Bifurcations in a Model of Criminal Organizations and a Corrupt Judiciary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Proposed Model
3. Analytical Results
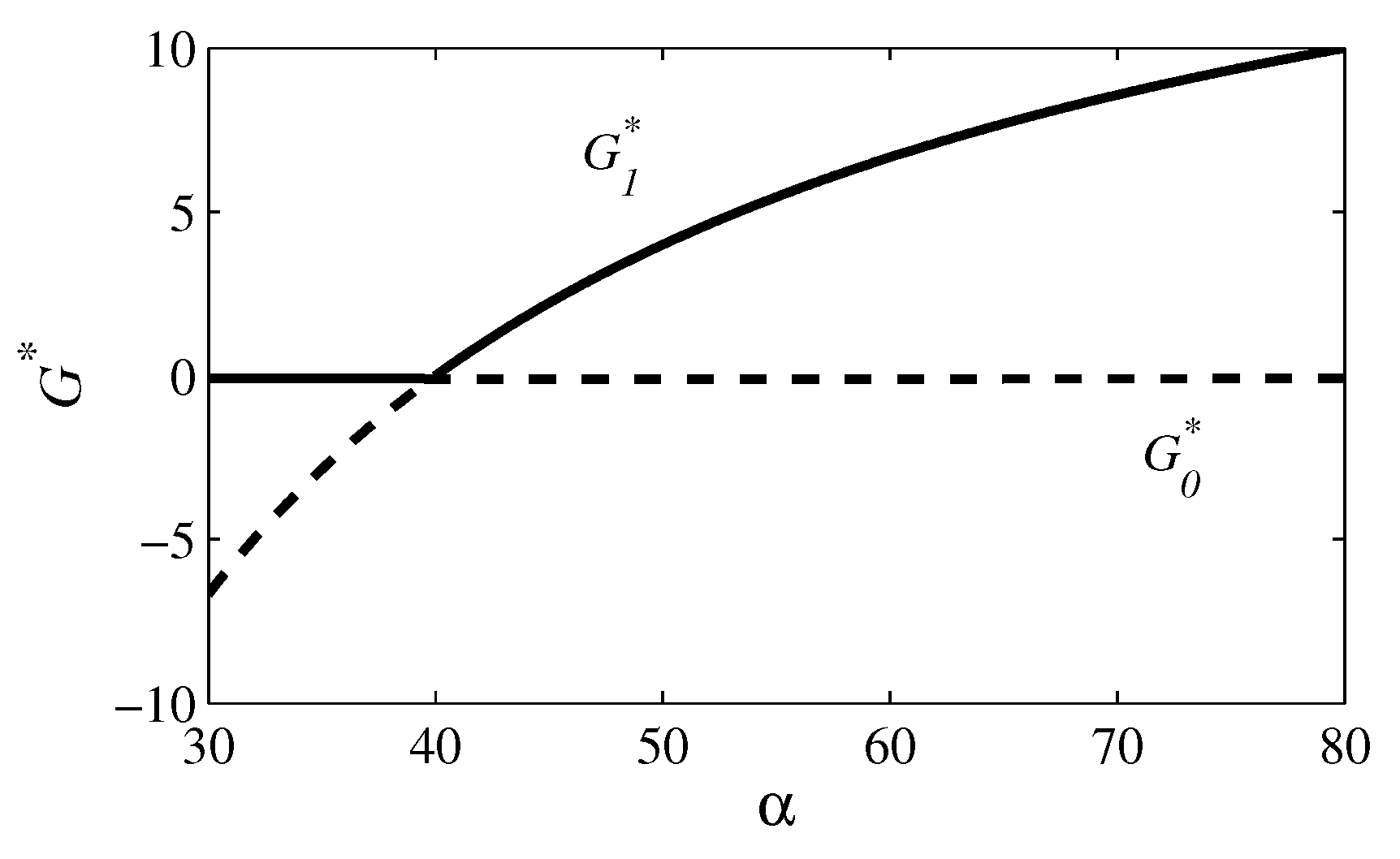
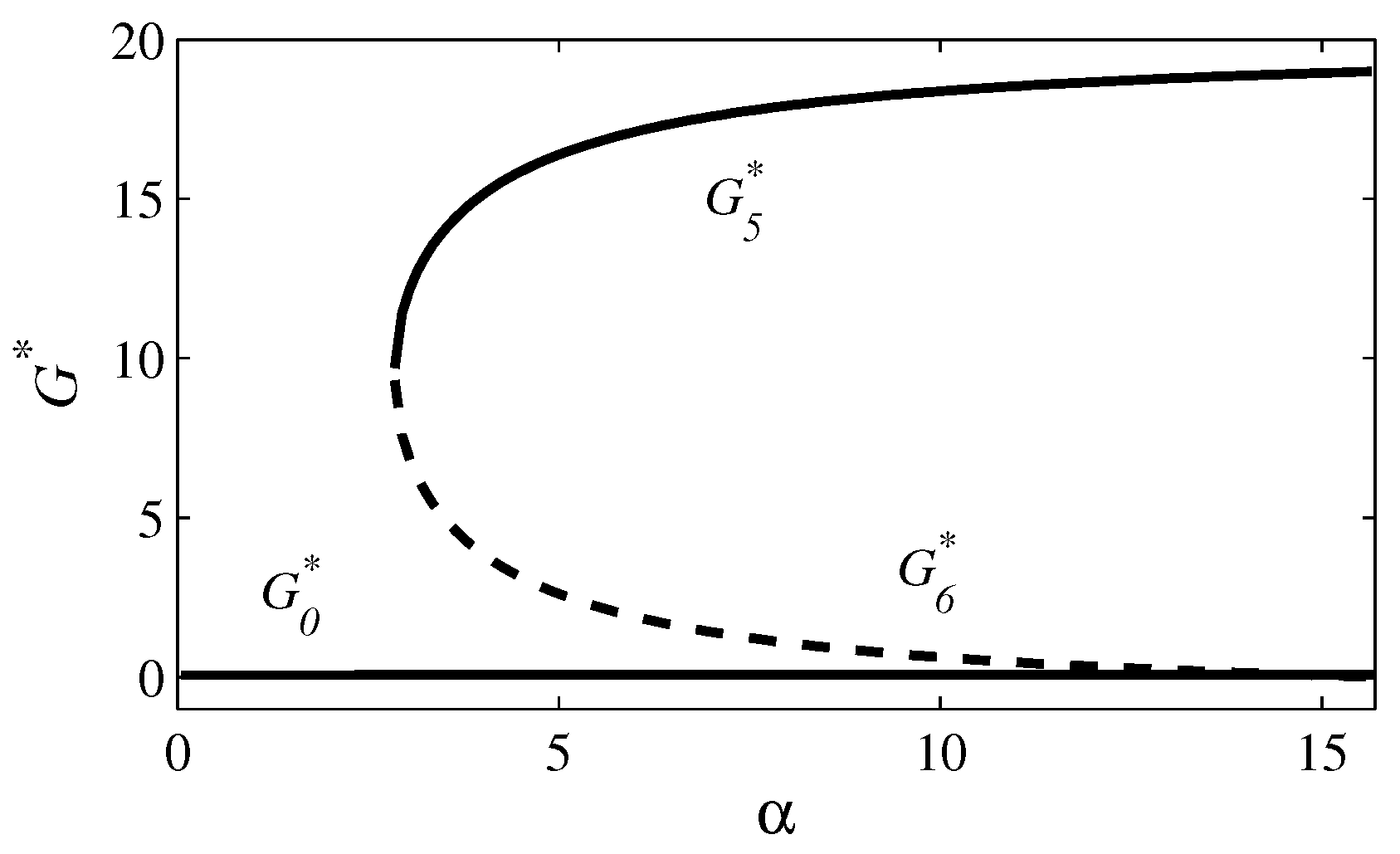
3.1. Case 1: and
3.2. Case 2: and
3.3. Case 3: and
3.4. Case 4: and
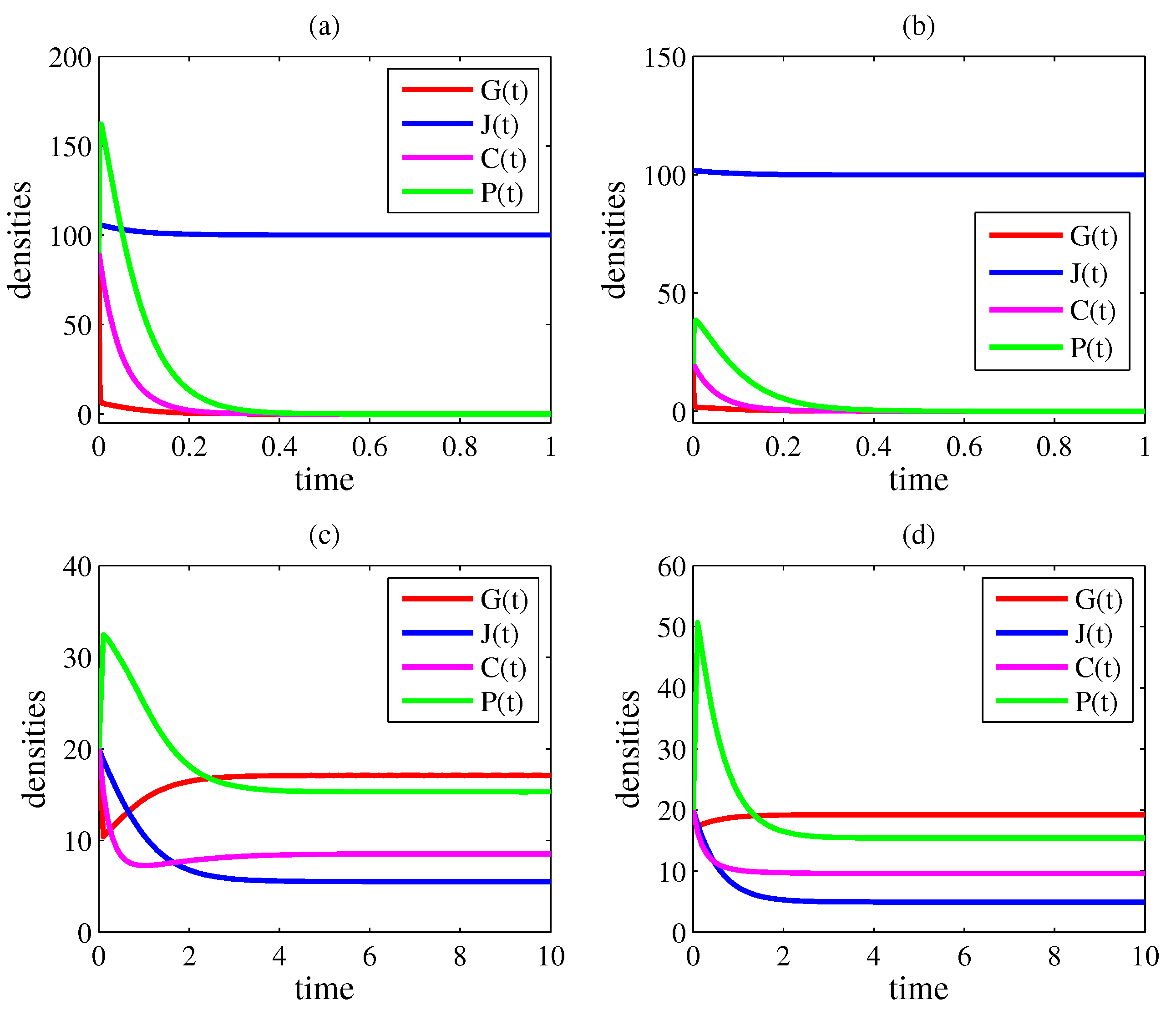
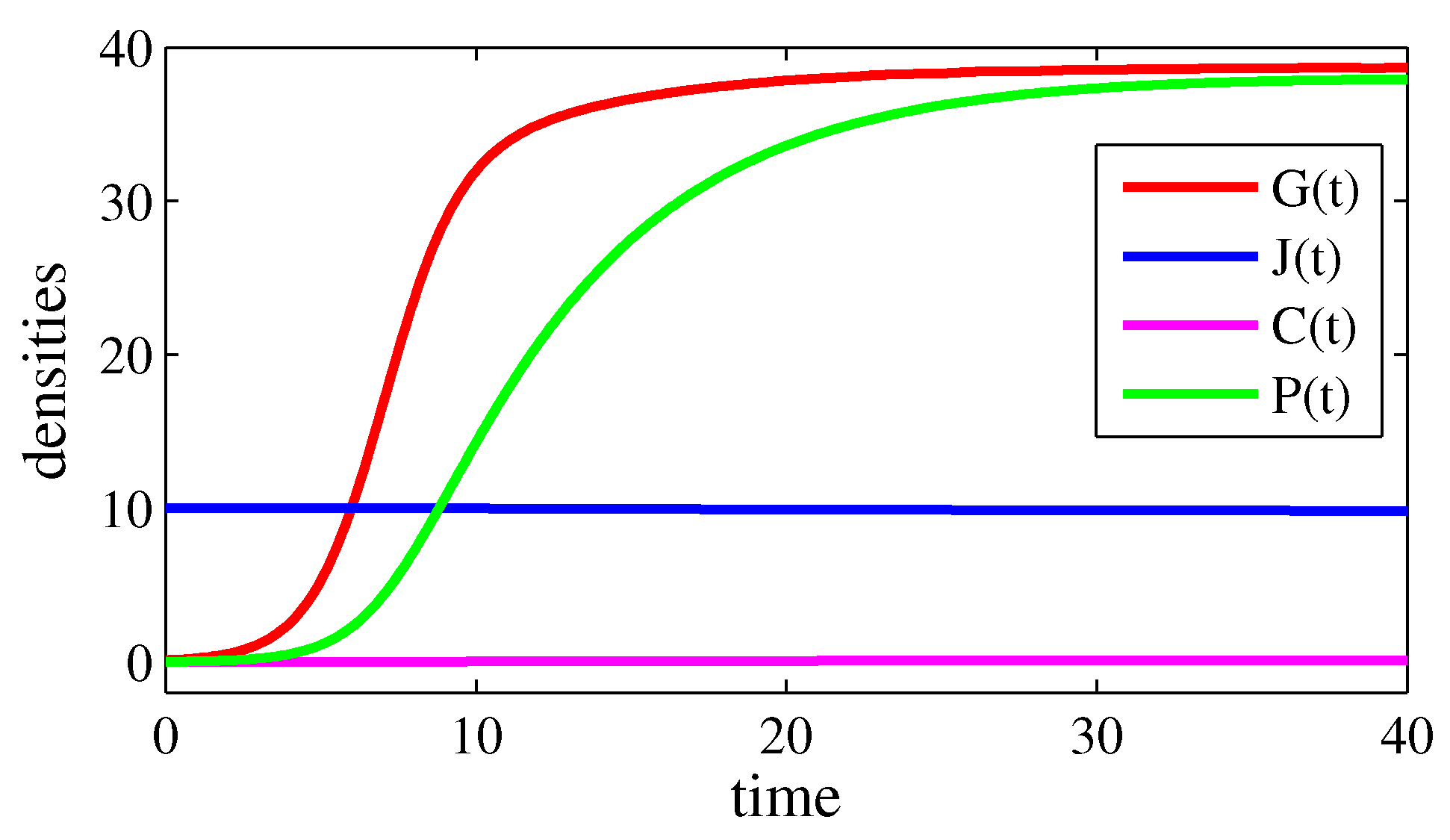
4. Numerical Simulations
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnan, S. Organised crime—A threat to democracy. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 6, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, P.; Paoli, L. How similar are modern criminal syndicates to traditional mafias? Crime Justice 2020, 49, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime. Global Organized Crime Index 2023; Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hauck, P.; Peterke, S. Organized crime and gang violence in national and international law. Int. Rev. Red Cross 2010, 92, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessing, B. Conceptualizing criminal governance. Perspect. Polit. 2021, 19, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatley, G.; Crick, T. Measuring UK crime gangs. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, Beijing, China, 17–20 August 2014; Volume 1, p. 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsoesie, E.O.; Lima Neto, A.S.; Jay, J.; Wang, H.; Zinszer, K.; Saha, S.; Maharana, A.; Marinho, F.; Soares Filho, A.M. Mapping disparities in homicide trends across Brazil: 2000–2014. Inj. Epidemiol. 2020, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugato, M.; Calderoni, F.; Berlusconi, G. Forecasting organized crime homicides: Risk terrain modeling of Camorra violence in Naples, Italy. J. Interpers. Violence 2020, 35, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.M.; Vorobyeva, Y. State presence, armed actors, and criminal violence in Central America. Sociol. Q. 2022, 63, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-Ackerman, S. Trust, honesty and corruption: Reflection on the state-building process. Arch. Eur. Sociol. 2001, 42, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transparency International. Global Corruption Report 2007; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, H.; Hakimi, A. Corruption, imported innovation, and growth: Evidence using the panel smooth transition regression approach for developing countries. