Foveal Pit Morphology Characterization: A Quantitative Analysis of the Key Methodological Steps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
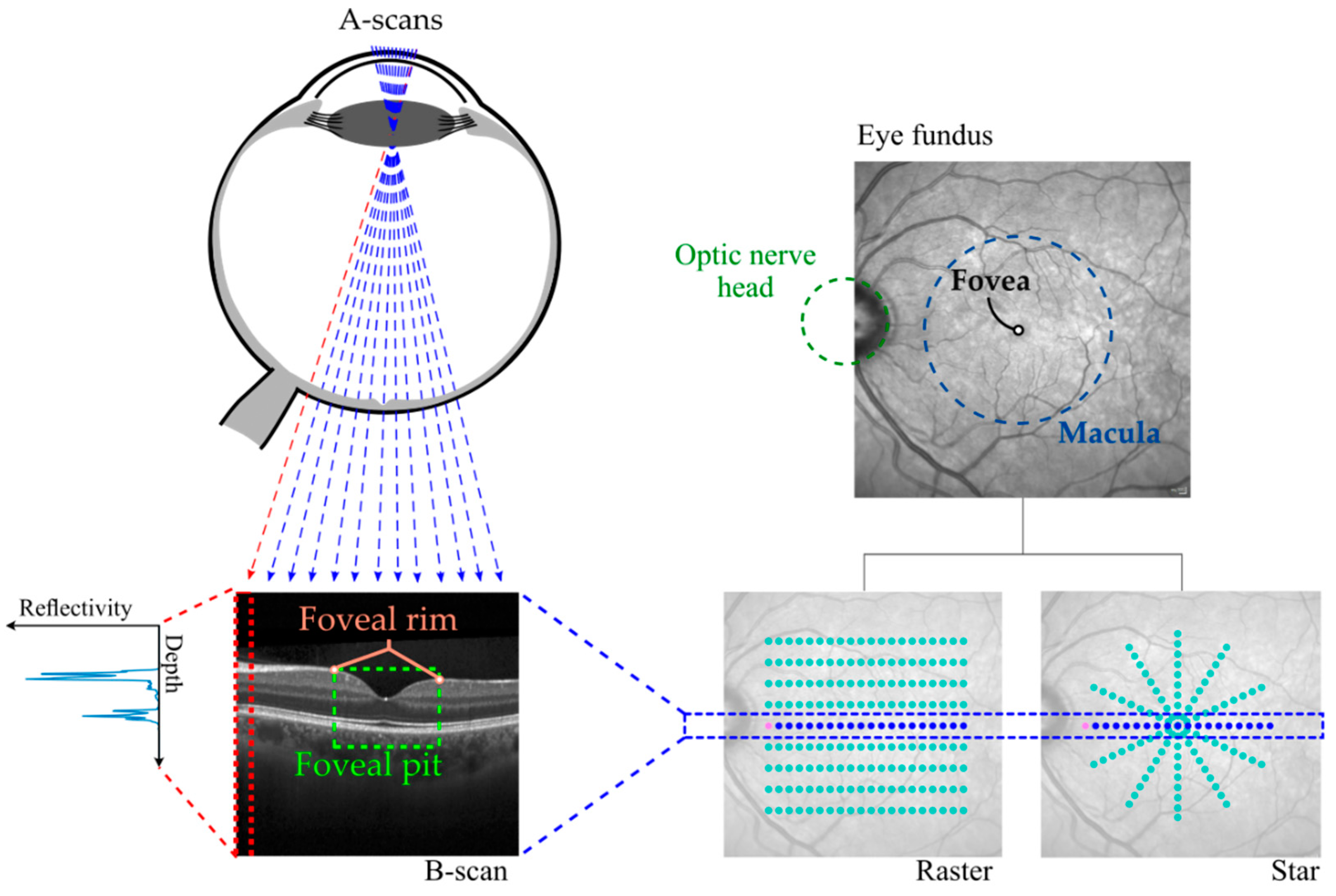
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Image Processing Pipeline
- Regular grid of 3 × 3 mm2 and a spacing of 0.02 mm. This was used for foveal center location method comparison (see Section 2.4.1).
- Radial pattern with 2 mm radius, 24 angular directions and a spacing of 0.02 mm. This was used for morphology analysis and mathematical model comparison (see Section 2.4.2). This was calculated after using only the smooth + min method to locate the foveal center, as it was the method that provided the best alignment.
- Central foveal thickness (CFT): the TRT value at the foveal center.
