Frequency-Aware Degradation Modeling for Real-World Thermal Image Super-Resolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Thermal Image Super-Resolution
2.2. Unsupervised Image Super-Resolution
3. Degradation Model
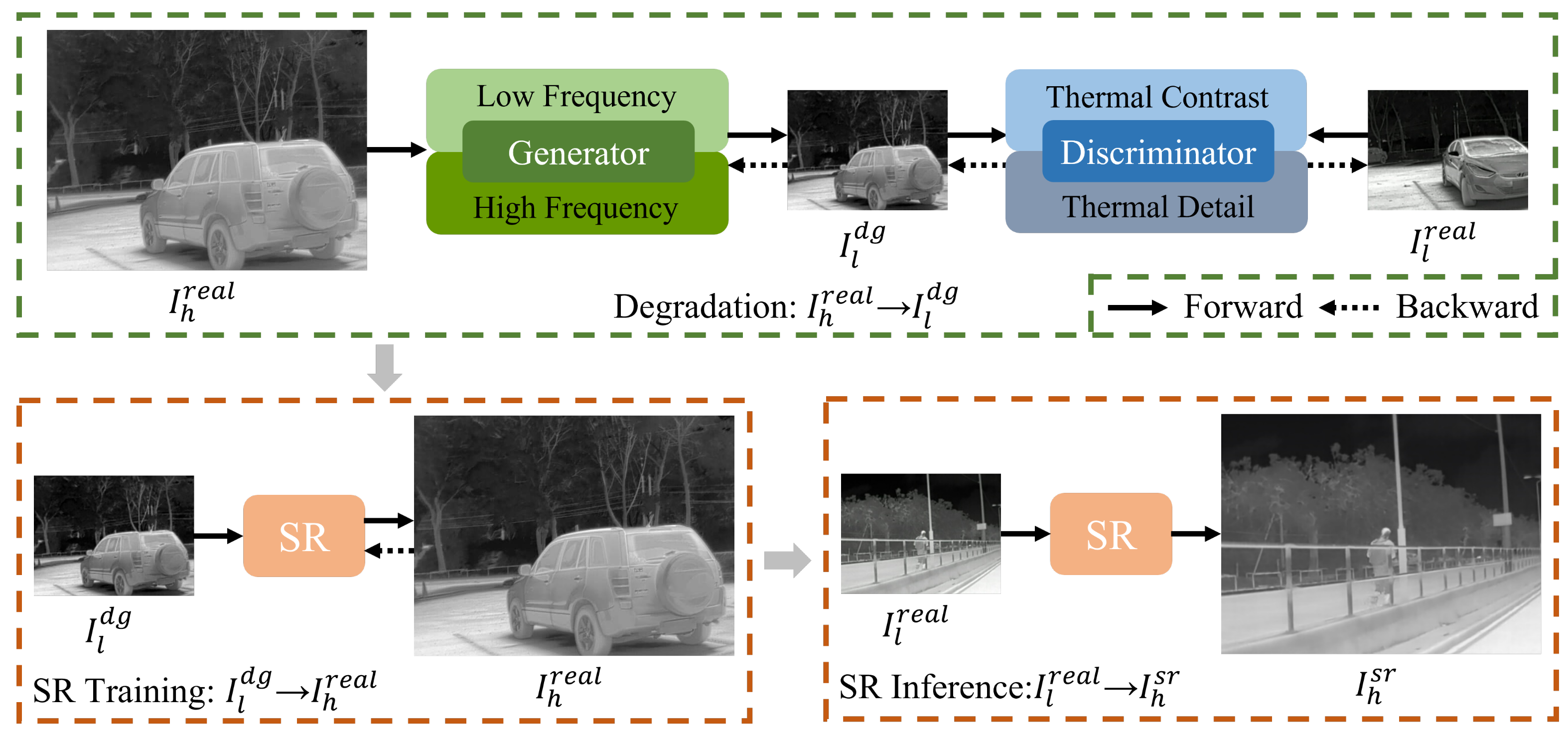
4. Proposed Method
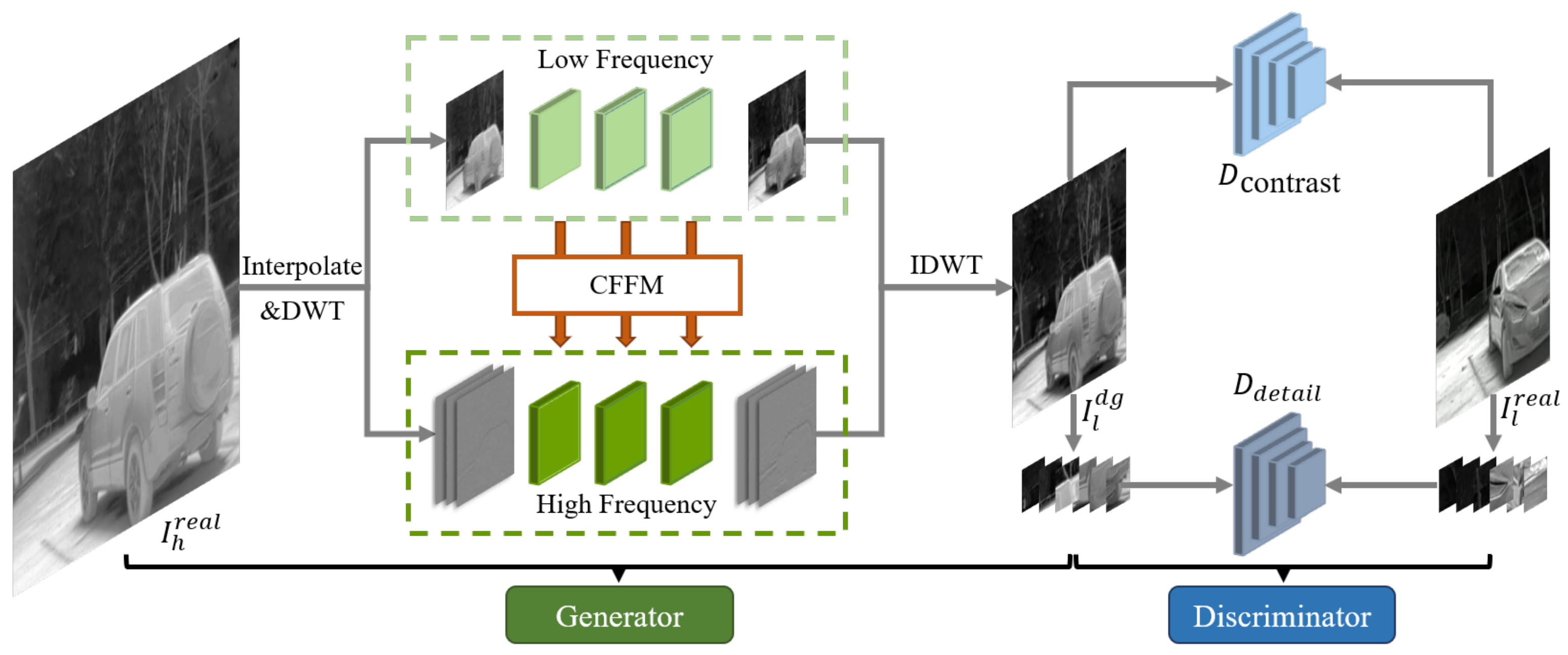
4.1. Thermal Image Frequency-Aware Degradation