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2023, 15, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Monetary Fund. Corruption: Costs and Mitigating Strategies. 2016. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/Staff-Discussion-Notes/Issues/2016/12/31/Corruption-Costs-and-Mitigating-Strategies-43888 (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Garcia, P.J. Corruption in global health: The open secret. Lancet 2019, 394, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-Ackerman, S. The economics of corruption. J. Public Econ. 1975, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, S.; Rothstein, B. Dying of corruption. Health Econ. Policy Law 2011, 6, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achim, M.V.; Väidean, V.L.; Borlea, S.N. Corruption and health outcomes within an economic and cultural framework. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2020, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambraseys, N.; Bilham, R. Corruption kills. Nature 2011, 469, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transparency International. Corruption Perceptions Index 2023. 2024. Available online: https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2023 (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Keyuan, Z. Judicial reform versus judicial corruption: Recent developments in China. Crim. Law Forum 2000, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.N.C. Corruption in the courts: The Achilles’ heel of Nigeria’s regulatory framework? Third World Q. 2010, 31, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloppen, S. Courts, corruption and judicial independence. In Corruption, Grabbing and Development: Real World Challenges; Søreide, T., Williams, A., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2014; Chapter 5; pp. 68–79. Available online: https://www.cmi.no/publications/5091-courts-corruption-and-judicial-independence (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Voigt, S.; Gutmann, J. On the wrong side of the law - Causes and consequencesof a corrupt judiciary. Int. Rev. Law Econ. 2015, 43, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Justice Project. The World Justice Project Rule of Law Index 2021. 2021. Available online: https://worldjusticeproject.org/sites/default/files/documents/WJP-INDEX-2021.