Adapting SAM2 Model from Natural Images for Tooth Segmentation in Dental Panoramic X-Ray Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We adopt a fine-tuning approach based on a pretrained model. While some researchers have attempted to transform SAM into a U-shaped architecture [20,23], these efforts were limited by the simple structure of the standard ViT encoder [24], which lacks the hierarchy required for more complex segmentation tasks. The introduction of SAM2 offers new opportunities for designing more efficient U-shaped networks [25]. Direct application to medical images is less effective, mainly due to the significant differences in structure and features between medical and natural images, such as the low contrast and complex anatomical structures of X-ray images. Therefore, relying solely on the SAM2 model pretrained on natural images is insufficient for medical image segmentation. To address this, we used adapter modules for fine-tuning and introduced feature fusion and selection modules to enhance the model’s semantic understanding and multi-scale detail capture for medical images. Specifically, we added adapter modules to the part of the SAM2 model and used it as the part of our model. Then, ScConv [26] modules were introduced before the skip connections to reduce redundancy in feature extraction. We also applied gated attention in the skip connections to further enhance detail segmentation, resulting in a model suitable for small-sample dental segmentation datasets, named S2AgScUNet. Experimentally, on the UFBA-UESC dataset [3], the S2AgScUNet model achieved an IoU score of 0.8612, surpassing the 0.8477 achieved by the UNet model.
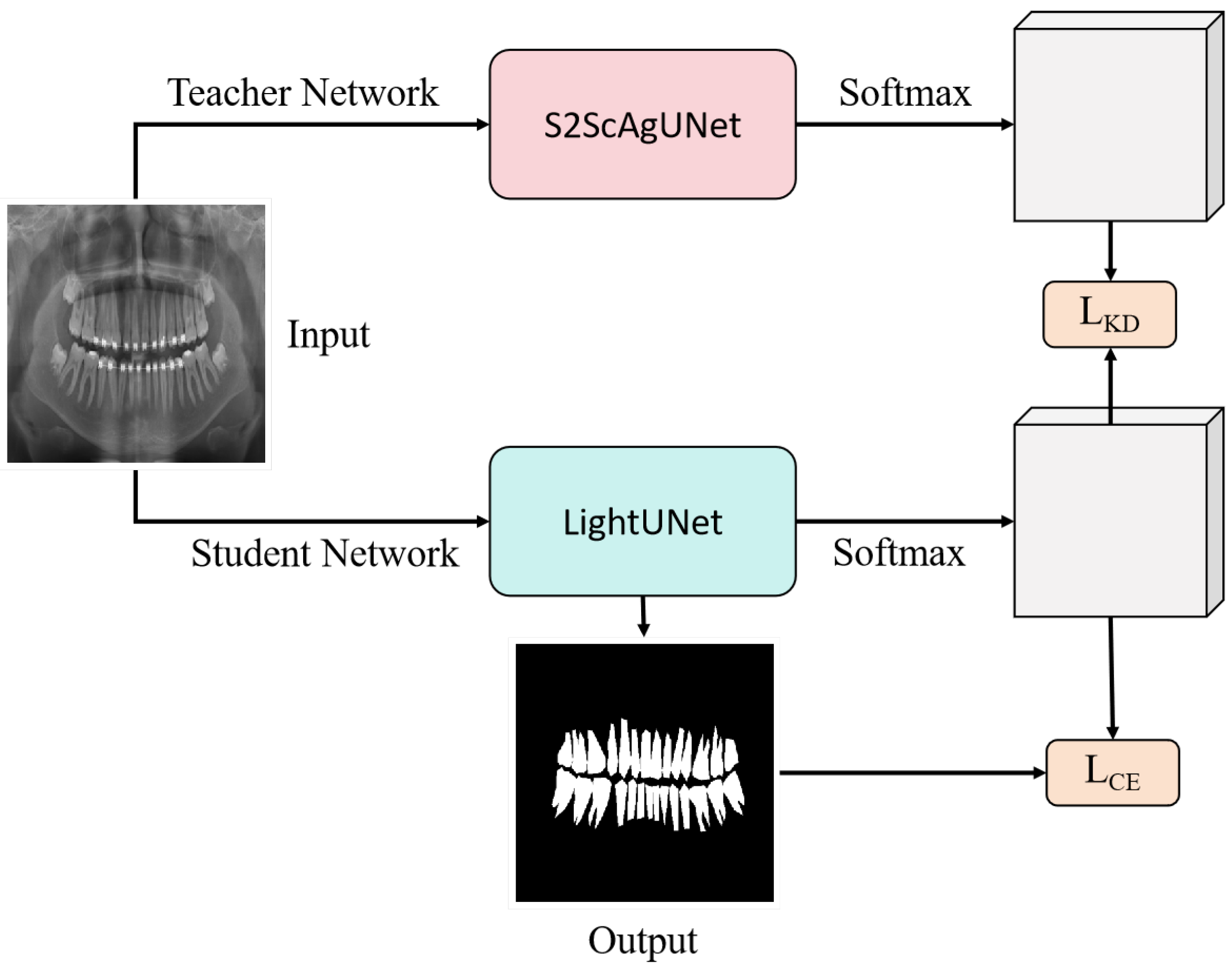
- We employ a knowledge distillation approach to create a more efficient model suitable for practical deployment. We use the fine-tuned model as the teacher model and then create a lightweight model called LightUNet, which has the same architecture as the UNet model but only 0.016 times its parameters. The inference time on the entire test set is only 0.24 times that of UNet.
