Novel Sequence Types of Listeria monocytogenes of Different Origin Obtained in the Republic of Serbia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. L. Monocytogenes Strains and Culture Cultivation
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR
2.4. Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST) and Multi-Virulent-Locus Sequence Typing (MvLST) Analysis
2.5. PCR Product Sequencing
2.6. Phylogenetic and Data Analysis
2.7. Cartographic and Phylogeographic Analysis
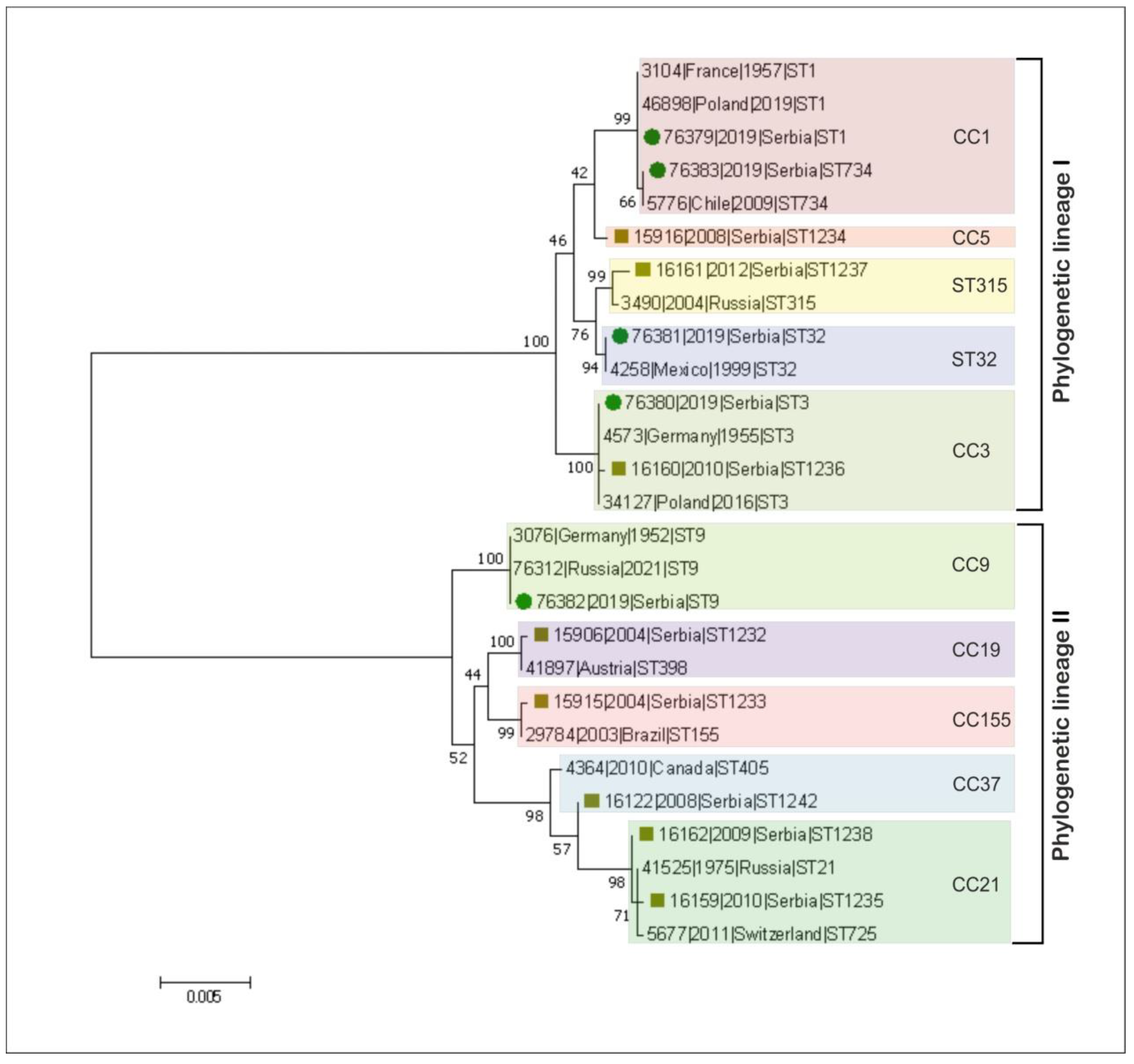
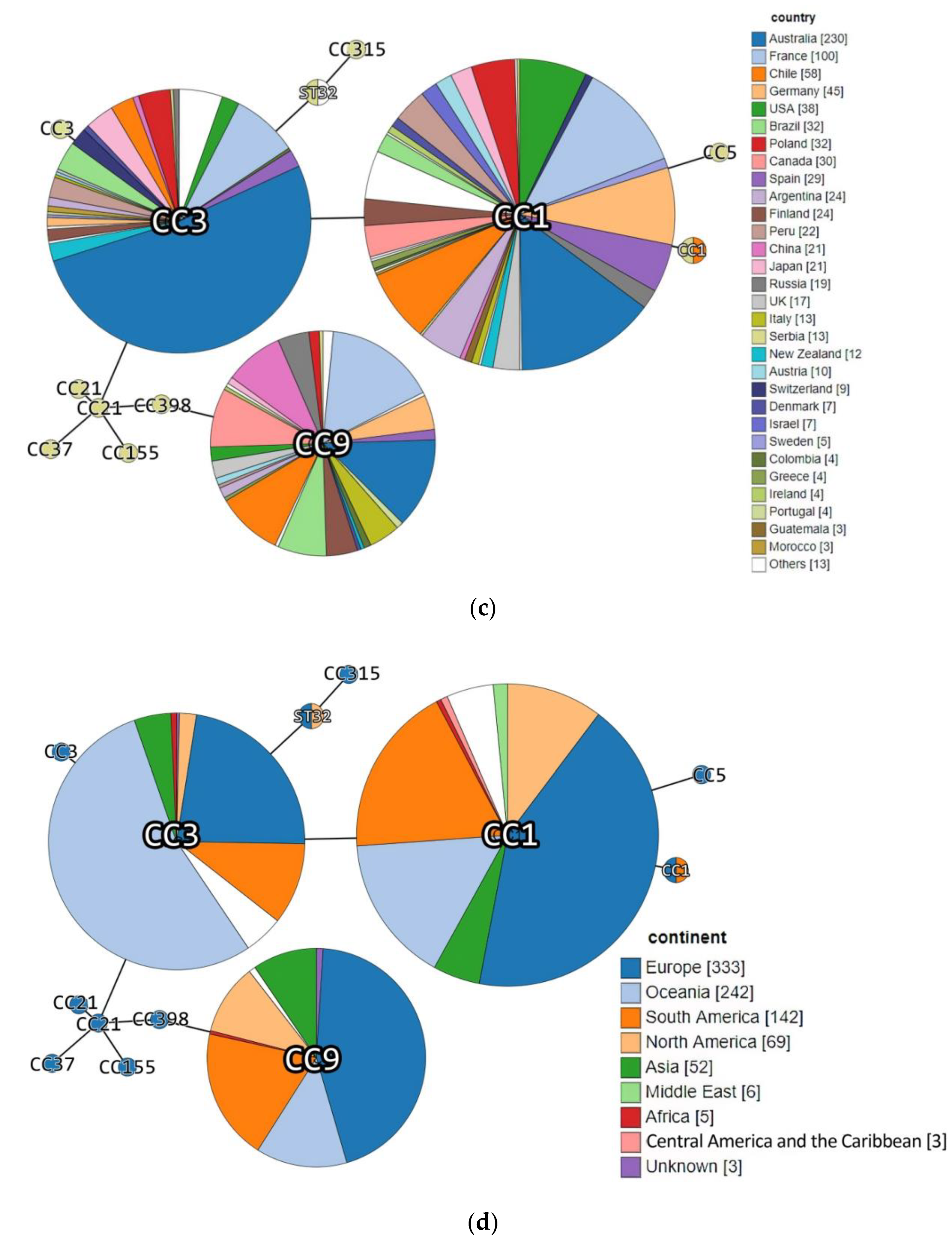
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adgamov, R.; Zaytseva, E.; Thiberge, J.M.; Brisse, S.; Ermolaeva, S. Genetically related Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from lethal human cases and wild animals. Genet. Divers. Microorg. 2012, 9, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreyer, M.; Aguilar-Bultet, L.; Rupp, S.; Guldimann, C.; Stephan, R.; Schock, A.; Otter, A.; Schupbach, G.; Brisse, S.; Lecuit, M.; et al. Listeria monocytogenes sequence type 1 is predominant in ruminant rhombencephalitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matle, I.; Mbatha, K.R.; Madoroba, E. A review of Listeria monocytogenes from meat and meat products: Epidemiology, virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance and diagnosis. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2020, 87, e1–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakicevic, B.; Nastasijevic, I. Listeria monocytogenes in retail establishments: Contamination routes and control strategies. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psareva, E.K.; Egorova, I.Y.; Liskova, E.A.; Razheva, I.V.; Gladkova, N.A.; Sokolova, E.V.; Potemkin, E.A.; Zhurilov, P.A.; Mikhaleva, T.V.; Blokhin, A.A.; et al. Retrospective Study of Listeria Monocytogenes Isolated in the Territory of Inner Eurasia from 1947 to 1999. Pathogens 2019, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oevermann, A.; Zurbriggen, A.; Vandevelde, M. Rhombencephalitis Caused by Listeria monocytogenes in Humans and Ruminants: A Zoonosis on the Rise? Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2010, 632513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ECDC. The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. 25 February 2021. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/european-union-one-health-2018-zoonoses-report (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Rocha, P.R.D.A.; Lomonaco, S.; Bottero, M.T.; Dalmasso, A.; Dondo, A.; Grattarola, C.; Zuccon, F.; Iulini, B.; Knabel, S.J.; Capucchio, M.T.; et al. Ruminant rhombencephalitis-associated Listeria monocytogenes strains constitute a genetically homogeneous group related to human outbreak strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walland, J.; Lauper, J.; Frey, J.; Imhof, R.; Stephan, R.; Seuberlich, T.; Oevermann, A. Listeria monocytogenes infection in ruminants: Is there a link to the environment, food and human health? A review. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2015, 157, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricci, A.; Allende, A.; Bolton, D.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; Fernandez Escàmez, P.S.; Girones, R.; Herman, L.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Nørrung, B.; et al. Listeria monocytogenes contamination of ready-to-eat foods and the risk for human health in the EU. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, J. Officials Report More Patients in Listeria Outbreak Linked to Cheese. Available online: https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2020/05/more-patients-reported-in-listeria-outbreak-linked-to-cheese (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Smith, A.M.; Tau, N.P.; Smouse, S.L.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Ramalwa, N.R.; Disenyeng, B.; Ngomane, M.; Thomas, J. Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes in South Africa, 2017–2018: Laboratory Activities and Experiences Associated with Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Isolates. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Noordhout, C.M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Angulo, F.J.; Verbeke, G.; Haagsma, J.; Kirk, M.; Havelaar, A.; Speybroeck, N. The global burden of listeriosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aanensen, D.M.; Spratt, B.G. The multilocus sequence typing network: Mlst.net. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W728–W733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stessl, B.; Wagner, M.; Ruppitsch, W. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) and Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2220, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenal-Francisque, V.; Lopez, J.; Cantinelli, T.; Caro, V.; Tran, C.; Leclercq, A.; Lecuit, M.; Brisse, S. Worldwide distribution of major clones of Listeria monocytogenes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo, C.; Arreaza, L.; Alcala, B.; de la Fuente, L.; Vazquez, J.A. Development of a multilocus sequence typing method for analysis of Listeria monocytogenes clones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ragon, M.; Wirth, T.; Hollandt, F.; Lavenir, R.; Lecuit, M.; Le Monnier, A.; Brisse, S. A new perspective on Listeria monocytogenes evolution. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orsi, R.H.; den Bakker, H.C.; Wiedmann, M. Listeria monocytogenes lineages: Genomics, evolution, ecology, and phenotypic characteristics. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.C.; Woodward, J.J.; Nero, L.A. The Continuous Challenge of Characterizing the Foodborne Pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Latorre, L.; Normanno, G.; Miccolupo, A.