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Zhilla, F. Organised crime and judicial corruption in the Western Balkans. J. Financ. Crime 2011, 18, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brands, H. Crime, irregular warfare, and institutional failure in Latin America: Guatemala as a case study. Stud. Confl. Terror. 2011, 34, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezelj, I.; Vogrincic, N.O. Criminal and networked state capture in the Western Balkans: The case of the Zemun clan. South. Eur. Eur. Black Sea Stud. 2020, 20, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.L.; Rodgers, D.; Weegels, J. Debunking the myth of Nicaraguan exceptionalism: Crime, drugs and the political economy of violence in a ‘narco-state’. J. Lat. Am. Stud. 2023, 55, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raistenskis, E.; Krivins, A.; Aleksejeva, L. Phehomenon of corruption in Albania: Towards cigarrete smugling. Access-Sci. Bus. Innov. Digit. Econ. 2023, 4, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsenafi, A.; Barbaro, A.B.T. A convection-diffusion model for gang territoriality. Physica A 2018, 510, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, M.B.; D’Orsogna, M.R.; Pasour, V.B.; Tita, G.E.; Brantingham, P.J.; Bertozzi, A.L.; Chayes, L.B. A statistical model of criminal behavior. Math. Model. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2008, 18, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipkin, J.R.; Short, M.B.; Bertozzi, A.L. Cops on the dots in a mathematical model of urban crime and police response. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. B 2014, 19, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, J.; Jornet, M.; Mateu, J. Spatio-temporal stochastic differential equations for crime incidence modeling. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczynska, B.; Gruszczynski, M. Crime and punishment-crime rates and prison population in Europe. Laws 2023, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spelman, W. Specifying the relationship between crime and prisons. J. Quant. Criminol. 2008, 24, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataru, B.; Abonyo, O.J.; Malonza, D. Mathematical model for crimes in developing countries with some control strategies. J. Appl. Math. 2023, 2023, 8699882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soemarsono, A.R.; Fitria, I.; Nugraheni, K.; Hanifa, N. Analysis of mathematical model on impact of unemployment growth to crime rates. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1726, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.B.; Goyal, A.; Agrawal, K.; Kushwah, H.; Shukla, A. Role of technology in combating social crimes: A modeling study. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 2013, 24, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, A.A.; Tsardakas, M.N. A mathematical model of serious and minor criminal activity. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 2016, 27, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, P. Mathematical analysis of crime dynamics in and out of prisons. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2021, 44, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.K.; Heineke, J.M. A labor theoretic analysis of the criminal choice. Am. Econ. Rev. 1975, 65, 314. [Google Scholar]
- Caulkins, J.P.; Feichtinger, G.; Grass, D.; Hartl, R.F.; Kort, P.M.; Novak, A.J.; Seidl, A.; Wirl, F. A dynamic analysis of Schelling’s binary corruption model: A competitive equilibrium approach. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2014, 161, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinteros, M.J.; Villena, M.J. On the dynamics and stability of the crime and punishment game. Complexity 2022, 2022, 2449031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brianzoni, S.; Coppier, R.; Michetti, E. Complex dynamics in a growth model with corruption in public procurement. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2011, 2011, 862396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.H.A. More guns, less crime? A dynamical systems approach. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 369, 124804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooknanan, J.; Bhatt, B.; Comissiong, D.M.G. Catching a gang—A mathematical model of the spread of gangs in a population treated as an infectious disease. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2013, 83, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillon, D.; Simon, C.P.; Morenoff, J. Modeling the underlying dynamics of the spread of crime. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyabadza, F.; Ogbogbo, C.P.; Mushanyu, J. Modelling the role of correctional services on gangs: Insights through a mathematical model. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.; Tripathi, J.P.; Neha, A.A. Dynamical analysis of a model of social behavior: Criminal vs non-criminal population. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 98, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Ghosh, M.; Chandra, P. Modeling dynamics of the spread of crime in a society. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 2019, 37, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Athithan, S.; Ghosh, M. Modeling and analysis of crime prediction and prevention. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2020, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, N.K.D.; Bader, G.; Fiatsonu, E. Controlling crime with its associated cost during festive periods using mathematical techniques. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderoni, F.; Comunale, T.; Campedelli, G.M.; Marchesi, M.; Manzi, D.; Frualdo, N. Organized crime groups: A systematic review of individual-level risk factors related to recruitment. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nu no, J.C.; Herrero, M.A.; Primicerio, M. A triangle model of criminality. Physica A 2008, 387, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.K. Modeling the effect of police deterrence on the prevalence of crime in the society. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 237, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, S. Stability analysis of the transmission dynamics and control of corruption. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 15, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Eguda, F.Y.; Oguntolu, F.; Ashezua, T. Understanding the dynamics of corruption using mathematical modeling approach. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Kolokoltsov, V.N.; Malafeyev, O.A. Mean-field-game model of corruption. Dyn. Games Appl. 2017, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.H.; Yeolekar, B.M.; Patel, Z.A. Epidemics of corruption using incidence function. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. Stud. 2017, 51, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Lemecha, L.; Feyissa, S. Mathematical modeling and analysis of corruption dynamics. Ethiop. J. Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 5, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Alemneh, H.T. Mathematical modeling, analysis, and optimal control of corruption dynamics. J. Appl. Math. 2020, 2020, 5109841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danford, O.; Kimathi, M.; Mirau, S. Mathematical modelling and analysis of corruption dynamics with control measures in Tanzania. J. Math. Inform. 