Interaction between an Impurity and Nonlinear Excitations in a Polariton Condensate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Theoretical Model and Lagrangian Approach
3. Interaction between an Impurity and a Bright Soliton
- (i)
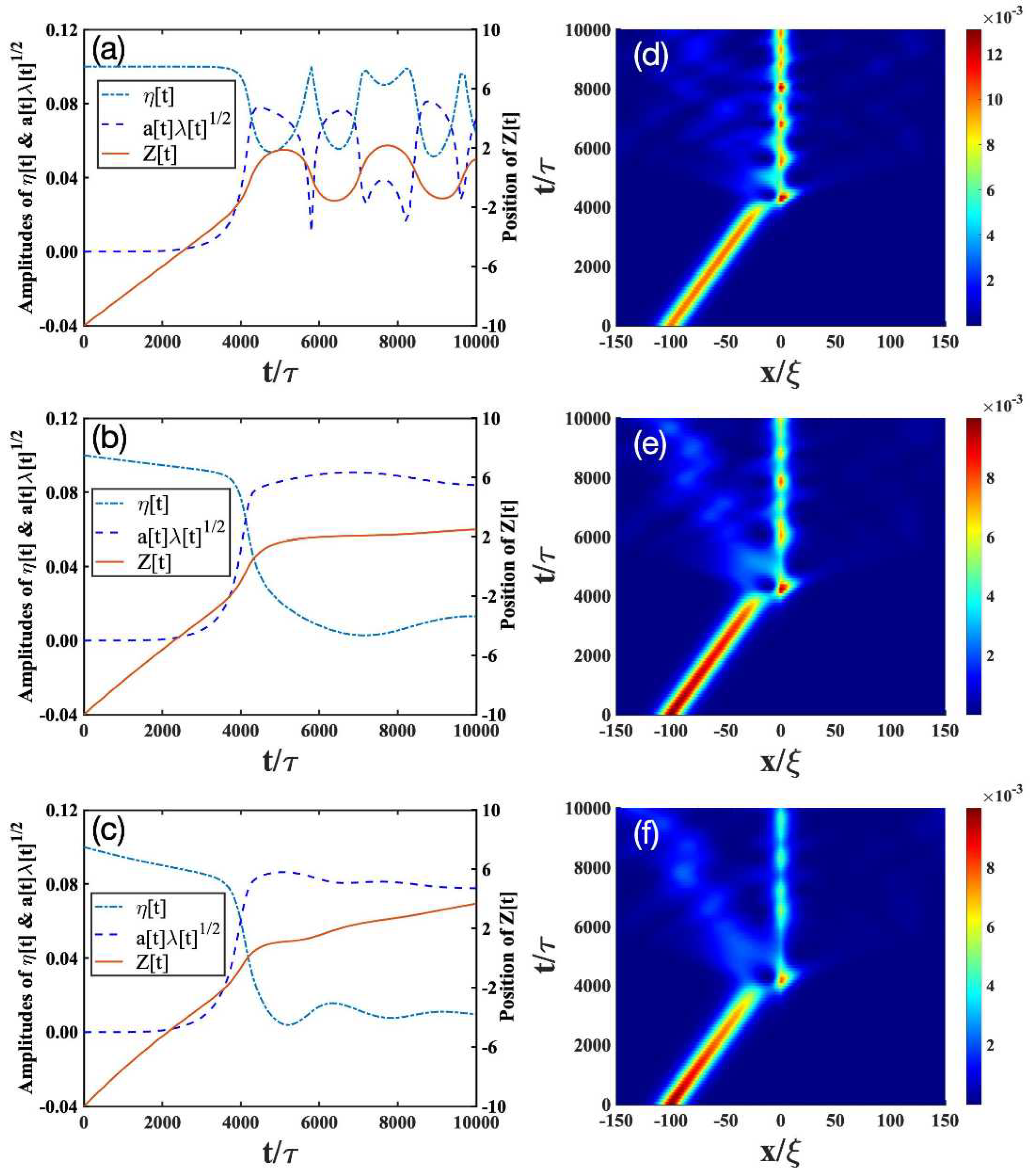
- Transmission scenario: As mentioned before, in the absence of dissipation (Figure 1a), the bright soliton can simply pass through a light impurity (), almost unaffected by the latter. The dotted lines in Figure 1a denotes the amplitude of the impurity. There, the appearance of the maximal amplitude of the impurity indicates that the impurity mode can be excited during the collision with the bright soliton, but after the collision, the excitation returns to a very small level. This analysis is consistent with Figure 1d obtained from the numerical simulation of Equation (6). Thus, we conclude that the analytical results in Equations (11a)–(11g) not only provide a good solution to Equation (6), but also allow us to follow independently the evolution of the bright soliton and the impurity. In the presence of dissipation, the amplitude of soliton gradually decreases after the collision with the impurity; see the solid lines in Figure 1b,c. These results are consistent with the full numerical simulations in Figure 1e,f. Comparing Figure 1b,c, therefore, we see that the soliton amplitude decays faster when the dissipation parameter increases.