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Lorusso, V.; Santagada, G. Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism and Multi-Locus Sequence Typing for high-resolution genotyping of Listeria monocytogenes from foods and the environment. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matereke, L.T.; Okoh, A.I. Listeria monocytogenes Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Environmental Persistence: A Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, V.; Petrovic, M.; Dragovac, G.; Ristic, M.; Medic, S.; Ilic, S.; Rachevic, S.; Shtrbac, M. Infectious Diseases in Vojvodina in 2018; Institute of Public Health of Vojvod: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2019; pp. 97–98. ISBN 1452-8916. [Google Scholar]
- Banovic, F.; Schroten, H.; Schwerk, C. Potential Roles and Functions of Listerial Virulence Factors during Brain Entry. Toxins 2020, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostowy, S.; Cossart, P. Chapter 3—Virulence Factors That Modulate the Cell Biology of Listeria Infection and the Host Response. In Advances in Immunology; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 113, pp. 19–32. ISBN 9780123945907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, M.M.; Tsai, Y.H.; Charlier, C.; Touchon, M.; Chenal-Francisque, V.; Leclercq, A.; Criscuolo, A.; Gaultier, C.; Roussel, S.; Brisabois, A.; et al. Uncovering Listeria monocytogenes hypervirulence by harnessing its biodiversity. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpova, T.l.; Ermolaeval, S.A.; Lopirev, I.V.; Brodinova, N.S.; Tartakovski, I.S.; Vazquez-Boland, J.A. New Methods for Identification of Listeria monocytogenes. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 3, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Voronina, O.L.; Ryzhova, N.N.; Kunda, M.S.; Kurnaeva, M.A.; Semenov, A.N.; Aksenova, E.I.; Egorova, I.Y.; Kolbasov, D.V.; Ermolaeva, S.A.; Gintsburg, A.L. Diversity and Pathogenic Potential of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Environmental Sources in the Russian Federation. IJMER 2015, 5, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carrico, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papic, B.; Pate, M.; Felix, B.; Kusar, D. Genetic diversity of Listeria monocytogenes strains in ruminant abortion and rhombencephalitis cases in comparison with the natural environment. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papic, B.; Kusar, D.; Zdovc, I.; Golob, M.; Pate, M. Retrospective investigation of listeriosis outbreaks in small ruminants using different analytical approaches for whole genome sequencing-based typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, C.; Felix, B.; Guillier, L.