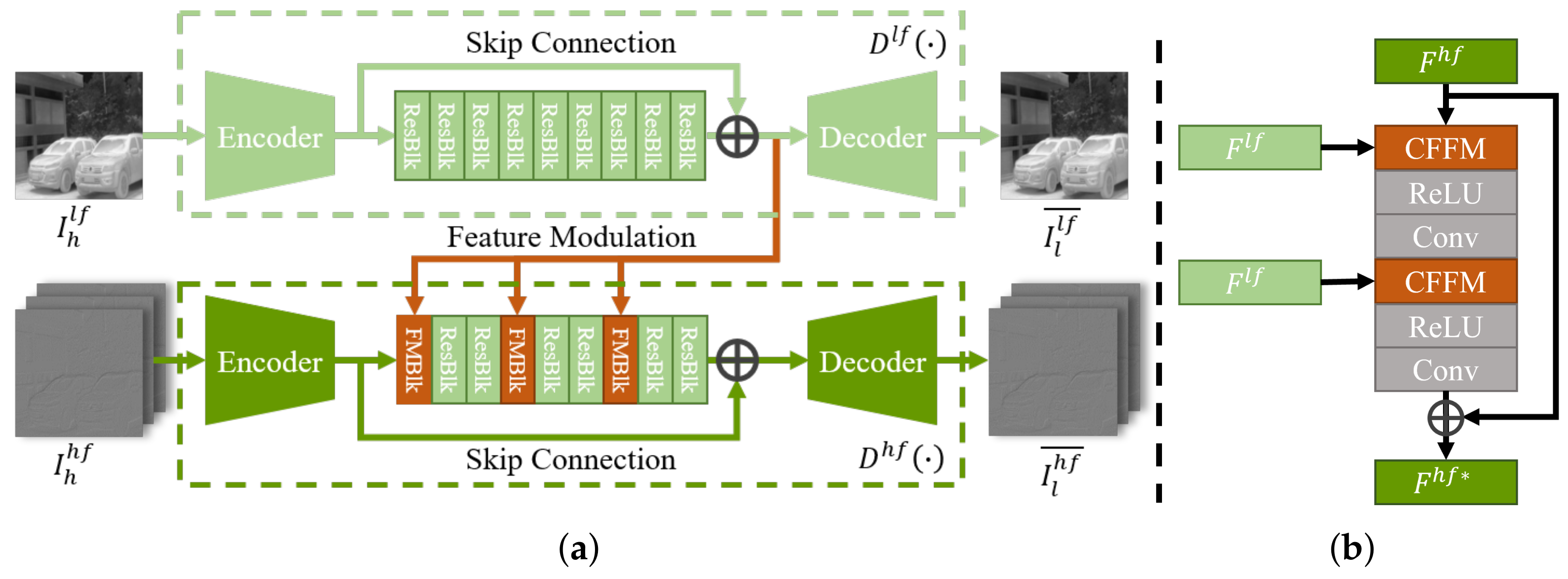
4.1.1. Dual-Frequency Decomposition
4.1.2. Cross-Frequency Feature Modulation
4.1.3. Dual-Frequency Degradation Generator
4.1.4. Discriminator for Detail and Contrast
4.1.5. Loss Functions
4.2. Degradation-Based Super-Resolution
4.3. The Algorithm Combining Degradation and Super-Resolution
- Lines 1–5: The degradation model TFADGAN is trained using unpaired LR-HR thermal images. Through N iterations, TFADGAN generates the reliable degraded LR thermal image .
- Lines 6–10: The SR network is trained using degraded LR thermal image and corresponding HR thermal image . Through M iterations, the SR network reconstructs high-quality HR thermal image .
