Entropy Production of Run-and-Tumble Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Setup within the Fokker–Planck Equation
3. Run-and-Tumble Motion
3.1. Free Run-and-Tumble Particles
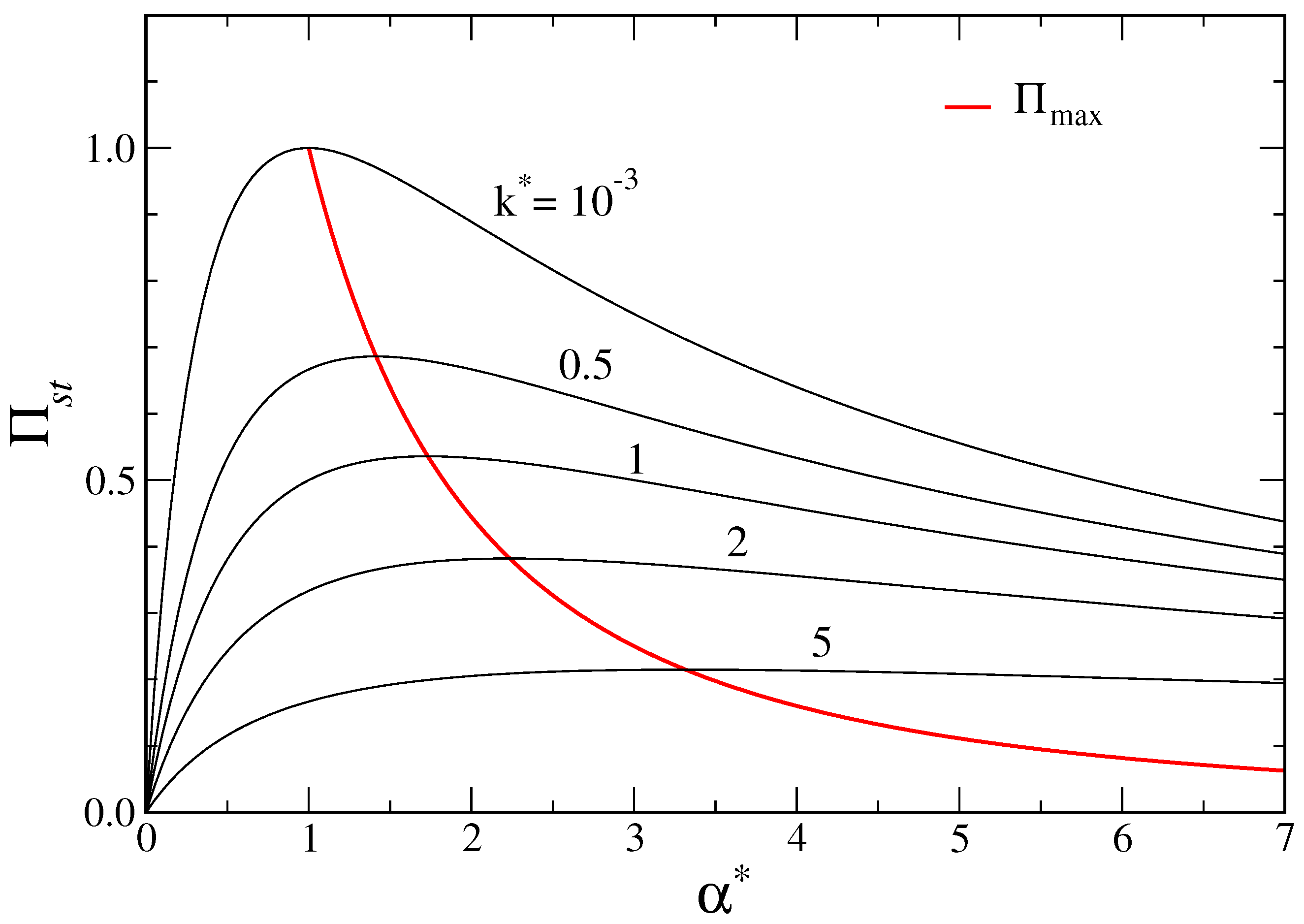
3.2. Run-and-Tumble Particles in Harmonic Potential
4. Anisotropic Run-and-Tumble Motion
5. General Run-and-Tumble Motion
- Photokinetic bacteria. Photokinetic bacteria are characterized by spatially varying speed which depends on local light intensity I [40]. For static nonhomogeneous light fields , we can describe the particle dynamics through a space-dependent speed [41] (we assume equal left and right speeds)Chemotaxis. In the presence of nutrient concentration, some motile bacteria modify their tumble rates to effectively direct their movement toward the food source [31,35]. We can describe such a phenomenon by expressing the tumble rates in terms of the chemotactic field . In the limit of a weak concentration gradient, we can write [35,42,43]with measuring the strength of the particle reaction to chemical gradients, and we have assumed equal speeds . Moreover, it is interesting to consider more realistic models of bacterial dynamics including noninstantaneous tumbling, with the addition of finite dwell times in the tumble state and possibly different rates of transition between the run and tumble states [44,45].
