Video Action Recognition Using Motion and Multi-View Excitation with Temporal Aggregation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We design three submodules, including ME, MvE and DCTA, to learn enriched spatiotemporal and motion representations in a very efficient way and in an end-to-end manner.
- We propose META and insert it in 2D ResNet-50 with a few additional model parameters and low computation cost.
- We conduct extensive experiments on three popular benchmarking datasets, including Something-Something v1, Jester and Moments-in-Time Mini, and the results show the superiority of our approach.
2. Related Work
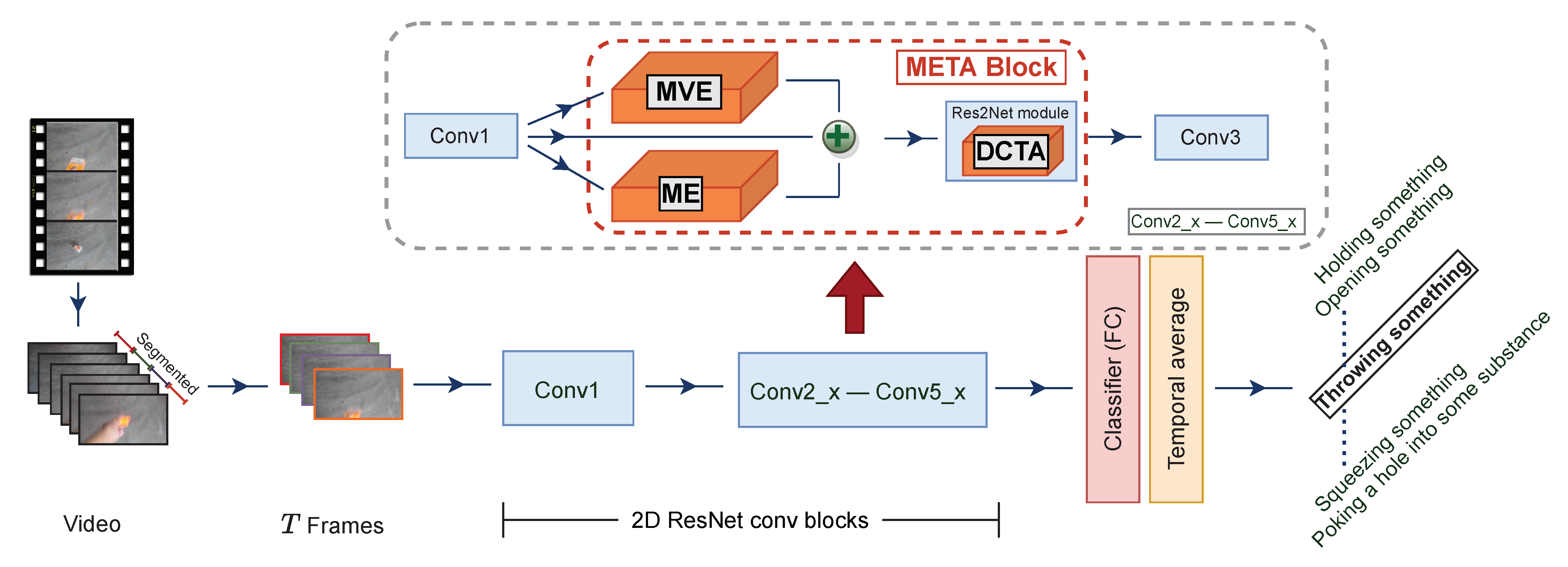
3. Our Proposed Method
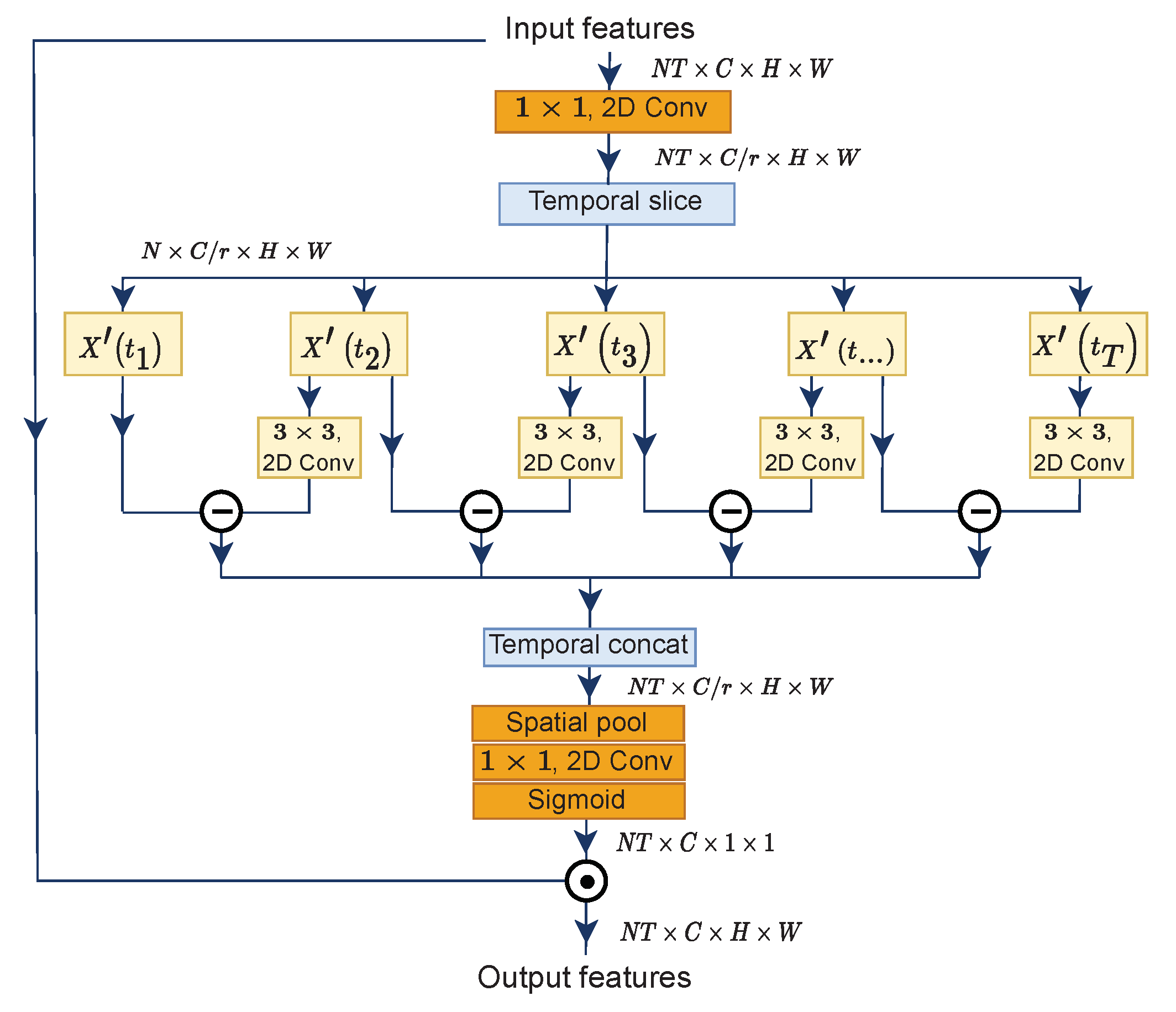
3.1. Motion Excitation (ME)
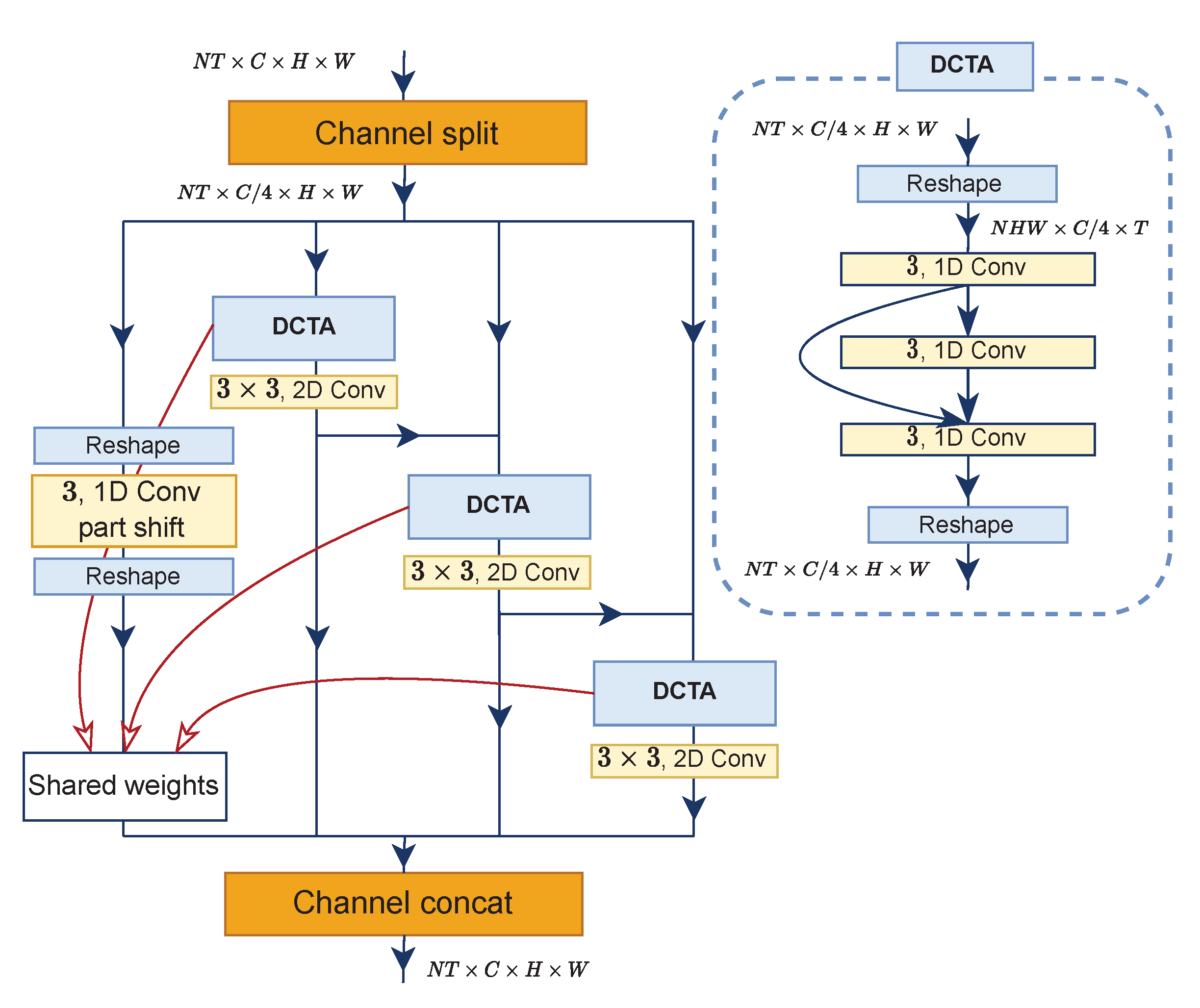
3.2. Densely Connected Temporal Aggregation (DCTA)
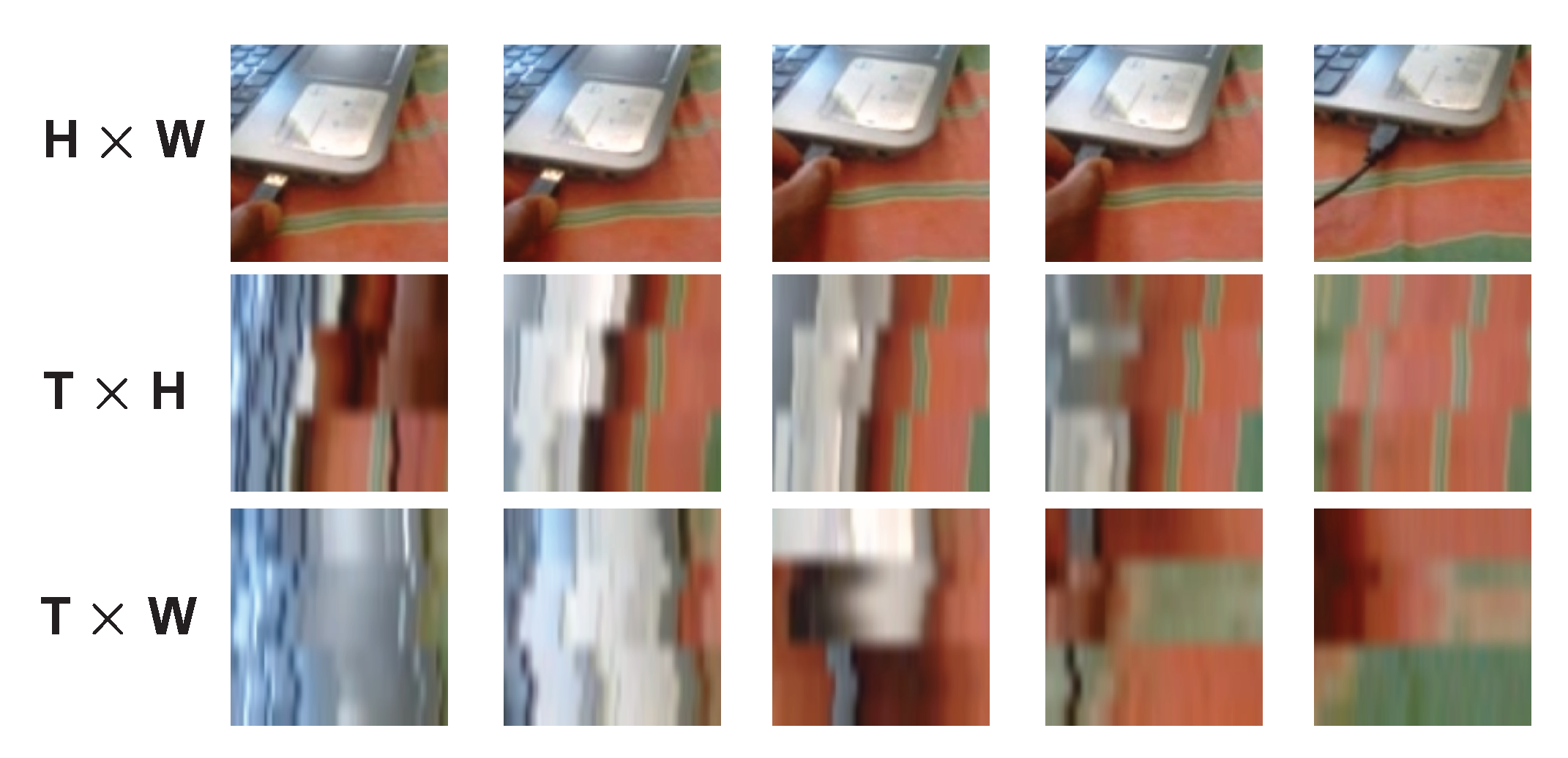
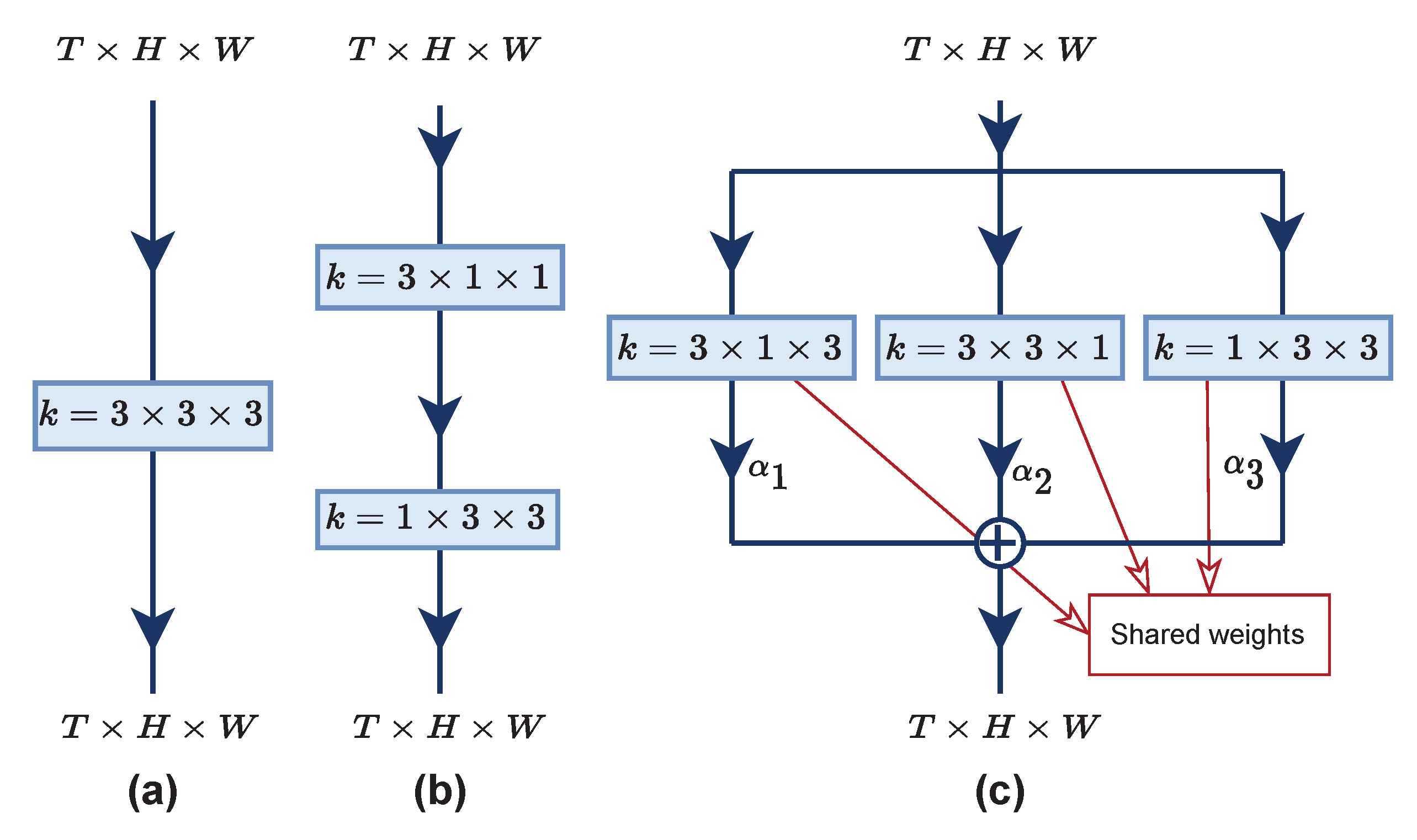
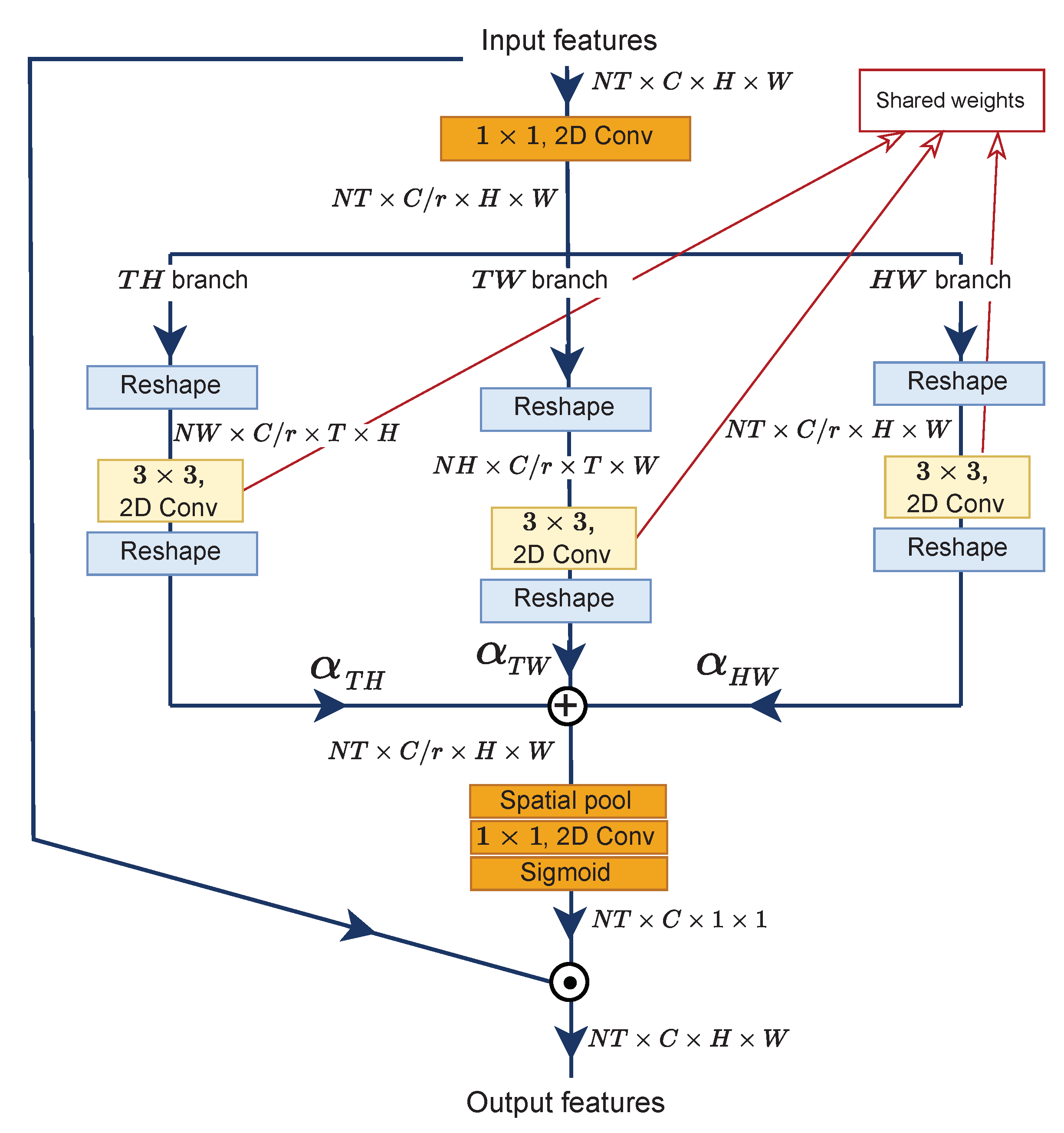
3.3. Multi-View Excitation (MvE)
3.4. Meta Block
3.5. Discussion with TEA
4. Experiment and Evaluation
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Implementation Details
4.2.1. Training
4.2.2. Testing
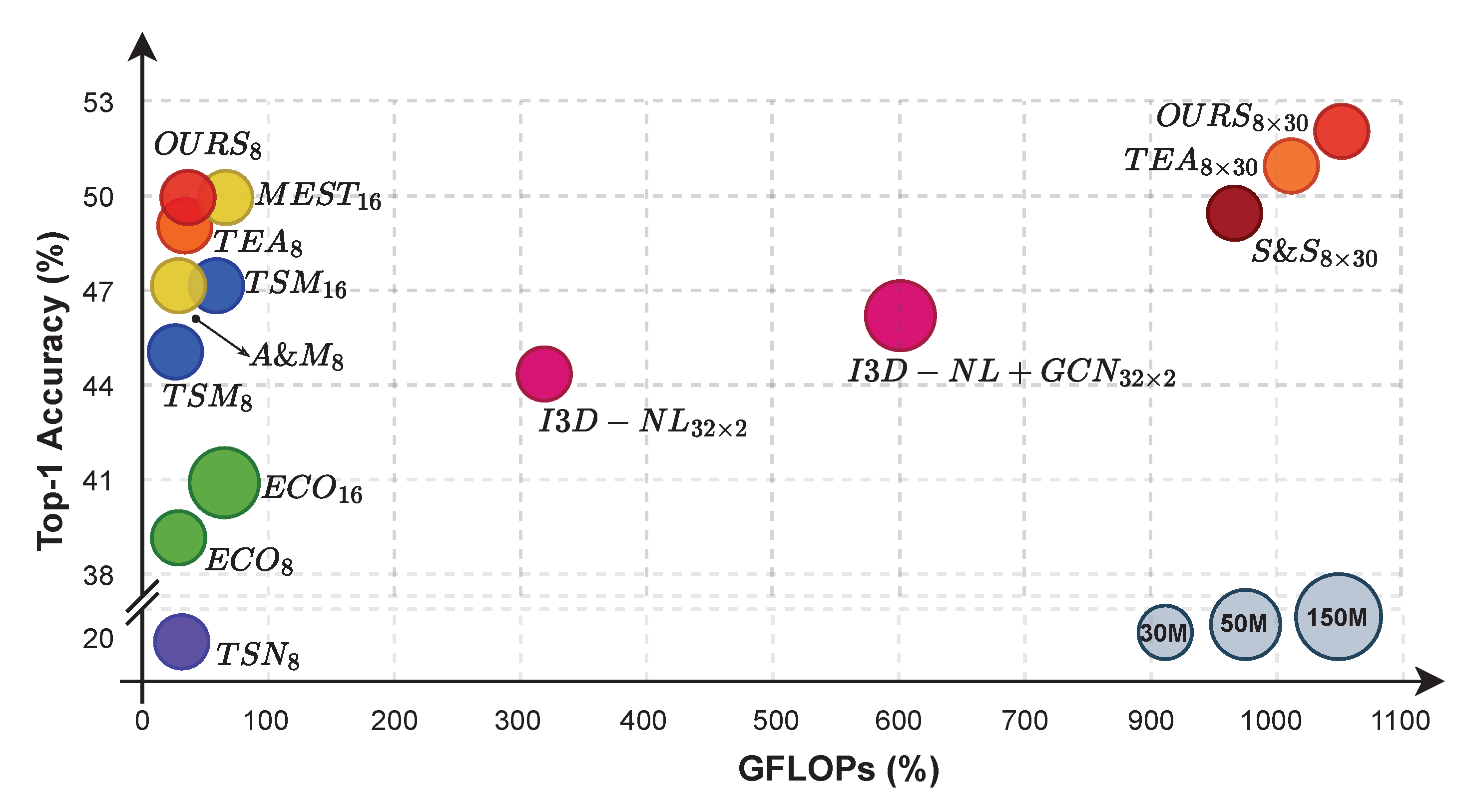
4.3. Results on Benchmarking Datasets
4.3.1. Something-Something V1
4.3.2. Jester
4.3.3. Moments-In-Time Mini
4.3.4. Example of Successful Predictions
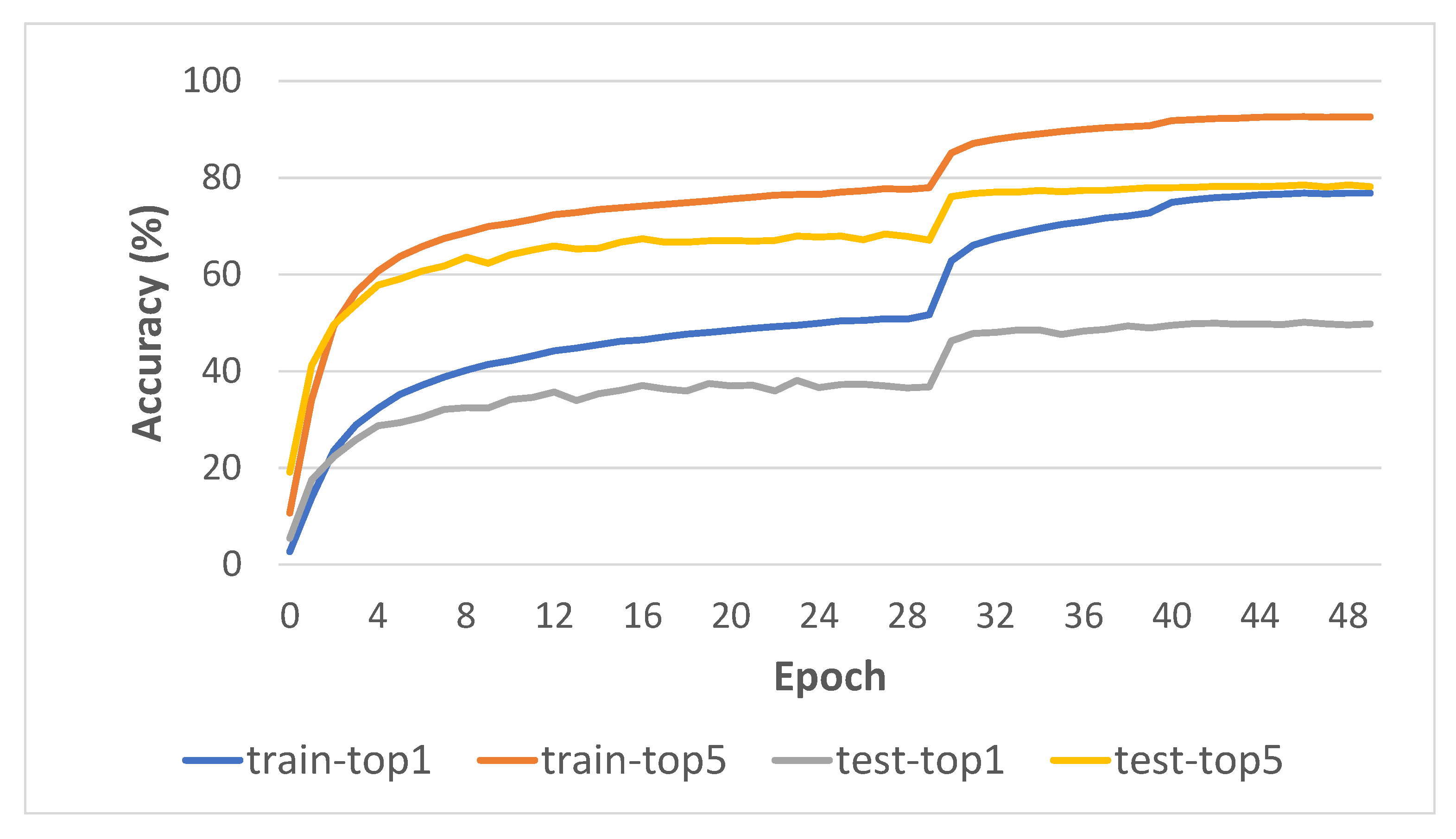
4.3.5. Learning Curve Analysis
4.4. Ablation Study
- Impact of each moduleWe examine how each submodule affects the performance and present the findings in Table 4. It is clear that, in comparison with the baseline, each submodule continuously improves the performance of the 2D ResNet on video action recognition. The DCTA submodule makes the most contribution, improving top-1 accuracy by 2.4% while being computationally efficient with only a 1.7 G overhead gap and the least number of parameters, whereas the other two add 2.0 G of extra FLOPs.
