Robust Minimum Divergence Estimation for the Multinomial Circular Logistic Regression Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description
3. The Minimum DPD Estimators under the MCLR Models
4. Simulation Studies
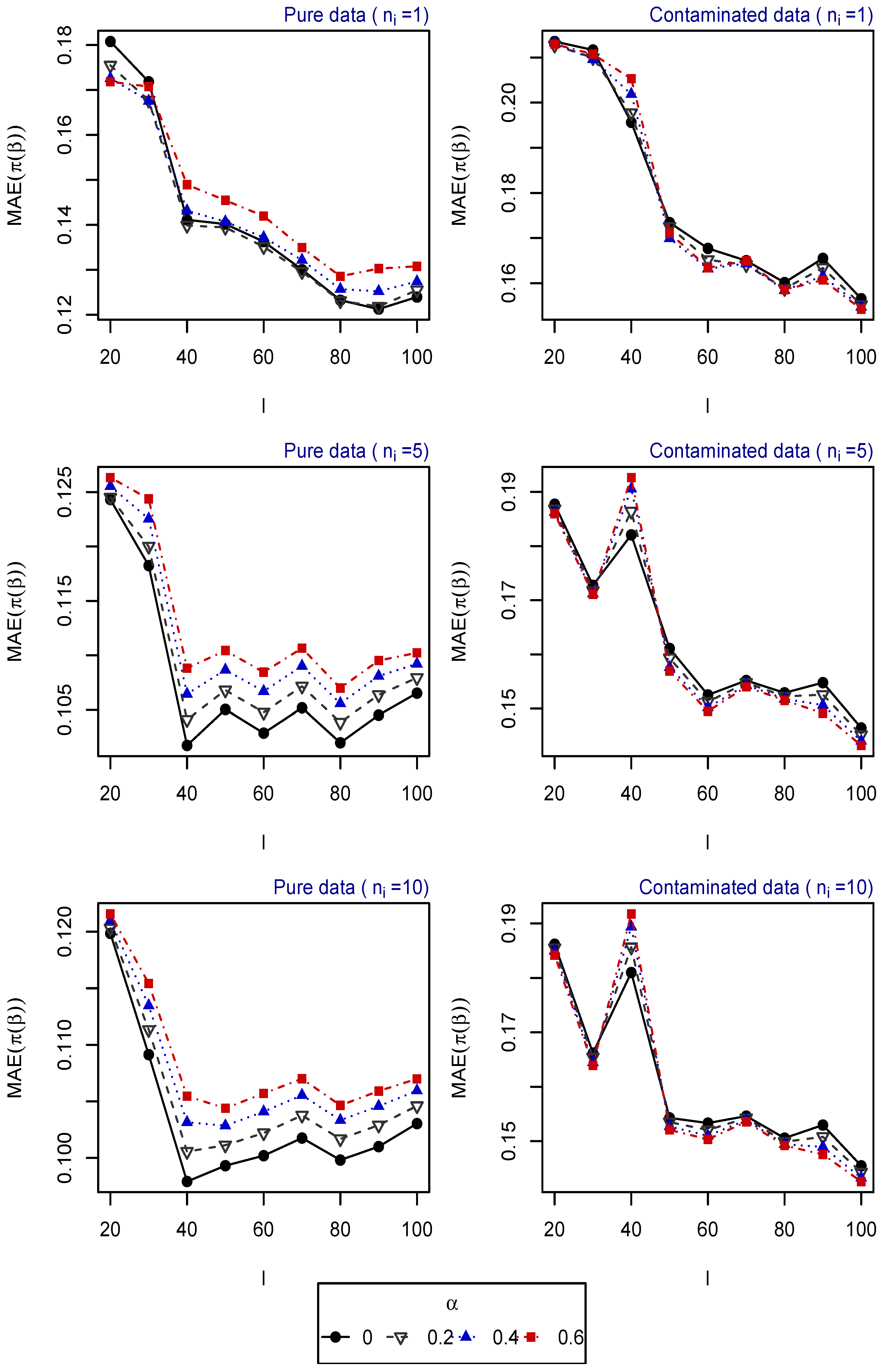
- Scenario 1: , for . Explanatory variables generated from uniform distribution (Figure 1).
