financial risk spillovers and their external impact. Soc. Sci. China 2018, 12, 69–90+200–201. [Google Scholar]
- Onnela, J.P.; Kaski, K.; Kertész, J. Clustering and information in correlation based financial networks. Eur. Phys. J. B 2004, 38, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billio, M.; Getmansky, M.; Lo, A.W.; Pelizzon, L. Econometric measures of connectedness and systemic risk in the finance and insurance sectors. J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 104, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukny, T.; Bersini, H.; Pirotte, H.; Caldarelli, G.; Battiston, S. Default cascades in complex networks: Topology and systemic risk. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautsch, N.; Schaumburg, J.; Schienle, M. Financial network systemic risk contributions. Rev. Financ. 2015, 19, 685–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Cont, R.; Minca, A. Resilience to contagion in financial networks. Math. Financ. 2016, 26, 329–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Q.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Y.J. Network analysis of SIFIs based on tail systemic linkage. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 897721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, B. Externalities, economic geography, and spatial econometrics: Conceptual and modeling developments. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2003, 26, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, S.; Maurer, A. Measuring the effects of geographical distance on stock market correlation. J. Empir. Financ. 2011, 18, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Erba, S.; Baldacci, E.; Poghosyan, T. Spatial spillovers in emerging market spreads. Empir. Econ. 2013, 45, 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelejian, H.H.; Prucha, I.R. Specification and estimation of spatial autoregressive models with autoregressive and heteroskedastic disturbances. J. Econom. 2010, 157, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, S.; Peng, X.H.; Zhong, H.W. Asset pricing with spatial interaction. Manag. Sci. 2017, 64, 2083–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acedanski, J.; Karkowska, R. Instability spillovers in the banking sector: A spatial econometrics approach. N. Am. J. Econ. Finance 2022, 61, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Zhuang, X.T.; Li, Y.S. Dynamic evolution process of financial impact path under the multidimensional spatial effect based on G20 financial network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 532, 121876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, Y. Research on dynamic measurement of systemic financial risk and cross-sector network spillover effect. Stud. Int. Financ. 2022, 1, 72–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Haus, B.; Mercorelli, P. Extension of SEIR compartmental Models for constructive lyapunov control of COVID-19 and analysis in terms of practical stability. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, J.; Mercorelli, P. Simulation of SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in Germany with ordinary differential equations in MATLAB. In Proceedings of the 2021 25th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Iași, Romania, 20–23 October 2021; pp. 