- Proposed S2AgScUNet based on the pre-trained SAM2 model: This paper introduces S2AgScUNet, which leverages the pre-trained SAM2 model as an encoder, combined with ScConv modules and gated attention mechanisms, providing an effective solution for dental panoramic X-ray image segmentation under limited sample conditions.
- Effectively alleviated the overfitting problem in tooth segmentation: By incorporating the pre-trained SAM2 model with hierarchical feature learning capabilities, the proposed method significantly reduces overfitting in dental X-ray small-sample datasets, enhancing both the model’s generalization ability and robustness.
- Significant improvement in segmentation performance: Experimental results on the UFBA-UESC dataset demonstrate that the S2AgScUNet model significantly outperforms the traditional UNet model in multiple metrics, such as IoU and Dice, particularly excelling in capturing details and segmenting complex structures.
- Efficient deployment on edge devices using knowledge distillation: To facilitate deployment on edge devices, we utilized knowledge distillation to achieve comparable performance to the UNet model, while reducing the parameter count to only 0.49 million compared to UNet’s 31.05 million parameters, making our model more efficient and lightweight.
2. Related Work
2.1. Classical Statistical Methods
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods
3. Method
3.1. Model Architecture
3.1.1. Semantic Medical Adapter for Fast Tuning
3.1.2. Receptive Field Block for Feature Enhancement and Redundancy Reduction
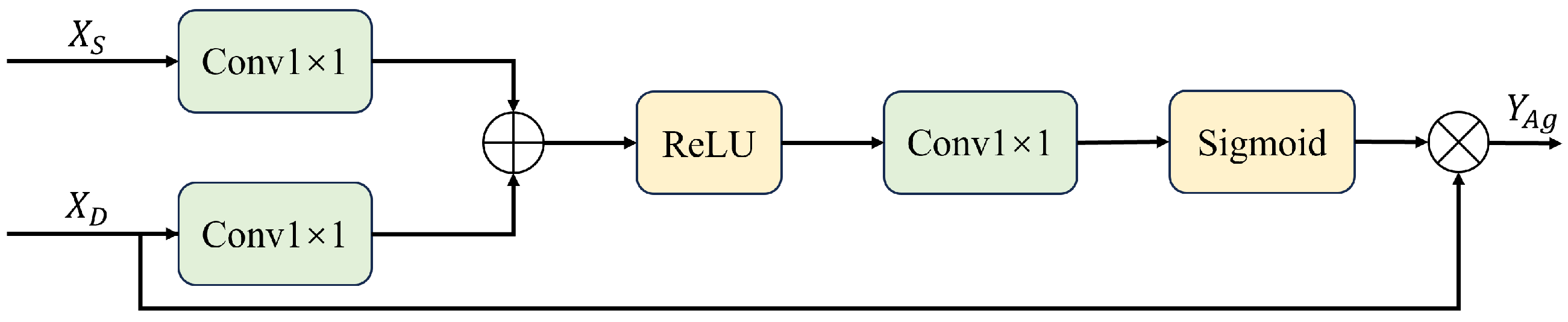
3.1.3. Attentional Gating for Multi-Scale Fusion
3.1.4. Decoder
3.2. Training
3.2.1. Fine-Tuning
3.2.2. Knowledge Distillation and Model Lightweighting
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset and Experimental Setup
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Quantitative Analysis
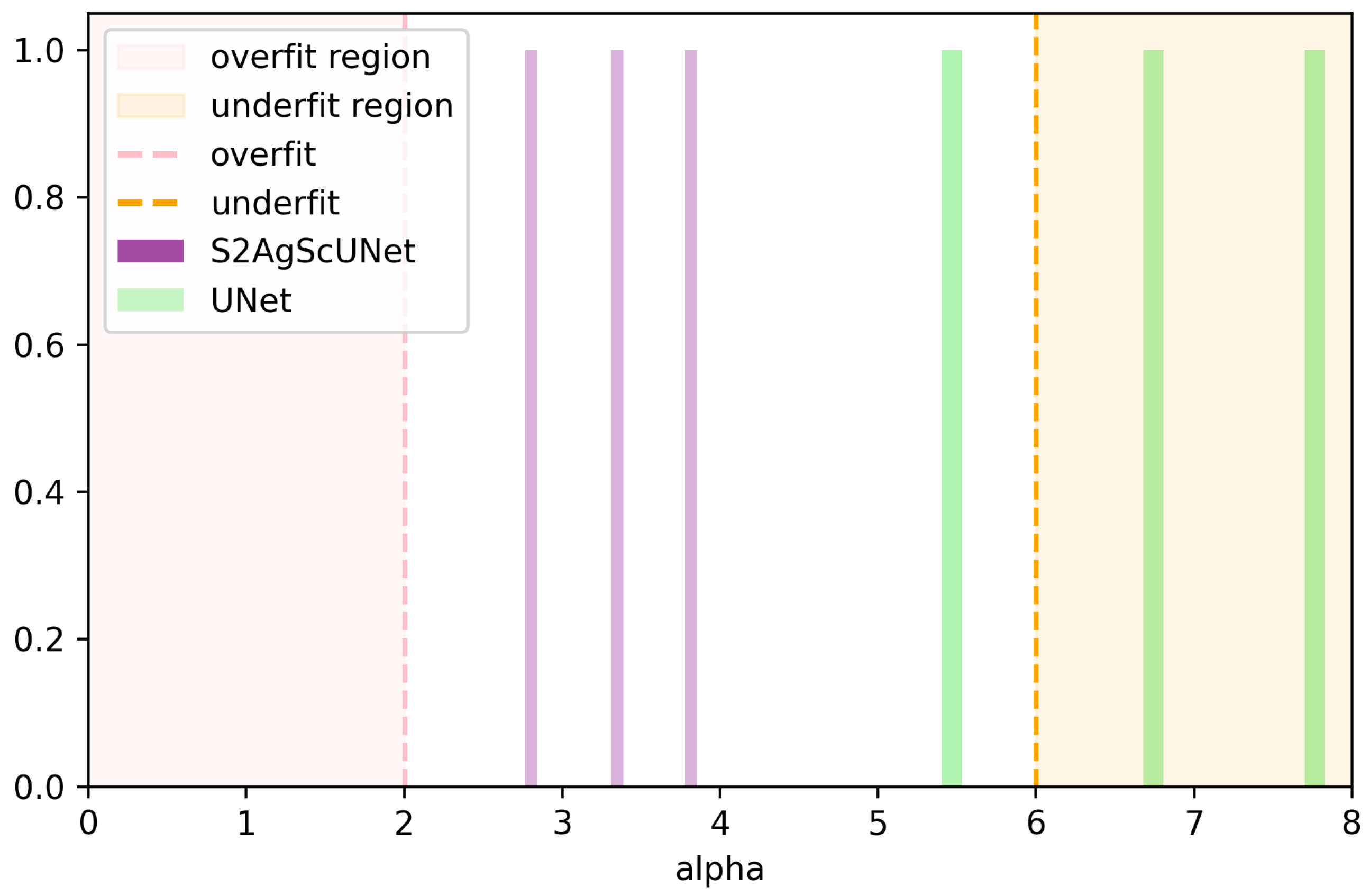
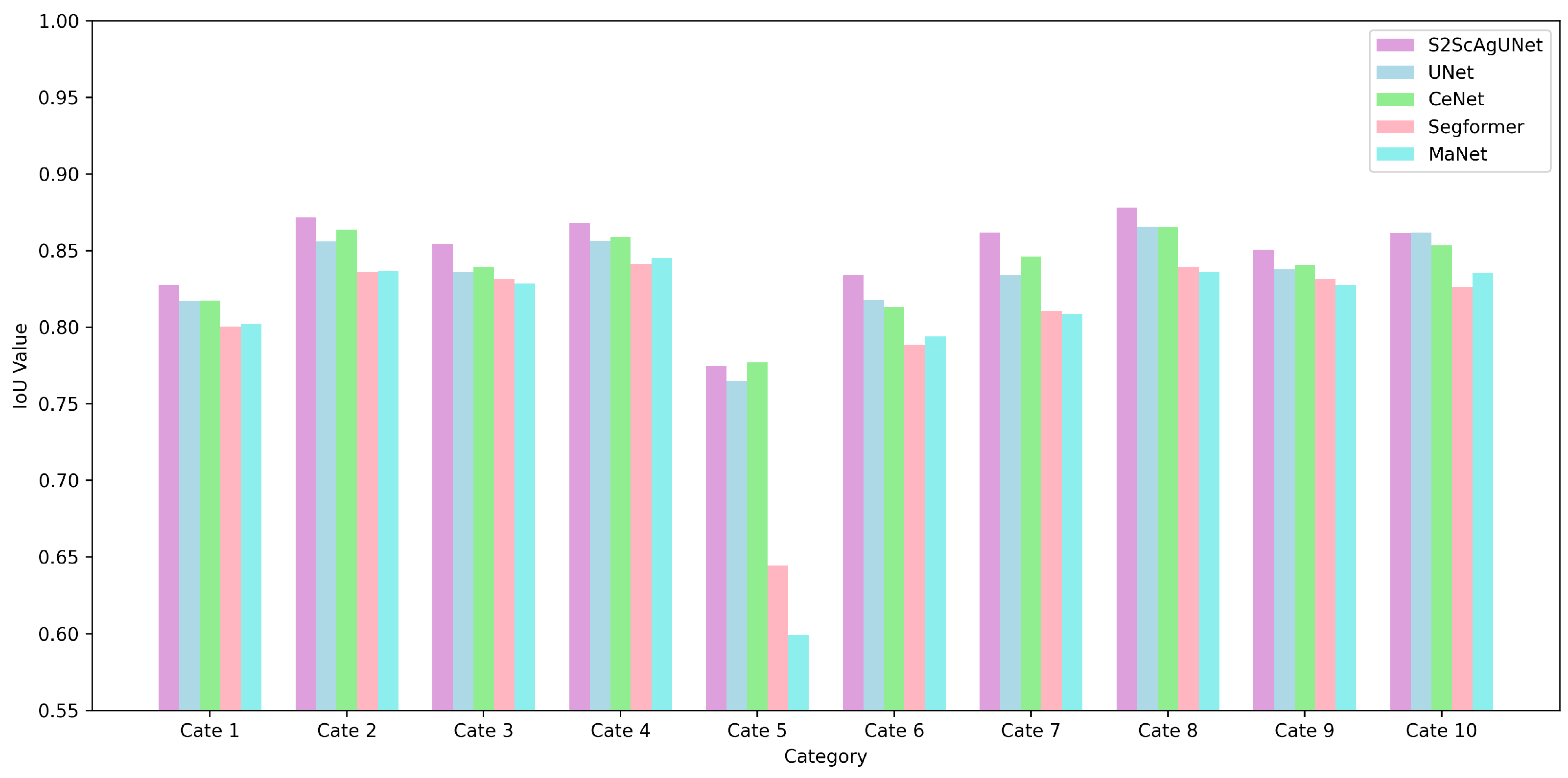
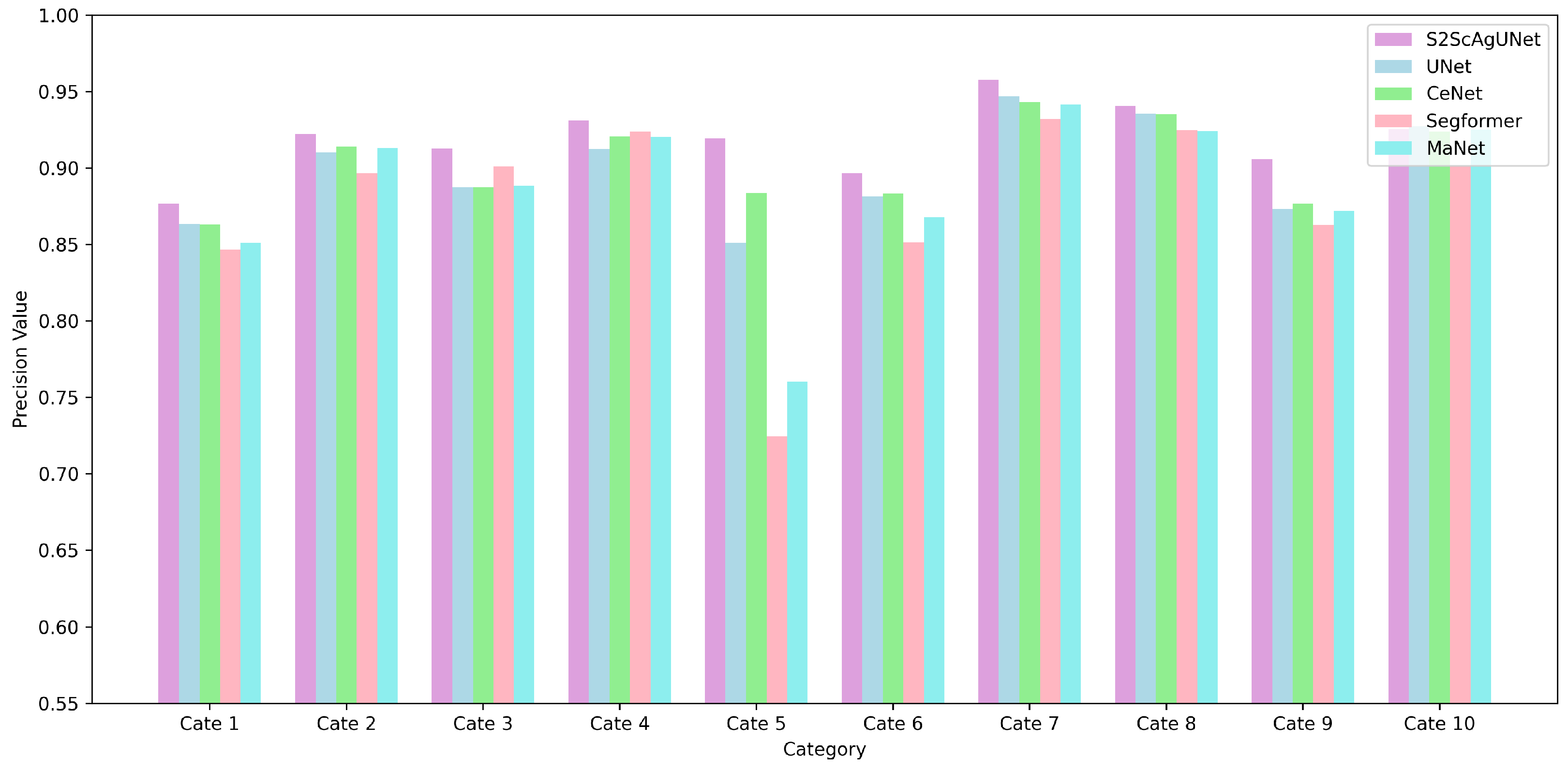
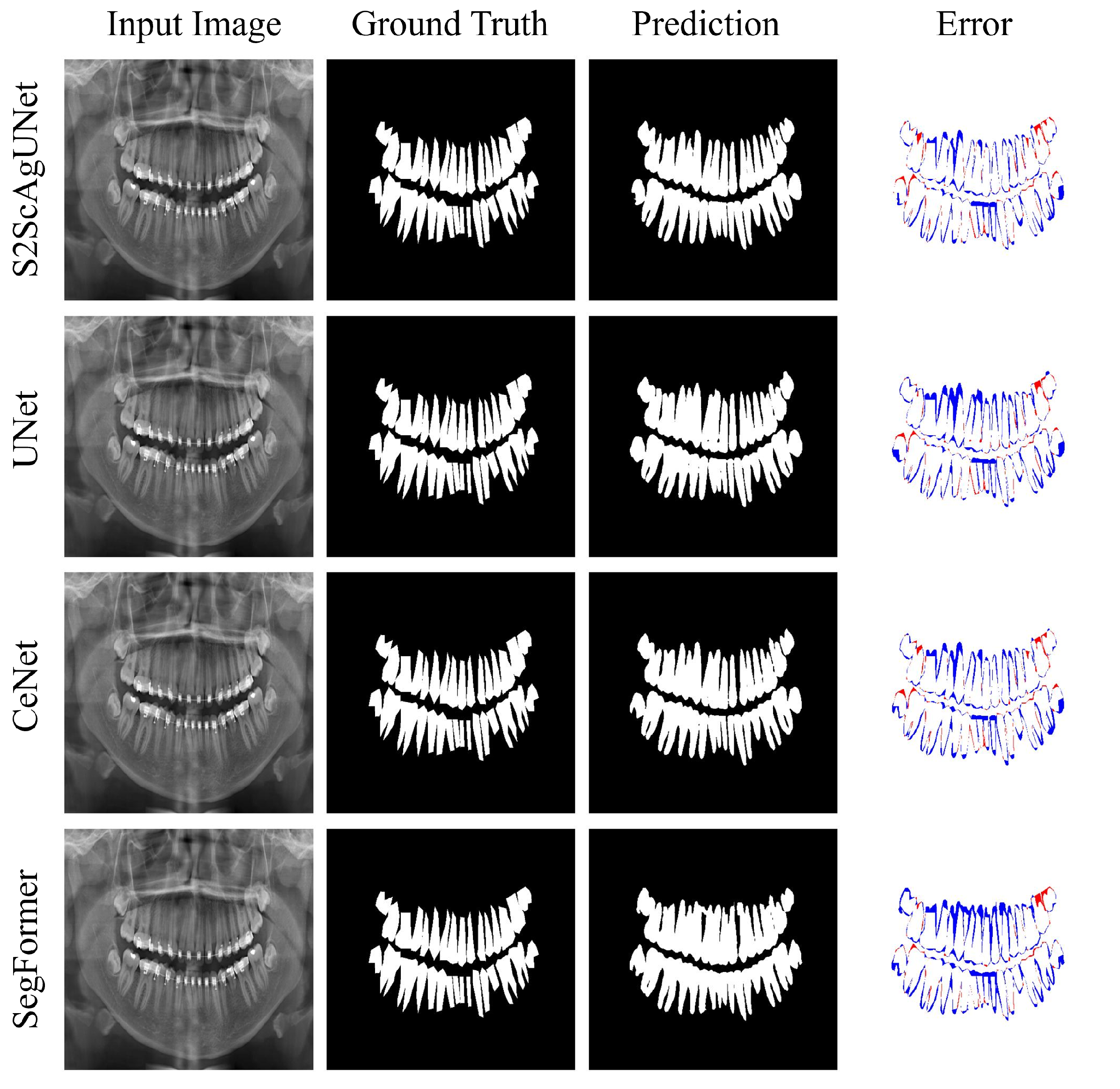
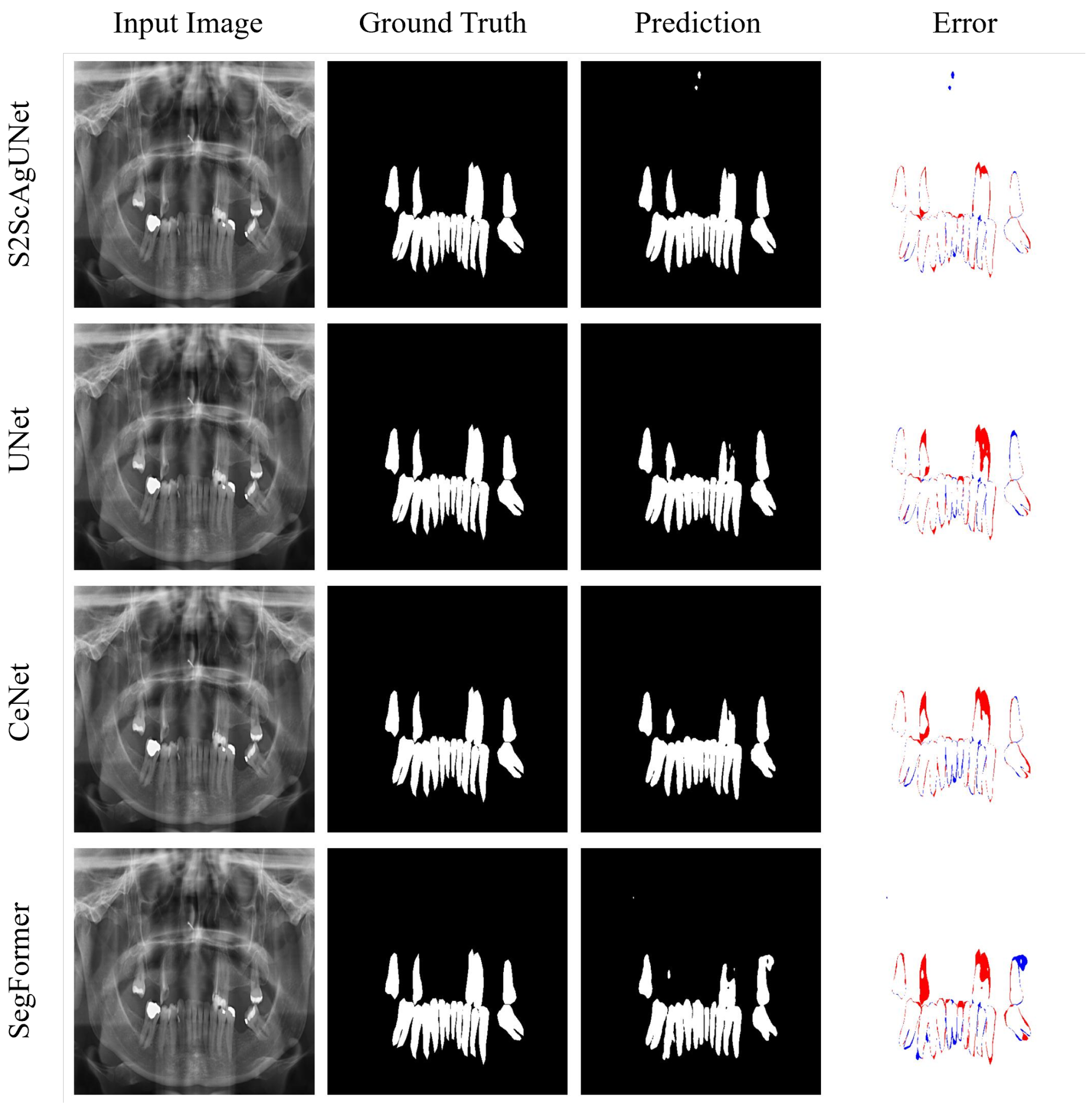
4.4. Further Analysis
4.5. Ablation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terlemez, A.; Tassoker, M.; Kizilcakaya, M.; Gulec, M. Comparison of cone-beam computed tomography and panoramic radiography in the evaluation of maxillary sinus pathology related to maxillary posterior teeth: Do apical lesions increase the risk of maxillary sinus pathology? Imaging Sci. Dent. 2019, 49, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.W.; Huang, C.T.; Lee, J.H.; Li, C.H.; Chang, S.W.; Siao, M.J.; Lai, T.M.; Ibragimov, B.; Vrtovec, T.; Ronneberger, O.; et al. A benchmark for comparison of dental radiography analysis algorithms. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 31, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.; Oliveira, L.; Pithon, M. Automatic segmenting teeth in X-ray images: Trends, a novel data set, benchmarking and future perspectives. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 107, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hao, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, D.; Liu, J.; Zhong, M. Lightweight deep learning methods for panoramic dental X-ray image segmentation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 8295–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Dang, P.; Lu, H.; Shi, H. Teeth U-Net: A segmentation model of dental panoramic X-ray images for context semantics and contrast enhancement. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.; Pinheiro, L.; Oliveira, L.; Pithon, M. A study on tooth segmentation and numbering using end-to-end deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 33rd SIBGRAPI conference on graphics, patterns and images (SIBGRAPI), Recife/Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, 7–10 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, I.; Yan, J.; Abbas, Q.; Shaheed, K.; Riaz, A.B.; Wahid, A.; Khan, M.W.J.; Szczuko, P. Medical image segmentation using deep semantic-based methods: A review of techniques, applications and emerging trends. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 316–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Rauland, A.; Jia, Y.; Avval, A.H.; Bozorgpour, A.; Karimijafarbigloo, S.; Cohen, J.P.; Adeli, E.; Merhof, D. Medical image segmentation review: The success of u-net. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 10076–10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q. Transformers in medical image segmentation: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023, 84, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Fang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, J. Cross-Modality LGE-CMR Segmentation Using Image-to-Image Translation Based Data Augmentation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.B.; Teng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Woźniak, M.; Wang, W. A Robust Deep Learning Framework Based on Spectrograms for Heart Sound Classification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2024, 21, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.b.; Yang, B.; Wang, W. Compressed sensing framework for heart sound acquisition in internet of medical things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, J.; Du, H.; Liu, J.; Pang, B.