- Location of METAWe examine the number of META implemented inside four convolution blocks toward accuracy. From Table 5, it is evident that better precision can be attained with more profound METAs placed in convolution blocks. Interestingly, META only requires installing one convolution block to dramatically increase the performance, with top-1 and top-5 accuracies exceeding the baseline by 2.6% and 2.9%, respectively.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stroud, J.C.; Ross, D.A.; Sun, C.; Deng, J.; Sukthankar, R. D3D: Distilled 3D Networks for Video Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV 2020, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2018; pp. 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezovský, M.; Sopiak, D.; Oravec, M. Action recognition by 3d convolutional network. In Proceedings of the Elmar-International Symposium Electronics in Marine, Zadar, Croatia, 16–19 September 2018; pp. 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Satoh, Y. Learning spatio-Temporal features with 3D residual networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, ICCVW 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3154–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Van Gool, L. Appearance-and-Relation Networks for Video Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Andonian, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Temporal Relational Reasoning in Videos. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinform. 2017, 11205 LNCS, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Gan, C.; Han, S. TSM: Temporal Shift Module for Efficient Video Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7082–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal Segment Networks: Towards Good Practices for Deep Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Diba, A.; Fayyaz, M.; Sharma, V.; Karami, A.H.; Arzani, M.M.; Yousefzadeh, R.; Gool, L.V. Temporal 3D ConvNets: New Architecture and Transfer Learning for Video Classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.08200. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Yao, T.; Mei, T. Learning Spatio-Temporal Representation with Pseudo-3D Residual Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5534–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; Lecun, Y.; Paluri, M. A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hou, Z.; Chen, J.; Bu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D.; Pu, S. Team DEEP-HRI Moments in Time Challenge 2018 Technical Report; Hikvision Research Institute: Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arunnehru, J.; Chamundeeswari, G.; Bharathi, S.P. Human Action Recognition using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks with 3D Motion Cuboids in Surveillance Videos. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 133, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4724–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gupta, A. Videos as Space-Time Region Graphs. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Satoh, Y. Can Spatiotemporal 3D CNNs Retrace the History of 2D CNNs and ImageNet? In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–27 July 2017; pp. 6546–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Kai, L.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2014, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Hao, S. I3D-LSTM: A New Model for Human Action Recognition. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 569, 32035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joefrie, Y.Y.; Aono, M. Action Recognition by Composite Deep Learning Architecture I3D-DenseLSTM. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference of Advanced Informatics: Concepts, Theory and Applications (ICAICTA), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 20–21 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutegeki, R.; Han, D.S. A CNN-LSTM Approach to Human Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Fukuoka, Japan, 19–21 February 2020; pp. 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Tu, Z.; Murphy, K. Rethinking Spatiotemporal Feature Learning: Speed-Accuracy Trade-offs in Video Classification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Singh, K.; Brox, T. ECO: Efficient Convolutional Network for Online Video Understanding. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Incl. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinform. 2018, 11206, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; Malik, J.; He, K. Slowfast Networks for Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, P.; Gao, X.; Xu, T.; Wu, J.; He, X. Attention in Attention: Modeling Context Correlation for Efficient Video Classification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 7120–7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla-Lara, L.; Liao, Y.; Güney, F.; Jampani, V.; Geiger, A.; Black, M.J. On the Integration of Optical Flow and Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; Brox, T., Bruhn, A., Fritz, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelbaky, A.; Aly, S. Two-stream spatiotemporal feature fusion for human action recognition. Vis. Comput. 2021, 37, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Pinz, A.; Wildes, R. Spatiotemporal Multiplier Networks for Video Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zach, C.; Pock, T.; Bischof, H. A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L 1 Optical Flow. In Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Gool, L.V. Temporal Segment Networks for Action Recognition in Videos. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 2740–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.; Wu, W.; Yan, J. STM: Spatiotemporal and motion encoding for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Ji, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Kang, B.; Wang, L. TEA: Temporal Excitation and Aggregation for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; She, Q.; Smolic, A. ACTION-Net: Multipath Excitation for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13209–13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. MEST: An Action Recognition Network with Motion Encoder and Spatio-Temporal Module. Sensors 2022, 22, 6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Lu, T.; Zhou, H. A Spatio-Temporal Motion Network for Action Recognition Based on Spatial Attention. Entropy 2022, 24, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnab, A.; Dehghani, M.; Heigold, G.; Sun, C.; Lucic, M.; Schmid, C. ViViT: A Video Vision Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6816–6826. [Google Scholar]
- Bertasius, G.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L. Is Space-Time Attention All You Need for Video Understanding? In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T.D.; Bui, Q.H.; Duong, C.N.; Seo, H.S.; Phung, S.L.; Li, X.; Luu, K. DirecFormer: A Directed Attention in Transformer Approach to Robust Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Gao, P.; Song, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y. UniFormer: Unified Transformer for Efficient Spatiotemporal Representation Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.04676. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yan, Y.; Min, X.; Lu, G.; Zhai, G.; Guo, G.; Gao, Z. EAN: Event Adaptive Network for Enhanced Action Recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Torr, P. Res2Net: A New Multi-scale Backbone Architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Kahou, S.E.; Michalski, V.; Materzynska, J.; Westphal, S.; Kim, H.; Haenel, V.; Fründ, I.; Yianilos, P.; Mueller-Freitag, M.; et al. The “something something” video database for learning and evaluating visual common sense. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5843–5851. [Google Scholar]