- (ii)
- Trapping scenario: In the absence of dissipation (Figure 2a,d), the bright soliton can be trapped by an impurity with a moderate mass (), as indicated by the position of the bright soliton (solid lines in Figure 2a). Furthermore, the impurity mode (dashed lines in Figure 2a) is strongly excited and begins to oscillate, whereas the soliton amplitude (dashed-dotted lines in Figure 2a) decreases drastically. This result is verified by the numerical simulations in Figure 2d. In the presence of dissipation (Figure 2b,c,e,f), the bright soliton can still be trapped by the impurity, but the oscillating behavior of the bright soliton begins to disappear. This can be understood, as the dissipation will destroy the low-energy excitations generated from the collisions of the bright soliton and the impurity.
- (iii)
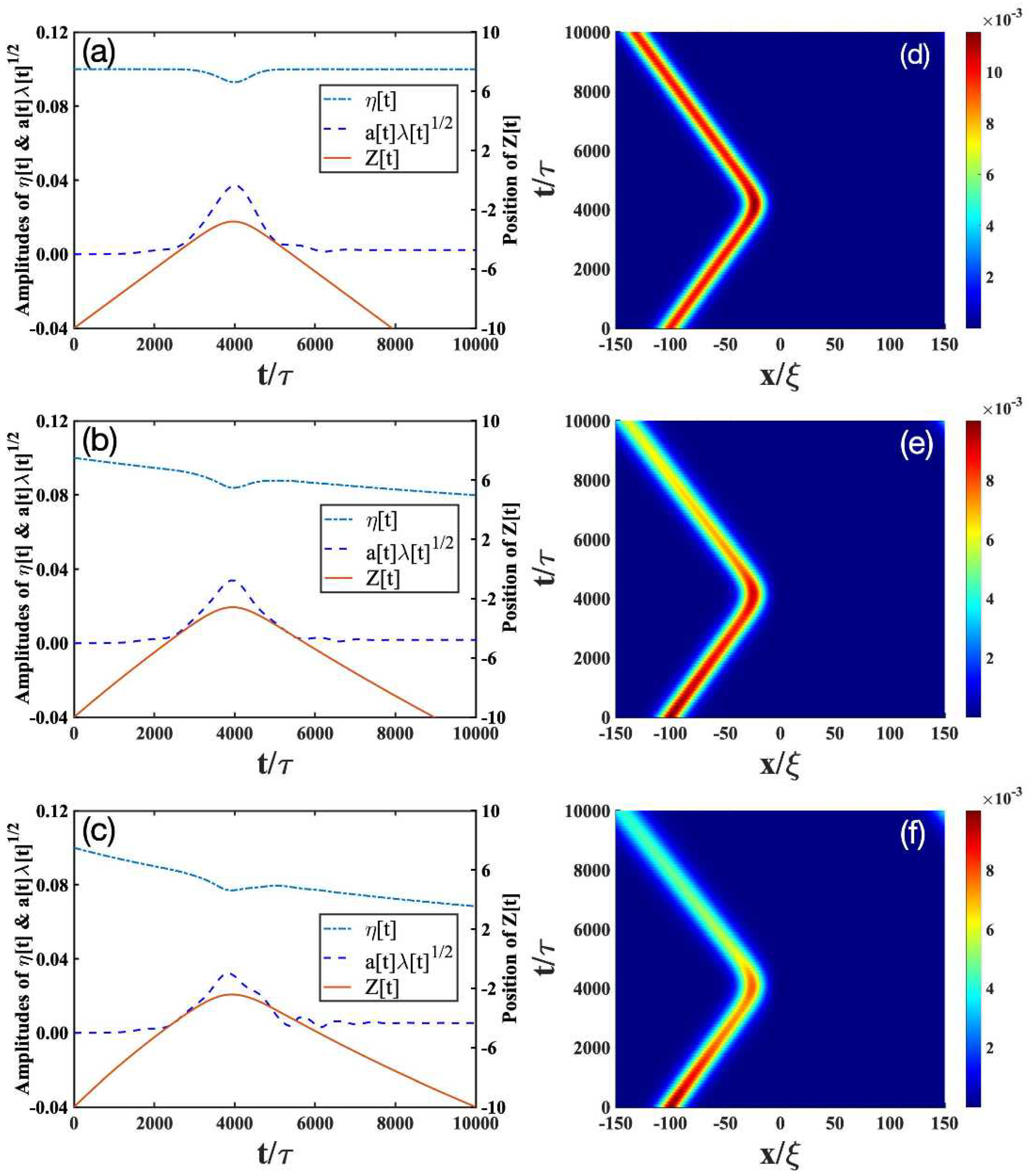
- Reflection scenario: In the absence of dissipation (Figure 3a,d), the bright soliton can be reflected by a heavy impurity (). In contrast to the above transmission and trapping scenarios, dissipation has relatively small effects on the reflection scenario, as shown in Figure 3b,d–f. This can be expected, because the heavier the impurity is, the less excitations are created from the collisions.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landau, L.D. The Movement of Electrons in the Crystal Lattice. Phys. Z. Sowjetunion 1933, 3, 644. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Pekar, S.I. Effective Mass of a Polaron. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1948, 18, 419. [Google Scholar]
- Hewson, A.C. The Kondo Problem to Heavy Fermions; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bolotovskii, B.M. Vavilov–Cherenkov radiation: Its discovery and application. Phys.-Uspekhi 2009, 52, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carusotto, I.; Hu, S.X.; Collins, L.A.; Smerzi, A. Bogoliubov-Čerenkov Radiation in a Bose-Einstein Condensate Flowing against an Obstacle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 260403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharam, K.; Shchadilova, Y.; Grusdt, F.; Zvonarev, M.B.; Demler, E. Dynamical Quantum Cherenkov Transition of Fast Impurities in Quantum Liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 185302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, G. Many-Particle Physics; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Astrakharchik, G.E.; Boronat, J.; Casulleras, J.; Giorgini, S. Superfluidity versus Bose-Einstein condensation in a Bose gas with disorder. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 66, 23603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.; Carusotto, I. Superfluidity and Critical Velocities in Nonequilibrium Bose-Einstein Condensates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 20602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wu, B. Sound speed of a Bose-Einstein condensate in an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 23622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelio, I.; Carusotto, I. Perspectives in superfluidity in resonantly driven polariton fluids. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 101, 64505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.S.; Liang, Z. Drag force of an exciton-polariton condensate under nonresonant pumping. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevy, F.; Mora, C. Ultra-cold polarized Fermi gases. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2010, 73, 112401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massignan, P.; Zaccanti, M.; Bruun, G.M. Polarons, dressed molecules and itinerant ferromagnetism in ultracold Fermi gases. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2014, 77, 34401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlong, H.S.; Liu, W.E.; Scazza, F.; Zaccanti, M.; Oppong, N.D.; Fölling, S.; Parish, M.M.; Levinsen, J. Quasiparticle Lifetime of the Repulsive Fermi Polaron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 133401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Knap, M.; Ivanov, D.A.; You, J.S.; Cetina, M.; Demler, E. Universal many-body response of heavy impurities coupled to a Fermi sea: A review of recent progress. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2018, 81, 24401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.B.; Wacker, L.; Skalmstang, K.T.; Parish, M.M.; Levinsen, J.; Christensen, R.S.; Bruun, G.M.; Arlt, J.J. Observation of Attractive and Repulsive Polarons in a Bose-Einstein Condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 55302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.G.; Van de Graaff, M.J.; Kedar, D.; Corson, J.P.; Cornell, E.A.; Jin, D.S. Bose Polarons in the Strongly Interacting Regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 55301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.Z.; Ni, Y.; Robens, C.; Zwierlein, M.W. Bose polarons near quantum criticality. Science 2020, 368, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisht, A.; Richard, M.; Minguzzi, A. Bose polaron in a quantum fluid of light. SciPost Phys. 2022, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flayac, H.; Solnyshkov, D.D.; Shelykh, I.A.; Malpuech, G. Transmutation of Skyrmions to Half-Solitons Driven by the Nonlinear Optical Spin Hall Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 16404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.; Carusotto, I. Excitations in a Nonequilibrium Bose-Einstein Condensate of Exciton Polaritons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 140402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, M.H.; Keeling, J.; Littlewood, P.B. Nonequilibrium Quantum Condensation in an Incoherently Pumped Dissipative System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 230602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, T.; Horikiri, T.; Ishida, N.; Fraser, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Negative Bogoliubov dispersion in exciton-polariton condensates. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 75130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z. Spinor polariton condensates under nonresonant pumping: Steady states and elementary excitations. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 144511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczarka, M.; Syperek, M.; Dusanowski, L.; Misiewicz, J.; Langer, F.; Forchel, A.; Kamp, M.; Schneider, C.; Höfling, S.; Kavokin, A.; et al. Ghost Branch Photoluminescence From a Polariton Fluid Under Nonresonant Excitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 186401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janot, A.; Hyart, T.; Eastham, P.R.; Rosenow, B. Superfluid Stiffness of a Driven Dissipative Condensate with Disorder. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 230403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, J. Superfluid Density of an Open Dissipative Condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 080402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Regemortel, M.; Wouters, M. Negative drag in nonequilibrium polariton quantum fluids. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 85303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladilin, V.N.; Wouters, M. Normal and superfluid fractions of inhomogeneous nonequilibrium quantum fluids. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 134511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juggins, R.T.; Keeling, J.; Szymańska, M.H. Coherently driven microcavity-polaritons and the question of superfluidity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Nardin, G.; Morier-Genoud, F.; Léger, Y.; Deveaud-Plédran, B. Soliton Instabilities and Vortex Street Formation in a Polariton Quantum Fluid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 245301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmerov, A.R. Topological quantum computation away from the ground state using Majorana fermions. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 20509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amo, A.; Pigeon, S.; Sanvitto, D.; Sala, V.G.; Hivet, R.; Carusotto, I.; Pisanello, F.; Lemenager, G.; Houdre, R.; Giacobino, E.; et al. Polariton Superfluids Reveal Quantum Hydrodynamic Solitons. Science 2011, 332, 1167–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barland, S.; Giudici, M.; Tissoni, G.; Tredicce, J.R.; Brambilla, M.; Lugiato, L.; Prati, F.; Barbay, S.; Kuszelewicz, R.; Ackemann, T.; et al. Solitons in semiconductor microcavities. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvitto, D.; Kéna-Cohen, S. The road towards polaritonic devices. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sich, M.; Krizhanovskii, D.N.; Skolnick, M.S.; Gorbach, A.V.; Hartley, R.; Skryabin, D.V.; Cerda-Méndez, E.A.; Biermann, K.; Hey, R.; Santos, P.V. Observation of bright polariton solitons in a semiconductor microcavity. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, E.; Ferrier, L.; Solnyshkov, D.D.; Johne, R.; Sanvitto, D.; Lemaître, A.; Sagnes, I.; Grousson, R.; Kavokin, A.V.; Senellart, P.; et al. Spontaneous formation and optical manipulation of extended polariton condensates. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, J.; Berloff, N.G. Spontaneous Rotating Vortex Lattices in a Pumped Decaying Condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 250401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, L.A.; Smirnova, D.A.; Ostrovskaya, E.A.; Kivshar, Y.S. Dynamics and stability of dark solitons in exciton-polariton condensates. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 235310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.F.; Xue, J.K.; Zhuang, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, W.M. Non-Hermitian spectrum and multistability in exciton-polariton condensates. Phys. Rev. B 2021, 104, 235408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, S.; Kumar, R.K.; Radha, R.; Muruganandam, P. Stability window of trapless polariton Bose-Einstein condensates. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 105, 224315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofolini, P.; Dreismann, A.; Christmann, G.; Franchetti, G.; Berloff, N.G.; Tsotsis, P.; Hatzopoulos, Z.; Savvidis, P.G.; Baumberg, J.J. Optical Superfluid Phase Transitions and Trapping of Polariton Condensates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 186403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitnik, K.A.; Alyatkin, S.; Töpfer, J.D.; Gnusov, I.; Cookson, T.; Sigurdsson, H.; Lagoudakis, P.G. Spontaneous Formation of Time-Periodic Vortex Cluster in Nonlinear Fluids of Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 237402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerna, R.; Sarchi, D.; Paraïso, T.K.; Nardin, G.; Léger, Y.; Richard, M.; Pietka, B.; El Daif, O.; Morier-Genoud, F.; Savona, V.; et al. Coherent optical control of the wave function of zero-dimensional exciton polaritons. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 121309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sigurdsson, H.; Töpfer, J.D.; Lagoudakis, P.G. Reservoir optics with exciton-polariton condensates. Phys. Rev. B 2021, 104, 235306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivshar, Y.S.; Królikowski, W. Lagrangian approach for dark solitons. Opt. Commun. 1995, 114, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, G.; Schmelcher, P.; Oberthaler, M.K.; Kevrekidis, P.G.; Frantzeskakis, D.J. Lagrangian approach to the dynamics of dark matter-wave solitons. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 23609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, C.; Liang, Z. Dynamics of Two Dark Solitons in a Polariton Condensate. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2022, 39, 20501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.Y.; Liang, Z.X. Dark Soliton of Polariton Condensates under Nonresonant PT-Symmetric Pumping. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2020, 37, 40502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z. Dark–bright solitons in spinor polariton condensates under nonresonant pumping. J. Phys. B 2018, 52, 025303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forinash, K.; Peyrard, M.; Malomed, B. Interaction of discrete breathers with impurity modes. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 3400–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrakharchik, G.E.; Pitaevskii, L.P. Motion of a heavy impurity through a Bose-Einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, C.; Liang, Z. Interaction between an Impurity and Nonlinear Excitations in a Polariton Condensate. Entropy 2022, 24, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121789
Jia C, Liang Z. Interaction between an Impurity and Nonlinear Excitations in a Polariton Condensate. Entropy. 2022; 24(12):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121789
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Chunyu, and Zhaoxin Liang. 2022. "Interaction between an Impurity and Nonlinear Excitations in a Polariton Condensate" Entropy 24, no. 12: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121789
APA StyleJia, C., & Liang, Z. (2022). Interaction between an Impurity and Nonlinear Excitations in a Polariton Condensate. Entropy, 24(12), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24121789