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Garas, A.; Argyrakis, P.; Rozenblat, C.; Tomassini, M.; Havlin, S. Worldwide spreading of economic crisis. N. J. Phys. 2010, 12, 113043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic spreading in scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, H.Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J. Risk contagion simulation on cross financial business based on complex network. Syst. Eng. 2018, 36, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Zhuang, X.T.; Li, L.Z. Susceptible-infected-removed (SIR) model of crisis spreading in the correlated network of listed companies and their main stock-holders. J. Manag. Sci. China 2013, 16, 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kanno, M. The network structure and systemic risk in the Japanese interbank market. Jpn. World Econ. 2015, 36, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiris, N.; Kypraios, T.; Vanessa Smith, L. On the epidemic of financial crises. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Stat. Soc.) 2014, 177, 697–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.H.; Li, X.H. Contagion and bailout strategy in complex financial network-SIRS model on the Chinese scale-free financial network. Financ. Trade Econ. 2017, 38, 101–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.H.; Zhang, S.Y. Dependence analysis of finance markets: Copula-GARCH model and its application. Syst. Eng. 2004, 4, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, R.F. Dynamic conditional correlation: A simple class of multivariate generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2003, 20, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Perron, P. Computation and analysis of multiple structural change models. J. Appl. Econom. 2003, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegna, R.N.; Stanley, H.E. Introduction to Econophysics: Correlations and Complexity in Finance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Aviles, G.; Montero, J.M.; Orlov, A.G. Spatial modeling of stock market comovements. Finance Res. Lett. 2012, 9, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tian, Y.X.; Mu, S.D. Financial shock path dynamic evolution mechanism considering generalized multidimensional space effect. Syst. Eng. 2017, 35, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, M.; Stahlberg, S.; Wied, D. Modeling different kinds of spatial dependence in stock returns. Empir. Econ. 2013, 44, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Cole, E.; Kirilenko, A.; Patacchini, E. Trading networks and liquidity provision. J. Financ. Econ. 2013, 113, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Elhorst, J.P. Spatial Econometrics: From Cross-Sectional Data to Spatial Panels; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.L.; Li, J.; Tan, L.M.; Yang, H.S. The high-dimensional time-varying measurement and transmission Mechanism of Systemic Financial Risk in China. J. World Econ. 2021, 44, 28–54. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, K.J.; Rigobon, R. No contagion, only interdependence: Measuring stock market comovements. J. Finance 2002, 57, 2223–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boginski, V.; Butenko, S.; Pardalos, P.M. Statistical analysis of financial networks. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2005, 48, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P. Some unique properties of eigenvector centrality. Soc. Netw. 2007, 29, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contessi, S.; Pace, P.D.; Guidolin, M. How did the financial crisis alter the correlations of US yield spreads? J. Empir. Finance 2014, 28, 362–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollerslev, T. Generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity. J. Econom. 1986, 31, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollerslev, T.; Chou, R.Y.; Kroner, K.F. ARCH modeling in finance: A review of the theory and empirical evidence. J. Econom. 1992, 52, 5–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Perron, P. Estimating and testing linear models with multiple structural changes. Econometrica 1998, 66, 47–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Bera, A.K.; Florax, R.; Yoon, M.J. Simple diagnostic tests for spatial dependence. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1996, 26, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Zhuang, X.T.; Wang, J. Systematic risk spatial spillover correlation and risk prediction analysis of cross-industry in China’ stock market based on the tail risk network model. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2021, 29, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Gong, P. Modeling spatial and temporal dependencies among global stock markets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 43, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Zhang, J.L. Investor sentiment and stock market returns: A study based on multiple fractal analysis. Chin. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2017, 9, 92–102+126. [Google Scholar]


| Company ID | Mean | Std Dev | Min | Max | Skew | Kurtosis | SE | JB | ADF Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.00027 | 0.01925 | −0.34079 | 0.0958 | −3.01984 | 50.745 | 0.00035 | 325,158 *** | −15.2 *** |
| 2 | −0.00025 | 0.01723 | −0.19705 | 0.09544 | −1.22628 | 22.034 | 0.00032 | 61,207 *** | −14.57 *** |
| 3 | 0.00030 | 0.01852 | −0.1044 | 0.09554 | 0.23946 | 3.528 | 0.00034 | 1580 *** | −13.99 *** |
| 4 | −0.00016 | 0.02371 | −0.60744 | 0.09562 | −7.14441 | 166.674 | 0.00043 | 3,484,119 *** | −15.16 *** |
| 5 | −0.00020 | 0.02401 | −0.6198 | 0.09579 | −8.01889 | 193.890 | 0.00044 | 4,712,481 *** | −12.78 *** |
| 6 | −0.00047 | 0.01833 | −0.21092 | 0.0958 | −2.01532 | 28.096 | 0.00034 | 100,316 *** | −13.58 *** |
| 7 | −0.00020 | 0.01559 | −0.10954 | 0.09625 | −0.25476 | 11.978 | 0.00029 | 17,902 *** | −13.88 *** |
| 8 | −0.00004 | 0.01343 | −0.1233 | 0.09531 | −0.30273 | 11.605 | 0.00025 | 16,819 *** | −15.12 *** |
| 9 | 0.00000 | 0.0154 | −0.10577 | 0.09566 | −0.26081 | 9.377 | 0.00028 | 10,986 *** | −13.81 *** |
| 10 | −0.00010 | 0.01352 | −0.11629 | 0.09658 | −0.11378 | 14.146 | 0.00025 | 24,926 *** | −13.74 *** |
| 11 | −0.00015 | 0.01906 | −0.10564 | 0.09613 | 0.34581 | 6.509 | 0.00035 | 5338 *** | −14.15 *** |
| 12 | −0.00013 | 0.02423 | −0.54286 | 0.09563 | −4.08067 | 89.131 | 0.00044 | 997,405 *** | −13.34 *** |
| 13 | 0.00027 | 0.02271 | −0.27236 | 0.09563 | −0.857 | 13.314 | 0.00042 | 22,440 *** | −13.68 *** |
| 14 | −0.00033 | 0.01872 | −0.30037 | 0.0956 | −2.67124 | 42.730 | 0.00034 | 230,896 *** | −14.93 *** |
| 15 | −0.00061 | 0.02789 | −0.39267 | 0.09651 | −1.84074 | 27.983 | 0.00051 | 99,189 *** | −13.68 *** |
| 16 | −0.00015 | 0.02541 | −0.42703 | 0.0957 | −1.45014 | 29.638 | 0.00047 | 110,427 *** | −15.05 *** |
| 17 | −0.00031 | 0.03093 | −0.68444 | 0.09579 | −3.61948 | 81.313 | 0.00057 | 829,734 *** | −16.39 *** |