- Rim height: the point of maximum TRT in each angular direction.
- Rim radius: the lateral distance between the foveal center and the rim.
- Maximum slope: the maximum derivative value in the region from the foveal center to the rim.
2.3.1. Foveal Center Location
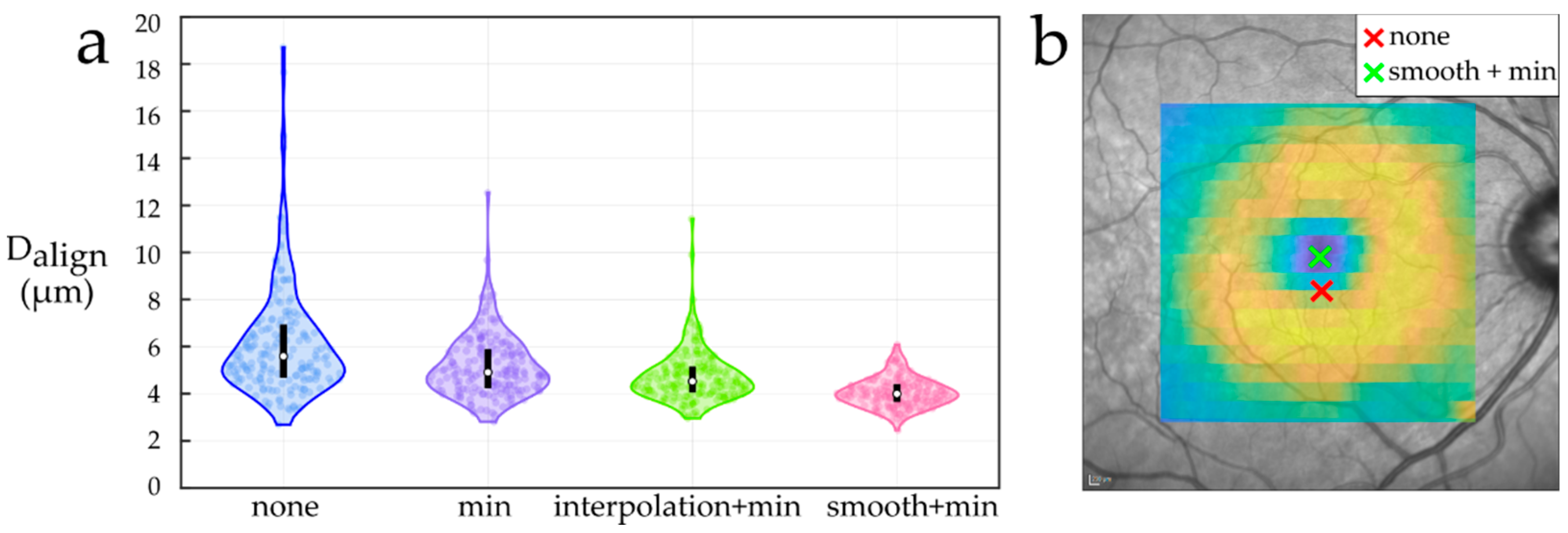
- None: assume the center of the acquired scan as the foveal center.
- Min: locate the foveal center at the A-Scan point of minimum TRT in the central 0.85 mm radius region.
- Interpolation + min: resample the central part of the TRT map to a regular grid of 0.85 × 0.85 mm2 and a 0.02 mm spacing using cubic interpolation. Then, locate the foveal center at the grid point with minimum TRT.
- Smooth + min: resample the central part of the TRT map to a regular grid of 0.85 × 0.85 mm2 and 0.02 mm spacing, and smooth it before locating the foveal center at the grid point with minimum TRT. We used the implementation of AURA Tools (foveaFinder.m function) [44] to smooth the resampled TRT map by applying a filter with a 0.05 mm radius circular kernel.