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Michelon, D.; Mariet, J.F.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Mistou, M.Y.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Roussel, S. Population Genetic Structure of Listeria monocytogenes Strains as Determined by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis and Multilocus Sequence Typing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5720–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Félix, B.; Feurer, C.; Maillet, A.; Guillier, L.; Boscher, E.; Kerouanton, A.; Denis, M.; Roussel, S. Population Genetic Structure of Listeria monocytogenes Strains Isolated From the Pig and Pork Production Chain in France. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fagerlund, A.; Langsrud, S.; Moretro, T. In-Depth Longitudinal Study of Listeria monocytogenes ST9 Isolates from the Meat Processing Industry: Resolving Diversity and Transmission Patterns Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, F.; Orsini, M.; Chiaverini, A.; Torresi, M.; Centorame, P.; Acciari, V.A.; Salini, R.; Palombo, B.; Brandi, G.; Amagliani, G.; et al. Hypo- and Hyper-Virulent Listeria monocytogenes Clones Persisting in Two Different Food Processing Plants of Central Italy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuit, M.; Nelson, D.M.; Smith, S.D.; Khun, H.; Huerre, M.; Vacher-Lavenu, M.C.; Gordon, J.I.; Cossart, P. Targeting and crossing of the human maternofetal barrier by Listeria monocytogenes: Role of internalin interaction with trophoblast E-cadherin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6152–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Chung, T.; Chen, Y.; Macarisin, D.; LaBorde, L.; Kovac, J. The occurrence of Listeria monocytogenes is associated with built environment microbiota in three tree fruit processing facilities. Microbiome 2019, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macarisin, D.; Sheth, I.; Hur, M.; Wooten, A.; Kwon, H.; Gao, Z.; De Jesus, A.; Jurick, W.; Chen, Y. Survival of outbreak, food, and environmental strains of Listeria monocytogenes on whole apples as affected by cultivar and wax coating. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, K.M.; Conrad, A.R.; Saupe, A.; Dragoo, H.; West, N.; Sorenson, A.; Barnes, A.; Doyle, M.; Beal, J.; Jackson, K.A.; et al. Multistate outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections linked to whole apples used in commercially produced, prepackaged caramel apples: United States, 2014–2015. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, C.; Balanovsky, O.; Lukianova, E.; Kahbatkyzy, N.; Flegontov, P.; Zaporozhchenko, V.; Immel, A.; Wang, C.C.; Ixan, O.; Khussainova, E.; et al. The genetic history of admixture across inner Eurasia. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Acc. No in BIGSdb-Lm 1 | Strain ID | Source Category | Sample Origin | ST | CC (MLST) | Phylogenetic Lineage (MLST) | Isolation Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76379 | DP 9228/2019 | Animal | Sheep brain | ST1 | CC1 | I | 2019 | This study |