- Scenario 2: , for . Explanatory variables generated from uniform distribution (Figure 2).
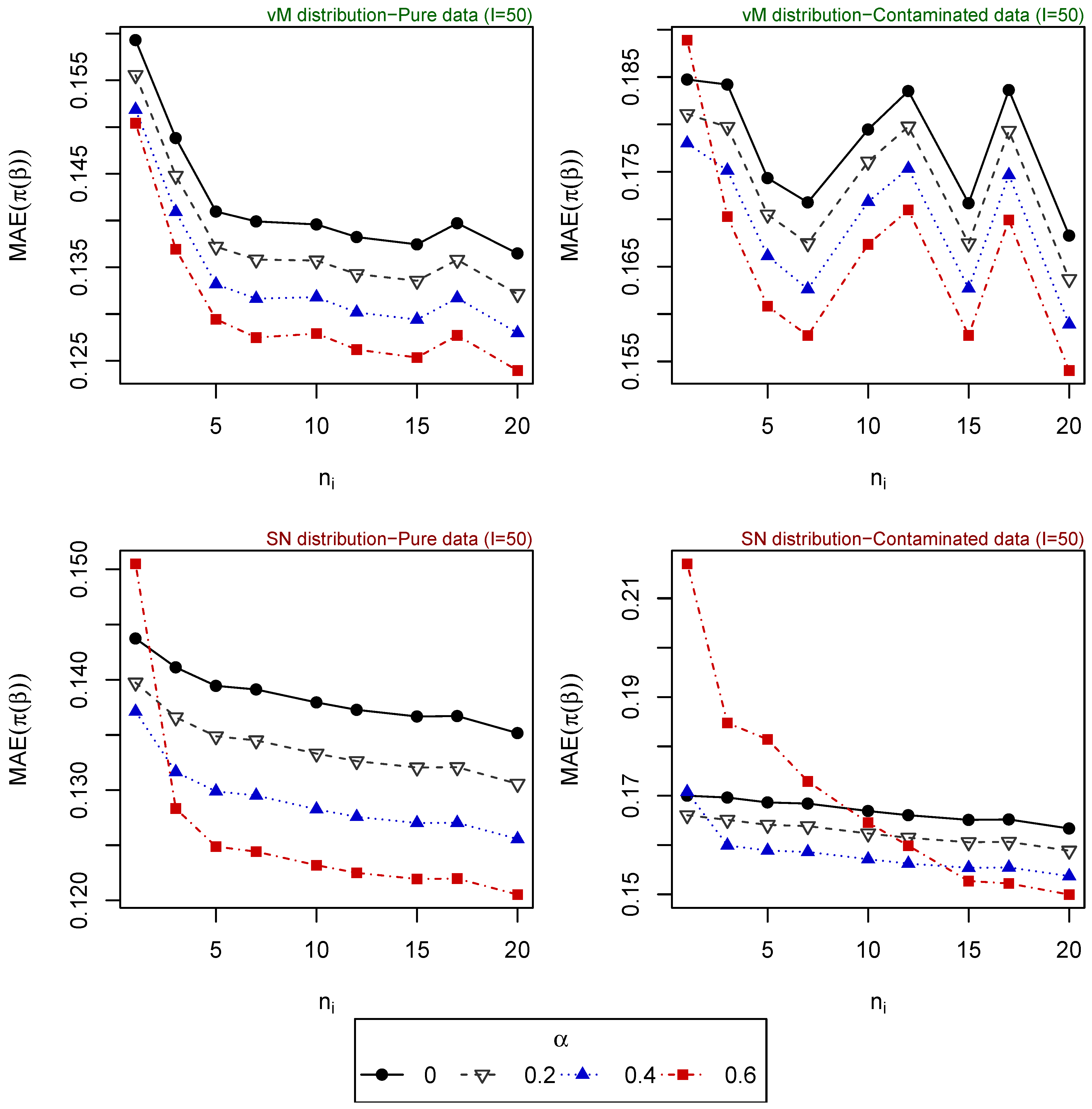
- Scenario 3: , for . Explanatory variables generated from vM distribution (top of Figure 3).