2.3.2. Foveal Pit Mathematical Modelling
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Foveal Center Location
2.4.2. Foveal pit mathematical modelling
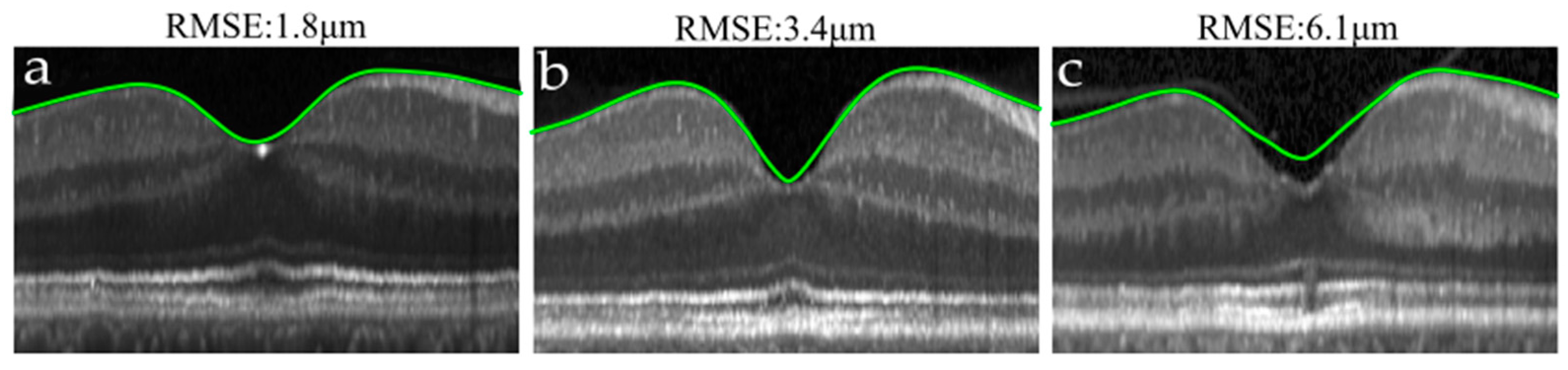
- Fitting error: to measure how well each model adjusted the data. For that, the root mean square error (RMSE) between the TRT maps obtained without using any model () and the TRT maps derived after fitting () was used:where and account for the x and y axes position in the grid, and refers to the number of points in each grid direction.
- The absolute agreement between raster and star: to assess the capability of each approach to increase the agreement between two different acquisitions of the same eye (raster and star). It was evaluated for each morphological parameter by the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) based on a single measurement and 2-way mixed-effects model (ICC (2,1)), see [46] for a detailed explanation). Along with the mean ICC, 95% confidence intervals were computed based on the percentile bootstrap method resampling the data 104 times.
- Estimation bias: to determine the effect of the modelling/smoothing step on each parameter estimate. It was evaluated using the relative bias, which is the relative difference between the estimation of each parameter before () and after applying any model or smoothing ():where accounts for the mean value of the parameter in an eye. The four analyzed parameters were: CFT, rim height, rim radius and maximum slope. Both the RMSE and the estimation bias were computed separately for raster and star scans.
3. Results
3.1. Foveal Center Location
3.2. Foveal Pit Mathematical Modelling
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolb, H. How the Retina Works. Am. Sci. 2003, 91, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Nelson, R.F.; Ahnelt, P.K.; Ortuño-Lizarán, I.; Cuenca, N. The Architecture of the Human Fovea. In Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System; Kolb, H., Nelson, R.F., Fernandez, E., Jones, B., Eds.; University of Utah Health Sciences Center: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, S.L. The Retina; Univ. Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Anstis, S.M. A Chart Demonstrating Variations in Acuity with Retinal Position. Vision Res. 1974, 14, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.S.; Mitchell, P.; Seddon, J.M.; Holz, F.G.; Wong, T.Y. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Lancet 2012, 379, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufai, S.R.; Thomas, M.G.; Purohit, R.; Bunce, C.; Lee, H.; Proudlock, F.A.; Gottlob, I. Can Structural Grading of Foveal Hypoplasia Predict Future Vision in Infantile Nystagmus?: A Longitudinal Study. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical Coherence Tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bille, J.F.; Hell, S.W.; Weinreb, R.N. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Principle and Technical Realization. In High Resolution Imaging in Microscopy and Ophthalmology; Bille, J.F., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, M.R.; Puliafito, C.A.; Wong, C.; Duker, J.S.; Reichel, E.; Schuman, J.S.; Swanson, E.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Optical Coherence Tomography of Macular Holes. Ophthalmology 1995, 102, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, S.; Tugal-Tutkun, I.; Neri, P.; Herbort, C.P. Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging in Uveitis. Int. Ophthalmol. 2014, 34, 401–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuman, J.S.; Hee, M.R.; Arya, A.V.; Pedut-Kloizman, T.; Puliafito, C.A.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Swanson, E.A. Optical Coherence Tomography: A New Tool for Glaucoma Diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 1995, 6, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.; Murthy, R.K.; Brar, V.S.; Chalam, K.V. Normative Data for Macular Thickness by High-Definition Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (Spectralis). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 148, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Acquistapace, A.; Benatti, E.; Erba, S.; Cozzi, M.; Cigada, M.; Viola, F.; Gillies, M.; Staurenghi, G. Normative Data for Retinal-Layer Thickness Maps Generated by Spectral-Domain OCT in a White Population. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2018, 2, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, U.; Alm, A. Macular Thickness Decreases with Age in Normal Eyes: A Study on the Macular Thickness Map Protocol in the Stratus OCT. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 1448–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.K.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, S.S. Macular Thickness Variations with Sex, Age, and Axial Length in Healthy Subjects: A Spectral Domain-Optical Coherence Tomography Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3913–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chrysou, A.; Jansonius, N.M.; van Laar, T. Retinal Layers in Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Studies. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 64, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohman, E.M.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Frohman, T.C.; Calabresi, P.A.; Cutter, G.; Balcer, L.J. Optical Coherence Tomography: A Window into the Mechanisms of Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2008, 4, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.T.T.; Sun, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, L.J.; Wong, A.; Tham, C.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Chen, C.; Ikram, M.K.; Whitson, H.E.; et al. Spectral-Domain OCT Measurements in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Schuman, M.; Dubis, A.M.; Nordgren, R.N.; Lei, Y.; Odell, D.; Chiao, H.; Weh, E.; Fischer, W.; Sulai, Y.; Dubra, A.; et al. Race- and Sex-Related Differences in Retinal Thickness and Foveal Pit Morphology. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouache, M.A.; Silvestri, G.; Amoaku, W.M.; Silvestri, V.; Hubbard, W.C.; Pappas, C.; Akafo, S.; Lartey, S.; Mastey, R.R.; Carroll, J.; et al. Comparison of the Morphology of the Foveal Pit Between African and Caucasian Populations. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Bascones, D.; Gabilondo, I.; Barrenechea, M.; Ayala, U. Caracterización de La Morfología Foveal: Parametrización, Diferencias de Sexo y Efectos de La Edad. Proceeding of the XXXVIII Congreso Anual de la Sociedad Española de Ingeniería Biomédica, Online, 25–27 November 2017; Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València: Valencia, Spain, 2020; pp. 356–359. [Google Scholar]
- Scheibe, P.; Zocher, M.T.; Francke, M.; Rauscher, F.G. Analysis of Foveal Characteristics and Their Asymmetries in the Normal Population. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 148, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Spund, B.; Glazman, S.; Shrier, E.M.; Miri, S.; Selesnick, I.; Bodis-Wollner, I. Application of an OCT Data-Based Mathematical Model of the Foveal Pit in Parkinson Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotnick, S.; Ding, Y.; Glazman, S.; Durbin, M.; Miri, S.; Selesnick, I.; Sherman, J.; Bodis-Wollner, I. A Novel Retinal Biomarker for Parkinson’s Disease: Quantifying the Foveal Pit with Optical Coherence Tomography. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1692–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.B.; Godara, P.; Williams, V.; Summerfelt, P.; Connor, T.B.; Tarima, S.; Visotcky, A.; Cooper, R.F.; Blindauer, K.; Carroll, J. Assessing Retinal Structure in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Neurophysiol. 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, J.D.; Arellano, I.A.; Swanson, E.A.; Favazza, T.L.; Bowe, T.S.; Munro, R.J.; Ferguson, R.D.; Hansen, R.M.; Moskowitz, A.; Fulton, A.B. The Fovea in Retinopathy of Prematurity. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedi, S.; Oertel, F.C.; Yadav, S.K.; Kadas, E.M.; Weise, M.; Havla, J.; Ringelstein, M.; Aktas, O.; Albrecht, P.; Ruprecht, K.; et al. Altered Fovea in AQP4-IgG–Seropositive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7, e805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Motamedi, S.; Oberwahrenbrock, T.; Oertel, F.C.; Polthier, K.; Paul, F.; Kadas, E.M.; Brandt, A.U. CuBe: Parametric Modeling of 3D Foveal Shape Using Cubic Bézier. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4181–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepulveda, J.A.; Turpin, A.; McKendrick, A.M. Individual Differences in Foveal Shape: Feasibility of Individual Maps between Structure and Function within the Macular Region. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubis, A.M.; McAllister, J.T.; Carroll, J. Reconstructing Foveal Pit Morphology from Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheibe, P.; Lazareva, A.; Braumann, U.-D.; Reichenbach, A.; Wiedemann, P.; Francke, M.; Rauscher, F.G. Parametric Model for the 3D Reconstruction of Individual Fovea Shape from OCT Data. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 119, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Marsh-Tootle, W.; Harb, E.N.; Hou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Anderson, H.A.; Norton, T.T.; Weise, K.K.; Gwiazda, J.E.; Hyman, L. A Sloped Piecemeal Gaussian Model for Characterising Foveal Pit Shape. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2016, 36, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breher, K.; Agarwala, R.; Leube, A.; Wahl, S. Direct Modeling of Foveal Pit Morphology from Distortion-Corrected OCT Images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 4815–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knighton, R.W.; Gregori, G. The Shape of the Ganglion Cell plus Inner Plexiform Layers of the Normal Human Macula. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7412–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.L.; Galea, M.; Loane, E.; Stack, J.; Beatty, S.; Nolan, J.M. Foveal Anatomic Associations with the Secondary Peak and the Slope of the Macular Pigment Spatial Profile. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tick, S.; Rossant, F.; Ghorbel, I.; Gaudric, A.; Sahel, J.-A.; Chaumet-Riffaud, P.; Paques, M. Foveal Shape and Structure in a Normal Population. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gella, L.; Pal, S.S.; Ganesan, S.; Sharma, T.; Raman, R. Foveal Slope Measurements in Diabetic Retinopathy: Can It Predict Development of Sight-Threatening Retinopathy? Sankara Nethralaya Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology and Molecular Genetics Study (SN-DREAMS II, Report No 8). Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 63, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewarie, P.; Balk, L.; Costello, F.; Green, A.; Martin, R.; Schippling, S.; Petzold, A. The OSCAR-IB Consensus Criteria for Retinal OCT Quality Assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ctori, I.; Gruppetta, S.; Huntjens, B. The Effects of Ocular Magnification on Spectralis Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Scan Length. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchinson, D.; Smith, G. Schematic Eyes. In Optics of the Human Eye; Heinemann, B., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenSaïda, A. Shapiro-Wilk and Shapiro-Francia Normality Tests. MATLAB Central File Exchange. Available online: https://es.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/13964-shapiro-wilk-and-shapiro-francia-normality-tests (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Bechtold, B. Violin Plots for Matlab, Github Project. Available online: https://github.com/bastibe/Violinplot-Matlab (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Salarian, A. Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC), MATLAB Central File Exchange. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/22099-intraclass-correlation-coefficient-icc (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- AURA Tools: AUtomated Retinal Analysis Tools. Available online: https://www.nitrc.org/projects/aura_tools (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Lang, A.; Carass, A.; Hauser, M.; Sotirchos, E.S.; Calabresi, P.A.; Ying, H.S.; Prince, J.L. Retinal Layer Segmentation of Macular OCT Images Using Boundary Classification. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Sex | Subjects (Eyes) | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Female | 111 | 52.8 ± 11.9 |
| Male | 74 | 57.7 ± 11.2 |
| Total | 185 | 54.8 ± 11.9 |
| Model | Mathematical Principle | Modelled Region | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dubis et al. [30] | Difference of two Gaussians | B-scan | 6 |
