Adiponectin Gene Variant rs3774261, Effects on Lipid Profile and Adiponectin Levels after a High Polyunsaturated Fat Hypocaloric Diet with Mediterranean Pattern
Abstract
1. Introduction
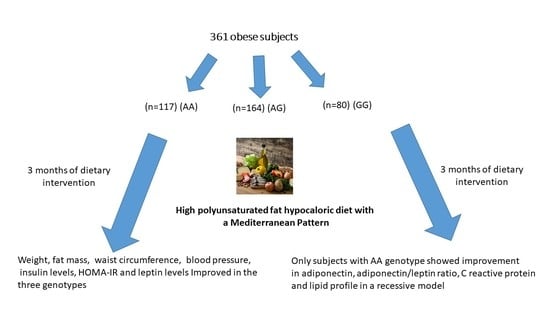
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Clinical Investigation
2.2. Dietary Intervention
2.3. Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Genotyping ADIPOQ Gene
2.5. Anthropometric Parameters and Blood Pressure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants and Dietary Intakes
3.2. Anthropometric Results
3.2.1. Biochemical Parameters
3.2.2. Adipokine Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein, S. Outcome Success in Obesity. Obes. Res. 2001, 9, 354S–358S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.-S.; Chuang, L.-M. Human genetics of adiponectin in the metabolic syndrome. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 84, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Novel modulator for endotelial adhesion molecules: Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999, 100, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, F.; Meyre, D.; Froguel, P. Adiponectin, type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: Lessons from human genetic studies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2006, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose Tissue, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Narkiewicz, K.; De Toni, R.; Aldighieri, E.; Williams, C.; Rossi, G.P. Heritability of Plasma Adiponectin Levels and Body Mass Index in Twins. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanu, J.S.; Gu, Y.; Zhi, S.; Yu, M.; Lu, Y.; Cong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism rs3774261 in the AdipoQ gene is associated with the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) in Northeast Han Chinese population: A case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Rampal, S.; Salim, A.; Moy, F.M.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Association of ADIPOQ gene with obesity and adiponectin levels in Malaysian Malays. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2917–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, K.; Keller, M.; Horstmann, A.; Liu, X.; Eichelmann, F.; Stumvoll, M.; Villringer, A.; Kovacs, P.; Tönjes, A.; Böttcher, Y. Role of genetic variants in ADIPOQ in human eating behavior. Genes Nutr. 2014, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luis, D.A.; Primo, D.; Izaola, O.; Gómez, E.; Bachiller, R. Serum Lipid and Adiponectin Improvements after a Mediterranean Dietary Pattern in Non-G-Allele Carriers of the Variant rs3774261. Lifestyle Genom. 2020, 13, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Primo, D.; Izaola, O.; Bachiller, R. Role of the variant rs37774261 of ADIPOq gene on cardiovascular risk factors and adipoencton levels after a high fat hypocaloric diet with Mediterranean Pattern. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, J.G.; Filion, K.B.; Atallah, R.; Eisenberg MJMancini, J.G.; Filion, K.B.; Atallah, R.; Eisenberg, M.J. Systematic Review of the Mediterranean Diet for Long-Term Weight Loss. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Takahashi, M.; Fiunahashi, T.; Kihara, S. PPArgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, and adipose derived protein. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, M.; Matsuda, M.; Maeda, N.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Makishima, M.; Shimomura, I. Induction of Adiponectin, a Fat-Derived Antidiabetic and Antiatherogenic Factor, by Nuclear Receptors. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mataix, J.; Mañas, M. Tablas de Composición de Alimentos Españoles; University of Granada: Granada, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfützner, A.; Langenfeld, M.; Kunt, T.; Löbig, M.; Forst, T. Evaluation of human resistin assays with serum from patients with type 2 diabetes and different degrees of insulin resistance. Clin. Lab. 2003, 49, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Suominen, P. Evaluation of an Enzyme Immunometric Assay to Measure Serum Adiponectin Concentrations. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Smith, M.S.; Reda, D.; Suffredini, A.F.; McCoy, J.P. Multiplex bead array assays for detection of soluble cytokines: Comparisons of sensitivity and quantitative values among kits from multiple manufacturers. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2004, 61, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Johnson, P.E.; Bolonchuk, W.W.; Lykken, G.I. Assessment of fat-free mass using bioelectrical impedance measurements of the human body. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 41, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassel, C.L.; Pankow, J.S.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Steffes, M.W.; Li, N.; Schreiner, P.J. Variants in the Adiponectin Gene and Serum Adiponectin: The Coronary Artery Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Obesity 2010, 18, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, K.; Ashok Ayyappa, K.; Ghosh, S.; Mohan, V. Radha Genetic Association of ADIPOQ Gene Variants with Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity and Serum Adiponectin Levels in South Indian Population. Gene 2013, 32, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzidi, I.; Mtiraoui, N.; Ali, M.E.M.; Al Masoudi, A.; Abu Duhier, F. Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) gene variants and haplotypes in Saudi Arabian women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): A case—Control study. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2019, 36, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y. Adiponectin and adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NFkappa B signaling through a C AMP dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, A.; O´Dell, S.D.; Frost, G.S.; Griffin, B.A.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Jebb, S.A.; Sanders, T.A. RISK Study Group SNP at the DIPOQ gene locus interact with age and dietary intake of fat to determine serum adiponectin in subjects at risk of the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 262–269. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita, K.; Yatsuya, H.; Tamakoshi, K.; Wada, K.; Otsuka, R.; Zhang, H.; Sugiura, K.; Kondo, T.; Murohara, T.; Toyoshima, H. Inverse association between adiponectin and C-reactive protein in substantially healthy Japanese men. Atherosclerosis 2006, 188, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.; Gillespie, S.; Orchard, T.; Tan, A.; McDaniel, J.C. Systematic review of marine-derived omega-3 fatty acid supplementation effects on leptin, adiponectin, and the leptin-to-adiponectin ratio. Nutr. Res. 2021, 85, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, N.; Li, Z.; Jiao, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Yu, T. Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism and Ischemic Stroke Subtypes in a Chinese Population. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchia, C.; Scott, K.; Fortina, P.; Devoto, M.; Falkner, B. Association of a Polymorphic Variant of the Adiponectin Gene with Insulin Resistance in African Americans. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2008, 1, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin Ratio is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Control of body weight: A physiologic and transgenic perspective. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: A promising index to estimate adipose tissue dysfunction. Relation with obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, D.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, R.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; He, G.; Liu, B. Association and functional study between ADIPOQ and metabolic syndrome in elderly Chinese Han population. Aging 2020, 12, 25819–25827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| AA (n = 117) | AG (n = 164) | AG (n = 80) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 time | At 12 weeks | 0 time | At 12 weeks | 0 time | At 12 weeks | p Time AA Time AG Time GG Basal Genotype 12 weeks Genotype | |
| Age | 46.3 ± 4.1 | - | 47.3 ± 4.0 | - | 46.9 ± 2.3 | - | p = 0.46 Basal genotype |
| Gender/male/female%) | 76.1/23.9% | - | 73.2/26.8% | - | 71.7/28.3% | - | p = 0.43 Basal genotype |
| BMI | 37.9 ± 4.1 | 35.9 ± 3.8 * | 37.8 ± 4.0 | 36.1 ± 3.4 * | 38.0 ± 2.0 | 36.3 ± 2.9 * | p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.01 p = 0.46 p = 0.43 |
| Weight (kg) | 96.4 ± 2.1 | 92.4 ± 3.0 * | 97.5 ± 2.1 | 93.1 ± 1.4 * | 97.3 ± 2.1 * | 93.4 ± 2.2 * | p = 0.01 p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.45 p = 0.11 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 39.8 ± 2.1 | 36.4 ± 2.0 * | 39.7 ± 2.0 | 36.0 ± 2.1 * | 39.8 ± 2.0 * | 36.2 ± 1.1 * | p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.03 p = 0.39 p = 0.31 |
| WC (cm) | 113.1 ± 7.0 | 109.2 ± 5.2 * | 113.4 ± 6.1 | 109.1 ± 4.1 * | 116.2 ± 4.0 * | 111.7 ± 3.9 * | p = 0.03 p = 0.04 p = 0.02 p = 0.35 p = 0.59 |
| SB (mmHg) | 127.1 ± 5.1 | 123.2 ± 6.0 * | 127.8 ± 5.0 | 122.3 ± 4.1 * | 126.2 ± 4.0 * | 123.1 ± 3.1 * | p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.02 p = 0.33 p = 0.41 |
| DB (mmHg) | 81.5 ± 4.1 | 79.3 ± 3.1 | 81.7 ± 5.1 | 79.1 ± 6.0 | 78.7 ± 4.1 | 78.7 ± 3.1 | p = 0.41 p = 0.42 p = 0.51 p = 0.49 p = 0.61 |
| Energy intake (cal day) | 1739.2 ± 129.2 | 1439.1 ± 119.2 | 1801.7 ± 113.1 | 1503.1 ± 112.2 | 1718.9 ± 112.1 | 1489.1 ± 123.1 | p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.01 p = 0.48 p = 0.46 |
| Carbohydrates (g/day) | 181.9 ± 14.1 | 159.1 ± 19.1 | 192.7 ± 13.2 | 148.1 ± 13.2 | 179.7 ± 11.1 | 149.1 ± 10.1 | p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.02 p = 0.41 p = 0.39 |
| Fat (g/day) | 61.5 ± 4.1 | 53.3 ± 3.2 | 79.7 ± 4.1 | 50.1 ± 7.2 | 76.9 ± 3.9 | 49.9 ± 4.1 | p = 0.01 p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.33 p = 0.37 |
| Protein (g/day) | 84.5 ± 5.1 | 75.1 ± 9.2 | 86.7 ± 2.1 | 76.2 ± 7.2 | 88.0 ± 2.1 | 77.1 ± 8.1 | p = 0.02 p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.60 p = 0.49 |
| Monounsaturated fat (%) | 34.5% | 55.5% | 34.9% | 55.0% | 35.1% | 55.1% | p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.01 p = 0.37 p = 0.48 |
| Polyunsaturated fat (%) | 13.4% | 22.7% | 13.8% | 22.0% | 14.0% | 23.0% | p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.04 p = 0.41 p = 0.42 |
| Saturated fat (%) | 52.1% | 21.8% | 53.5% | 23.0% | 50.9% | 21.9% | p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.38 p = 0.43 |
| Physical activity (min/week) | 121.1 ± 12.3 | 149.3 ± 21.1 | 123.1 ± 9.9 | 152.0 ± 23.2 | 122.1 ± 7.2 | 151.9 ± 18.1 | p = 0.11 p = 0.22 p = 0.34 p = 0.30 p = 0.33 |
| AA (n = 117) | AG (n = 164) | AG (n = 80) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 time | At 12 weeks | 0 time | At 1 2 weeks | 0 time | At 12 weeks | p Time AA Time AG Time GG Basal Genotype 12 weeks Genotype | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 102.1 ± 7.0 | 99.3 ± 7.1 | 101.5 ± 7.1 | 99.9 ± 5.1 | 101.1 ± 5.1 | 98.9 ± 4.1 | p = 0.16 p = 0.19 p = 0.30 p = 0.45 p = 0.34 |