- Scenario 4: , for . Explanatory variables generated from SN distribution (bottom of Figure 3).
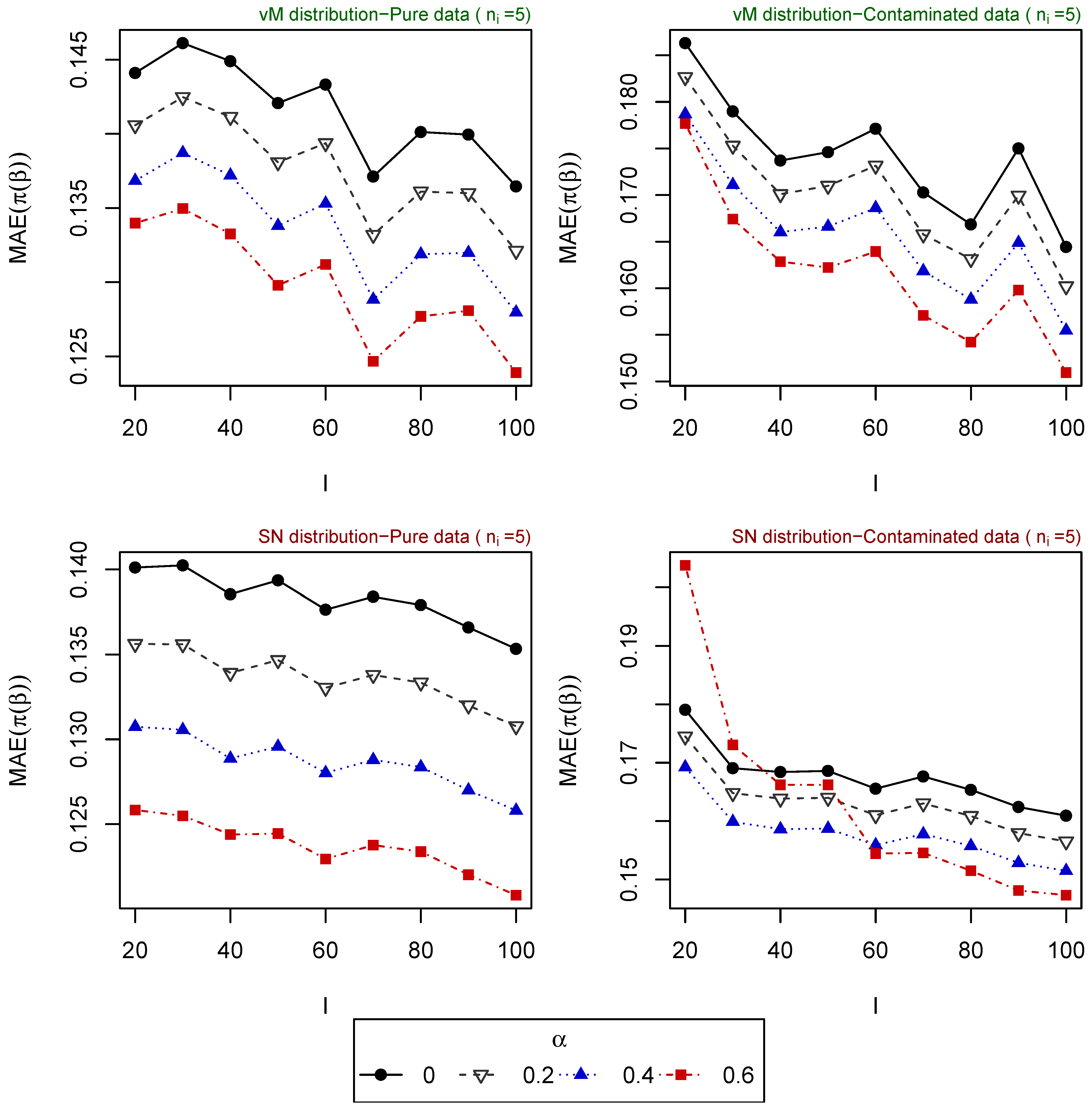
- Scenario 5: , for . Explanatory variables generated from vM distribution (top of Figure 4).
- Scenario 6: , for . Explanatory variables generated from SN distribution (bottom of Figure 4).
