Decentralized Stochastic Control with Finite-Dimensional Memories: A Memory Limitation Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
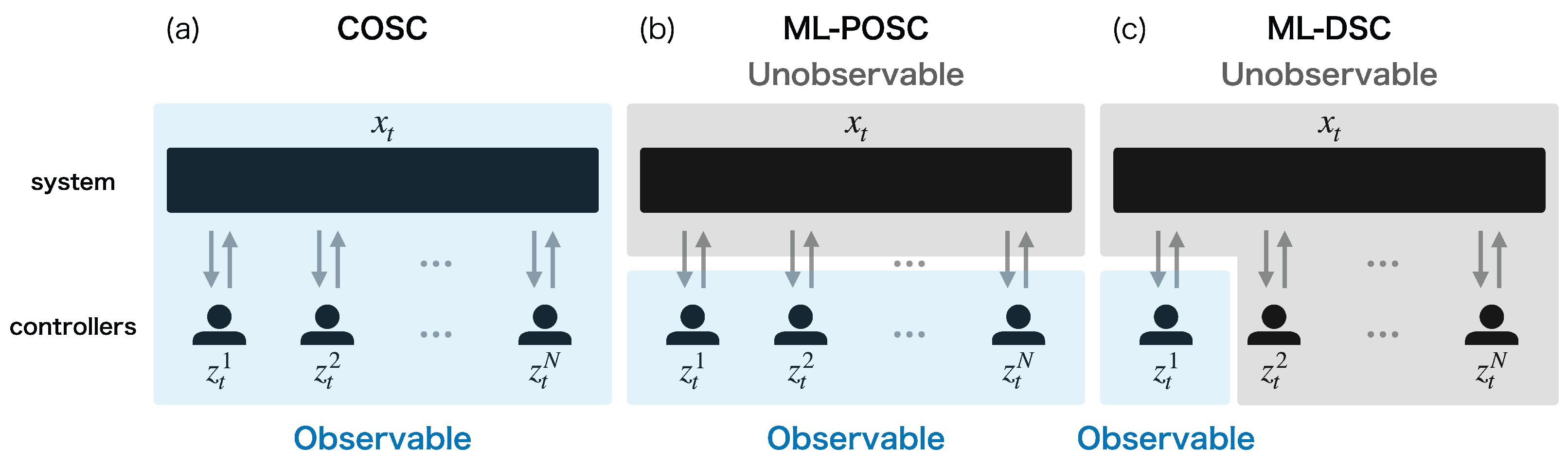
2. Review of Decentralized Stochastic Control
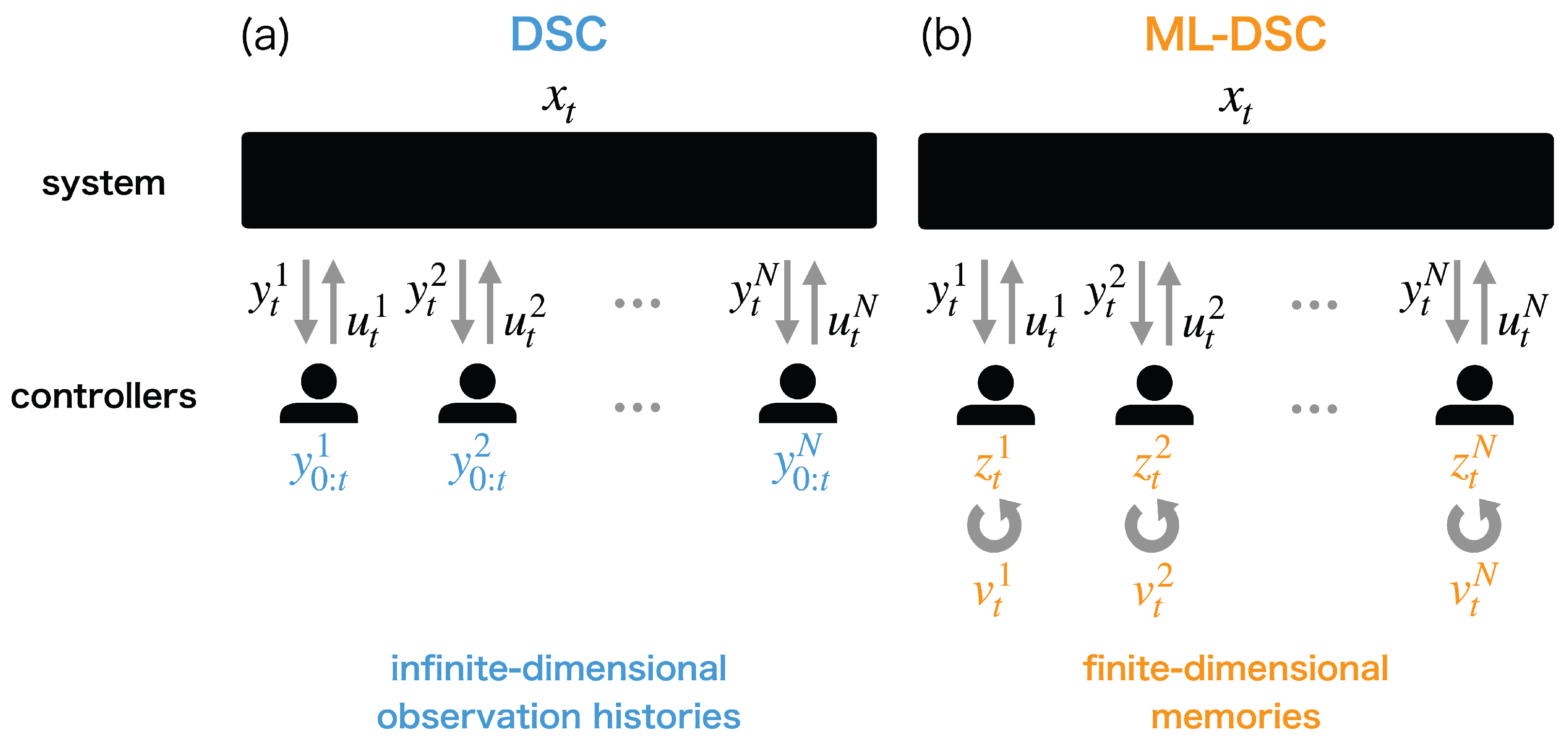
3. Memory-Limited Decentralized Stochastic Control
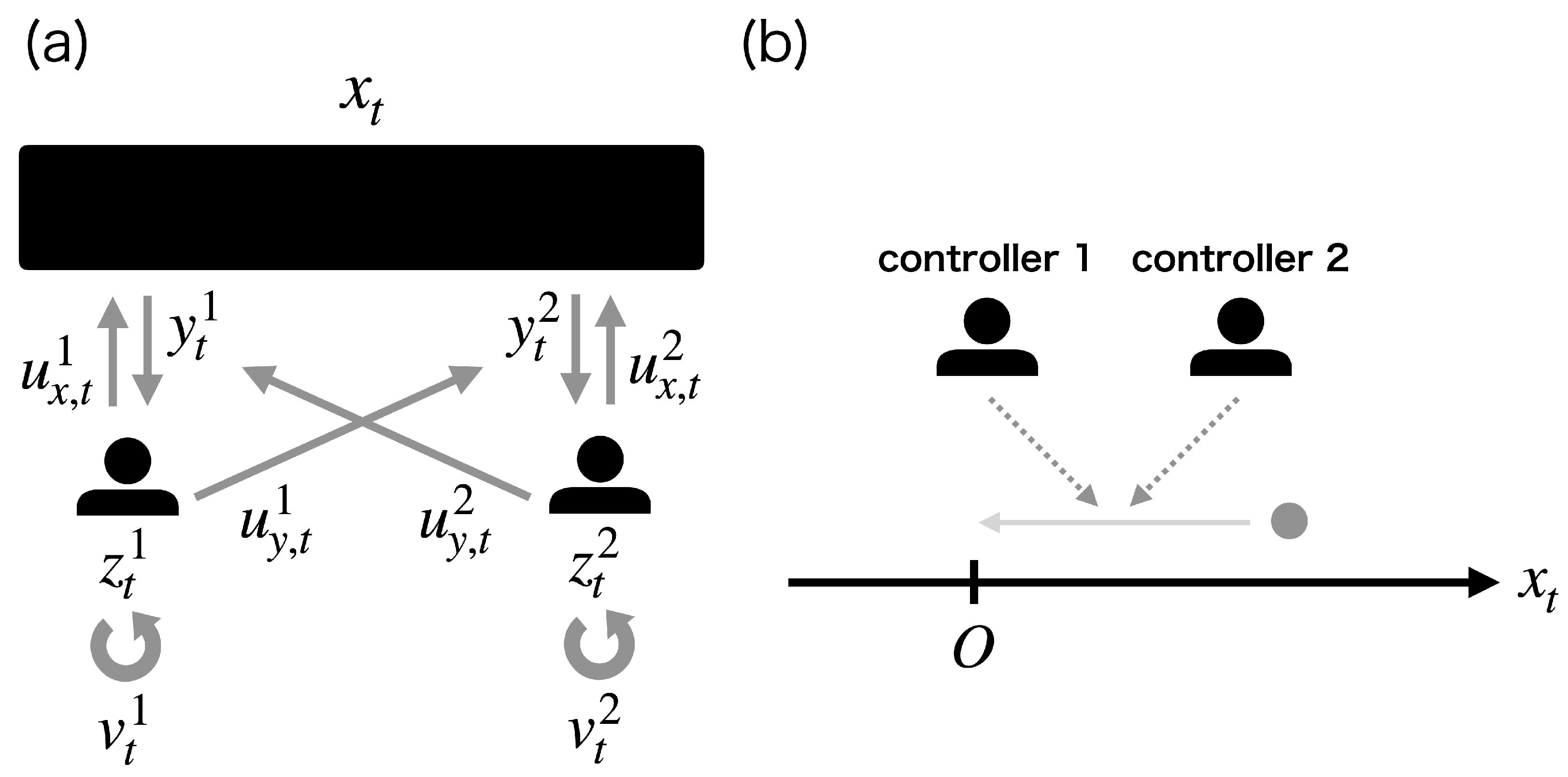
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Extended State
4. Derivation of Optimal Control Function
4.1. Derivation of Optimal Control Function
4.2. Numerical Algorithm
4.3. Comparison with Completely Observable Stochastic Control or Memory-Limited Partially Observable Stochastic Control
5. Linear-Quadratic-Gaussian Problem
5.1. Problem Formulation
5.2. Derivation of Optimal Control Function
5.3. Comparison with Completely Observable Stochastic Control or Memory-Limited Partially Observable Stochastic Control
5.4. Decentralized Riccati Equation
6. Numerical Experiments
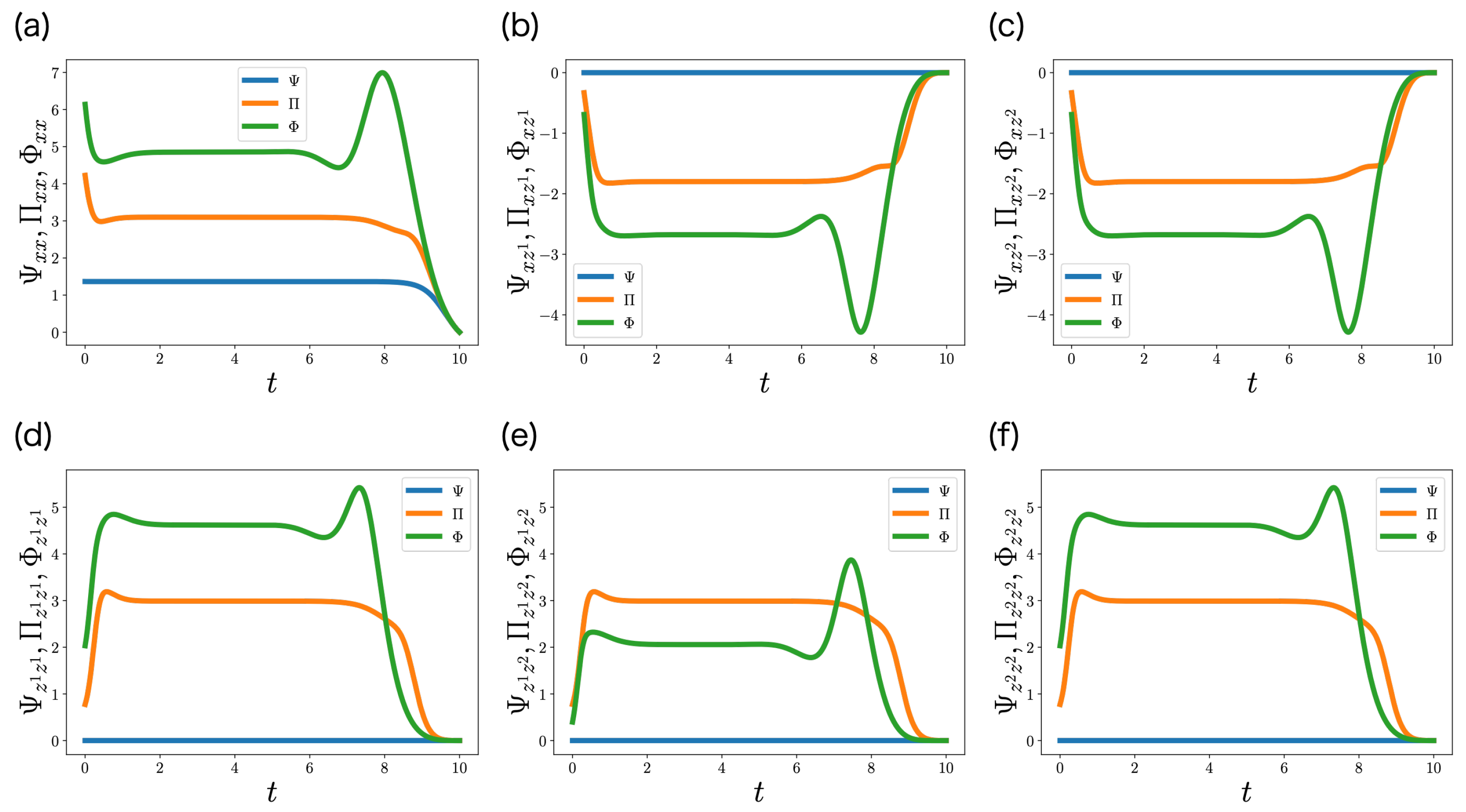
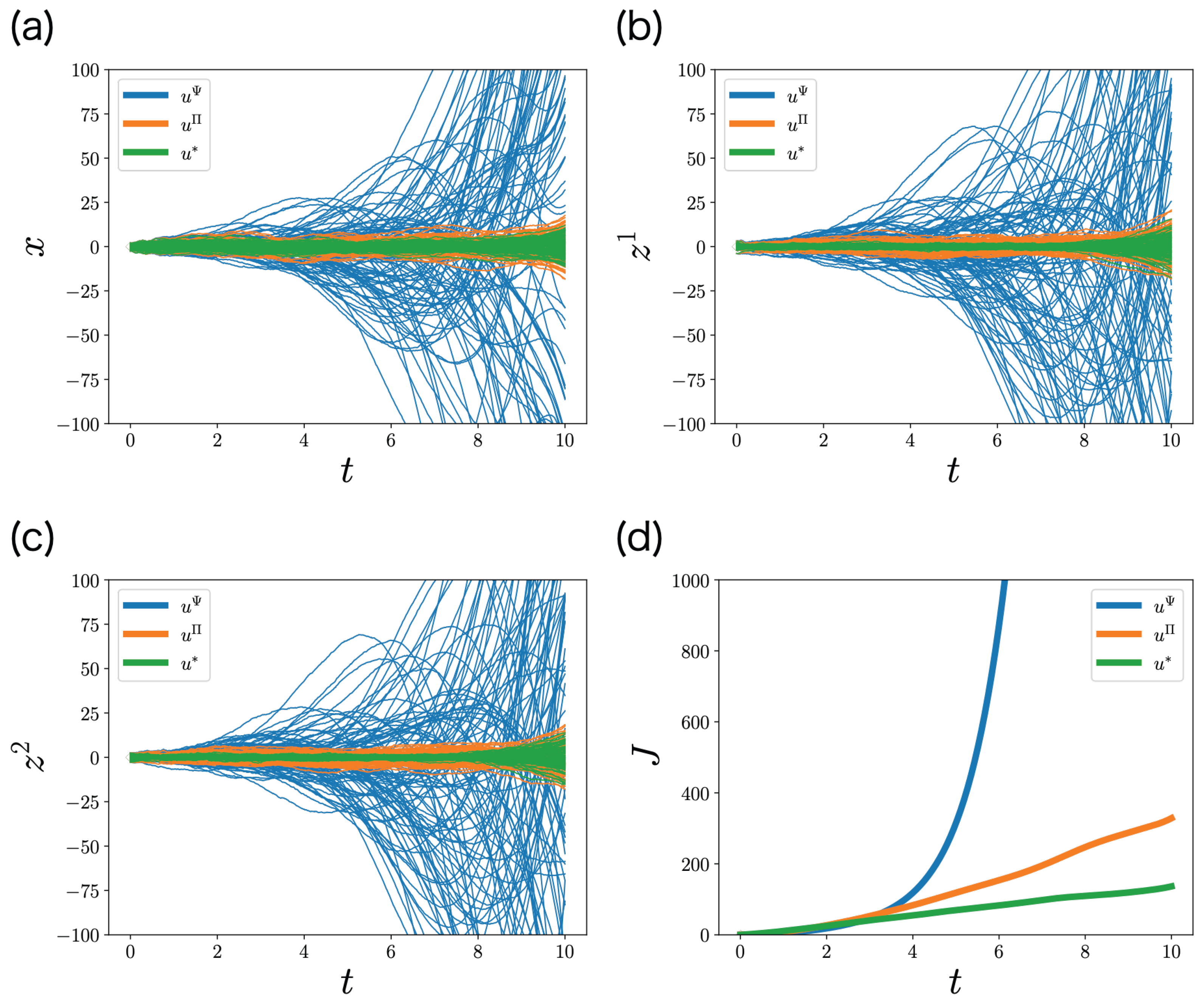
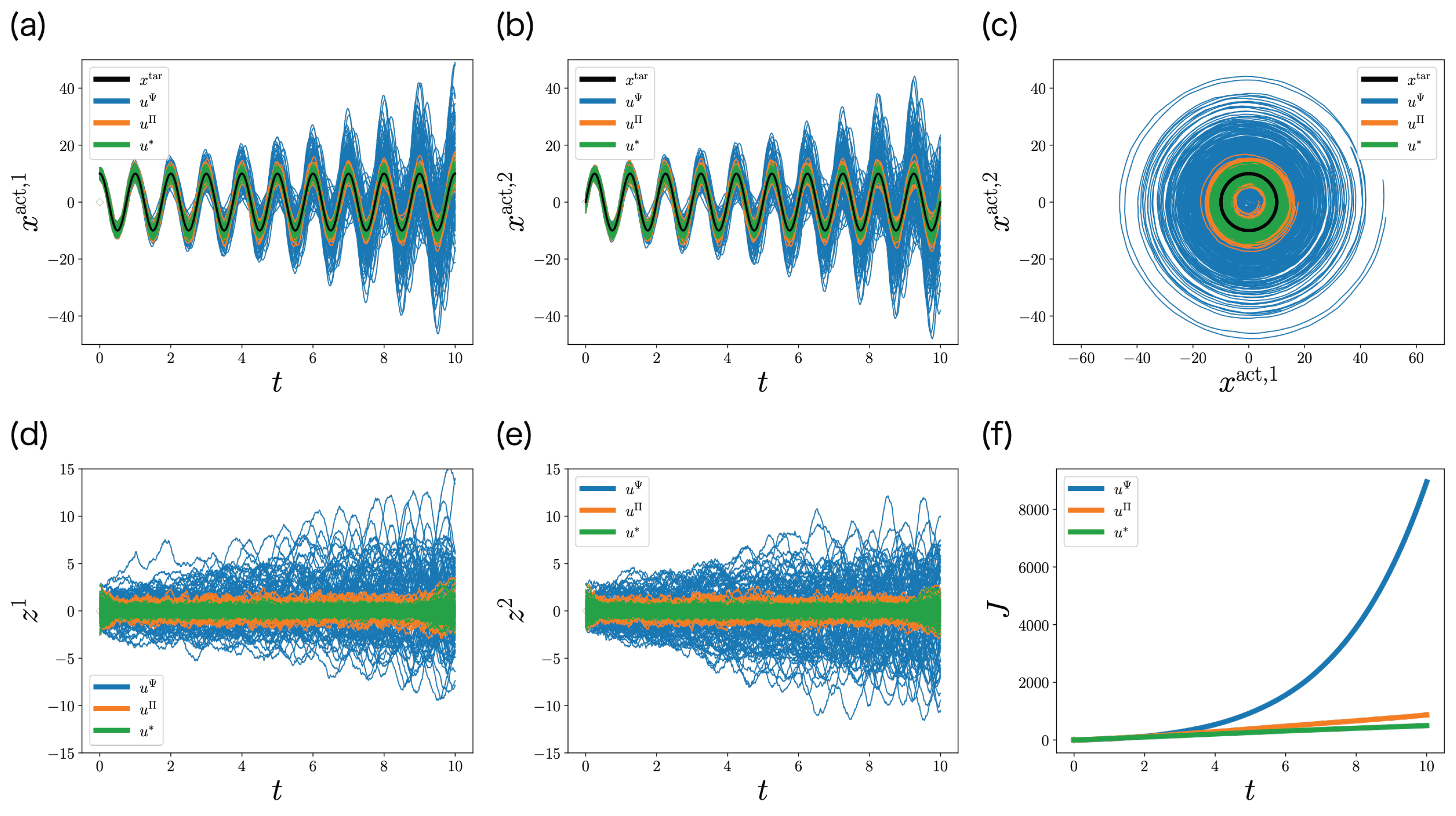
6.1. One-Dimensional State Case
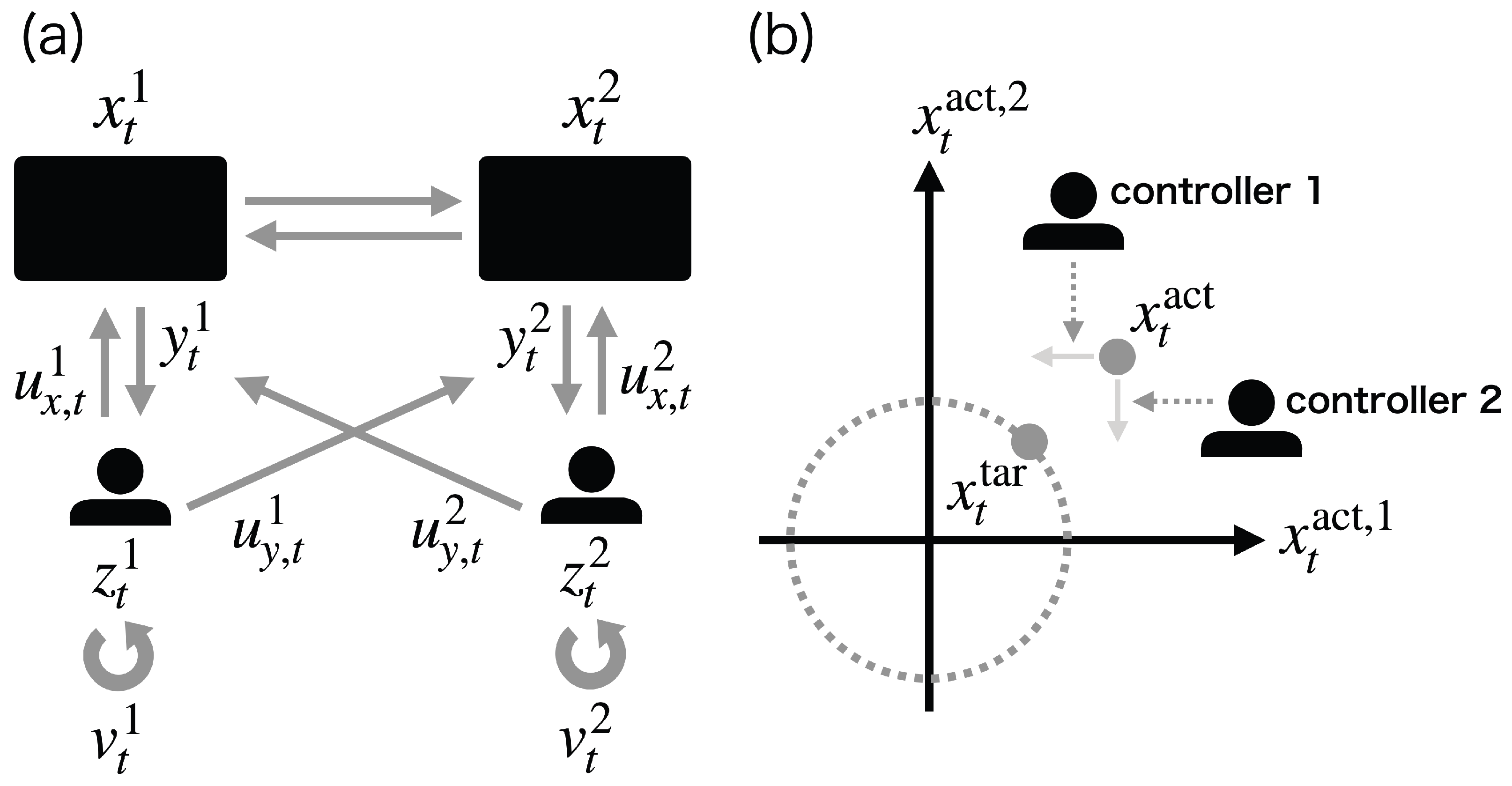
6.2. Two-Dimensional State Case
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COSC | Completely Observable Stochastic Control |
| POSC | Partially Observable Stochastic Control |
| DSC | Decentralized Stochastic Control |
| ML-POSC | Memory-Limited Partially Observable Stochastic Control |
| ML-DSC | Memory-Limited Decentralized Stochastic Control |
| DEC-POMDP | Decentralized Partially Observable Markov Decision Process |
| HJB | Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman |
| FP | Fokker-Planck |
