Lower Limit of Percolation Threshold on Square Lattice with Complex Neighborhoods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
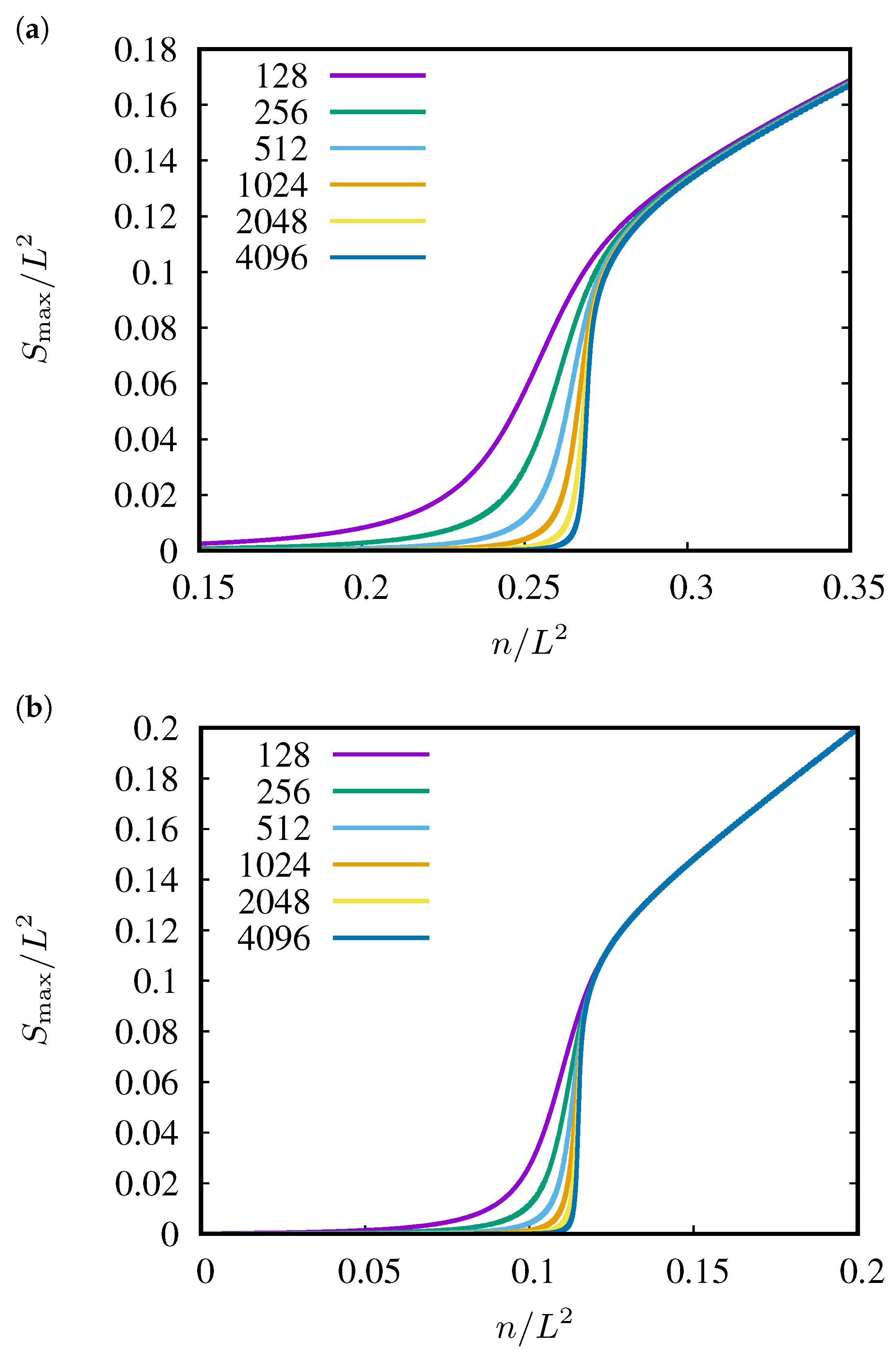
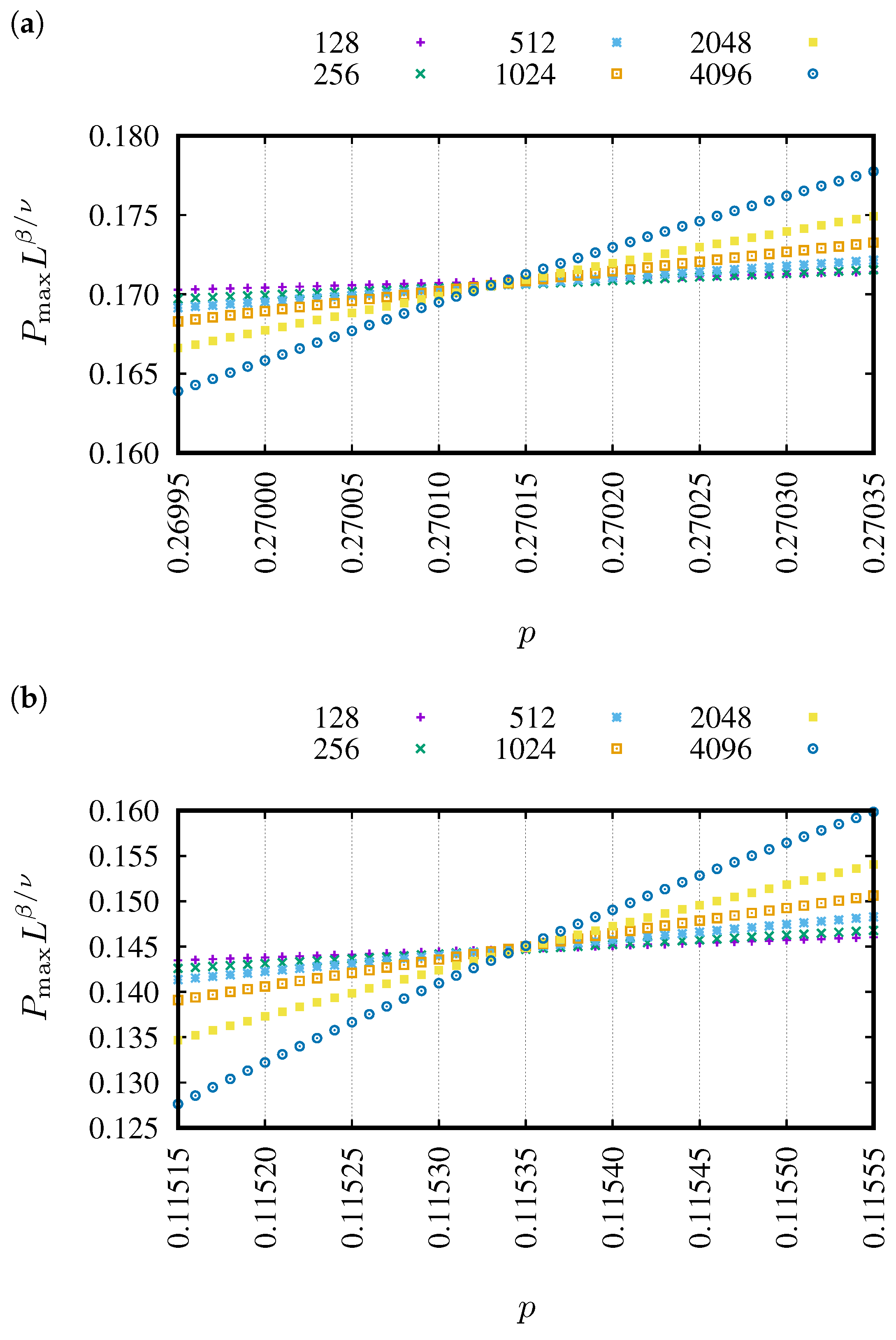