| 18 | −0.00049 | 0.0278 | −0.71451 | 0.0963 | −5.62786 | 147.158 | 0.00051 | 2,711,957 *** | −14.92 *** |
| 19 | −0.00021 | 0.02359 | −0.10553 | 0.09576 | 0.16266 | 4.334 | 0.00043 | 2354 *** | −13.3 *** |
| 20 | −0.00023 | 0.02497 | −0.28319 | 0.09567 | −0.3357 | 10.196 | 0.00046 | 13,003 *** | −13.75 *** |
| 21 | −0.00023 | 0.02656 | −0.10702 | 0.09585 | 0.0826 | 3.710 | 0.00049 | 1719 *** | −14.48 *** |
| 22 | −0.00053 | 0.02932 | −0.69188 | 0.0958 | −4.35806 | 104.728 | 0.00054 | 1,375,017 *** | −14.18 *** |
| 23 | −0.00035 | 0.02754 | −0.49118 | 0.0958 | −1.97168 | 36.176 | 0.0005 | 164,888 *** | −13.87 *** |
| 24 | −0.00038 | 0.02878 | −0.74308 | 0.09605 | −5.69682 | 149.797 | 0.00053 | 2,809,910 *** | −14.62 *** |
| 25 | −0.00048 | 0.03376 | −0.10604 | 0.09646 | −0.046 | 1.806 | 0.00062 | 408 *** | −14.34 *** |
| 26 | −0.00005 | 0.02434 | −0.79079 | 0.09545 | −11.4086 | 373.166 | 0.00045 | 17,402,008 *** | −14.32 *** |
| 27 | −0.00004 | 0.02199 | −0.10544 | 0.09545 | 0.07104 | 2.326 | 0.0004 | 677 *** | −14.29 *** |
| 28 | −0.00006 | 0.02223 | −0.12358 | 0.09563 | 0.39041 | 3.961 | 0.00041 | 2031 *** | −13.61 *** |
| 29 | −0.00029 | 0.02868 | −0.71823 | 0.09679 | −5.15102 | 133.160 | 0.00052 | 2,220,858 *** | −14.94 *** |
| 30 | −0.0006 | 0.03112 | −0.14812 | 0.09659 | −0.03155 | 2.031 | 0.00057 | 515 *** | −14.24 *** |
| 31 | 0.00012 | 0.03071 | −0.24064 | 0.09603 | 0.18239 | 3.655 | 0.00056 | 1682 *** | −15.32 *** |
| 32 | −0.0006 | 0.02265 | −0.10886 | 0.0992 | −0.38755 | 5.436 | 0.00041 | 3756 *** | −15.19 *** |
| 33 | −0.00013 | 0.02964 | −0.41689 | 0.09635 | −0.87503 | 15.464 | 0.00054 | 30,163 *** | −15.48 *** |
| 34 | 0.00005 | 0.03311 | −0.10582 | 0.09623 | 0.07885 | 1.976 | 0.00061 | 490 *** | −14.93 *** |
| 35 | −0.00029 | 0.02976 | −0.35953 | 0.096 | −1.88577 | 21.654 | 0.00054 | 60,157 *** | −13.94 *** |
| 36 | −0.00089 | 0.03259 | −0.54302 | 0.09671 | −1.6518 | 28.293 | 0.0006 | 101,034 *** | −15.03 *** |
| 37 | 0.00018 | 0.02754 | −0.10558 | 0.09613 | 0.25149 | 2.896 | 0.0005 | 1077 *** | −14.24 *** |
| 38 | −0.00004 | 0.03538 | −0.6978 | 0.09604 | −2.41286 | 51.841 | 0.00065 | 337,518 *** | −14.99 *** |
| 39 | −0.00033 | 0.03157 | −0.65214 | 0.09572 | −3.11113 | 62.836 | 0.00058 | 496,427 *** | −14.03 *** |
| 40 | −0.00041 | 0.02972 | −0.56389 | 0.09659 | −2.31462 | 45.068 | 0.00054 | 255,569 *** | −15.09 *** |
| 41 | −0.00032 | 0.03219 | −0.10558 | 0.09599 | −0.04499 | 2.152 | 0.00059 | 579 *** | −14.76 *** |
| 42 | 0.00009 | 0.03019 | −0.10575 | 0.09635 | −0.10173 | 2.440 | 0.00055 | 747 *** | −13.71 *** |
| 43 | −0.0002 | 0.0252 | −0.25874 | 0.0958 | −0.38966 | 6.841 | 0.00046 | 5906 *** | −13.96 *** |
| 44 | −0.00021 | 0.03509 | −0.72762 | 0.09566 | −3.10695 | 62.533 | 0.00064 | 491,681 *** | −12.95 *** |
| 45 | −0.00023 | 0.02832 | −0.10572 | 0.09659 | −0.00914 | 3.434 | 0.00052 | 1470 *** | −14.68 *** |
| 46 | −0.00064 | 0.02934 | −0.72177 | 0.09764 | −4.88404 | 123.482 | 0.00054 | 1,910,299 *** | −14.24 *** |
| 47 | −0.00028 | 0.02812 | −0.10603 | 0.09675 | 0.04238 | 3.078 | 0.00051 | 1182 *** | −14.67 *** |
| 48 | −0.00047 | 0.03314 | −0.70163 | 0.09685 | −6.1338 | 128.233 | 0.00061 | 2,066,026 *** | −13.73 *** |
| 49 | 0.0002 | 0.03236 | −0.38446 | 0.0959 | −0.54472 | 8.284 | 0.00059 | 8695 *** | −14.61 *** |
| 50 | −0.00038 | 0.02802 | −0.35474 | 0.0959 | −0.80014 | 11.282 | 0.00051 | 16,171 *** | −13.91 *** |
