Quantum Stream Cipher Based on Holevo–Yuen Theory
Abstract
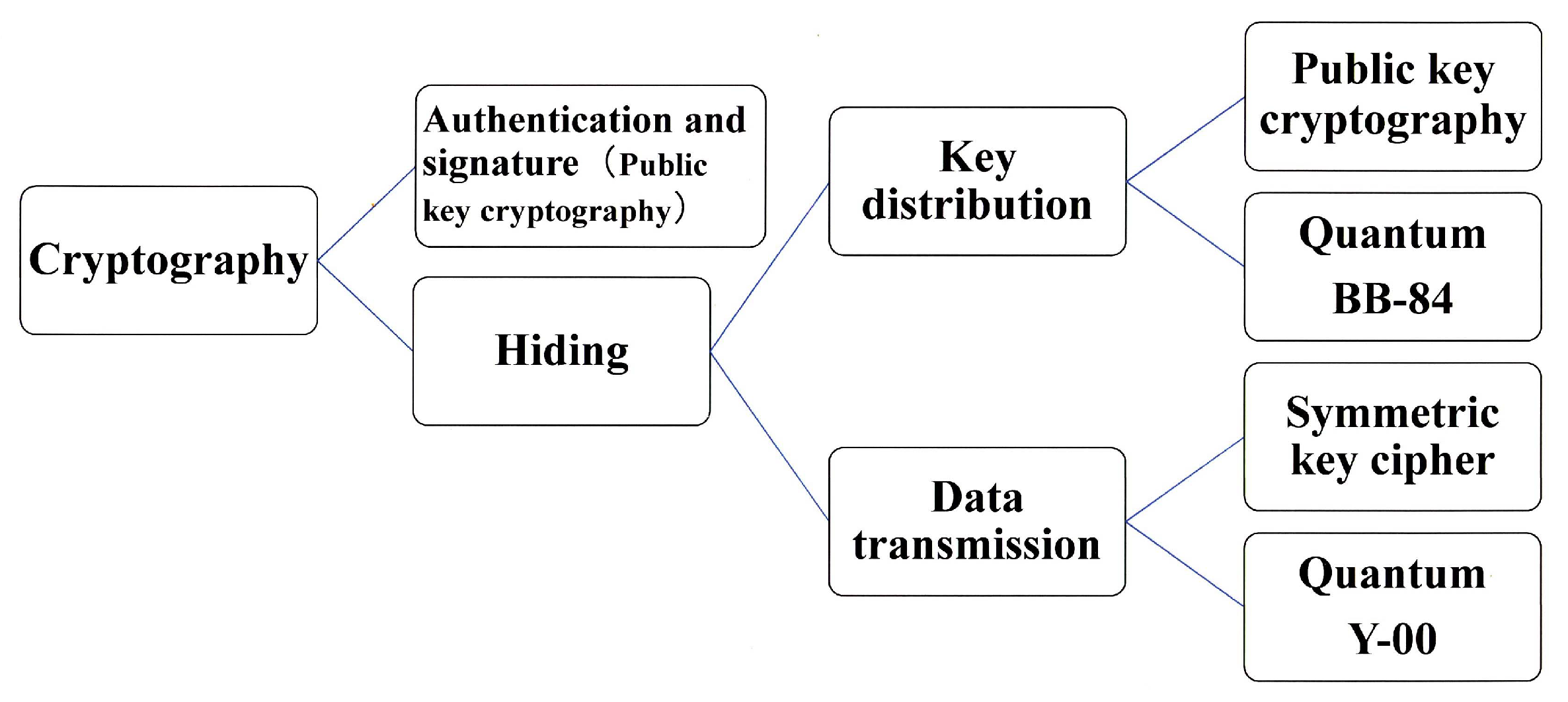
:1. General View of Cryptography or Cipher in Social Network Systems
2. Current Status of Quantum Communication Security Technology
2.1. Quantum Cryptography
- (1)
- Quantum Key Distribution
- (2)
- Quantum Stream Cipher
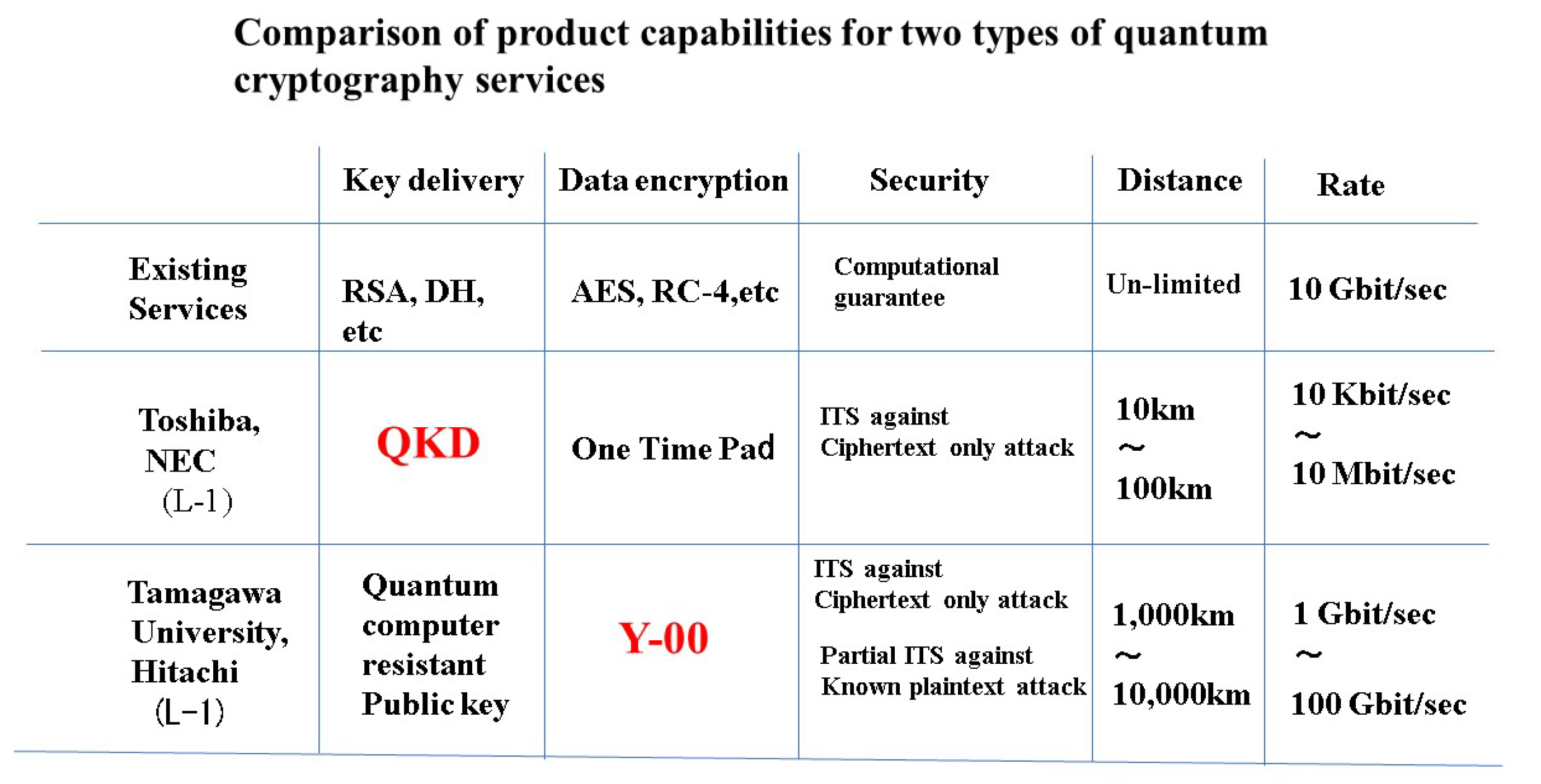
2.2. Comparison of Services Based on Each Quantum Cryptosystem
3. Feature of Quantum Stream Cipher
3.1. Basic Scheme
3.2. Progress in Security Theory
4. Survey of the Mathematical Security Analysis
4.1. The Main Story of Security
4.2. Randomization Technology
5. Concrete Applications of Quantum Stream Cipher
5.1. Optical Fiber Communication
5.2. Optical Satellite Communication
5.3. Optical Communication from Base on the Moon to Earth
6. Future Outlook and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Explanation of Symbols
- (a) Conventional cipher:
- X is plaintext; , is secret key, is running key; ,
- C is ciphertext; .
- (b) Y-00 quantum stream cipher:
- X is plaintext; , is secret key, is running key of PRNG; ,
- Y-00 running key is ; ,
- Y-00 ciphertext is ; ,
- is additional randomization,
- Y-00 signal (quantum) is ,
- is binary representation of Y-00 ciphertext;,
- is ciphertext received by eavesdropper; , is the true random sequence.