- Materzynska, J.; Berger, G.; Bax, I.; Memisevic, R. The Jester Dataset: A Large-Scale Video Dataset of Human Gestures. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Monfort, M.; Andonian, A.; Zhou, B.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Bargal, S.A.; Yan, T.; Brown, L.; Fan, Q.; Gutfreund, D.; Vondrick, C.; et al. Moments in Time Dataset: One Million Videos for Event Understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goyal, P.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; Noordhuis, P.; Wesolowski, L.; Kyrola, A.; Tulloch, A.; Jia, Y.; Facebook, K.H. Accurate, Large Minibatch SGD: Training ImageNet in 1 Hour. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, M.; Unterthiner, T.; Kornblith, S.; Zhang, C.; Dosovitskiy, A. Do Vision Transformers See Like Convolutional Neural Networks? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12116–12128. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D. Trimmed Event Recognition (Moments in Time): Submission to ActivityNet Challenge 2018. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/1801.03150 (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Guan, S.; Li, H. SYSU iSEE Submission to Moments in Time Challenge 2018; Technical Report; School of Data and Computer Science Sun Yat-Sen University: Guangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | Backbone | Pre-Train | Inputs | FLOPs | Param. | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-Dimensional CNNs: ECO RGB from [6] | BNInception | Kinetics | 8 × 1 × 1 | 32.0 G | 47.5 M | 39.6 | – |
| ECO RGB from [6] | [1.2px]+ 3D RN-18 | 16 × 1 × 1 | 64.0 G | 47.5 M | 41.4 | – | |
| I3D NL RGB [14] | 3D RN-50 | ImgNet | 32 × 1 × 2 | 168.0 G × 2 | 35.3 M | 44.4 | 76.0 |