| 51 | −0.00012 | 0.02716 | −0.10568 | 0.09563 | −0.26153 | 3.416 | 0.0005 | 1488 *** | −14.74 *** |
| 52 | −0.00012 | 0.03092 | −0.69084 | 0.09566 | −3.75775 | 84.529 | 0.00057 | 896,650 *** | −14.06 *** |
| 53 | −0.00006 | 0.03129 | −0.60268 | 0.09612 | −2.32364 | 47.531 | 0.00057 | 283,982 *** | −14.75 *** |
| 54 | −0.00042 | 0.02932 | −0.4416 | 0.09583 | −1.51514 | 24.655 | 0.00054 | 76,834 *** | −15.19 *** |
| 55 | 0.00007 | 0.04142 | −0.75922 | 0.16436 | −4.69051 | 83.319 | 0.00076 | 875,291 *** | −13.79 *** |
| 56 | −0.00052 | 0.03658 | −0.89126 | 0.09638 | −8.88564 | 208.805 | 0.00067 | 5,467,534 *** | −14.95 *** |
| Sub-Stage | Starting Time | Ending Time | Typical Extreme Events and Stage Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | 4 January 2010 | 21 October 2013 | Post-financial crisis and 2010 European debt crisis |
| Stage 2 | 22 October 2013 | 13 January 2017 | 2013 money crisis and 2015 stock market crash in China |
| Stage 3 | 14 January 2017 | 10 April 2018 | Stabilization period |
| Stage 4 | 11 April 2018 | 23 October 2020 | US-China trade conflict and COVID-19 epidemic |
| Stage 5 | 24 October 2020 | 18 April 2022 | Post-COVID-19 era |
| Spatial Effect Test | Wgene | Warea | Wp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.237 *** | 0.239 *** | 0.356 *** |
| Z(I) | 65.717 | 65.54 | 161.58 |
| Geary C | 0.481 *** | 0.478 *** | 0.656 *** |
| LMlag | 8970.12 *** | 8732.40 *** | 19665.95 *** |
| LMerro | 9128.71 *** | 8868.87 *** | 22966.41 *** |
| robust LMlag | 159.19 *** | 157.45 *** | 66.38 *** |
| robust LMerro | 318.04 *** | 293.92 *** | 3366.84 *** |
| Variable Name | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Log return rate | r | Daily log return rate of listed financial institutions |
| Turnover rate | turnover | Turnover rate of circulating capital stock of financial institutions |
| Low-volatility dummy variable | lvar | Takes 0 for the high-volatility group and 1 for the low-volatility group, and the value for the middle groups remains unchanged |
| High-volatility dummy variable | hvar | Takes 1 for the high-volatility group and 0 for the low-volatility group, and the value for the middle groups remains unchanged |
| Exchange rate | Erate | Change rate of daily central parity rate of RMB against USD |
| Interest rate | DR001 | Change rate of weighted average interest rate of overnight repo between banks with interest rate bonds as collateral |
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | Stage 4 | Stage 5 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wgene | Warea | WP | Wgene | Warea | WP | WP | Warea | WP | Wgene | Warea | WP | Wgene | Warea | WP | |
| λ | 0.808 *** (328.29) | 0.809 *** (344.56) | 0.806 *** (177.54) | 0.703 *** (154.99) | 0.704 *** (161.13) | 0.796 *** (154.95) | 0.383 *** (25.27) | 0.405 *** (28.37) | 0.661 *** (47.86) | 0.829 *** (282.38) | 0.833 *** (296.05) | 0.833 *** (174.59) | 0.680 *** (92.10) | 0.691 *** (98.11) | 0.756 *** (83.34) |
| turnover | 0.0023 *** (35.43) | 0.0022 *** (35.44) | 0.0024 ** (37.28) | 0.0019 *** (29.15) | 0.0019 *** (29.12) | 0.0019 *** (29.95) | 0.0012 *** (11.37) | 0.0012 ** (11.43) | 0.0012 ** (12.51) | 0.0017 *** (29.66) | −0.0017 *** (29.59) | 0.0015 *** (27.56) | 0.0016 *** (15.63) | 0.0017 *** (15.59) | 0.0016 *** (15.36) |