2.1. Finite-Size Scaling Hypothesis
2.2. Efficient Newman–Ziff Algorithm
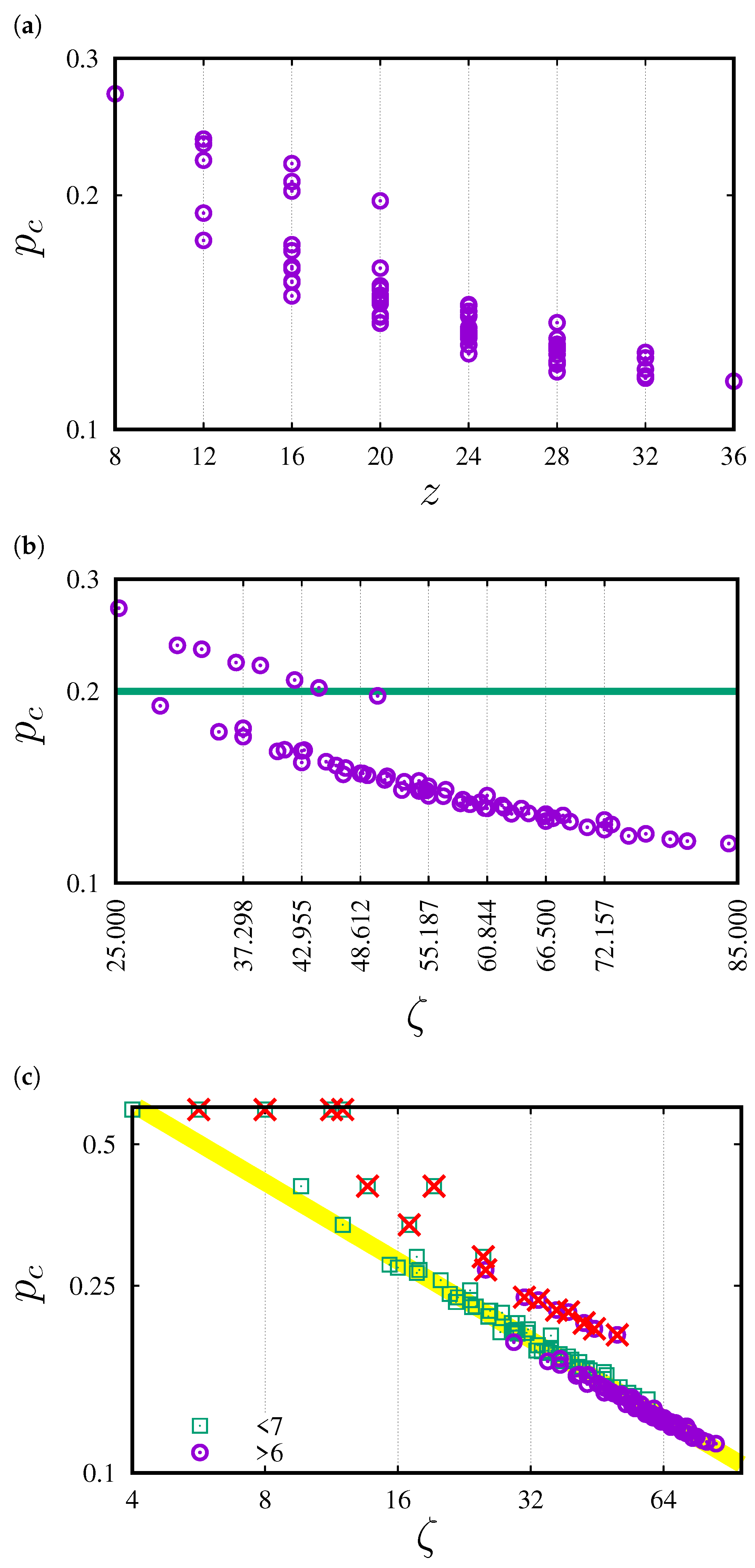
2.3. Effective Coordination Number
3. Results
4. Discussion
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- .
