Dynamic Weighting Translation Transfer Learning for Imbalanced Medical Image Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Class-Imbalanced Medical Image Classification
2.2. Transfer Learning-Based Medical Image Classification
3. Method
3.1. Overview of Our DTTL Approach
3.2. Cross-Domain Discriminability Adaptation
3.3. Cross-Domain Minority Translation
3.4. Balanced Target Learning
| Algorithm 1 Training of the DTTL model. |
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Compared Methods
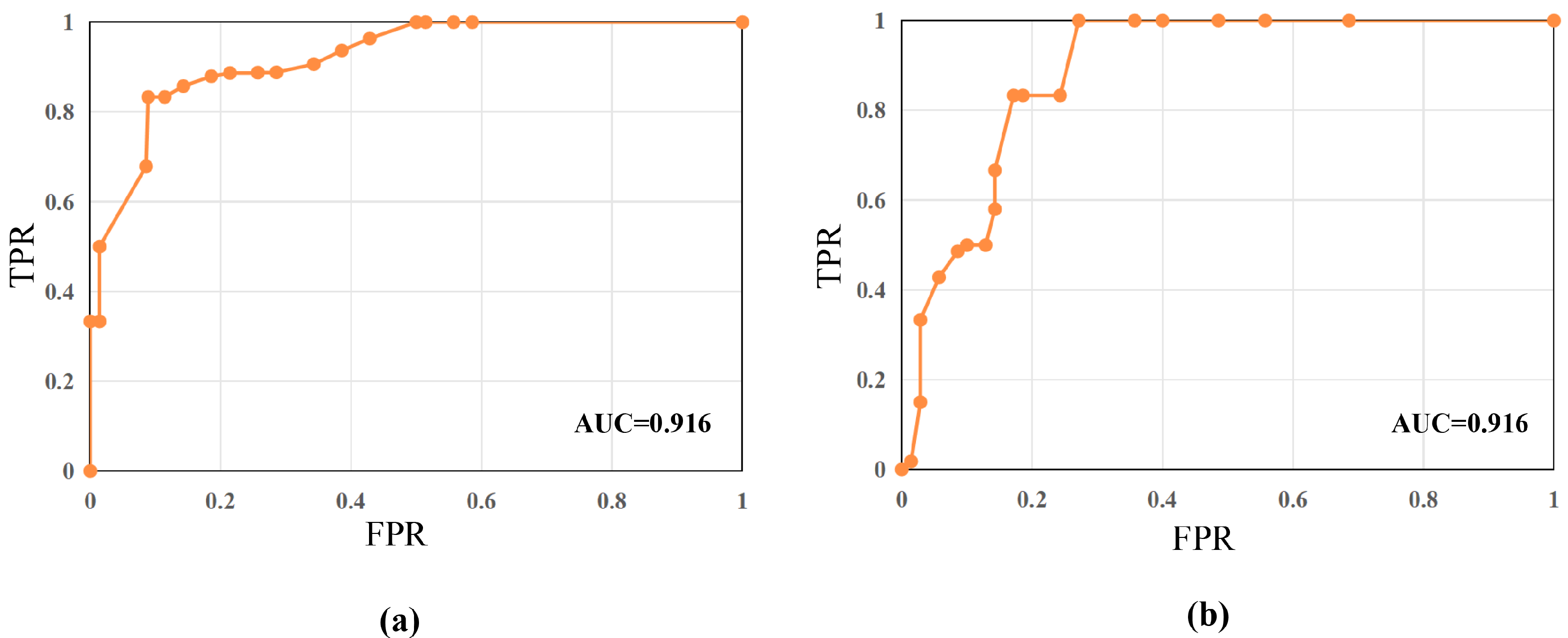
4.4. Results
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Validation of Cross-Domain Discriminability Adaptation
4.5.2. Validation of Cross-Domain Minority Class Sample Translation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boreiko, V.; Ilanchezian, I.; Ayhan, M.S.; Müller, S.; Koch, L.M.; Faber, H.; Berens, P.; Hein, M. Visual explanations for the detection of diabetic retinopathy from retinal fundus images. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Proceedings, Part II. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Atwany, M.; Yaqub, M. DRGen: Domain Generalization in Diabetic Retinopathy Classification. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Proceedings, Part II. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- Quellec, G.; Al Hajj, H.; Lamard, M.; Conze, P.H.; Massin, P.; Cochener, B. ExplAIn: Explanatory artificial intelligence for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 72, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, L. Deep multi-task learning for diabetic retinopathy grading in fundus images. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtuall, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 2826–2834. [Google Scholar]
- Mehnatkesh, H.; Jalali, S.M.J.; Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S. An intelligent driven deep residual learning framework for brain tumor classification using MRI images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zang, M.; An, D.; Feng, Y.; Yu, B. MBANet: A 3D convolutional neural network with multi-branch attention for brain tumor segmentation from MRI images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.V.; Chaudhari, G.; Hess, C.P.; Glenn, O.A.; Sugrue, L.P.; Rauschecker, A.M.; Li, Y. Deep Learning to Predict Neonatal and Infant Brain Age from Myelination on Brain MRI Scans. Radiology 2022, 305, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; So, S.; Yun, S.; Lee, S.; Barg, J. Spatial Feature Conservation Networks (SFCNs) for Dilated Convolutions to Improve Breast Cancer Segmentation from DCE-MRI. In Proceedings of the Applications of Medical Artificial Intelligence: First International Workshop, AMAI 2022, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2022, Singapore, 18 September 2022; Proceedings. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Duran, A.; Dussert, G.; Rouvière, O.; Jaouen, T.; Jodoin, P.M.; Lartizien, C. ProstAttention-Net: A deep attention model for prostate cancer segmentation by aggressiveness in MRI scans. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 77, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Initiative, A.D.N. Orthogonal latent space learning with feature weighting and graph learning for multimodal Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 84, 102698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, S.; Zhen, L.; Lei, X.; Cui, Y.; Ting, J.S.Z.; et al. Contrastive domain adaptation with consistency match for automated pneumonia diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 83, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altini, N.; Prencipe, B.; Cascarano, G.D.; Brunetti, A.; Brunetti, G.; Triggiani, V.; Carnimeo, L.; Marino, F.; Guerriero, A.; Villani, L.; et al. Liver, kidney and spleen segmentation from CT scans and MRI with deep learning: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 490, 30–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, B.H.; Kuijf, H.J.; Gilhuijs, K.G.; Viergever, M.A. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Bi, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Bian, C. Label-efficient hybrid-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, QC, Canada, 20–27 February 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2026–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Cheplygina, V.; de Bruijne, M.; Pluim, J.P. Not-so-supervised: A survey of semi-supervised, multi-instance, and transfer learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 54, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Nie, S. Transfer Learning Strategy Based on Unsupervised Learning and Ensemble Learning for Breast Cancer Molecular Subtype Prediction Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 1518–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Guan, D.; Xiao, A.; Lu, S.; Shao, L. Category contrast for unsupervised domain adaptation in visual tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1203–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Xiang, T.; Loy, C.C. Domain generalization: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 4396–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, Z.; Li, D.; Zhong, P.; Chen, Y. Probability-Based Graph Embedding Cross-Domain and Class Discriminative Feature Learning for Domain Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, M.; Potter, G.G.; Liu, M. Unsupervised cross-domain functional MRI adaptation for automated major depressive disorder identification. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 84, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, P.; Pai, A.; Igel, C.; Krag, C.H. Histogram-Based Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Classification. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Proceedings, Part VII. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 755–764. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, P.; Niu, S.; Huang, J.; Tan, M. Collaborative unsupervised domain adaptation for medical image diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7834–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Ji, W.; Xing, F.; Lu, J.; You, J.; Kuo, C.C.J.; El Fakhri, G.; Woo, J. Subtype-aware unsupervised domain adaptation for medical diagnosis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtuall, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 2189–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, T.; Nibali, A.; He, Z. Semi-supervised learning for medical image classification using imbalanced training data. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 2022, 216, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zheng, G. Handling Imbalanced Data: Uncertainty-Guided Virtual Adversarial Training With Batch Nuclear-Norm Optimization for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, D.; Korevaar, S.; Bozorgtabar, B.; Tennakoon, R. Unsupervised domain adaptation using feature disentanglement and GCNs for medical image classification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022 Workshops, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part VII. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 735–748. [Google Scholar]
- Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Marchand, M.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 17, 2030–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Jordan, M.I. Conditional adversarial domain adaptation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, J.; Tzeng, E.; Park, T.; Zhu, J.Y.; Isola, P.; Saenko, K.; Efros, A.; Darrell, T. Cycada: Cycle-consistent adversarial domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1989–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rozantsev, A.; Salzmann, M.; Fua, P. Beyond sharing weights for deep domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Watanabe, K.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3723–3732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Long, M.; Jordan, M. Bridging theory and algorithm for domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 7404–7413. [Google Scholar]
- Na, J.; Jung, H.; Chang, H.J.; Hwang, W. Fixbi: Bridging domain spaces for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1094–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Latecki, L.J. Entropy minimization versus diversity maximization for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSNA. RSNA Pneumonia Detection Challenge. 2018. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. Chestx-ray8: Hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2097–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]



| Label | RSNA | Child X-ray |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia | 6011 | 300 |
| Normal and others | 20,672 | 1349 |
| Method | EfficientNet | DenseNet121 | ResNet50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DANN [28] | 85.42 | 87.08 | 86.24 |
| CyCADA [30] | 79.76 | 79.09 | 77.22 |
| BSW [31] | 84.33 | 86.79 | 86.37 |
| CDAN [29] | 84.33 | 86.46 | 86.96 |
| MCD [32] | 83.41 | 85.43 | 86.51 |
| MDD [33] | 88.18 | 85.11 | 86.77 |
| FixBi [34] | 84.07 | 87.28 | 85.88 |
| MEDM [35] | 84.65 | 81.46 | 82.51 |
| CDACM [11] | 90.57 | 88.33 | 88.08 |
| DTTL | 91.68 | 90.46 | 89.90 |
| Method | EfficientNet | DenseNet121 | ResNet50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DANN [28] | 75.87 | 73.77 | 73.96 |
| CyCADA [30] | 67.71 | 59.3 | 68.61 |
| BSW [31] | 74.31 | 54.84 | 69.99 |
| CDAN [29] | 76.25 | 74.64 | 75.08 |
| MCD [32] | 81.69 | 81.21 | 84.72 |
| MDD [33] | 84.80 | 84.23 | 84.01 |
| FixBi [34] | 75.92 | 73.65 | 81.14 |
| MEDM [35] | 79.86 | 78.70 | 70.76 |
| CDACM [11] | 86.89 | 85.04 | 87.35 |
| DTTL | 87.23 | 85.28 | 87.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Pei, H. Dynamic Weighting Translation Transfer Learning for Imbalanced Medical Image Classification. Entropy 2024, 26, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050400
Yu C, Pei H. Dynamic Weighting Translation Transfer Learning for Imbalanced Medical Image Classification. Entropy. 2024; 26(5):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050400
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Chenglin, and Hailong Pei. 2024. "Dynamic Weighting Translation Transfer Learning for Imbalanced Medical Image Classification" Entropy 26, no. 5: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050400
APA StyleYu, C., & Pei, H. (2024). Dynamic Weighting Translation Transfer Learning for Imbalanced Medical Image Classification. Entropy, 26(5), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050400