| ODE | Ordinary Differential Equation |
| SDE | Stochastic Differential Equation |
| LQ | Linear-Quadratic |
| LQG | Linear-Quadratic-Gaussian |
Appendix A. Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix A.1. Bellman’s Dynamic Programming Principle
Appendix A.2. Conversion from Bellman’s Dynamic Programming Principle to Pontryagin’s Minimum Principle
Appendix B. Proof of Theorem 2
References
- Mahajan, A.; Teneketzis, D. On the design of globally optimal communication strategies for real-time noisy communication systems with noisy feedback. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2008, 26, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Teneketzis, D. Optimal Design of Sequential Real-Time Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2009, 55, 5317–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A.; Teneketzis, D. Sequential Problems in Decentralized Detection with Communication. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 5410–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Teneketzis, D. Optimal Performance of Networked Control Systems with Nonclassical Information Structures. SIAM J. Control Optim. 2009, 48, 1377–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witsenhausen, H.S. A Counterexample in Stochastic Optimum Control. SIAM J. Control 1968, 6, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A.; Mahajan, A.; Teneketzis, D. Decentralized Stochastic Control with Partial History Sharing: A Common Information Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 1644–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Nayyar, A. Sufficient Statistics for Linear Control Strategies in Decentralized Systems With Partial History Sharing. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 2046–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, C.D.; Ahmed, N.U. Team Optimality Conditions of Distributed Stochastic Differential Decision Systems with Decentralized Noisy Information Structures. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, C.D.; Ahmed, N.U. Centralized Versus Decentralized Optimization of Distributed Stochastic Differential Decision Systems with Different Information Structures—Part I: A General Theory. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, C.D.; Ahmed, N.U. Centralized Versus Decentralized Optimization of Distributed Stochastic Differential Decision Systems with Different Information Structures—Part II: Applications. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2018, 63, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonham, W.M. On the Separation Theorem of Stochastic Control. SIAM J. Control 1968, 6, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A. Stochastic Control of Partially Observable Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisio, M. Stochastic Control Theory. In Probability Theory and Stochastic Modelling; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; Volume 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A. Estimation and Control of Dynamical Systems. In Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, J. An Introduction to Optimal Control of FBSDE with Incomplete Information; SpringerBriefs in Mathematics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A.; Yam, S.C.P. Mean field approach to stochastic control with partial information. ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var. 2021, 27, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L.; Lall, S. A state-space solution to the two-player decentralized optimal control problem. In Proceedings of the 2011 49th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, IL, USA, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L.; Lall, S. Optimal controller synthesis for the decentralized two-player problem with output feedback. In Proceedings of the 2012 American Control Conference (ACC), Montréal, QC, Canada, 27–29 June 2012; pp. 6314–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L. Decentralized LQG control of systems with a broadcast architecture. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Maui, HI, USA, 10–13 December 2012; pp. 6241–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L.; Nayyar, A. Structural results and explicit solution for two-player LQG systems on a finite time horizon. In Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Firenze, Italy, 10–13 December 2013; pp. 6542–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L.; Lall, S. Optimal Control of Two-Player Systems With Output Feedback. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A.; Lessard, L. Structural results for partially nested LQG systems over graphs. In Proceedings of the 2015 American Control Conference (ACC), Chicago, IL, USA, 1–3 July 2015; pp. 5457–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottori, T.; Kobayashi, T.J. Memory-Limited Partially Observable Stochastic Control and Its Mean-Field Control Approach. Entropy 2022, 24, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottori, T.; Kobayashi, T.J. Forward-Backward Sweep Method for the System of HJB-FP Equations in Memory-Limited Partially Observable Stochastic Control. Entropy 2023, 25, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A.; Frehse, J.; Yam, S.C.P. The Master equation in mean field theory. J. Math. Pures Appl. 2015, 103, 1441–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A.; Frehse, J.; Yam, S.C.P. On the interpretation of the Master Equation. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 2017, 127, 2093–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A.; Frehse, J.; Yam, P. Mean Field Games and Mean Field Type Control Theory; Springer Briefs in Mathematics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, R.; Delarue, F. Probabilistic Theory of Mean Field Games with Applications I. In Probability Theory and Stochastic Modelling; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, R.; Delarue, F. Probabilistic Theory of Mean Field Games with Applications II. In Probability Theory and Stochastic Modelling; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achdou, Y. Finite Difference Methods for Mean Field Games. In Hamilton-Jacobi Equations: Approximations, Numerical Analysis and Applications: Cetraro, Italy 2011; Loreti, P., Tchou, N.A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achdou, Y.; Laurière, M. Mean Field Games and Applications: Numerical Aspects. In Mean Field Games: Cetraro, Italy 2019; Achdou, Y., Cardaliaguet, P., Delarue, F., Porretta, A., Santambrogio, F., Cardaliaguet, P., Porretta, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 249–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriere, M. Numerical Methods for Mean Field Games and Mean Field Type Control. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.06231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.S. Bounded Policy Iteration for Decentralized POMDPs. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Edinburgh, UK, 30 July–5 August 2005; pp. 1287–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, D.S.; Amato, C.; Hansen, E.A.; Zilberstein, S. Policy Iteration for Decentralized Control of Markov Decision Processes. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2009, 34, 89–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, C.; Bernstein, D.S.; Zilberstein, S. Optimizing Memory-Bounded Controllers for Decentralized POMDPs. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–22 July 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, C.; Bonet, B.; Zilberstein, S. Finite-State Controllers Based on Mealy Machines for Centralized and Decentralized POMDPs. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2010, 24, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Zilberstein, S. Anytime Planning for Decentralized POMDPs using Expectation Maximization. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Catalina Island, CA, USA, 8–11 July 2010; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Oliehoek, F.A.; Amato, C. A Concise Introduction to Decentralized POMDPs; SpringerBriefs in Intelligent Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottori, T.; Kobayashi, T.J. Forward and Backward Bellman Equations Improve the Efficiency of the EM Algorithm for DEC-POMDP. Entropy 2021, 23, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Zhou, X.Y. Stochastic Controls; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, H. Optimal stochastic control. IRE Trans. Autom. Control 1962, 7, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, E.; Silva, F.J. Semi-Lagrangian schemes for mean field game models. In Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Firenze, Italy, 10–13 December 2013; pp. 3115–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, E.; Silva, F.J. A Fully Discrete Semi-Lagrangian Scheme for a First Order Mean Field Game Problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2014, 52, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, E.; Silva, F.J. A semi-Lagrangian scheme for a degenerate second order mean field game system. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 2015, 35, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, H.J.; Dupuis, P.G. Numerical Methods for Stochastic Control Problems in Continuous Time; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, W.H.; Soner, H.M. Controlled Markov Processes and Viscosity Solutions, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puterman, M.L. Markov Decision Processes: Discrete Stochastic Dynamic Programming; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Charalambous, C.D.; Ahmed, N. Equivalence of decentralized stochastic dynamic decision systems via Girsanov’s measure transformation. In Proceedings of the 53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2014; pp. 