| Algorithm 1 Complete algorithm with TFADGAN and SR method |
| Input: HR thermal image , Unpaired LR thermal image |
| Output: Degraded LR thermal image , Reconstructed HR thermal image |
| 1: for i in range(N) do |
| 2: Select unpaired HR thermal image and LR thermal image |
| 3: Train TFADGAN to generate degraded LR thermal image corresponding to HR thermal image and compute total loss in Equation (13) |
| 4: Update TFADGAN |
| 5: end for |
| 6: for i in range(M) do |
| 7: Select the degraded LR thermal image and paired HR thermal image |
| 8: Train SR network, generate reconstructed HR thermal image and compute reconstruction loss |
| 9: Update SR network |
| 10: end for |
5. Experiment and Results
5.1. Datasets and Details
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.3. Ablation Study
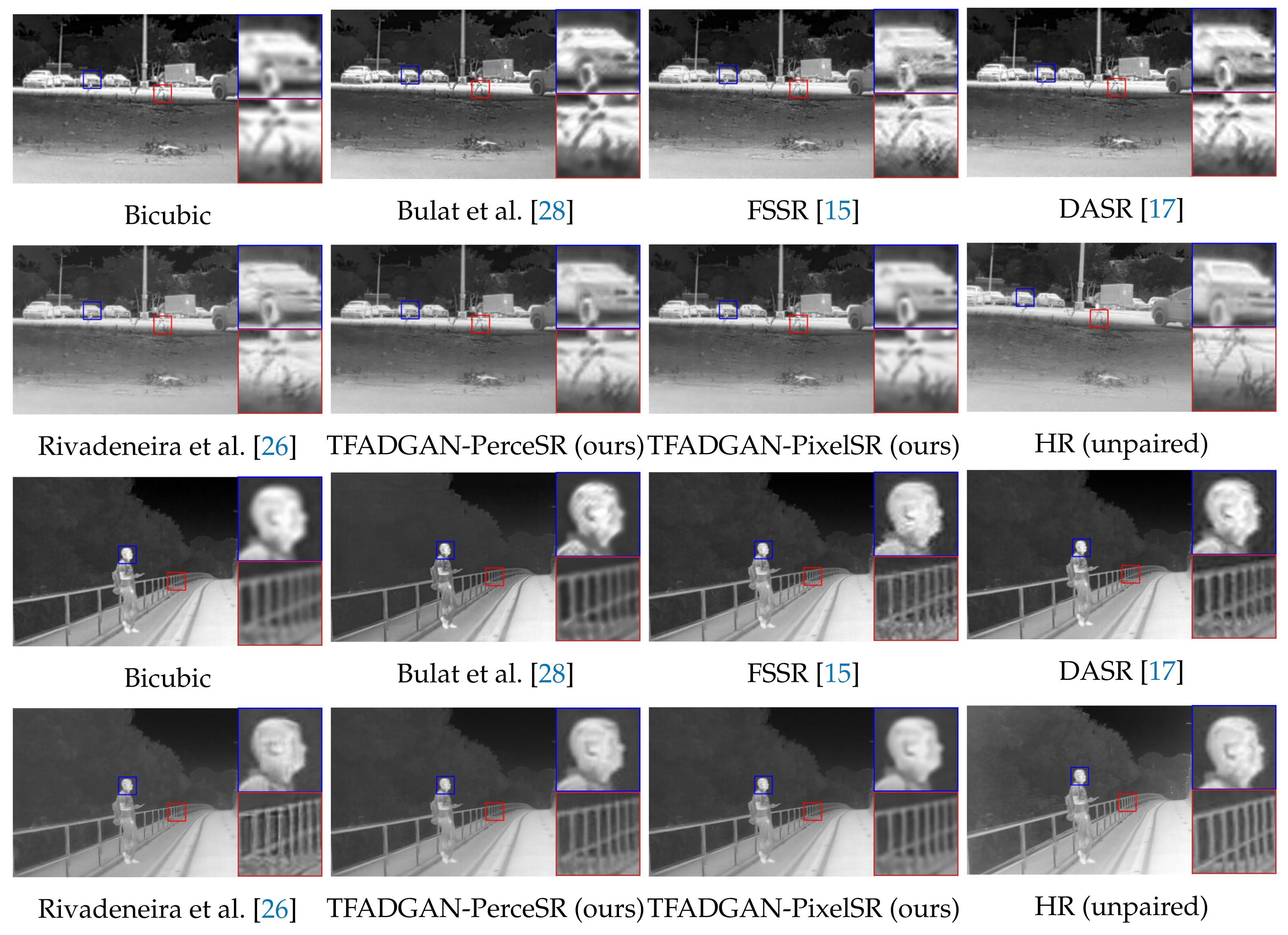
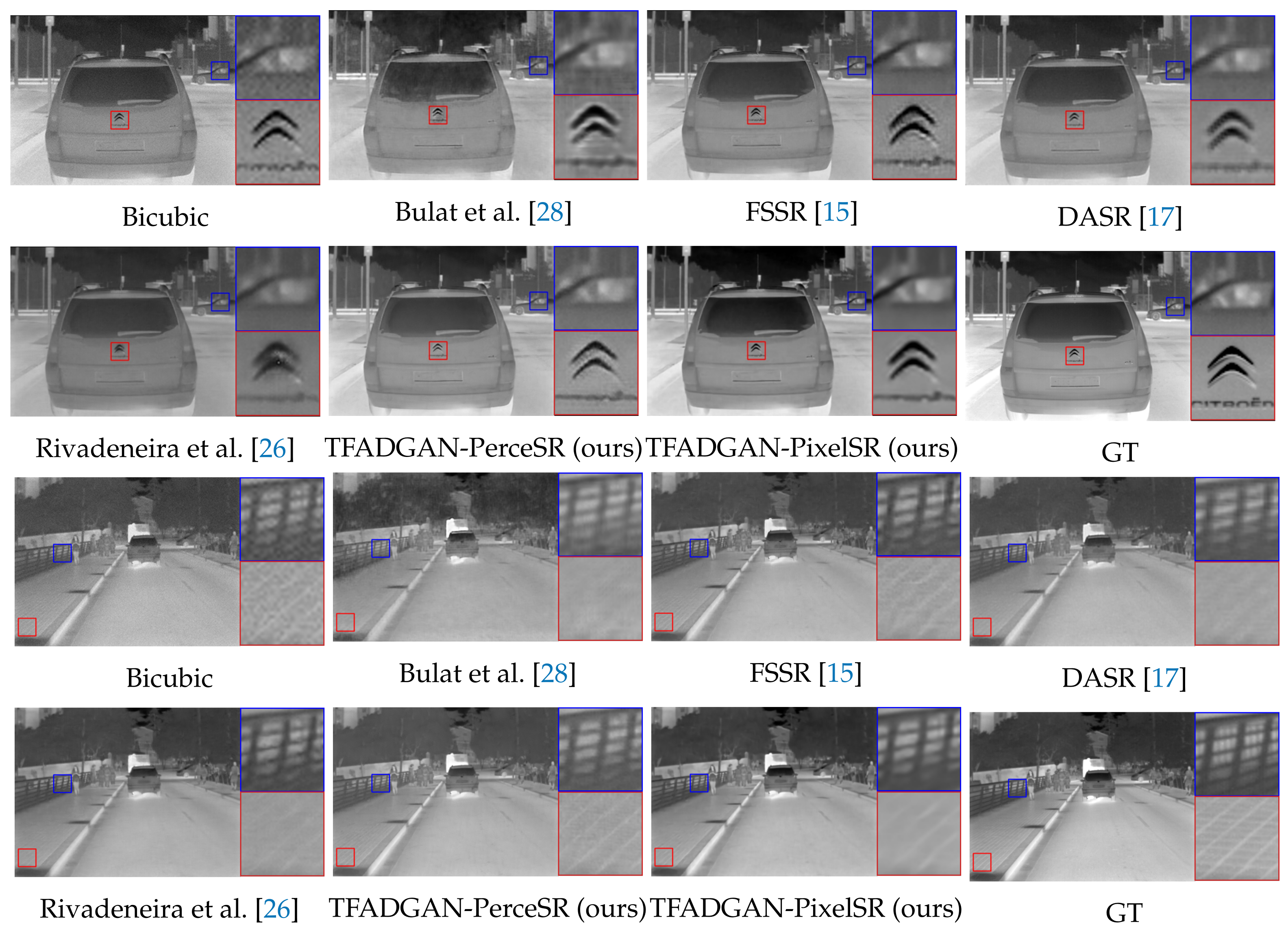
5.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
5.5. Effectiveness of TFADGAN
5.6. Model Complexity Analysis
6. Limitations and Prospects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldberg, A.C.; Fischer, T.; Derzko, Z.I. Application of dual-band infrared focal plane arrays to tactical and strategic military problems. In Proceedings of the Infrared Technology and Applications XXVIII, SPIE, Seattle, WA, USA, 23 January 2003; Volume 4820, pp. 500–514. [Google Scholar]
- Ring, E.; Ammer, K. Infrared thermal imaging in medicine. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, R33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, R.; Moeslund, T.B. Thermal cameras and applications: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A.; Martyniuk, P.; Kopytko, M. Challenges of small-pixel infrared detectors: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 046501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.K.; Kim, H.M. Modified cubic convolution scaler with minimum loss of information. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 540–546. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Sui, X.; Gu, G. A novel infrared image super-resolution method based on sparse representation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 71, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, R.; Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Ma, J. Facial image hallucination through coupled-layer neighbor embedding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 26, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, N.; Hwang, S.; Kweon, I.S. Thermal image enhancement using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Tang, S.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Cao, Y. Cascaded deep networks with multiple receptive fields for infrared image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 29, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, G.; Tu, E.; Yang, J. Infrared super-resolution imaging using multi-scale saliency and deep wavelet residuals. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 97, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, V.; Patel, H.; Prajapati, K.; Upla, K.P.; Ramachandra, R.; Raja, K.; Busch, C. Therisurnet-a computationally efficient thermal image super-resolution network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, H.; Cheng, G.; Duan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, S. Automatic Search Dense Connection Module for Super-Resolution. Entropy 2022, 24, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zhu, D. Improved Thermal Infrared Image Super-Resolution Reconstruction Method Base on Multimodal Sensor Fusion. Entropy 2023, 25, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Han, Z.; Dai, E.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z.; Xing, L.; Zou, X.; Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q. Unsupervised image super-resolution with an indirect supervised path. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 468–469. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche, M.; Gu, S.; Timofte, R. Frequency separation for real-world super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 3599–3608. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, S. Unpaired image super-resolution using pseudo-supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, Y.; Timofte, R.; Jin, L.; Song, H. Unsupervised real-world image super resolution via domain-distance aware training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13385–13394. [Google Scholar]
- Demirel, H.; Ozcinar, C.; Anbarjafari, G. Satellite image contrast enhancement using discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 7, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Wu, Y. Infrared image enhancement based on wavelet transformation and retinex. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, Nanjing, China, 26–28 August 2010; Volume 1, pp. 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.R. Enhancement of contrast and resolution of gray scale and color images by wavelet decomposition and histogram shaping and shifting. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Medical Imaging, m-Health and Emerging Communication Systems (MedCom), Greater Noida, India, 7–8 November 2014; pp. 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J. Two-branch crisscross network for realistic and accurate image super-resolution. Displays 2023, 80, 102549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part IV 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 184–199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Tang, R.; Anisetti, M.; Yang, X. A lightweight iterative error reconstruction network for infrared image super-resolution in smart grid. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, L.; Yang, L.; Qin, T. Dual discriminators generative adversarial networks for unsupervised infrared super-resolution. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 133, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Lin, L. Unsupervised image super-resolution using cycle-in-cycle generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Rivadeneira, R.E.; Sappa, A.D.; Vintimilla, B.X.; Hammoud, R. A Novel Domain Transfer-Based Approach for Unsupervised Thermal Image Super-Resolution. Sensors 2022, 22, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Bulat, A.; Yang, J.; Tzimiropoulos, G. To learn image super-resolution, use a gan to learn how to do image degradation first. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, R.C.; Barnard, K.J.; Bognar, J.G.; Armstrong, E.E.; Watson, E.A. High-resolution image reconstruction from a sequence of rotated and translated frames and its application to an infrared imaging system. Opt. Eng. 1998, 37, 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.C.; Park, M.K.; Kang, M.G. Super-resolution image reconstruction: A technical overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2003, 20, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yang, R.; Xu, M.; Dragotti, P.L. Wavelet domain style transfer for an effective perception-distortion tradeoff in single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3076–3085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Abdal, R.; Qin, Y.; Wonka, P. Sean: Image synthesis with semantic region-adaptive normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5104–5113. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Hou, X. Demystifying neural style transfer. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.01036. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur-Martineau, A. The relativistic discriminator: A key element missing from standard GAN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.00734. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, L.I.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Change Loy, C. Esrgan: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Socarrás, Y.; Ramos, S.; Vázquez, D.; López, A.M.; Gevers, T. Adapting pedestrian detection from synthetic to far infrared images. In Proceedings of the ICCV Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rivadeneira, R.E.; Sappa, A.D.; Vintimilla, B.X. Thermal Image Super-resolution: A Novel Architecture and Dataset. In Proceedings of the VISIGRAPP (4: VISAPP), Valletta, Malta, 27–29 February 2020; pp. 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, A. Digital Picture Processing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]




| Degradation | PSNR | SSIM | Contrast |
