Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ States
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Our protocol does not require QKD protocol for sharing a secret key to ensure the security of the inputs. This results in no consumption of quantum resources for key sharing.
- (2)
- The quantum sequence is transmitted between the TP and two users in a circular mode. The inputs of the two users are encoded into the transmitted quantum sequence, leading to the multiplexing of quantum resources and improving the utilization of quantum resources.
- (3)
- One GHZ state can be compared to three-bit classical information, enabling qubit efficiency to reach 100%.
2. Preliminary Knowledge
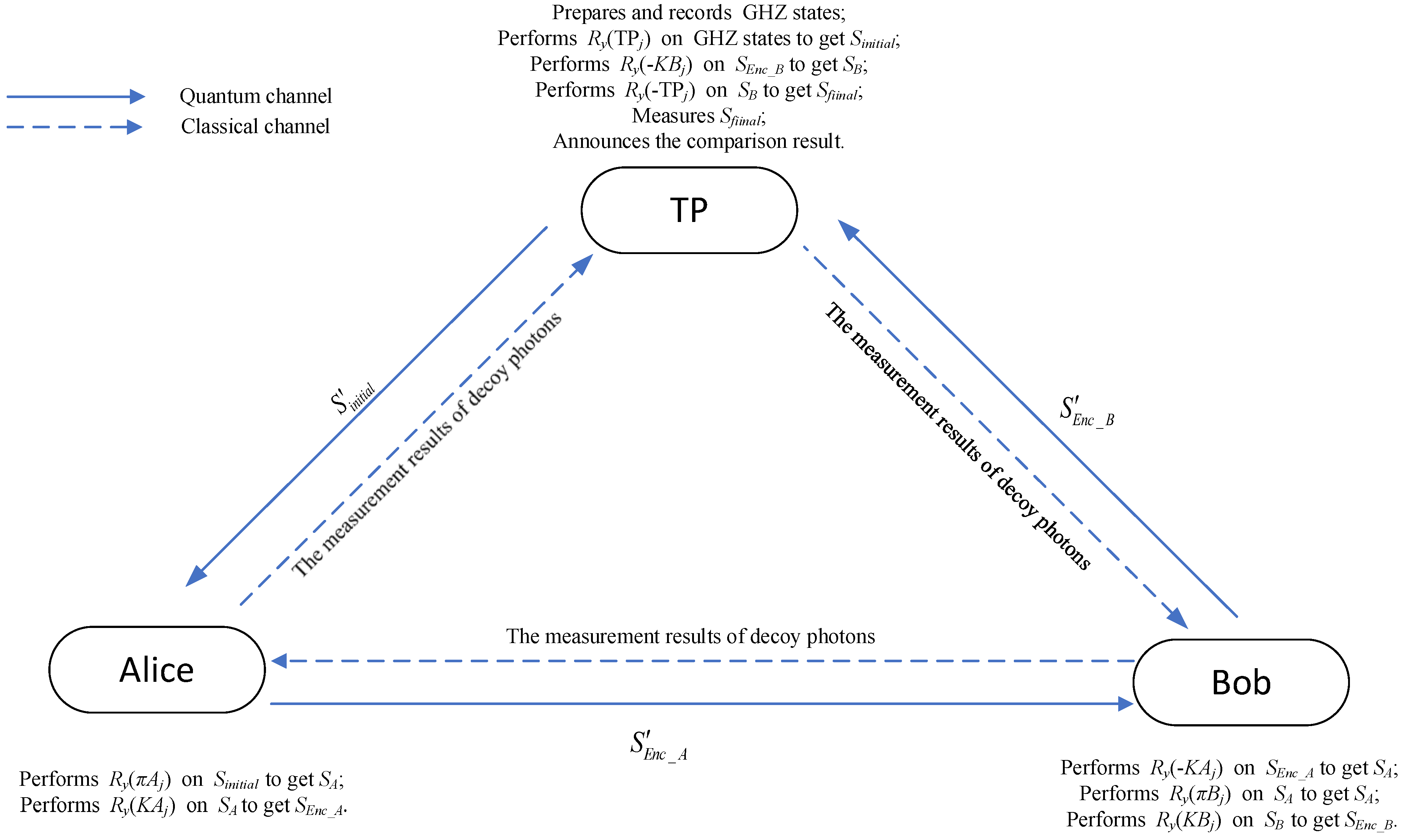
3. Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ States
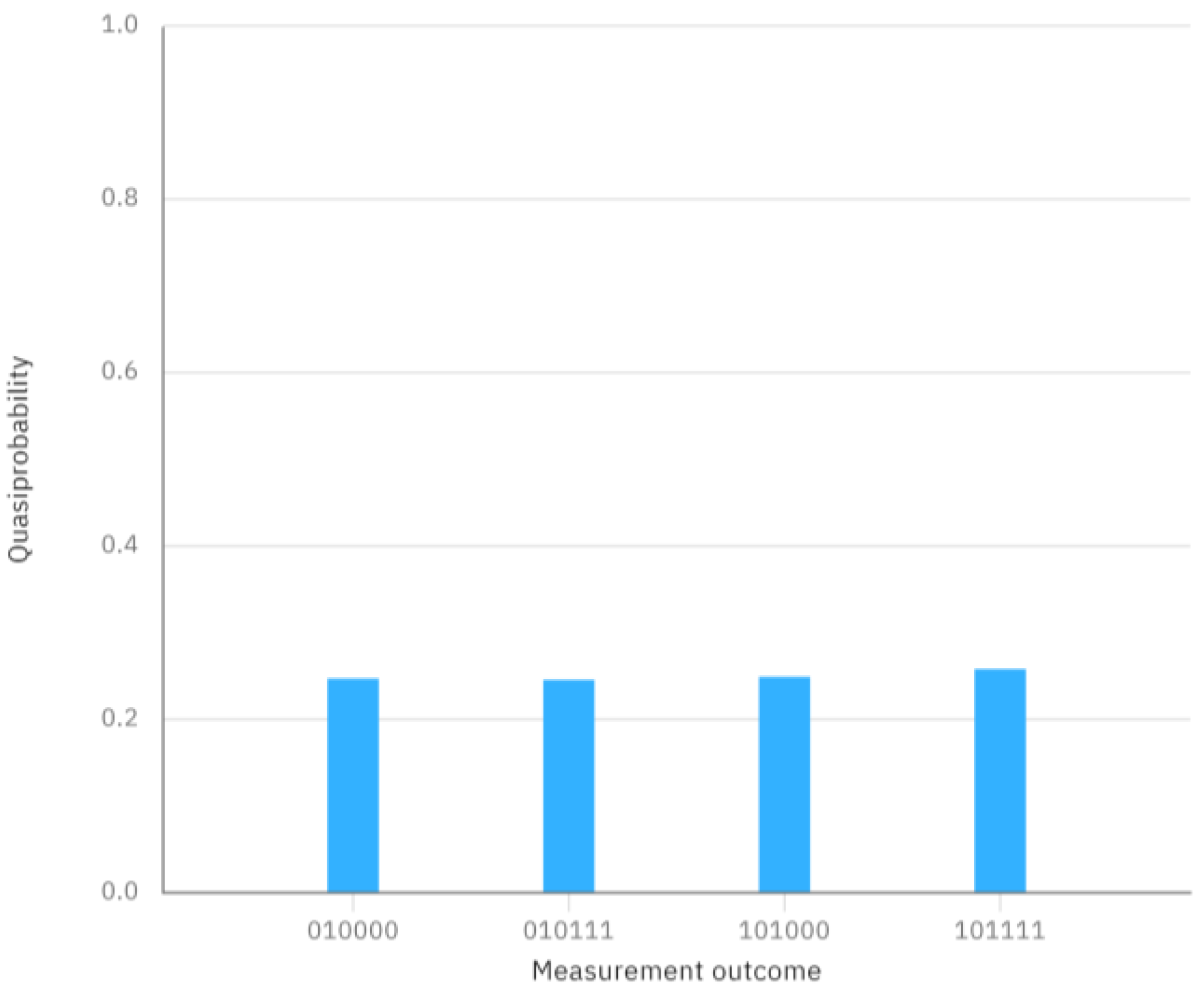
4. Simulation Experiment
5. Security Analysis
5.1. External Attacks
5.1.1. The Intercept–Measurement–Resend Attack
5.1.2. The Entanglement-Measure Attack
5.1.3. The Trojan-Horse Attacks
5.2. Participant Attacks
5.2.1. TP’s Attack
5.2.2. Alice’s Attack
5.2.3. Bob’s Attack
6. Efficiency Analysis and Comparison
6.1. Efficiency Analysis
6.2. Comparison
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shor, P.W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, L.K. Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Wen, Q.Y. An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2009, 42, 055305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Xu, G.; Niu, X.X.; Wen, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.X. An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single-particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tseng, H.Y.; Hwang, T. Intercept–resend attacks on Chen et al.’s quantum private comparison protocol and the improvements. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2412–2414. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, H.Y.; Lin, J.; Hwang, T. New quantum private comparison protocol using EPR pairs. Quantum Inf. Process. 2012, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.Y.; Wen, Q.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Gao, F. Quantum private comparison using genuine four-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2012, 51, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wen, Q.Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, F.; Sun, Y. Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2013, 56, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, L.; Wu, C. Quantum private comparison with a malicious third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 2015, 14, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, T.Y.; Che, B.C.; Dou, Z.; Chen, X.-B.; Lai, Y.-P.; Li, J. Efficient quantum private comparison protocol utilizing single photons and rotational encryption. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 060307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.F.; Zhang, S.B. Efficient multiparty quantum private comparison protocol based on single photons and rotation encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.Y.; Ji, Z.X. Two-party quantum private comparison with five-qubit entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2017, 56, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Ye, C.; Che, F. A Semi-Quantum Private Comparison Base on W-States. Entropy 2023, 25, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.X.; Zhang, H.G.; Fan, P.R. Two-party quantum private comparison protocol with maximally entangled seven-qubit state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2019, 34, 1950229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Quantum private comparison protocols with a number of multi-particle entangled states. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44613–44621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.B.; Chang, Y.; Hou, M.; Cheng, W. Efficient quantum private comparison based on entanglement swapping of bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2021, 60, 3783–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, J.; Guo, L. Multi-Party Quantum Private Comparison Based on Bell States. Entropy 2023, 25, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Rahman, A.U.; Ji, Z.; Ji, X.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, H. Two-party quantum private comparison based on eight-qubit entangled state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 37, 2250026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Ming, P. Quantum private comparison based on χ-type entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2017, 56, 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.X.; Ye, T.Y. Quantum private comparison of equal information based on highly entangled six-qubit genuine state. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2016, 65, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Che, F.; Wang, Z.; Fu, A. Efficient Quantum Private Comparison without Sharing a Key. Entropy 2023, 25, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Efficient quantum private comparison protocol based on the entanglement swapping between four-qubit cluster state and extended Bell state. Quantum Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Long, D. Quantum private comparison protocol based on cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.K. Improvements of quantum private comparison protocol based on cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2018, 57, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.W.; Yu, X.Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.-K. Quantum private comparison protocol with five-particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2018, 57, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhang, S.B.; Wang, H.-C.; Yan, L.-L.; Han, G.-H.; Sheng, Z.-W.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Suo, W.; Xiong, J.-X. Quantum private comparison of equality based on five-particle cluster state. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2016, 66, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.Y. Quantum private comparison via cavity QED. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2017, 67, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.F. Quantum gate-based quantum private comparison. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2020, 59, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Xu, G.; Chen, X.B.; Chang, Y.; Dong, Z.-C. Improved multiparty quantum private comparison based on quantum homomorphic encryption. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 610, 128397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Hou, M.; Zhang, S.B. Quantum private comparison of arbitrary single qubit states based on swap test. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 040303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S. (t, n) Threshold Quantum Secret Sharing Using Rotation Operation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2022, 61, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Hong, C.H.; Heo, J.; Lim, J.-I.; Yang, H.-J. Quantum signature scheme using a single qubit rotation operator. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2015, 54, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, P. Efficient multiparty quantum key agreement protocol based on commutative encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 2016, 15, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Anisimova, E.; Khan, I.; Makarov, V.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. Trojan-horse attacks threaten the security of practical quantum cryptography. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 123030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S. Practical quantum protocols for blind millionaires’ problem based on rotation encryption and swap test. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2024, 637, 129614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, A. Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianni, J.; Qu, Z. New quantum private comparison using hyperentangled ghz state. J. Quantum Comput. 2021, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, S.; Gong, L.H.; Chen, H.-Y. Quantum private comparison protocol based on 4D GHZ-like states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.B. Quantum private comparison based on GHZ entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2012, 51, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.D.; Chen, H.Y.; Gong, L.H.; Zhou, N.R. Quantum private comparison protocol based on four-particle GHZ states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2020, 59, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ref. [9] | Ref. [16] | Ref. [18] | Ref. [22] | Ref. [26] | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantum resource | Single photons | Bell states | Eight-qubit entangled state | Four-qubit cluster state and extended Bell state | Five-particle cluster state | GHZ states |
| Unitary operation | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Entanglement swapping | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| QKD method | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Quantum measurement | Single-particle | GHZ-basis | single-particle | Bell-basis and extend Bell basis | single-particle | GHZ-basis |
| Qubit efficiency | 33% | 50% | 25% | 50% | 40% | 100% |
| Ref. [37] | Ref. [38] | Ref. [39] | Ref. [40] | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantum resource | Hyperentangled GHZ state | 4D GHZ-like states | GHZ state | four-particle GHZ state | GHZ states |
| Unitary operation | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Entanglement swapping | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| QKD method | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Quantum measurement | Bell-basis | single-particle | Bell-basis | Bell-basis and single-particle | GHZ-basis |
| Qubit efficiency | 66% | 33% | 33% | 75% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ States. Entropy 2024, 26, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050413
Hou M, Wu Y, Zhang S. Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ States. Entropy. 2024; 26(5):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050413
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Min, Yue Wu, and Shibin Zhang. 2024. "Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ States" Entropy 26, no. 5: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050413
APA StyleHou, M., Wu, Y., & Zhang, S. (2024). Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ States. Entropy, 26(5), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050413