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Listing A1. boundaries() procedure for sq-7 neighborhood to be inserted in the Newman–Ziff algorithm code published in Reference [85]. |
 |
References
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollobás, B.; Riordan, O. Percolation; Cambridge UP: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sahimi, M. Applications of Percolation Theory; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kesten, H. Percolation Theory for Mathematicians; Brikhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, A.A. Recent advances in percolation theory and its applications. Phys. Rep. 2015, 578, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, R.R.; Lü, L.; Hu, M.B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.C. Percolation on complex networks: Theory and application. Phys. Rep. 2021, 907, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.F.; Essam, J.W. Exact Critical Percolation Probabilities for Site and Bond Problems in Two Dimensions. J. Math. Phys. 1964, 5, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziff, R.M.; Scullard, C.R. Exact bond percolation thresholds in two dimensions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2006, 39, 15083–15090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scullard, C.R. Exact site percolation thresholds using a site-to-bond transformation and the star-triangle transformation. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 016107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, J.L. High-precision percolation thresholds and Potts-model critical manifolds from graph polynomials. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2014, 47, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupette, F.; Schilling, T. Exactly solvable percolation problems. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 044108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhunzhanov, R.K.; Eserkepov, A.V.; Tarasevich, Y.Y. Exact percolation probabilities for a square lattice: Site percolation on a plane, cylinder, and torus. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2022, 55, 204004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, S.R.; Hammersley, J.M. Percolation processes: I. Crystals and mazes. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1957, 53, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammersley, J.M. Percolation processes: II. The connective constant. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1957, 53, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Gomez, D.; Vazquez Juiz, L.; Perez-Rodriguez, P.; Eugenio Lopez-Periago, J.; Paradelo, M.; Koestel, J. Percolation theory applied to soil tomography. Geoderma 2020, 357, 113959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolandtaba, S.F.; Skauge, A. Network Modeling of EOR Processes: A Combined Invasion Percolation and Dynamic Model for Mobilization of Trapped Oil. Transp. Porous Media 2011, 89, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.C.; Kim, M.; Prakashan, K.; Jung, H.J.; Son, Y.; Park, O.O. A new approach to determine rheological percolation of carbon nanotubes in microstructured polymer matrices. Carbon 2014, 67, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, B.; Liang, F.; Liu, H.H. Modeling gas relative permeability in shales and tight porous rocks. Fuel 2020, 272, 117686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueland, B.G.; Jo, N.H.; Sapkota, A.; Tian, W.; Masters, M.; Hodovanets, H.; Downing, S.S.; Schmidt, C.; McQueeney, R.J.; Bud’ko, S.L.; et al. Reduction of the ordered magnetic moment and its relationship to Kondo coherence in Ce1−xLaxCu2Ge2. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 165121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, L.; Downing, C.; Schmidt, M.; Pemble, M.E.; Nicolosi, V.; Whatmore, R.W. Direct atomic scale determination of magnetic ion partition in a room temperature multiferroic material. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczek, P.; Sandratskii, L.M.; Buczek, N.; Thomas, S.; Vignale, G.; Ernst, A. Magnons in disordered nonstoichiometric low-dimensional magnets. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 054407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, Y.; Bonfá, P.; Sanna, S.; De Renzi, R.; Carretta, P.; McGuire, M.A.; Huq, A.; Nagler, S.E. Tuning the magnetic and structural phase transitions of PrFeAsO via Fe/Ru spin dilution. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 064515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, M. Possible new phase transition in the 3D Ising model associated with boundary percolation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2023, 35, 285401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Park, K.J.; Cho, E.J.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, H.D. Electronic structure change of NiS2−xSex in the metal-insulator transition probed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, A.; Oles, A.M.; Horsch, P. Defect-Induced Orbital Polarization and Collapse of Orbital Order in Doped Vanadium Perovskites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 127206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Yan, P.; Yang, X.; Zou, H.; Yang, H.; Liang, H. High conductivity, percolation behavior and dielectric relaxation of hybrid ZIF-8/CNT composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 825, 154132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xu, Z.; Yakobson, B.I. Site-percolation threshold of carbon nanotube fibers—Fast inspection of percolation with Markov stochastic theory. Phys. A 2014, 407, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.; Glen, M. Percolation processes in 2 dimensions. 1. Low-density series expansions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1976, 9, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.; Gaunt, D.; Glen, M. Percolation processes in 2 dimensions. 2. Critical concentrations and mean size index. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1976, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.; Gaunt, D.; Glen, M. Percolation processes in 2 dimensions. 3. High-density series expansions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1976, 9, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.; Gaunt, D.; Glen, M. Percolation processes in 2 dimensions. 4. Percolation probability. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1976, 9, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, D.; Sykes, M. Percolation processes in 2 dimensions. 5. Exponent δp and scaling theory. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1976, 9, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, L.A. Contact network epidemiology: Bond percolation applied to infectious disease prediction and control. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 2007, 44, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Zhu, M. Epidemic spreading in a social network with facial masks wearing individuals. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2021, 8, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziff, R.M. Percolation and the pandemic. Phys. A 2021, 568, 125723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K.; Kaczanowska, S.; Kułakowski, K. Are forest fires predictable? Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2002, 13, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisoni, N.; Loscar, E.S.; Albano, E.V. Phase diagram and critical behavior of a forest-fire model in a gradient of immunity. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 011125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoni, A.; Salinesi, P.; Morandini, F. Physical modelling of forest fire spreading through heterogeneous fuel beds. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2011, 20, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelo-Neto, G.; Coutinho, S. Forest-fire model with resistant trees. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2011, 2011, P06018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abades, S.R.; Gaxiola, A.; Marquet, P.A. Fire, percolation thresholds and the savanna forest transition: A neutral model approach. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.E.; Pajares, C.; Martínez, M.I.; Rodríguez Fernández, R.; Molina-Gayosso, E.; Lozada-Lechuga, J.; Fernández Téllez, A. Site-bond percolation solution to preventing the propagation of Phytophthora zoospores on plantations. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 101, 032301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Herrera, D.; Ramírez, J.E.; Martínez, M.I.; Cruz-Suárez, H.; Fernández Téllez, A.; López-Olguín, J.F.; Aragón García, A. Percolation-intercropping strategies to prevent dissemination of phytopathogens on plantations. Chaos 2021, 31, 063105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.R.; Velázquez-Castro, J.; Téllez, A.F.; López-Olguín, J.F.; Ramírez, J.E. Site percolation threshold of composite square lattices and its agroecology applications. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, 014304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Dong, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y. Quantifying urban areas with multi-source data based on percolation theory. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.K.M.; Shabrina, Z.; Sarkar, S.; Han, H.; Pettit, C. From urban clusters to megaregions: Mapping Australia’s evolving urban regions. Comput. Urban Sci. 2024, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguero, M.; Perez-Cerdan, M.; del Real, R.P.; Ricote, J.; Castro, A. Novel Aurivillius Bi4Ti3−2xNbxFexO12 phases with increasing magnetic-cation fraction until percolation: A novel approach for room temperature multiferroism. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12457–12469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Andrade, J.; Stauffer, D. Sznajd social model on square lattice with correlated percolation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2001, 12, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K.; Wołoszyn, M. Thermal properties of structurally balanced systems on classical random graphs. Chaos 2023, 33, 073115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirigliano, L.; Castellano, C.; Timár, G. Extended-range percolation in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 044304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolucci, S.; Caccioli, F.; Vivo, P. A percolation model for the emergence of the Bitcoin Lightning Network. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddoe, M.; Gölz, T.; Barkey, M.; Bau, E.; Godejohann, M.; Maier, S.A.; Keilmann, F.; Moldovan, M.; Prodan, D.; Ilie, N.; et al. Probing the micro- and nanoscopic properties of dental materials using infrared spectroscopy: A proof-of-principle study. Acta Biomater. 