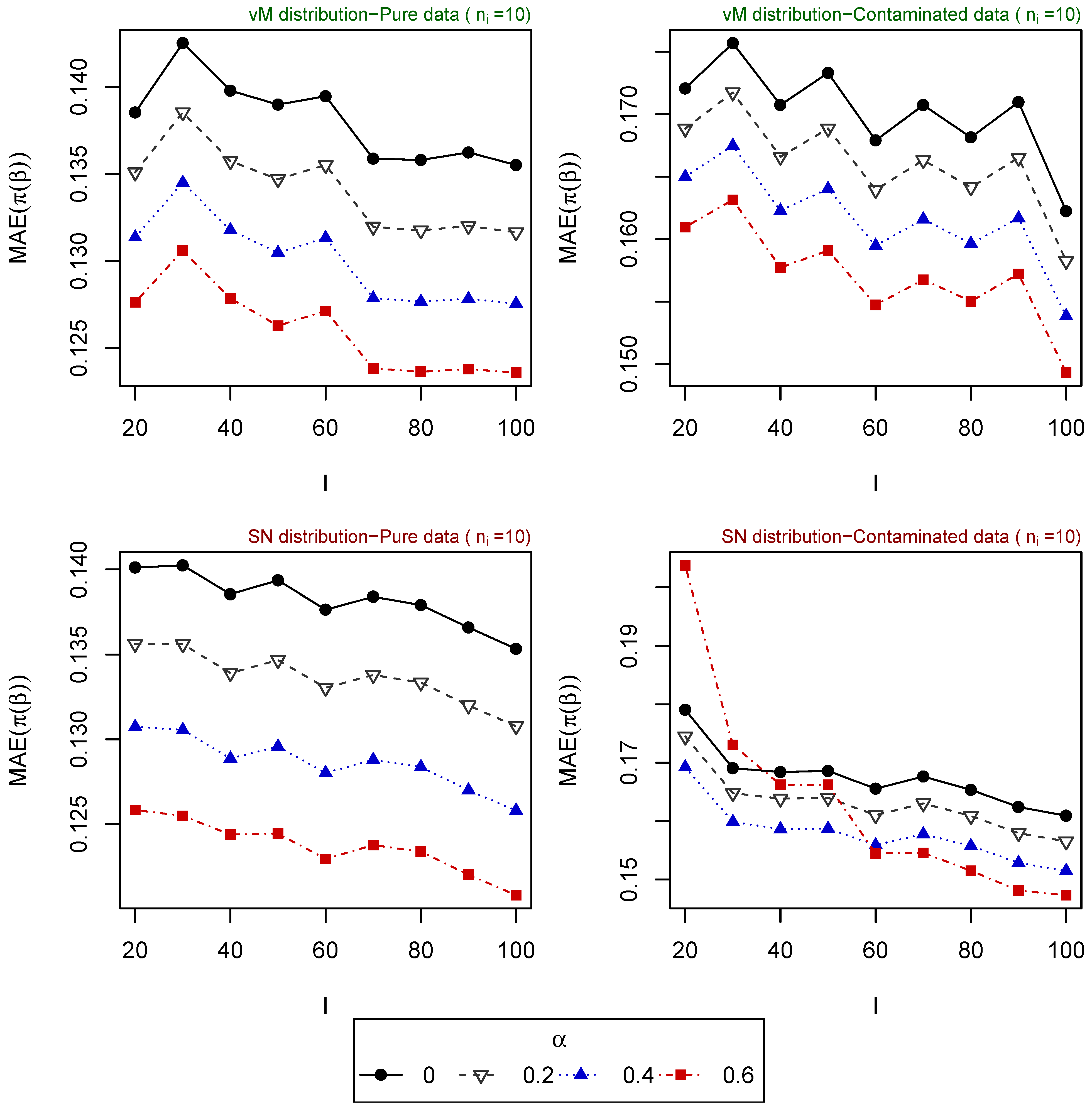
- Scenario 7: , for . Explanatory variables generated from vM distribution (top of Figure 5).
- Scenario 8: , for . Explanatory variables generated from SN distribution (bottom of Figure 5).