| I3D NL+GCN RGB [14] | [1.2px]+ Kinetics | 303.0 G × 2 | 62.2 M | 46.1 | 76.8 | ||
| Two-Dimensional CNNs: TSM RGB [6] | 2D RN-50 | ImgNet | 8 × 1 × 1 | 33.0 G | 24.3 M | 45.6 | 74.2 |
| TSM RGB | 16 × 1 × 1 | 65.0 G | 24.3 M | 47.2 | 77.1 | ||
| TSN from [6] | 8 × 1 × 1 | 33.0 G | 24.3 M | 19.7 | 46.4 | ||
| STM [32] | 8 × 3 × 10 | 33.3 G × 30 | 24.0 M | 49.2 | 79.3 | ||
| STM | 16 × 3 × 10 | 67.0 G × 30 | 24.0 M | 50.7 | 80.4 | ||
| TEA [33] | 8 × 1 × 1 | 35.1 G 2 | 26.1 M 2 | 48.9 | 78.1 | ||
| TEA | 8 × 3 × 10 | 35.1 G × 30 2 | 26.1 M 2 | 51.7 | 80.5 | ||
| ACTION-NET [34] | 8 × 1 × 1 | 34.7 G | 28.1 M | 47.2 3 | 75.2 3 | ||
| MEST [35] | 8 × 1 × 1 | 34.0 G | 25.7 M | 47.8 | 77.1 | ||
| MEST | 16 × 1 × 1 | 67.0 G | 25.7 M | 50.1 | 79.1 | ||
| AIA TSM [26] | 8 × 1 × 1 | 33.1 G | 23.9 M | 49.2 | 77.5 | ||
| SMNet [36] | 8 × 3 × 10 | 33.1 G × 30 | 23.9 M | 49.8 | 79.6 | ||
| Transformers: | |||||||
| UniFormer-B [40] | Transformer | Kinetics | 16 × 1 × 1 | 96.7 G | 49.7 M | 55.4 | 82.9 |
| UniFormer-S [40] | 41.8 G | 21.3 M | 53.8 | 81.9 | |||
| EAN RGB+LMC [41] | Transformer + 2D RN-50 | ImgNet | (8 × 5) × 1 × 1 | 37.0 G | 36.0 M 1 | 53.4 | 81.1 |
| Ours: | |||||||
| META | 2D RN-50 | ImgNet | 8 × 1 × 1 | 35.6 G | 26.6 M | 50.1 | 78.5 |
| META | 8 × 3 × 1 | 35.6 G × 3 | 26.6 M | 51.0 | 79.3 | ||
| META | 8 × 3 × 10 | 35.6 G × 30 | 26.6 M | 52.1 | 80.2 |
| Methods | FLOPs × Views | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Dimensioal ResNet-50: | |||
| TSM [6] | 33.0 G × 2 | 97.0 | 99.9 |
| TSN from [6] | – | 83.9 | 99.6 |
| STM [32] | 33.3 G × 30 | 96.6 | 99.9 |
| TEA from [34] | – | 96.5 | 99.8 |
| ACTION-NET [34] | 34.7 G × 30 | 97.1 | 99.8 |
| MEST [35] | 34.0 G × 2 | 96.6 | 99.9 |
| Transformers: | |||
| ViViT-L/16x2 320 [37] from [39] | – | 81.7 | 93.8 |
| TimeSFormer [38] from [39] | – | 94.1 | 99.2 |
| DirecFormer [39] | 196.0 G × 3 | 98.2 | 99.6 |
| META (Ours) | 35.6 G × 30 | 97.1 | 99.8 |