Appendix A. Simple Explanation of Y-00 Principle
Appendix B. Quantum Computer and Quantum-Computer-Resistant Cryptography
Appendix C. Advanced Quantum Detection and Estimation Theory
References
- Tsujii, S. The Fight against Fakes; Kotoni Publishing Co.: Chiba Prefecture, Japan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, O.; Tsujii, S. Quantum noise analysis for quantum computer. IEICE Jpn. Tech. Rep. Inf. Theory 2021, 121, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, H.P. KCQ: Keyed communication in quantum noise. arXiv 2003, arXiv:0311061. [Google Scholar]
- Holevo, A.S. Statistical decision theory for quantum systems. J. Multivar. Anal. 1973, 3, 337–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuen, H.P.; Kennedy, R.S.; Lax, M. Optimum testing of multiple hypotheses in quantum detection theory. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1975, 21, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, O.; Ikehara, S. Minimax strategy in the quantum detection theory and its application to optical communications. Trans. IEICE Jpn. 1982, 65E, 627. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K. Non-orthogonality measures for a collection of pure quantum states. Entropy 2022, 24, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbosa, G.A.; Corndorf, E.; Kumar, P.; Yuen, H.P. Secure communication using mesoscopic coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 227901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanter, G.S.; Reillly, D.; Smith, N. Practical physical layer encryption:The marriage of optical noise with traditional cryptography. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, O.; Sohma, M.; Fuse, M.; Kato, K. Quantum stream cipher by Yuen 2000 protocol: Design and experiment by intensity modulation scheme. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 022335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohhata, K.; Hirota, O.; Honda, M.; Akutsu, S.; Doi, Y.; Harasawa, K.; Yamashita, K. 10 Gbit/s optical transceiver using the Yuen 2000 encryption protocol. IEEE. J. Lightw. Technol. 2010, 28, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Yuen, H.P.; Corndolf, E.; Kumar, P. Quantum noise randomized ciphers. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 74, 052309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, O.; Kurosawa, K. Immunity against correlation attack on quantum stream cipher by Yuen 2000 protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. 2007, 6, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, O. Practical security analysis of quantum stream cipher by Yuen protocol. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 032307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, H.P. Key generation: Foundation and new quantum approach. IEEE Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2009, 15, 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shor, P.; Preskill, J. Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renner, R. Security of quantum key distribution. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 2008, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, O. Application of quantum Pinsker inequality to quantum communications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.04553. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, H.P.; Nair, R.; Corndorf, E.; Kanter, G.S.; Kumar, P. On the security of αη response to some attacks on quantum-based cryptographic protocols. Quantum Inf. Comput. 2006, 6, 561–582. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, O.; Sohma, M.; Kawanishi, K. Quantum noise randamized stream cipher:Y-00. Jpn. J. Opt. 2010, 39, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Hirota, O. Quantum stream cipher part IV, Effects of the deliberate signal randomization and deliberate error randomization. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Quantum Communciations and Quantum Imaging IV, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2006; Volume 6305. [Google Scholar]
- Futami, F.; Guan, K.; Gripp, J.; Kato, K.; Tanizawa, K.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Winzer, P.J. Y-00 quantum stream cipher overlay in a coherent 256-Gbit/s polarization multiplexed 16-QAM WDM. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 33338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futami, F.; Tanizawa, K.; Kato, K. Y-00 quantum-noise randomized stream cipher using intensity modulation signals for physical layer security of optical communications. IEEE/OSA J. Lightw. Technol. 2020, 38, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizawa, K.; Futami, F. 214 intensity-level 10-Gbaud Y-00 quantum stream cipher enabled by coarse-to-fine modulation. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2018, 30, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizawa, K.; Futami, F. Digital coherent PSK Y-00 quantum stream cipher with 217 randomized phase levels. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizawa, K.; Futami, F. Single channel 48-Gbit/s DP-PSK Y-00 quantum stream cipher transmission over 400- and 800-km SSMF. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 25357–25363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizawa, K.; Futami, F. Quantum noise-assisted coherent radio-over-fiber cipher system for secure optical fronthaul and microwave wireless links. IEEE/OSA J. Lightw. Technol. 2020, 38, 4244–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tanizawa, K.; Winzer, P.; Dong, P.; Cho, J.; Futami, F.; Kato, K.; Melikyan, A.; Kim, K.W. Experimental demonstration of 4,294,967,296-QAM based Y-00 quantum stream cipher template carrying 160-Gb/s 16-QAM signals. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 5658–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizawa, K.; Futami, F. Ultra-long-haul digital coherent PSK Y-00 quantum stream cipher transmission system. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 10451–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, O.; Kato, K.; Sohma, M. Application of Y-00 quantum stream cipher to satellite communication-Mathematical model of weather disturbance. IEICE Jpn. Tech. Rep. Inf. Theory 2022, 121, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- NSA. Quantum Computing and Post-Quantum Cryptography FAQs, National Security Agency Central Security Service. 2021. Available online: https://www.quantum.gov/nsa-updates-faq-on-post-quantum-cybersecurity/?msclkid=525975f1cdce11eca34ea2e9f2b11545 (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Chen, Y.; Jiao, H.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J.; Pu, T. Security analysis of QAM quantum noise randomized cipher system. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 7904114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Pu, T.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J.; Su, G. Performance analysis of physical layer security in ISK quantum noise randomized cipher based on wiretap channel. Opt. Commun. 2020, 461, 125151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Pu, T.; Zheng, J.; Xiang, P.; Fang, T. Physical layer security analysis of a quantum noise randomized cipher based on the wire tap channel model. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, H.; Pu, T.; Zheng, J.; Xiang, P.; Fang, T.; Zhu, H. Physical-layer security analysis of PSK quantum-noise randomized cipher in optically amplified links. Quant. Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Security Analysis of Quantum Noise Stream Cipher under Fast Correlation Attack. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2021; Optical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. DFTs-OFDM based quantum noise stream cipher system. Opt. Commun. 2019, 445, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, H. Single Carrier QAM/QNSC and PSK/QNSC Transmission Systems with Bit Resolution Limited DACs; OECC Technical Digest, 5D1-3; OECC: Camden, AR, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Song, H.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Huang, L.; Cheng, M.; Liu, D.; Deng, L. Secure 100 Gb/s IMDD Transmission Over 100 km SSMF Enabled by Quantum Noise Stream Cipher and Sparse RLS-Volterra Equalizer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 63585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, O. Introduction to semi-classical analysis for digital errors of qubit in quantum prosessor. Entropy 2021, 23, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinc, F.; Bran, A.M. Non-Markovian super-superradiance in a linear chain of up to 100 qubits. Phys Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 032042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, K.; Liu, Z. No-Go Theorems for Quantum Resource Purification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 060405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousba, Y.; Russell, T. No quantum Ramsey theorem for stabilizer codes. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 2021, 67, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiani, M.; Chai, J.; Whitney, R.; Auffeves, A.; Ng, H. Limitations in quantum computing from resource constraints. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.01966. [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson, J.P.; Smeets, B.; Thormarker, E. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.00399. [Google Scholar]
- Helstrom, C.W. Quantum Detection and Estimation Theory; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Momose, R.; Hirota, O. Optimum measurements for discrimination among symmetric quantum states and parameter estimation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1997, 36, 1269–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Enk, S.J. Unambiguous state discrimination of coherent states with linear optics: Application to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 66, 042313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirandola, S. Quantum reading of a classical digital memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 090504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pirandola, S.; Lupo, C.; Giovannetti, V.; Mancini, S.; Braunstein, S.L. Quantum reading capacity. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.G.A. Quantum estimation for quantum technology. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 2009, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahira, K.; Kato, K.; Usuda, T. Minimax strategy in quantum signal detection with inconclusive results. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 032314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahira, K.; Kato, K.; Usuda, T. Generalized quantum state discrimination problems. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 052304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahria, K.; Usuda, T.; Kato, K. Finding Optimal Solutions for Generalized Quantum State Discrimination Problems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahira, K.; Kato, K. Generalized quantum process discrimination problems. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 062606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohma, M.; Hirota, O. Quantum Stream Cipher Based on Holevo–Yuen Theory. Entropy 2022, 24, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24050667
Sohma M, Hirota O. Quantum Stream Cipher Based on Holevo–Yuen Theory. Entropy. 2022; 24(5):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24050667
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohma, Masaki, and Osamu Hirota. 2022. "Quantum Stream Cipher Based on Holevo–Yuen Theory" Entropy 24, no. 5: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24050667
APA StyleSohma, M., & Hirota, O. (2022). Quantum Stream Cipher Based on Holevo–Yuen Theory. Entropy, 24(5), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24050667