5. Applications to Real Data
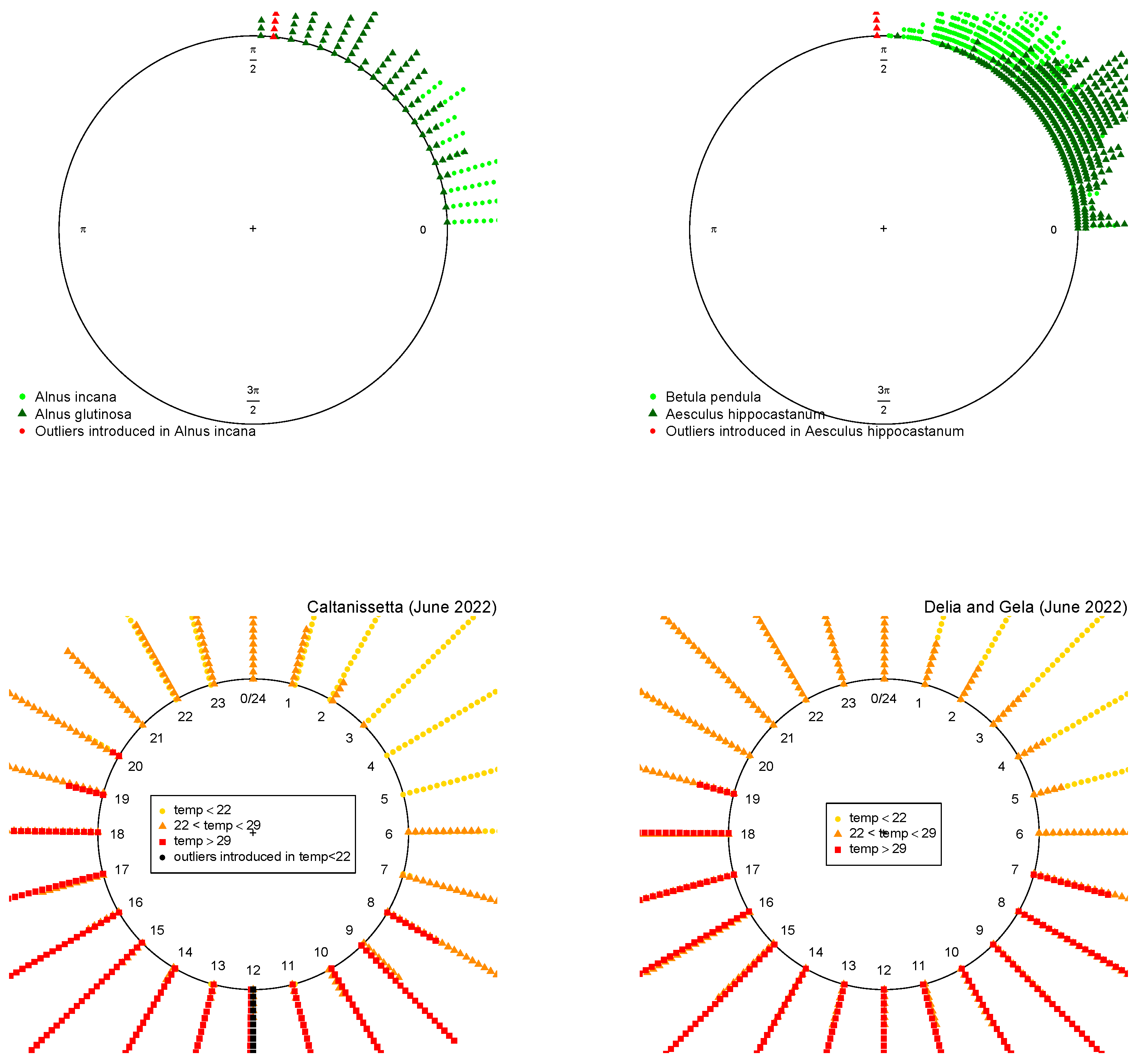
5.1. Application to Forest Science
5.1.1. First Example [Alnus incana vs. Alnus glutinosa]
5.1.2. Second Example [Betula pendula vs. Aesculus hippocastanum]
5.2. Application to Meteorological Science
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPD | Density Power Divergence |
| IID | Independent Identically Distributed |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MCLR | Multinomial Circular Logistic Regression |
| MDPDE | Minimum Density Power Divergence Estimator |
| MLE | Maximum Likelihood Estimator |
| MLR | Multinomial Logistic Regression |
| vM | Von Mises (distribution) |
| SN | Spherical Normal (distribution) |
Appendix A. Proof of Remark 1
Appendix B. Details on Circular Distributions
References
- Pewsey, A.; García-Portugués, E. Recent advances in directional statistics. Test 2021, 30, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ożarowska, A.; Ilieva, M.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Akesson, V.; Muś, K. A new approach to evaluate multimodal orientation behaviour of migratory passerine birds recorded in circular orientation cages. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 4038–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akesson, S.; Klaassen, R.; Holmgren, J.; Fox, J.W.; Hedenstrom, A. Migration routes and strategies in a highly aerial migrant, the common swift Apus apus, revealed by light-level geolocators. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilford, T.; Freeman, R.; Boyle, D.; Dean, B.; Kirk, H.; Phillips, R.; Perrins, C. A dispersive migration in the Atlantic puffin and its implications for migratory navigation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.B.; Kalaylioglu, Z.; Sengupta, A. A flexible Bayesian mixture approach for multi-modal circular data. Hacet. J. Math. Stat. 2022, 51, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkilawon, G.D.; Ferreira, J.; Nakhaeirad, N. Sine-skewed von Mises-and Lindley/Gumbel models as candidates for direction and distance in modelling animal movement. Braz. J. Biom. 2023, 41, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, C.L.; Partch, C.L. Emerging models for the molecular basis of mammalian circadian timing. Biochemistry 2014, 54, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshqaq, S.S.; Ahmadini, A.A.; Abuzaid, A.H. Some new robust estimators for circular logistic regression model with applications on meteorological and ecological data. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9944363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, E. Robust circular logistic regression model and its application to life and social sciences. Rev. Colomb. Estad. 2023, 46, 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Agostinelli, C. Robust estimation for circular data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2007, 51, 5867–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumond, M.; Réthoré, P.E.; Ott, S.; Peña, A.; Bechmann, A.; Hansen, K.S. Evaluation of the wind direction uncertainty and its impact on wake modeling at the Horns Rev offshore wind farm. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, A.; Ugwuowo, F.I. Asymmetric circular-linear multivariate regression models with applications to environmental data. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2006, 13, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Pewsey, A. Inverse Batschelet distributions for circular data. Biometrics 2012, 68, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, A.M.; Bogdanov, S.; Patruno, A.