2020, 19, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantaye, A.K.; Birhanu, Z.K. Mathematical model and analysis of corruption dynamics with optimal control. J. Appl. Math. 2022, 2022, 8073877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.A.; Raja, R.; Alzabut, J.; Rajchakit, G.; Cao, J.; Balas, V.E. Mathematical modeling on transmission and optimal control strategies of corruption dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, A.W.; Alemneh, H.T. Analysis of a stochastic model of corruption transmission dynamics with temporary immunity. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Parra, G.; Chen-Charpentier, B.; Kojouharov, H.V. Mathematical modeling of crime as a social epidemic. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2018, 21, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.D. Mathematical Biology I: An Introduction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guckenheimer, J.; Holmes, P. Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcations of Vector Fields; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Heesterbeek, J.A.P. A brief history of R0 and a recipe for its calculation. Acta Biotheor. 2002, 50, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, H.; Inaba, H. Discussion: Emergence of the concept of the basic reproduction number from mathematical demography. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 244, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Andres, T.; Campolongo, F.; Cariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Saisana, M.; Tarantola, S. Global Sensitivity Analysis. The Primer; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ellner, S.P.; Guckenheimer, J. Dynamic Models in Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dushoff, J.; Huang, W.Z.; Castillo-Chavez, C. Backwards bifurcations and catastrophe in simple models of fatal diseases. J. Math. Biol. 1998, 36, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Driessche, P.; Watmough, J. A simple SIS epidemic model with a backward bifurcation. J. Math. Biol. 2000, 40, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.L.S.; Monteiro, L.H.A. On considering the influence of recovered individuals in