|---|---|---|---|
| TFADGAN w/o FD | 24.13 | 0.7695 | 0.6808 |
| TFADGAN w/o CFFM | 23.09 | 0.7560 | 0.8877 |
| TFADGAN w/o | 23.91 | 0.7680 | 0.6696 |
| TFADGAN w/o | 24.09 | 0.7727 | 0.6244 |
| TFADGAN | 24.27 | 0.7758 | 0.6337 |
| PSNR | SSIM | Contrast | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 23.27 | 0.7576 | 1.0844 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 24.11 | 0.7723 | 0.7359 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 24.27 | 0.7758 | 0.6337 |
| Method | PSNR | SSIM | Contrast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | 27.95 | 0.7659 | 1.6067 |
| Bulat et al. [28] | 26.01 | 0.8445 | 1.9850 |
| FSSR | 28.71 | 0.8833 | 1.6955 |
| DASR | 28.59 | 0.8926 | 1.7350 |
| Rivadeneira et al. [26] | 28.21 | 0.8913 | 2.2993 |
| TFADGAN-PerceSR (ours) | 29.37 | 0.8941 | 1.9053 |
| TFADGAN-PixelSR (ours) | 30.28 | 0.9304 | 0.4465 |
| Method | PSNR | SSIM | Contrast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | 22.95 | 0.7431 | 1.0783 |
| Bulat et al. [28] | 20.58 | 0.7332 | 0.7434 |
| FSSR | 22.75 | 0.7237 | 1.0175 |
| DASR | 22.73 | 0.7264 | 1.0660 |
| Rivadeneira et al. [26] | 23.43 | 0.7513 | 0.8068 |
| TFADGAN-PerceSR (ours) | 24.17 | 0.7610 | 0.6522 |
| TFADGAN-PixelSR (ours) | 24.27 | 0.7758 | 0.6337 |
| Degradation | SR | PSNR | SSIM | Contrast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicubic | PixelSR | 22.99 | 0.7550 | 0.9998 |
| FSSR-DSGAN | 23.50 | 0.7731 | 0.6115 | |
| DASR-DSN | 23.30 | 0.7715 | 0.6195 | |
| TFADGAN (ours) | 24.27 | 0.7758 | 0.6337 | |
| Bicubic | PerceSR | 23.35 | 0.7557 | 0.9330 |
| FSSR-DSGAN | 23.32 | 0.7406 | 0.8301 | |
| DASR-DSN | 23.07 | 0.7344 | 0.9990 | |
| TFADGAN (ours) | 24.17 | 0.7610 | 0.6522 |
| Method | FSSR-DSGAN | DASR-DSN | TFADGAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters (M) | 0.59 | 0.63 | 28.06 |
| MACs (G) | 9.69 | 9.83 | 8.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, C.; Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Han, J. Frequency-Aware Degradation Modeling for Real-World Thermal Image Super-Resolution. Entropy 2024, 26, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030209
Qu C, Chen X, Xu Q, Han J. Frequency-Aware Degradation Modeling for Real-World Thermal Image Super-Resolution. Entropy. 2024; 26(3):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030209
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Chao, Xiaoyu Chen, Qihan Xu, and Jing Han. 2024. "Frequency-Aware Degradation Modeling for Real-World Thermal Image Super-Resolution" Entropy 26, no. 3: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030209
APA StyleQu, C., Chen, X., Xu, Q., & Han, J. (2024). Frequency-Aware Degradation Modeling for Real-World Thermal Image Super-Resolution. Entropy, 26(3), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030209