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Deller, A.T.; Bassa, C.; Janssen, G.H.; Kaspi, V.M.; Lyne, A.G.; Stappers, B.W.; et al. Accretion-powered pulsations in an apparently quiescent neutron star binary. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Hangartner, D. Circular data in political science and how to handle it. Political Anal. 2010, 18, 316–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibiak, T.; Jonas, C. Applying circular statistics to the analysis of monitoring data. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2007, 23, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, N.; Rua, A. Business cycle clocks: Time to get circular. Empir. Econ. 2023, 65, 1513–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.P. Studying crime and place with the crime open database: Social and behavioural scienes. Res. Data J. Humanit. Social Sci. 2019, 4, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mises, R. Uber Die Ganzzahligkeit der Atomgewichte und verwandte Fragen. Phys. Z. 1918, 19, 490–500. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, C.G.; Mardia, K.V. The von Mises-Fisher matrix distribution in orientation statistics. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Dhillon, I.S.; Ghosh, J.; Sra, S.; Ridgeway, G. Clustering on the unit hypersphere using von Mises-Fisher distributions. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 1345–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Bangert, M.; Hennig, P.; Oelfke, U. Using an infinite von mises-fisher mixture model to cluster treatment beam directions in external radiation therapy. In Proceedings of the 2010 Ninth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Washington, DC, USA, 12–14 December 2010; pp. 746–751. [Google Scholar]
- Hauberg, S. Directional statistics with the spherical normal distribution. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Cambridge, UK, 10–13 July 2018; pp. 704–711. [Google Scholar]
- You, K.; Suh, C. Parameter estimation and model-based clustering with spherical normal distribution on the unit hypersphere. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2022, 171, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, E. Robust estimation of the spherical normal distribution. Math. Appl. 2022, 50, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsen, O.; Taylor, C.C. Parametric circular-circular regression and diagnostic analysis. In Geometry Driven Statistics; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Dryden, I.L., Kent, J.T., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2015; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Presnell, B.; Morrison, S.P.; Littell, R.C. Projected multivariate linear models for directional data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1998, 93, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wehrly, T.E. Some angular-linear distributions and related regression models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1978, 73, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daffaie, K.; Khan, S. Logistic regression for circular data. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1842, 030022. [Google Scholar]