2023, 168, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P. Critical percolation in high dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 036101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.F.; Essam, J.W. Critical percolation probabilities by series methods. Phys. Rev. 1964, 133, A310–A315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, A.; Lebowitz, J.L.; Marro, J.; Kalos, M.H.; Kirkpatrick, S. Monte Carlo studies of percolation phenomena for a simple cubic lattice. J. Stat. Phys. 1976, 15, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, D.; Sykes, M. Series study of random percolation in 3 dimensions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1983, 16, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Ziff, R. Universality of the excess number of clusters and the crossing probability function in three-dimensional percolation. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1998, 31, 8147–8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzawski, Ł.; Malarz, K. Simple cubic random-site percolation thresholds for complex neighbourhoods. Rep. Math. Phys. 2012, 70, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwica, M.; Gronek, P.; Malarz, K. Efficient space virtualisation for Hoshen–Kopelman algorithm. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2019, 30, 1950055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yan, J.; Xun, Z.; Hao, D.; Ziff, R.M. Site and bond percolation on four-dimensional simple hypercubic lattices with extended neighborhoods. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2022, 2022, 033202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Ziff, R.M.; Stanley, H.E. Percolation threshold, Fisher exponent, and shortest path exponent for four and five dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 026115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Z.; Hao, D.; Ziff, R.M. Extended-range percolation in five dimensions. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Marck, S. Calculation of percolation thresholds in high dimensions for FCC, BCC and diamond lattices. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 1998, 9, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, Z.; Poła, J. From discrete to continuous percolation in dimensions 3 to 7. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2016, 2016, 103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji-Akbari, A.; Ziff, R.M. Percolation in networks with voids and bottlenecks. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 021118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Saha, D.; Sensharma, A. Percolation in a distorted square lattice. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 012117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Saha, D.; Sensharma, A. Percolation in a simple cubic lattice with distortion. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 106, 034109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sensharma, A. Site percolation in distorted square and simple cubic lattices with flexible number of neighbors. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, 064127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.A.M.; Ortiz, J.P.; Ortiz, M.P.; Balankin, A. Percolation on Fractal Networks: A Survey. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, N.W.; Domb, C.; Sykes, M.F. Dependence of critical concentration of a dilute ferromagnet on the range of interaction. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1964, 83, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domb, C.; Dalton, N.W. Crystal statistics with long-range forces: I. The equivalent neighbour model. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1966, 89, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K. Universality of percolation thresholds for two-dimensional complex non-compact neighborhoods. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, 034108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Z.; Hao, D.; Ziff, R.M. Site percolation on square and simple cubic lattices with extended neighborhoods and their continuum limit. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 103, 022126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Z.; Hao, D.; Ziff, R.M. Site and bond percolation thresholds on regular lattices with compact extended-range neighborhoods in two and three dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 024105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Z.; Hao, D. Monte Carlo simulation of bond percolation on square lattice with complex neighborhoods. Acta Phys. Sin. 2022, 71, 066401. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K.; Galam, S. Square-lattice site percolation at increasing ranges of neighbor bonds. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 016125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galam, S.; Malarz, K. Restoring site percolation on damaged square lattices. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 027103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.; Malarz, K. Square lattice site percolation thresholds for complex neighbourhoods. Acta Phys. Pol. B 2007, 38, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Malarz, K. Simple cubic random-site percolation thresholds for neighborhoods containing fourth-nearest neighbors. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 043301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K. Site percolation thresholds on triangular lattice with complex neighborhoods. Chaos 2020, 30, 123123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K. Percolation thresholds on triangular lattice for neighbourhoods containing sites up to the fifth coordination zone. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 103, 052107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malarz, K. Random site percolation on honeycomb lattices with complex neighborhoods. Chaos 2022, 32, 083123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malarz, K. Random site percolation thresholds on square lattice for complex neighborhoods containing sites up to the sixth coordination zone. Phys. A 2023, 632, 129347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privman, V. Finite-Size Scaling Theory. In Finite Size Scaling and Numerical Simulation of Statistical Systems; World Scientific: Singapore, 1990; pp. 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.P.; Binder, K. A Guide to Monte Carlo Simulations in Statistical Physics, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Ziff, R.M. Fast Monte Carlo algorithm for site or bond percolation. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 016706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarz, K.; Wołoszyn, M.; Ciepłucha, A.; Utnicki, M. Lower limit of percolation threshold on a square lattice with complex neighborhoods—supplemental material. RODBUK Crac. Open Res. Data Repos. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastas, N.; Kosmidis, K.; Giazitzidis, P.; Maragakis, M. Method for estimating critical exponents in percolation processes with low sampling. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, S.; Moore, C. Continuum percolation thresholds in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 061109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

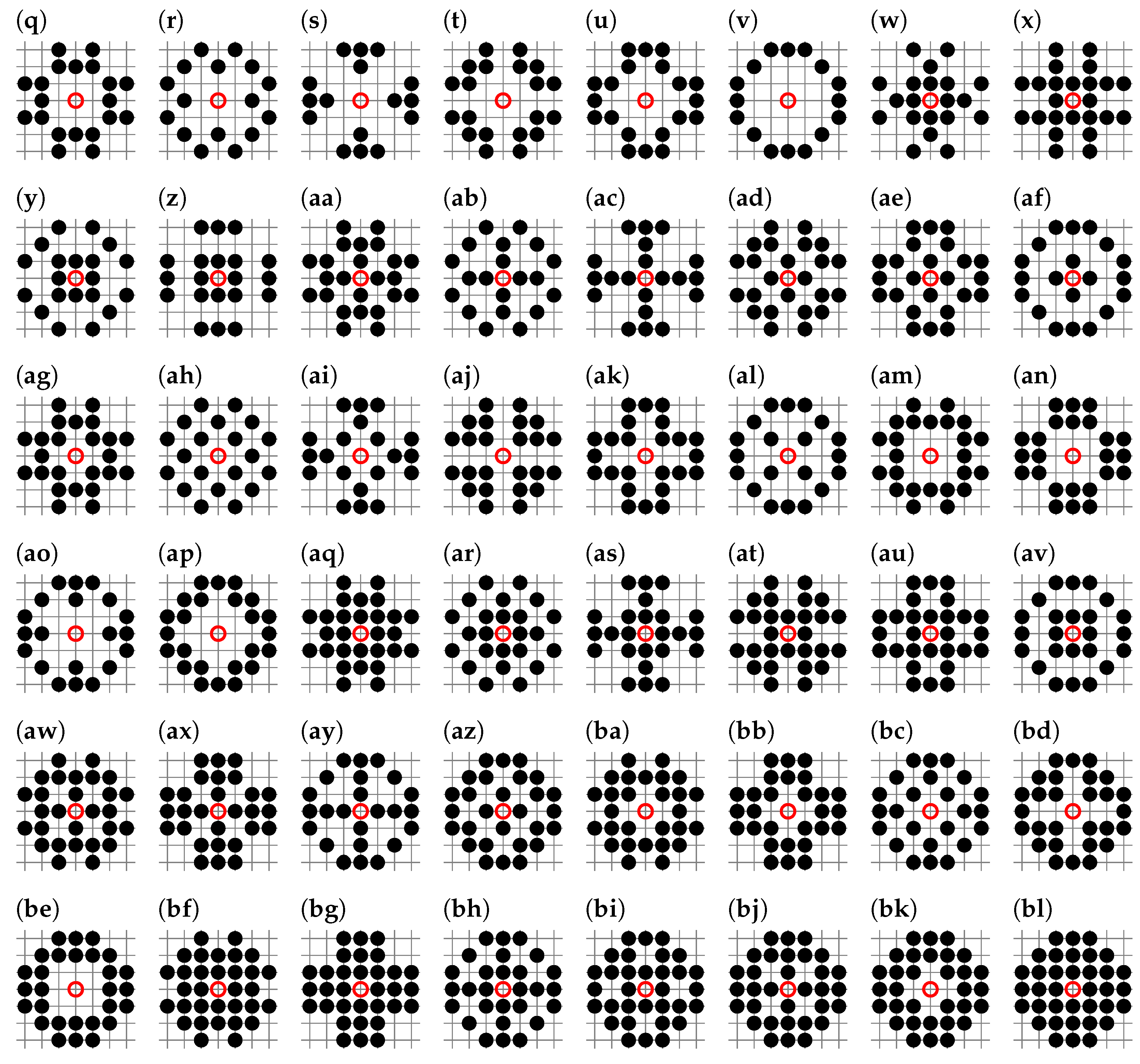