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Cao, D. Single Tooth Segmentation on Panoramic X-Rays Using End-to-End Deep Neural Networks. Open J. Stomatol. 2024, 14, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; Computer Vision Foundation; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, N.; Gabeur, V.; Hu, Y.T.; Hu, R.; Ryali, C.; Ma, T.; Khedr, H.; Rädle, R.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; et al. Sam 2: Segment anything in images and videos. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.00714. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Han, L.; You, C.; Wang, B. Segment anything in medical images. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y. Medical sam adapter: Adapting segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.12620. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, D. Customized segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.13785. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y. How to efficiently adapt large segmentation model (sam) to medical images. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.13731. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xia, W.; Hu, D.; Gao, X. Desam: Decoupling segment anything model for generalizable medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.00499. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Ye, J.; Deng, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; et al. Sam-med2d. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.16184. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.H.; Peng, T.; Mahoney, M.W. Predicting trends in the quality of state-of-the-art neural networks without access to training or testing data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Li, G. Mammo-sam: Adapting foundation segment anything model for automatic breast mass segmentation in whole mammograms. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8 October 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, D. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, Z.; Tan, S.; Li, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, J.; Li, G. SAM2-UNet: Segment Anything 2 Makes Strong Encoder for Natural and Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.08870. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; He, L. Scconv: Spatial and channel reconstruction convolution for feature redundancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; Computer Vision Foundation; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 6153–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Lurie, A.; Tosoni, G.M.; Tsimikas, J.; Walker Jr, F. Recursive hierarchic segmentation analysis of bone mineral density changes on digital panoramic images. Oral Surgery, Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 113, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, C.K.; Desai, N.P. A simple and novel algorithm for automatic selection of ROI for dental radiograph segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2011 24th Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering (CCECE), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 8–11 May 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 000504–000507. [Google Scholar]
- Radhiyah, A.; Harsono, T.; Sigit, R. Comparison study of Gaussian and histogram equalization filter on dental radiograph segmentation for labelling dental radiograph. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Knowledge Creation and Intelligent Computing (KCIC), Manado, Indonesia, 15–17 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Alsmadi, M.K. A hybrid Fuzzy C-Means and Neutrosophic for jaw lesions segmentation. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, T.M. A cooperative semi-supervised fuzzy clustering framework for dental X-ray image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 46, 380–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.B.; Ejbali, R.; Zaied, M. GPU-based segmentation of dental x-ray images using active contours without edges. In Proceedings of the 2015 15th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (ISDA), Marrakesh, Morocco, 14–16 December 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fevens, T.; Krzyżak, A.; Jin, C.; Li, S. Semi-automatic computer aided lesion detection in dental X-rays using variational level set. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fevens, T.; Krzyżak, A.; Li, S. An automatic variational level set segmentation framework for computer aided dental X-rays analysis in clinical environments. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2006, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, J.L.; Miller, M.E.; Tooze, J.; Ip, E. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 134, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaeghe, H.; Nijssen, S.; Pesant, G.; Quimper, C.G.; Schaus, P. Learning optimal decision trees using constraint programming. Constraints 2020, 25, 226–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, K.; Hu, Y.; Sheng, W.; Feng, Q. GrabCut algorithm for dental X-ray images based on full threshold segmentation. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 2330–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indraswari, R.; Arifin, A.Z.; Navastara, D.A.; Jawas, N. Teeth segmentation on dental panoramic radiographs using decimation-free directional filter bank thresholding and multistage adaptive thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and Systems (ICTS), Surabaya, Indonesia, 16 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C. MSLPNet: Multi-scale location perception network for dental panoramic X-ray image segmentation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 10277–10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, C.; Fan, X.; Lan, X.; Lu, X.; Ye, X.; Wu, T. Attention Mask R-CNN with edge refinement algorithm for identifying circulating genetically abnormal cells. Cytom. Part A 2023, 103, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, C.; Lan, X.; Fan, X.; Lv, X.; Ye, X.; Wu, T. A lightweight and robust framework for circulating genetically abnormal cells (CACs) identification using 4-color fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image and deep refined learning. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 1687–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Fu, C. Robust Imagined Speech Production Using AI-Generated Content Network for Patients with Language Impairments. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lv, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Empowering Semantic Segmentation with Selective Frequency Enhancement and Attention Mechanism for Tampering Detection. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 3270–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Fu, C.; Yang, L.; Yan, Y.; Lyu, Z. Robust Gaze Point Estimation for Metaverse With Common Mode Features Suppression Network. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cong, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Sleep Stage Classification with Multi-Modal Fusion and Denoising Diffusion Model. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Fang, B.; Liu, Y.; Yu, K.; Leung, V.C.M.; Hu, X. Digital Twin Empowered Wireless Healthcare Monitoring for Smart Home. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 3662–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, B.Y.; Ozcan, C.; Pekince, A.; Yasa, Y. An enhanced tooth segmentation and numbering according to FDI notation in bitewing radiographs. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105547. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Xia, B.; Cao, Z.; Guo, C. Automated dental image analysis by deep learning on small dataset. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Tokyo, Japan, 23–27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Gan, Y.; Chang, L.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, Q. Individual tooth segmentation from CT images scanned with contacts of maxillary and mandible teeth. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 138, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, T.L.; Perslev, M.; Igel, C.; Brandt, S.S. Accurate segmentation of dental panoramic radiographs with U-Nets. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Z.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Weng, J.; Fan, M. Automated maxillofacial segmentation in panoramic dental x-ray images using an efficient encoder-decoder network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 207822–207833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, P.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, F.; Meng, D. TSASNet: Tooth segmentation on dental panoramic X-ray images by Two-Stage Attention Segmentation Network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 206, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Zeng, K.; Li, Z. URNet: A U-Net based residual network for image dehazing. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 102, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liu, P.X. Hybrid dilation and attention residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, S.; Chang, F. CLCU-Net: Cross-level connected U-shaped network with selective feature aggregation attention module for brain tumor segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 207, 106154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryali, C.; Hu, Y.T.; Bolya, D.; Wei, C.; Fan, H.; Huang, P.Y.; Aggarwal, V.; Chowdhury, A.; Poursaeed, O.; Hoffman, J.; et al. Hiera: A hierarchical vision transformer without the bells-and-whistles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 29441–29454. [Google Scholar]