| 76380 | DP 1093/2019 | Food | Cheese with prosciutto | ST3 | CC3 | I | 2019 | |
| 76381 | DP 8605/2019 | Production environment | Fruit sorting machine | ST32 | ST32 | I | 2019 | |
| 76382 | DP 7675/2019 | Food | Smoked pork ribs | ST9 | CC9 | II | 2019 | |
| 76383 | DP 248/2019 | Animal | Aborted goat fetus | ST734 | CC1 | I | 2019 | |
| 15906 | 118/2004 | Human | Cerebrospinal fluid | 1232 | CC19 | II | 2004 | https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/listeria/, (accessed on 14 December 2016 for 118/2004, 124/2004, 2, 265/2010, 2184/2010, 2960/2012 and 4250/2009; January, 02, 2017 for 22/2008) |
| 15915 | 124/2004 | Human | Cerebrospinal fluid | 1233 | CC155 | II | 2004 | |
| 15916 | 2 | Food | Fresh rucola-rocket | 1234 | CC5 | I | 2008 | |
| 16159 | 265/2010 | Human | Cerebrospinal fluid | 1235 | CC21 | II | 2010 | |
| 16160 | 2184/2010 | Human | Cerebrospinal fluid | 1236 | CC3 | I | 2010 | |
| 16161 | 2960/2012 | Human | Blood | 1237 | CC315 | I | 2012 | |
| 16162 | 4250/2009 | Human | Blood | 1238 | CC21 | II | 2009 | |
| 16122 | 22/2008 | Human | Cerebrospinal fluid | 1242 | CC37 | II | 2008 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bespalova, T.Y.; Mikhaleva, T.V.; Meshcheryakova, N.Y.; Kustikova, O.V.; Matovic, K.; Dmitrić, M.; Zaitsev, S.S.; Khizhnyakova, M.A.; Feodorova, V.A. Novel Sequence Types of Listeria monocytogenes of Different Origin Obtained in the Republic of Serbia. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061289
Bespalova TY, Mikhaleva TV, Meshcheryakova NY, Kustikova OV, Matovic K, Dmitrić M, Zaitsev SS, Khizhnyakova MA, Feodorova VA. Novel Sequence Types of Listeria monocytogenes of Different Origin Obtained in the Republic of Serbia. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(6):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061289
Chicago/Turabian StyleBespalova, Tatiana Yu., Tatiana V. Mikhaleva, Nadezhda Yu Meshcheryakova, Olga V. Kustikova, Kazimir Matovic, Marko Dmitrić, Sergey S. Zaitsev, Maria A. Khizhnyakova, and Valentina A. Feodorova. 2021. "Novel Sequence Types of Listeria monocytogenes of Different Origin Obtained in the Republic of Serbia" Microorganisms 9, no. 6: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061289
APA StyleBespalova, T. Y., Mikhaleva, T. V., Meshcheryakova, N. Y., Kustikova, O. V., Matovic, K., Dmitrić, M., Zaitsev, S. S., Khizhnyakova, M. A., & Feodorova, V. A. (2021). Novel Sequence Types of Listeria monocytogenes of Different Origin Obtained in the Republic of Serbia. Microorganisms, 9(6), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061289