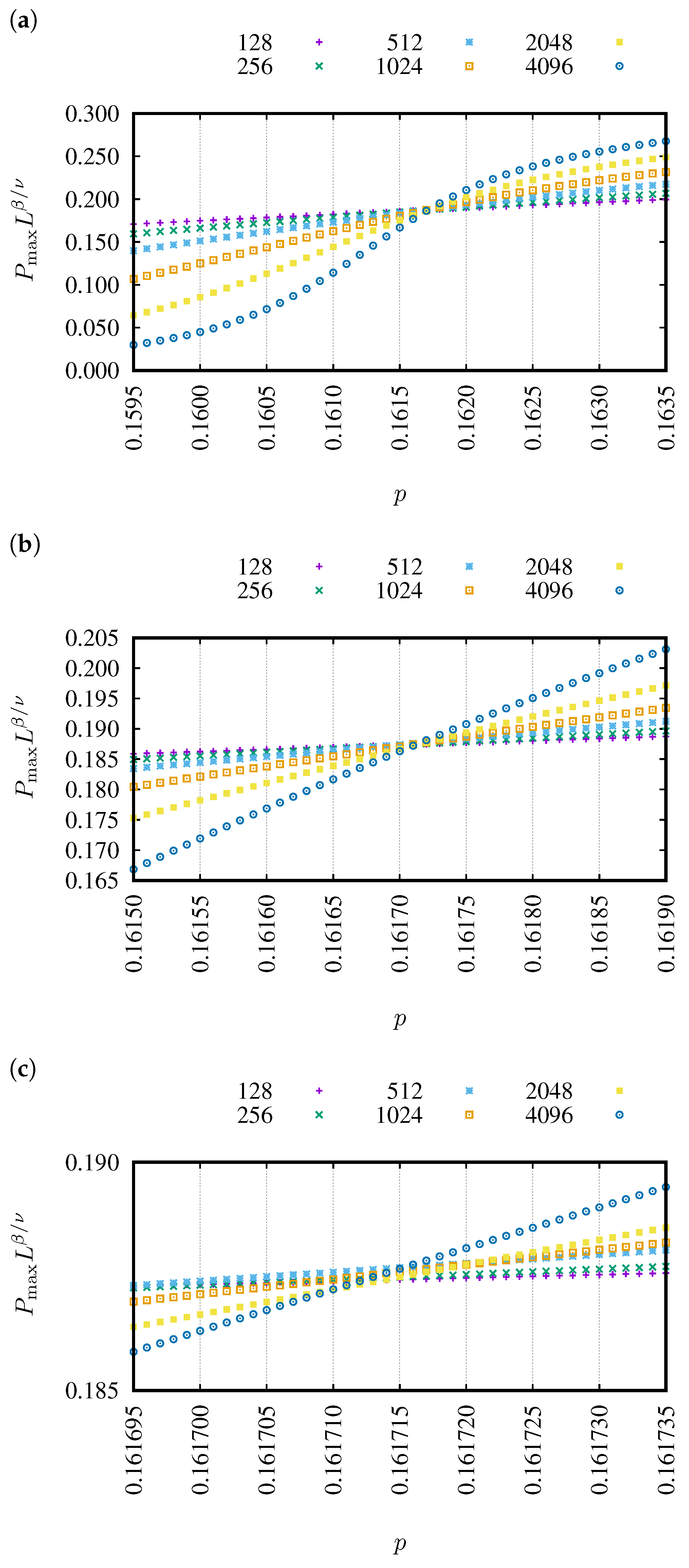
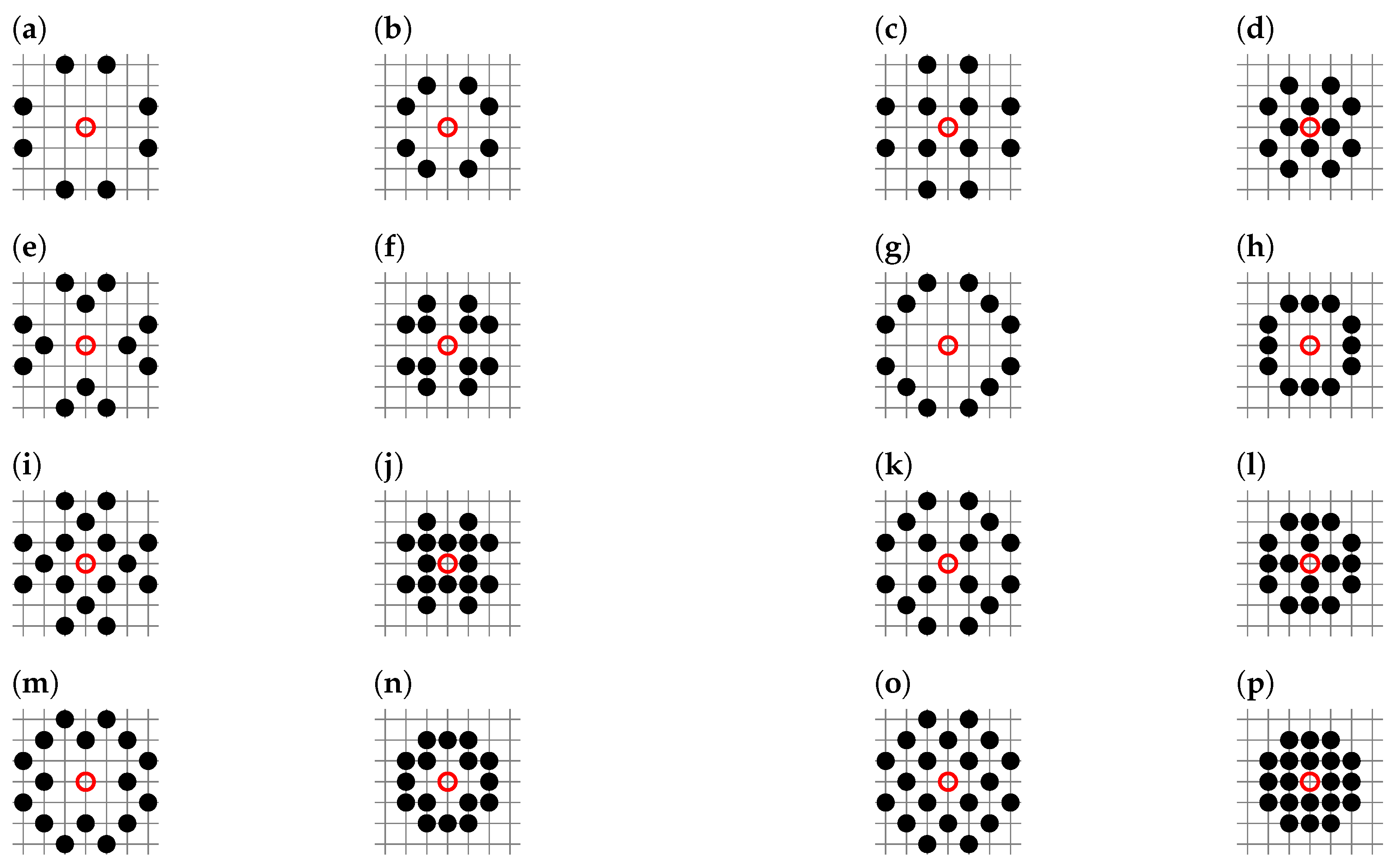
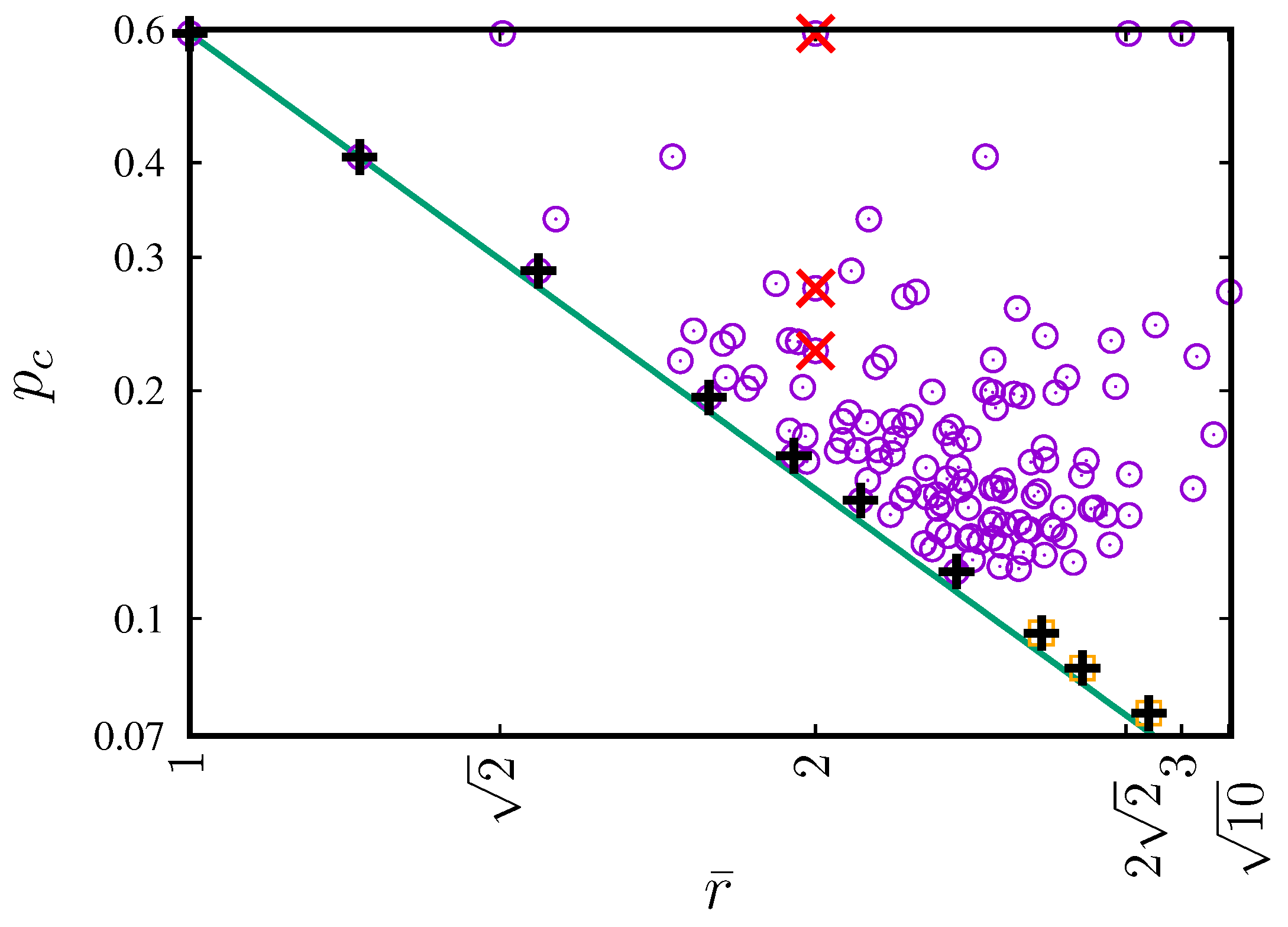

| Lattice | z | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| sq-1,2,3,4,5,6,7 | 36 | 84.157 | 0.11535 |
| sq-2,3,4,5,6,7 | 32 | 80.157 | 0.11636 |
| sq-1,3,4,5,6,7 | 32 | 78.500 | 0.11719 |
| sq-1,2,4,5,6,7 | 32 | 76.157 | 0.11949 |
| sq-1,2,3,5,6,7 | 28 | 66.269 | 0.12725 |
| sq-1,2,3,4,6,7 | 32 | 72.844 | 0.12358 |
| sq-1,2,3,4,5,7 | 32 | 72.157 | 0.12562 |
| sq-3,4,5,6,7 | 28 | 74.500 | 0.11859 |
| sq-2,4,5,6,7 | 28 | 72.157 | 0.12132 |
| sq-2,3,5,6,7 | 24 | 62.269 | 0.13241 |
| sq-2,3,4,6,7 | 28 | 68.844 | 0.12488 |
| sq-2,3,4,5,7 | 28 | 68.157 | 0.12770 |
| sq-1,4,5,6,7 | 28 | 70.500 | 0.12236 |
| sq-1,3,5,6,7 | 24 | 60.612 | 0.13112 |
| sq-1,3,4,6,7 | 28 | 67.187 | 0.12644 |
| sq-1,3,4,5,7 | 28 | 66.500 | 0.12830 |
| sq-1,2,5,6,7 | 24 | 58.269 | 0.13339 |
| sq-1,2,4,6,7 | 28 | 64.844 | 0.12864 |
| sq-1,2,4,5,7 | 28 | 64.157 | 0.13089 |
| sq-1,2,3,6,7 | 24 | 54.955 | 0.13973 |
| sq-1,2,3,5,7 | 24 | 54.269 | 0.14470 |
| sq-1,2,3,4,7 | 28 | 60.844 | 0.13718 |
| sq-4,5,6,7 | 24 | 66.500 | 0.12513 |
| sq-3,5,6,7 | 20 | 56.612 | 0.13689 |
| sq-3,4,6,7 | 24 | 63.187 | 0.12848 |
| sq-3,4,5,7 | 24 | 62.500 | 0.13121 |
| sq-2,5,6,7 | 20 | 54.269 | 0.13959 |
| sq-2,4,6,7 | 24 | 60.844 | 0.13104 |
| sq-2,4,5,7 | 24 | 60.157 | 0.13386 |
| sq-2,3,6,7 | 20 | 50.955 | 0.14523 |
| sq-2,3,5,7 | 20 | 50.269 | 0.19672 |
| sq-2,3,4,7 | 24 | 56.844 | 0.14015 |
| sq-1,5,6,7 | 20 | 52.612 | 0.13998 |
| sq-1,4,6,7 | 24 | 59.187 | 0.13298 |
| sq-1,4,5,7 | 24 | 58.500 | 0.13515 |
| sq-1,3,6,7 | 20 | 49.298 | 0.14760 |
| sq-1,3,5,7 | 20 | 48.612 | 0.14876 |
| sq-1,3,4,7 | 24 | 55.187 | 0.14187 |
| sq-1,2,6,7 | 20 | 46.955 | 0.14814 |
| sq-1,2,5,7 | 20 | 46.269 | 0.15298 |
| sq-1,2,4,7 | 24 | 52.844 | 0.14423 |
| sq-1,2,3,7 | 20 | 42.955 | 0.16125 |
| sq-5,6,7 | 16 | 48.612 | 0.14848 |
| sq-4,6,7 | 20 | 55.187 | 0.13708 |
| sq-4,5,7 | 20 | 54.500 | 0.14008 |
| sq-3,6,7 | 16 | 45.298 | 0.15503 |
| sq-3,5,7 | 16 | 44.612 | 0.20250 |
| sq-3,4,7 | 20 | 51.187 | 0.14709 |
| sq-2,6,7 | 16 | 42.955 | 0.15461 |
| sq-2,5,7 | 16 | 42.269 | 0.20831 |
| sq-2,4,7 | 20 | 48.844 | 0.14868 |
| sq-2,3,7 | 16 | 38.955 | 0.21963 |
| sq-1,6,7 | 16 | 41.298 | 0.16193 |
| sq-1,5,7 | 16 | 40.612 | 0.16095 |
| sq-1,4,7 | 20 | 47.187 | 0.15157 |
| sq-1,3,7 | 16 | 37.298 | 0.16973 |
| sq-1,2,7 | 16 | 34.955 | 0.17278 |
| sq-6,7 | 12 | 37.298 | 0.17497 |
| sq-5,7 | 12 | 36.612 | 0.22190 |
| sq-4,7 | 16 | 43.187 | 0.16171 |
| sq-3,7 | 12 | 33.298 | 0.23288 |
| sq-2,7 | 12 | 30.955 | 0.23619 |
| sq-1,7 | 12 | 29.298 | 0.18976 |
| sq-7 | 8 | 25.298 | 0.27013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciepłucha, A.P.; Utnicki, M.; Wołoszyn, M.; Malarz, K. Lower Limit of Percolation Threshold on Square Lattice with Complex Neighborhoods. Entropy 2025, 27, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040361
Ciepłucha AP, Utnicki M, Wołoszyn M, Malarz K. Lower Limit of Percolation Threshold on Square Lattice with Complex Neighborhoods. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040361
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiepłucha, Antoni Piotr, Marcin Utnicki, Maciej Wołoszyn, and Krzysztof Malarz. 2025. "Lower Limit of Percolation Threshold on Square Lattice with Complex Neighborhoods" Entropy 27, no. 4: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040361
APA StyleCiepłucha, A. P., Utnicki, M., Wołoszyn, M., & Malarz, K. (2025). Lower Limit of Percolation Threshold on Square Lattice with Complex Neighborhoods. Entropy, 27(4), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040361