| Ding et al. [23] | Polynomial surface and Gaussian | TRT map & | 8 |
| Scheibe et al. [31] | Second derivative of a Gaussian | Radial $ | 4 |
| Liu et al. [32] | Sloped piecemeal Gaussian | B-scan | 6 |
| Yadav et al. [28] | Cubic Bézier curves | Center-rim * Beyond rim * | 2 3 |
| Breher et al. [33] | Sum of three Gaussians | B-scan | 9 |
| Model | RMSE (µm) | ICC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raster | Star | Central Foveal Thickness | Rim Height | Rim Radius | Maximum Slope | |
| None | - | - | 0.976 [0.966, 0.983] | 0.990 [0.987, 0.992] | 0.894 [0.865, 0.919] | 0.307 [0.236, 0.381] |
| Dubis et al. | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 0.988 [0.984, 0.992] | 0.995 [0.994, 0.996] | 0.949 [0.934, 0.962] | 0.968 [0.957, 0.977] |
| Ding et al. | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 0.988 [0.984, 0.992] | 0.995 [0.994, 0.997] | 0.957 [0.945, 0.966] | 0.969 [0.958, 0.977] |
| Scheibe et al. | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | - | 0.995 [0.994, 0.997] | 0.949 [0.933, 0.962] | 0.956 [0.939, 0.969] |
| Liu et al. | 11.5 ± 2.7 | 11.5 ± 2.7 | 0.987 [0.983, 0.991] | 0.994 [0.992, 0.996] | 0.961 [0.949, 0.970] | 0.959 [0.944, 0.971] |
| Yadav et al. | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | - | - | - | 0.958 [0.943, 0.970] |
| Breher et al. | 2.9 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 1.3 | 0.986 [0.979, 0.990] | 0.995 [0.993, 0.996] | 0.941 [0.924, 0.955] | 0.958 [0.942, 0.971] |
| LOESS_20 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.985 [0.980, 0.989] | 0.994 [0.992, 0.996] | 0.901 [0.875, 0.924] | 0.953 [0.936, 0.966] |
| LOESS_50 | 5.9 ± 1.5 | 6.5 ± 1.6 | 0.989 [0.984, 0.993] | 0.995 [0.994, 0.997] | 0.960 [0.947, 0.970] | 0.986 [0.981, 0.990] |
| Model | Bias (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Foveal Thickness | Rim Height | Rim Radius | Maximum Slope | |||||
| Raster | Star | Raster | Star | Raster | Star | Raster | Star | |
| Dubis et al. | 1.3 ± 1.3 | 1.4 ± 1.9 | −0.2 ± 0.2 | −0.5 ± 0.3 | −7.8 ± 3.7 | −8.2 ± 4.1 | −14.1 ± 4.1 | −34.0 ± 9.7 |
| Ding et al. | 1.1 ± 1.4 | 1.2 ± 2.1 | −0.5 ± 0.3 | −0.8 ± 0.3 | −7.8 ± 3.8 | −8.1 ± 4.1 | −13.9 ± 3.9 | −33.9 ± 9.7 |
| Scheibe et al. | - | - | −0.1 ± 0.3 | −0.3 ± 0.3 | −3.8 ±2.4 | −3.5 ± 2.4 | −19.8 ± 4.2 | −38.6 ± 7.8 |
| Liu et al. | −1.1 ± 1.2 | −1.1 ± 1.8 | −3.6 ± 0.9 | −3.9 ± 0.9 | 35.0 ± 7.4 | 36.4 ± 8.0 | −5.3 ± 4.6 | −27.1 ± 9.8 |
| Yadav et al. | - | - | - | - | - | - | −9.1 ± 4.8 | −29.7 ± 11.9 |
| Breher et al. | 0.8 ± 1.1 | 0.9 ± 1.8 | −0.4 ± 0.2 | −0.6 ± 0.2 | −6.5 ± 2.9 | −6.6 ± 3.2 | −11.9 ± 3.4 | −32.1 ± 9.4 |
| LOESS_20 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 1.4 | −0.1 ± 0.1 | −0.4 ±0.1 | −0.1 ± 0.9 | −0.1 ± 1.5 | −9.1 ± 2.3 | −29.2 ± 10 |
| LOESS_50 | 6.0 ± 2.7 | 6.6 ± 3.3 | −0.3 ± 0.3 | −0.5 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 2.7 | 2.5 ± 2.8 | −28.8 ± 6.1 | −46.6 ± 8.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Bascones, D.; Barrenechea, M.; Murueta-Goyena, A.; Galdós, M.; Gómez-Esteban, J.C.; Gabilondo, I.; Ayala, U. Foveal Pit Morphology Characterization: A Quantitative Analysis of the Key Methodological Steps. Entropy 2021, 23, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060699
Romero-Bascones D, Barrenechea M, Murueta-Goyena A, Galdós M, Gómez-Esteban JC, Gabilondo I, Ayala U. Foveal Pit Morphology Characterization: A Quantitative Analysis of the Key Methodological Steps. Entropy. 2021; 23(6):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060699
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Bascones, David, Maitane Barrenechea, Ane Murueta-Goyena, Marta Galdós, Juan Carlos Gómez-Esteban, Iñigo Gabilondo, and Unai Ayala. 2021. "Foveal Pit Morphology Characterization: A Quantitative Analysis of the Key Methodological Steps" Entropy 23, no. 6: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060699
APA StyleRomero-Bascones, D., Barrenechea, M., Murueta-Goyena, A., Galdós, M., Gómez-Esteban, J. C., Gabilondo, I., & Ayala, U. (2021). Foveal Pit Morphology Characterization: A Quantitative Analysis of the Key Methodological Steps. Entropy, 23(6), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060699