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telsang, B.; Djouadi, S.; Charalambous, C. Numerical Evaluation of Exact Person-by-Person Optimal Nonlinear Control Strategies of the Witsenhausen Counterexample. In Proceedings of the 2021 American Control Conference (ACC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 May 2021; pp. 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthotto, L.; Osher, S.J.; Li, W.; Nurbekyan, L.; Fung, S.W. A machine learning framework for solving high-dimensional mean field game and mean field control problems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9183–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.T.; Fung, S.W.; Li, W.; Nurbekyan, L.; Osher, S.J. Alternating the population and control neural networks to solve high-dimensional stochastic mean-field games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024713118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tottori, T.; Kobayashi, T.J. Decentralized Stochastic Control with Finite-Dimensional Memories: A Memory Limitation Approach. Entropy 2023, 25, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25050791
Tottori T, Kobayashi TJ. Decentralized Stochastic Control with Finite-Dimensional Memories: A Memory Limitation Approach. Entropy. 2023; 25(5):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25050791
Chicago/Turabian StyleTottori, Takehiro, and Tetsuya J. Kobayashi. 2023. "Decentralized Stochastic Control with Finite-Dimensional Memories: A Memory Limitation Approach" Entropy 25, no. 5: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25050791
APA StyleTottori, T., & Kobayashi, T. J. (2023). Decentralized Stochastic Control with Finite-Dimensional Memories: A Memory Limitation Approach. Entropy, 25(5), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25050791