disease propagations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2016, 34, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.Q.; Qiu, Z.P.; Liu, W.B.; Hu, Z.Y. Complex dynamics of an SIR epidemic model with nonlinear saturate incidence and recovery rate. Entropy 2017, 19, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, K. Modern Control Engineering; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, D.F.; Higham, D.J. Numerical Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations: Initial Value Problems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Davoodi, H.; Alonso-Terme, R. Does corruption affect income inequality and poverty? Econ. Gov. 2002, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründler, K.; Potrafke, N. Corruption and economic growth: New empirical evidence. Eur. J. Polit. Econ. 2019, 60, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, W.F. The interdependence of autonomous human-machine teams: The entropy of teams, but not individuals, advances science. Entropy 2019, 21, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongi, C.; Saidi, K. The impact of corruption, government effectiveness, FDI, and GFC on economic growth: New evidence from global panel of 48 middle-income countries. J. Knowl. Econ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.Z.; Zhang, B.Q.; Xiong, F. Multimodal assessment of political corruption worsening national poverty: Evidence of mediating and moderating effects from global panel data. Chin. Public Adm. Rev. 2023, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harari, G.S.; Monteiro, L.H.A. Bifurcations in a Model of Criminal Organizations and a Corrupt Judiciary. Entropy 2024, 26, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26110906
Harari GS, Monteiro LHA. Bifurcations in a Model of Criminal Organizations and a Corrupt Judiciary. Entropy. 2024; 26(11):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26110906
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarari, G. S., and L. H. A. Monteiro. 2024. "Bifurcations in a Model of Criminal Organizations and a Corrupt Judiciary" Entropy 26, no. 11: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26110906
APA StyleHarari, G. S., & Monteiro, L. H. A. (2024). Bifurcations in a Model of Criminal Organizations and a Corrupt Judiciary. Entropy, 26(11), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26110906