| Methods | Backbone | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRN from [49] | BNInception + InceptionV3 | 26.1 | 48.5 |
| P3D from [49] | P3D ResNet | 14.7 | 33.4 |
| P3D-Kinetics from [50] | P3D ResNet | 26.3 | – |
| IR-Kinetics from [50] | Inception-ResNetV2 | 30.3 | – |
| I3D-DenseLSTM [19] | I3D + ResNext | 26.5 | 52.4 |
| META (Ours) | 2D ResNet-50 | 27.4 | 53.2 |
| Methods | FLOPs | Param. | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSM [6] | 33.0 G | 23.7 M | 45.6 | 74.2 |
| ME | 35.0 G | 26.1 M | 47.9 | 77.8 |
| MvE | 35.0 G | 26.1 M | 46.3 | 76.9 |
| DCTA | 34.7 G | 25.7 M | 48.0 | 77.0 |
| META | 35.6 G | 26.6 M | 50.1 | 78.5 |
| Location | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) | Δ Top-1 (%) | Δ Top-5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSM [6] | 45.6 | 74.2 | – | – |
| conv{2}_x | 48.2 | 77.1 | +2.6 | +2.9 |
| conv{2,3}_x | 49.5 | 78.1 | +3.9 | +3.9 |
| conv{2,3,4}_x | 49.9 | 78.2 | +4.3 | +4.0 |
| META | 50.1 | 78.5 | +4.5 | +4.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joefrie, Y.Y.; Aono, M. Video Action Recognition Using Motion and Multi-View Excitation with Temporal Aggregation. Entropy 2022, 24, 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111663
Joefrie YY, Aono M. Video Action Recognition Using Motion and Multi-View Excitation with Temporal Aggregation. Entropy. 2022; 24(11):1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111663
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoefrie, Yuri Yudhaswana, and Masaki Aono. 2022. "Video Action Recognition Using Motion and Multi-View Excitation with Temporal Aggregation" Entropy 24, no. 11: 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111663
APA StyleJoefrie, Y. Y., & Aono, M. (2022). Video Action Recognition Using Motion and Multi-View Excitation with Temporal Aggregation. Entropy, 24(11), 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111663