- Budagam, D.; Kumar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Shrivastav, A.; Imanbayev, A.Z.; Akhmetov, I.R.; Kaplun, D.; Antonov, S.; Rychenkov, A.; Cyganov, G.; et al. Instance Segmentation and Teeth Classification in Panoramic X-rays. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.03747. [Google Scholar]



| Category | 32 Teeth | Restoration | Dental Appliance | Images | Used Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✓ | ✓ | 73 | 24 | |
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | 220 | 72 | |
| 3 | ✓ | 45 | 15 | ||
| 4 | ✓ | 140 | 32 | ||
| 5 | ✓ | 120 | 37 | ||
| 6 | ✓ | 170 | 30 | ||
| 7 | ✓ | 115 | 33 | ||
| 8 | ✓ | 457 | 140 | ||
| 9 | 45 | 7 | |||
| 10 | 115 | 35 | |||
| Total | 1500 | 425 |
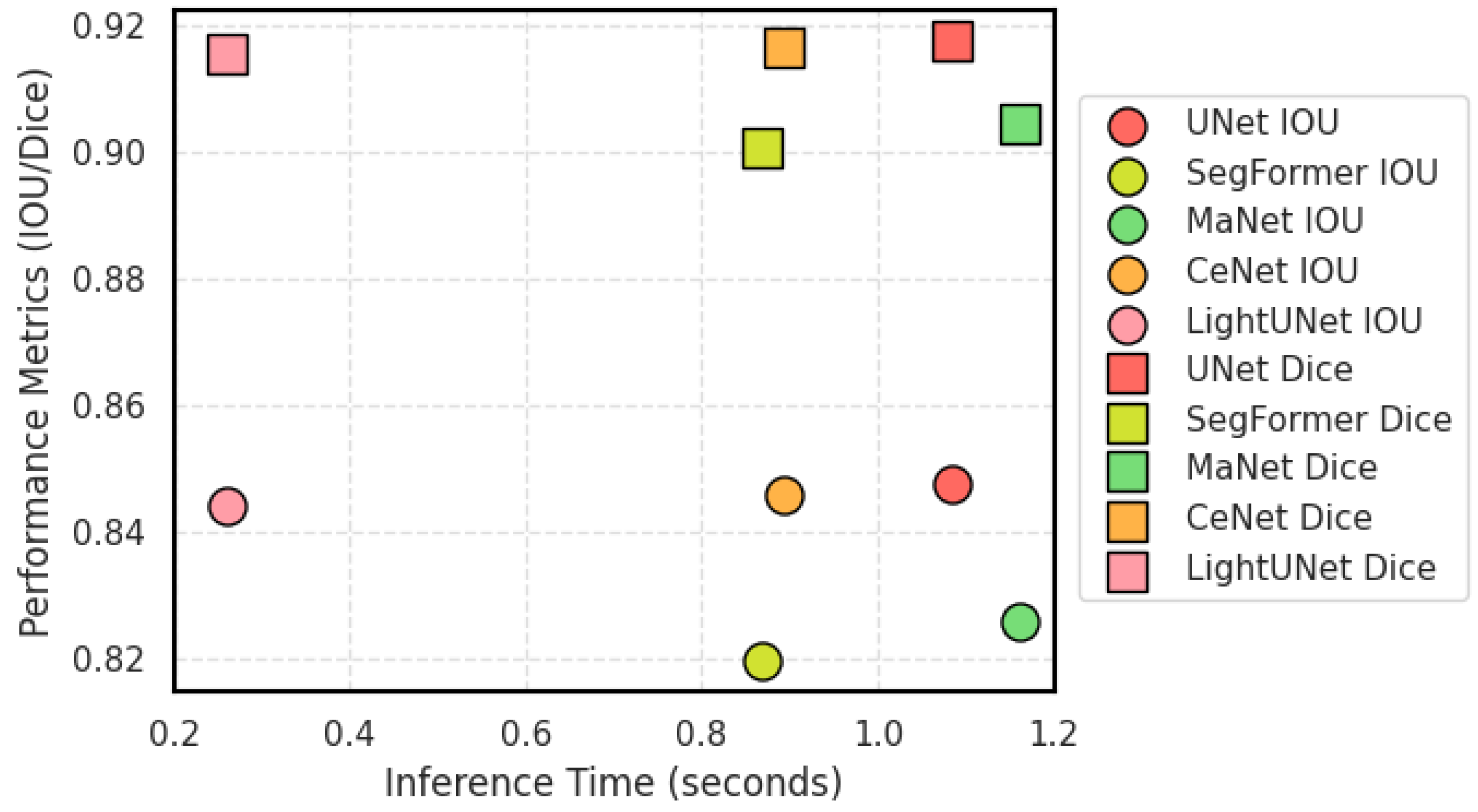
| Model | P(M) | F(G) | IOU | Dice | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet | 31.05 | 198.66 | 0.8477 | 0.9176 | 0.9188 | 0.9164 | 0.9176 |
| SegFormer | 13.68 | 15.40 | 0.8196 | 0.9009 | 0.8940 | 0.9079 | 0.9009 |
| MaNet | 35.86 | 54.18 | 0.8257 | 0.9046 | 0.9074 | 0.9018 | 0.9046 |
| CeNet | 13.40 | 126.98 | 0.8460 | 0.9165 | 0.9205 | 0.9126 | 0.9165 |
| S2AgScUNet | N/A | N/A | 0.8612 | 0.9254 | 0.9239 | 0.9270 | 0.9254 |
| LightUNet | 0.49 | 3.20 | 0.8443 | 0.9156 | 0.9160 | 0.9151 | 0.9156 |
| Method | IOU | Dice | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0.8477 | 0.9176 | 0.9188 | 0.9164 | 0.9176 |
| +SAM2 | 0.8546 | 0.9216 | 0.9226 | 0.9205 | 0.9216 |
| +AG | 0.8559 | 0.9224 | 0.9246 | 0.9201 | 0.9224 |
| +ScConvRFB | 0.8612 | 0.9254 | 0.9239 | 0.9270 | 0.9254 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Tang, W.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Adapting SAM2 Model from Natural Images for Tooth Segmentation in Dental Panoramic X-Ray Images. Entropy 2024, 26, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121059
Li Z, Tang W, Gao S, Wang Y, Wang S. Adapting SAM2 Model from Natural Images for Tooth Segmentation in Dental Panoramic X-Ray Images. Entropy. 2024; 26(12):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zifeng, Wenzhong Tang, Shijun Gao, Yanyang Wang, and Shuai Wang. 2024. "Adapting SAM2 Model from Natural Images for Tooth Segmentation in Dental Panoramic X-Ray Images" Entropy 26, no. 12: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121059
APA StyleLi, Z., Tang, W., Gao, S., Wang, Y., & Wang, S. (2024). Adapting SAM2 Model from Natural Images for Tooth Segmentation in Dental Panoramic X-Ray Images. Entropy, 26(12), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121059