- Uemura, M.; Meglic, A.; Zalucki, M.P.; Battisti, A.; Belusic, G. Spatial orientation of social caterpillars is influenced by polarized light. Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20200736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, N.; Tallon-Baudry, C. Coupling between the phase of a neural oscillation or bodily rhythm with behavior: Evaluation of different statistical procedures. NeuroImage 2021, 236, 118050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, E.; Chocano, P.J. A new robust approach for multinomial logistic regression with complex design model. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2022, 68, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.H.; Ahmed, H.I.E. On outliers detection in circular logistic regression. J. Appl. Probab. Stat. 2021, 16, 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Harris, I.R.; Hjort, N.L.; Jones, M.C. Robust and efficient estimation by minimising a density power divergence. Biometrika 1998, 85, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Shioya, H.; Park, C. Statistical Inference: The Minimum Distance Approach; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Basu, A. Robust estimation for independent non-homogeneous observations using density power divergence with applications to linear regression. Electron. J. Stat. 2013, 7, 2420–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Basu, A. Robust Estimation for Non-Homogeneous Data and the Selection of the Optimal Tuning Parameter: The DPD Approach. J. Appl. Stat. 2015, 42, 2056–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Majumdar, S. Ultrahigh-dimensional Robust and Efficient Sparse Regression using Non-Concave Penalized Density Power Divergence. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2020, 66, 7812–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, E.; Ghosh, A.; Martin, N.; Pardo, L. New robust statistical procedures for the polytomous logistic regression models. Biometrics 2018, 74, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castilla, E.; Ghosh, A.; Martin, N.; Pardo, L. Robust semiparametric inference for polytomous logistic regression with complex survey design. Adv. Data Anal. Classif. 2021, 15, 701–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianucci, F.; Pisek, J.; Raabe, K.; Marchino, L.; Ferrara, C.; Corona, P. A dataset of leaf inclination angles for temperate and boreal broadleaf woody species. Ann. For. Sci. 2018, 75, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset→ | First Forest Example | Second Forest Example | Meteorological Example | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Contaminated | Original | Contaminated | Original | Contaminated | New | |
| 0 (MLE) | 0.7625 | 0.7486 | 0.7339 | 0.6705 | 0.7135 | 0.6120 | 0.7208 |
| 0.2 | 0.7812 | 0.7486 | 0.7350 | 0.6727 | 0.7135 | 0.6218 | 0.7208 |
| 0.4 | 0.7812 | 0.7600 | 0.7350 | 0.7223 | 0.7135 | 0.6387 | 0.7208 |
| 0.6 | 0.7812 | 0.7771 | 0.7350 | 0.7307 | 0.7135 | 0.6387 | 0.7208 |
| 0.8 | 0.7812 | 0.7771 | 0.7350 | 0.7381 | 0.7135 | 0.6639 | 0.7208 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castilla, E.; Ghosh, A. Robust Minimum Divergence Estimation for the Multinomial Circular Logistic Regression Model. Entropy 2023, 25, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25101422
Castilla E, Ghosh A. Robust Minimum Divergence Estimation for the Multinomial Circular Logistic Regression Model. Entropy. 2023; 25(10):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25101422
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastilla, Elena, and Abhik Ghosh. 2023. "Robust Minimum Divergence Estimation for the Multinomial Circular Logistic Regression Model" Entropy 25, no. 10: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25101422
APA StyleCastilla, E., & Ghosh, A. (2023). Robust Minimum Divergence Estimation for the Multinomial Circular Logistic Regression Model. Entropy, 25(10), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25101422