- Generic confining potentials. In the previous sections, we analyzed the case of a force field originated by quadratic potentials . It would be interesting to consider the generic confining potential [46,47]and investigate the dependence on the exponent p. Furthermore, of interest is the case of double-well potentialsin its symmetric () or asymmetric () version.
- Ratchet potentials. Finally, we mention the study of the ratchet effect [5]. In this case, the active motion takes place in the presence of a periodic asymmetric potential, giving rise to unidirectional motion with a stationary flow of particles, . In the case of a piecewise-linear ratchet potential, the entropy production for particles with equal tumbling rates and speeds was analyzed in [48].
6. Run-and-Tumble Motion in
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchetti, M.C.; Joanny, J.F.; Ramaswamy, S.; Liverpool, T.B.; Prost, J.; Rao, M.; Simha, R.A. Hydrodynamics of soft active matter. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013, 85, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgeti, J.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G. Physics of microswimmers—Single particle motion and collective behavior: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 056601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavagna, A.; Giardina, I.; Grigera, T.S. The physics of flocking: Correlation as a compass from experiments to theory. Phys. Rep. 2018, 728, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, A.; Balda, A.B.; Argun, A.; Volpe, G. Playing with active matter. In Proceedings of the Optical Trapping and Optical Micromanipulation XX, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–24 August 2023; p. PC1264909. [Google Scholar]
- Angelani, L.; Costanzo, A.; Di Leonardo, R. Active ratchets. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 96, 68002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battle, C.; Broedersz, C.P.; Fakhri, N.; Geyer, V.F.; Howard, J.; Schmidt, C.F.; MacKintosh, F.C. Broken detailed balance at mesoscopic scales in active biological systems. Science 2016, 352, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnesotto, F.S.; Mura, F.; Gladrow, J.; Broedersz, C.P. Broken detailed balance and non-equilibrium dynamics in living systems: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2018, 81, 066601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, C.; Saglimbeni, F.; Sosa, V.C.; Di Leonardo, R.; Nath, B.; Puglisi, A. Thermodynamic limits of sperm swimming precision. PRX Life 2023, 1, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.R.; Mazur, P. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Livi, R.; Politi, P. Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics: A Modern Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy, S. The mechanics and statistics of active matter. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2010, 1, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, É.; Marchetti, M.C. The statistical physics of active matter: From self-catalytic colloids to living cells. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 504, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelani, L. Optimal escapes in active matter. Eur. Phys. J. E 2024, 47, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprini, L.; Marini Bettolo Marconi, U.; Löwen, H. Entropy production and collective excitations of crystals out of equilibrium: The concept of entropons. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 044603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechinger, C.; Di Leonardo, R.; Löwen, H.; Reichhardt, C.; Volpe, G.; Volpe, G. Active particles in complex and crowded environments. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2016, 88, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, J.; Tu, Y.; Ramaswamy, S. Hydrodynamics and phases of flocks. Ann. Phys. 2005, 318, 170–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailleur, J.; Cates, M.E. Statistical Mechanics of Interacting Run-and-Tumble Bacteria. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 218103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J. Motility-induced phase separation. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2015, 6, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, J.; Kafri, Y.; Tailleur, J.; van Wijland, F. Time irreversibility in active matter, from micro to macro. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2022, 4, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, K. Stochastic Energetics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, U. Stochastic thermodynamics, fluctuation theorems and molecular machines. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 126001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliti, L.; Pigolotti, S. Stochastic Thermodynamics: An Introduction; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fodor, É.; Nardini, C.; Cates, M.E.; Tailleur, J.; Visco, P.; Van Wijland, F. How far from equilibrium is active matter? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 038103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, U.M.B.; Puglisi, A.; Maggi, C. Heat, temperature and Clausius inequality in a model for active Brownian particles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Marchetti, M.C. Hidden entropy production and work fluctuations in an ideal active gas. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 020604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabelow, L.; Bo, S.; Eichhorn, R. Irreversibility in active matter systems: Fluctuation theorem and mutual information. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 021009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprini, L.; Marconi, U.M.B.; Puglisi, A.; Vulpiani, A. The entropy production of Ornstein–Uhlenbeck active particles: A path integral method for correlations. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2019, 2019, 053203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, N. Entropy production of an active particle in a box. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 030103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocconi, L.; Garcia-Millan, R.; Zhen, Z.; Buturca, B.; Pruessner, G. Entropy Production in Exactly Solvable Systems. Entropy 2020, 22, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frydel, D. Intuitive view of entropy production of ideal run-and-tumble particles. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 034113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.C. E. coli in Motion; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, H.C. Random Walks in Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cerino, L.; Puglisi, A. Entropy production for velocity-dependent macroscopic forces: The problem of dissipation without fluctuations. Europhys. Lett. 2015, 111, 40012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, T. Entropy production in nonequilibrium systems described by a Fokker-Planck equation. Braz. J. Phys. 2006, 36, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, M.J. Theory of continuum random walks and application to chemotaxis. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 2553–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, G.H. Some applications of persistent random walks and the telegrapher’s equation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2002, 311, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Millan, R.; Pruessner, G. Run-and-tumble motion in harmonic potential: Field theory and entropy production. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2021, 6, 063203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydel, D. Positing the problem of stationary distributions of active particles as third-order differential equation. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 106, 024121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.; Hou, Z. Improving estimation of entropy production rate for run-and-tumble particle systems by high-order thermodynamic uncertainty relation. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, 024112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangipane, G.; Dell’Arciprete, D.; Petracchini, S.; Maggi, C.; Saglimbeni, F.; Bianchi, S.; Vizsnyiczai, G.; Bernardini, M.L.; Di Leonardo, R. Dynamic density shaping of photokinetic E. coli. eLife 2018, 7, e36608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelani, L.; Garra, R. Run-and-tumble motion in one dimension with space-dependent speed. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 052147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cates, M.E. Diffusive transport without detailed balance in motile bacteria: Does microbiology need statistical physics? Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 042601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelani, L.; Di Leonardo, R.; Paoluzzi, M. First-passage time of run-and-tumble particles. Eur. Phys. J. E 2014, 37, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruani, F.; Chaudhuri, D. Active stop and go motion: A strategy to improve spatial exploration? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.05647. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Pham, P.H.; Ngo, K.V.; Do, V.H.; Li, S.; Phan, T.V. Remark on the entropy production of adaptive run-and-tumble chemotaxis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 634, 129452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Kundu, A.; Majumdar, S.N.; Sabhapandit, S.; Schehr, G. Run-and-tumble particle in one-dimensional confining potentials: Steady-state, relaxation, and first-passage properties. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 032132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéneau, M.; Majumdar, S.N.; Schehr, G. Optimal mean first-passage time of a run-and-tumble particle in a class of one-dimensional confining potentials. Europhys. Lett. 2024, 145, 61002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; Zhen, Z. Run-and-tumble motion in a linear ratchet potential: Analytic solution, power extraction, and first-passage properties. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 014139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, K.; Angelani, L.; Di Leonardo, R.; Bocquet, L. Probability distributions for the run-and-tumble bacterial dynamics: An analogy to the Lorentz model. Eur. Phys. J. E 2012, 35, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardini, C.; Fodor, E.; Tjhung, E.; van Wijland, F.; Tailleur, J.; Cates, M.E. Entropy Production in Field Theories without Time-Reversal Symmetry: Quantifying the Non-Equilibrium Character of Active Matter. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.; Cates, M.E. Stealth Entropy Production in Active Field Theories near Ising Critical Points. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 240604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoluzzi, M. Scaling of the entropy production rate in a φ4 model of active matter. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 044139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Terlizzi, I.; Gironella, M.; Herráez-Aguilar, D.; Betz, T.; Monroy, F.; Baiesi, M.; Ritort, F. Variance sum rule for entropy production. Science 2024, 383, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, S.; Guo, B.; Shih, A.; Phan, T.V.; Austin, R.H.; Levine, D.; Chaikin, P.M.; Martiniani, S. Model-Free Measurement of Local Entropy Production and Extractable Work in Active Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 220601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.V.; Li, S.; Ferreris, D.; Morris, R.; Bos, J.; Gou, B.; Martiniani, S.; Chaikin, P.; Kevrekidis, Y.G.; Austin, R.H. Social Physics of Bacteria: Avoidance of an Information Black Hole. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.16691. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paoluzzi, M.; Puglisi, A.; Angelani, L. Entropy Production of Run-and-Tumble Particles. Entropy 2024, 26, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060443
Paoluzzi M, Puglisi A, Angelani L. Entropy Production of Run-and-Tumble Particles. Entropy. 2024; 26(6):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060443
Chicago/Turabian StylePaoluzzi, Matteo, Andrea Puglisi, and Luca Angelani. 2024. "Entropy Production of Run-and-Tumble Particles" Entropy 26, no. 6: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060443
APA StylePaoluzzi, M., Puglisi, A., & Angelani, L. (2024). Entropy Production of Run-and-Tumble Particles. Entropy, 26(6), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060443