| lvar | 0 (−0.25) | 0.00007 (−0.26) | 0.00015 (0.57) | −0.00045 (1.23) | −0.00043 (1.20) | −0.00045 (1.29) | 0.00036 (0.74) | 0.0004 (0.75) | 0.00026 (0.55) | −0.00063 ** (−1.78) | −0.00061 ** (−1.72) | −0.00034 (−0.98) | −0.00032 (0.67) | −0.00033 (0.68) | 0.00021 (0.45) |
| hvar | −0.0025 *** (−9.23) | −0.0025 *** (−9.24) | −0.0026 *** (−10.30) | −0.0020 *** (−5.37) | −0.0020 *** (−5.37) | −0.0020 *** (−5.60) | −0.0016 *** (−3.35) | −0.0017 *** (−3.35) | −0.0018 *** (−3.81) | −0.0022 *** (−6.68) | −0.0022 *** (−6.61) | −0.0022 *** (−7.14) | −0.0027 *** (−6.54) | −0.0028 *** (−6.54) | −0.0027 *** (−6.64) |
| Erate | −0.406 (−0.67) | −0.394 (−0.65) | −1.817 *** (−3.21) | −0.254 (0.98) | 2.604 (1.00) | −0.099 (−0.28) | −0.089 (−0.65) | 0.090 (−0.63) | −0.030 (−0.13) | −0.802 ** (−2.52) | −0.815 ** (−2.51) | −0.43 * (−1.46) | −0.346 * (1.69) | −0.361 ** (1.70) | −0.231 (−0.89) |
| DR001 | −0.0104 ** (−2.38) | −0.0104 *** (−2.36) | −0.0047 (−1.14) | −0.0379 *** (−3.36) | −0.038 *** (−3.36) | −0.022 * (−1.45) | −0.009 ** (−1.74) | −0.009 *** (−1.71) | −0.007 (−0.79) | 0.015 *** (3.59) | 0.019 *** (3.62) | 0.0015 (−0.33) | 0.0003 (0.11) | 0.0003 (0.13) | −0.0039 (−1.11) |
| φ | 5.208333 | 5.235602 | 5.154639 | 3.367003 | 3.378378 | 4.901961 | 1.620746 | 1.680672 | 2.949853 | 5.847953 | 5.988024 | 5.988024 | 3.125 | 3.236246 | 4.098361 |
| Institution effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 51,240 | 51,240 | 51,240 | 44,408 | 44,408 | 44,408 | 16,744 | 16,744 | 16,744 | 34,552 | 34,552 | 34,552 | 20,160 | 20,160 | 20,160 |
| Rank | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | Stage 4 | Stage 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BJT (6.625) | DFH (1.240) | DXC (1.504) | DAX (1.065) | ST.DLT (2.564) |
| 2 | BMS (6.463) | DHD (0.872) | ST.DLT (1.115) | ST.DLB (0.901) | ST.DLB (2.352) |
| 3 | BGS (6.270) | DHH (0.812) | DSG (1.093) | ST.SAX (0.813) | DPF (1.823) |
| 4 | BJS (6.145) | BPF (0.643) | ST.DLB (1.077) | DJW (0.730) | IXS (1.752) |
| 5 | BBJ (5.682) | DAX (0.620) | ST.DPF (1.002) | ST.DLT (0.582) | DOW (1.664) |
| 6 | BPF (5.672) | BGS (0.597) | DOW (0.983) | DHD (0.468) | DHD (1.642) |
| 7 | BHX (5.400) | DPB (0.515) | DJW (0.953) | DAJ (0.349) | IHB (1.629) |
| 8 | DYX (5.154) | BIB (0.499) | DKW (0.825) | ST.DPF (0.310) | DKW (1.151) |
| 9 | BIB (5.071) | BBJ (0.475) | DMI (0.810) | ST.DWR (0.247) | BMC (1.146) |
| 10 | DLV (4.855) | DMI (0.430) | BCH (0.755) | DFH (0.215) | DLV (1.089) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Guo, L.; Qiang, Q. Spatial Spillovers of Financial Risk and Their Dynamic Evolution: Evidence from Listed Financial Institutions in China. Entropy 2022, 24, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111549
Chen S, Guo L, Qiang Q. Spatial Spillovers of Financial Risk and Their Dynamic Evolution: Evidence from Listed Financial Institutions in China. Entropy. 2022; 24(11):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111549
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shaowei, Long Guo, and Qiang (Patrick) Qiang. 2022. "Spatial Spillovers of Financial Risk and Their Dynamic Evolution: Evidence from Listed Financial Institutions in China" Entropy 24, no. 11: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111549
APA StyleChen, S., Guo, L., & Qiang, Q. (2022). Spatial Spillovers of Financial Risk and Their Dynamic Evolution: Evidence from Listed Financial Institutions in China. Entropy, 24(11), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111549







_Qiang.png)