| Total ch. (mg/dL) | 204.1 ± 7.2 | 186.3 ± 4.2 * | 208.7 ± 3.5 | 196.7 ± 6.0 | 205.1 ± 3.1 | 194.3 ± 7.2 | p = 0.01 p = 0.22 p = 0.30 p = 0.41 p = 0.31 |
| LDLch. (mg/dL) | 127.3 ± 6.1 | 110.3 ± 7.2 * | 129.1 ± 4.3 | 123.1 ± 8.2 | 127.1 ± 4.1 | 121.1 ± 9.1 | p = 0.01 p = 0.32 p = 0.31 p = 0.35 p = 0.51 |
| HDL-ch. (mg/dL) | 52.8 ± 3.1 | 50.6 ± 4.0 | 51.9 ± 3.0 | 50.1 ± 2.1 | 52.3 ± 3.0 | 51.1 ± 3.1 | p = 0.21 p = 0.32 p = 0.39 p = 0.25 p = 0.41 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 128.9 ± 11.1 | 93.1 ± 10.4 * | 131.1 ± 6.2 | 121.1 ± 10.8 | 129.8 ± 4.2 | 123.9 ± 9.3 | p = 0.03 p = 0.32 p = 0.30 p = 0.29 p = 0.31 |
| Insulin (mUI/L) | 13.1 ± 2.0 | 9.4 ± 1.9 * | 13.3 ± 2.1 | 9.5 ± 1.1 * | 12.7 ± 3.0 | 9.1 ± 3.0 * | p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.01 p = 0.45 p = 0.39 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.3 * | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.4 * | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.9 * | p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.02 p = 0.35 p = 0.41 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 5.1 ± 1.0 | 3.8 ± 0.8 * | 5.0 ± 2.9 | 4.9 ± 2.1 | 5.1 ± 3.1 | 5.0 ± 3.2 | p = 0.01 p = 0.42 p = 0.41 p = 0.55 p = 0.19 |
| AA (n = 117) | AG (n = 164) | AG (n = 80) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 time | At 12 weeks | 0 time | At 12 weeks | 0 time | At 12 weeks | p Time AA Time AG Time GG Basal Genotype 12 weeks genotype | |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 10.0 ± 3.1 | 21.6 ± 3.2 * | 12.3 ± 3.3 | 14.4 ± 4.7 | 12.0 ± 2.8 | 15.5 ± 4.2 | p = 0.01 p = 0.12 p = 0.31 p = 0.45 p = 0.11 |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 5.1 ± 2.0 | 5.0 ± 1.6 | 5.2 ± 2.1 | 5.1 ± 1.1 | 5.3 ± 3.9 | 5.1 ± 3.2 | p = 0.31 p = 0.32 p = 0.41 p = 0.45 p = 0.33 |
| Leptin(ng/mL) | 49.1 ± 9.1 | 12.9 ± 7.3 * | 42.0 ± 7.1 | 22.1 ± 6.1 * | 46.8 ± 4.2 | 19.4 ± 4.1 * | p = 0.01 p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.41 p = 0.31 |
| Ratio Adiponectin/leptin | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.3 * | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | p = 0.02 p = 0.33 p = 0.34 p = 0.41 p = 0.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Luis Roman, D.A.; Primo, D.; IZaola, O.; Gómez, E.; López, J.J. Adiponectin Gene Variant rs3774261, Effects on Lipid Profile and Adiponectin Levels after a High Polyunsaturated Fat Hypocaloric Diet with Mediterranean Pattern. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061811
de Luis Roman DA, Primo D, IZaola O, Gómez E, López JJ. Adiponectin Gene Variant rs3774261, Effects on Lipid Profile and Adiponectin Levels after a High Polyunsaturated Fat Hypocaloric Diet with Mediterranean Pattern. Nutrients. 2021; 13(6):1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061811
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Luis Roman, Daniel Antonio, David Primo, Olatz IZaola, Emilia Gómez, and Juan Jose López. 2021. "Adiponectin Gene Variant rs3774261, Effects on Lipid Profile and Adiponectin Levels after a High Polyunsaturated Fat Hypocaloric Diet with Mediterranean Pattern" Nutrients 13, no. 6: 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061811
APA Stylede Luis Roman, D. A., Primo, D., IZaola, O., Gómez, E., & López, J. J. (2021). Adiponectin Gene Variant rs3774261, Effects on Lipid Profile and Adiponectin Levels after a High Polyunsaturated Fat Hypocaloric Diet with Mediterranean Pattern. Nutrients, 13(6), 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061811