Ellagic Acid Suppresses ApoB Secretion and Enhances ApoA-1 Secretion from Human Hepatoma Cells, HepG2
Abstract
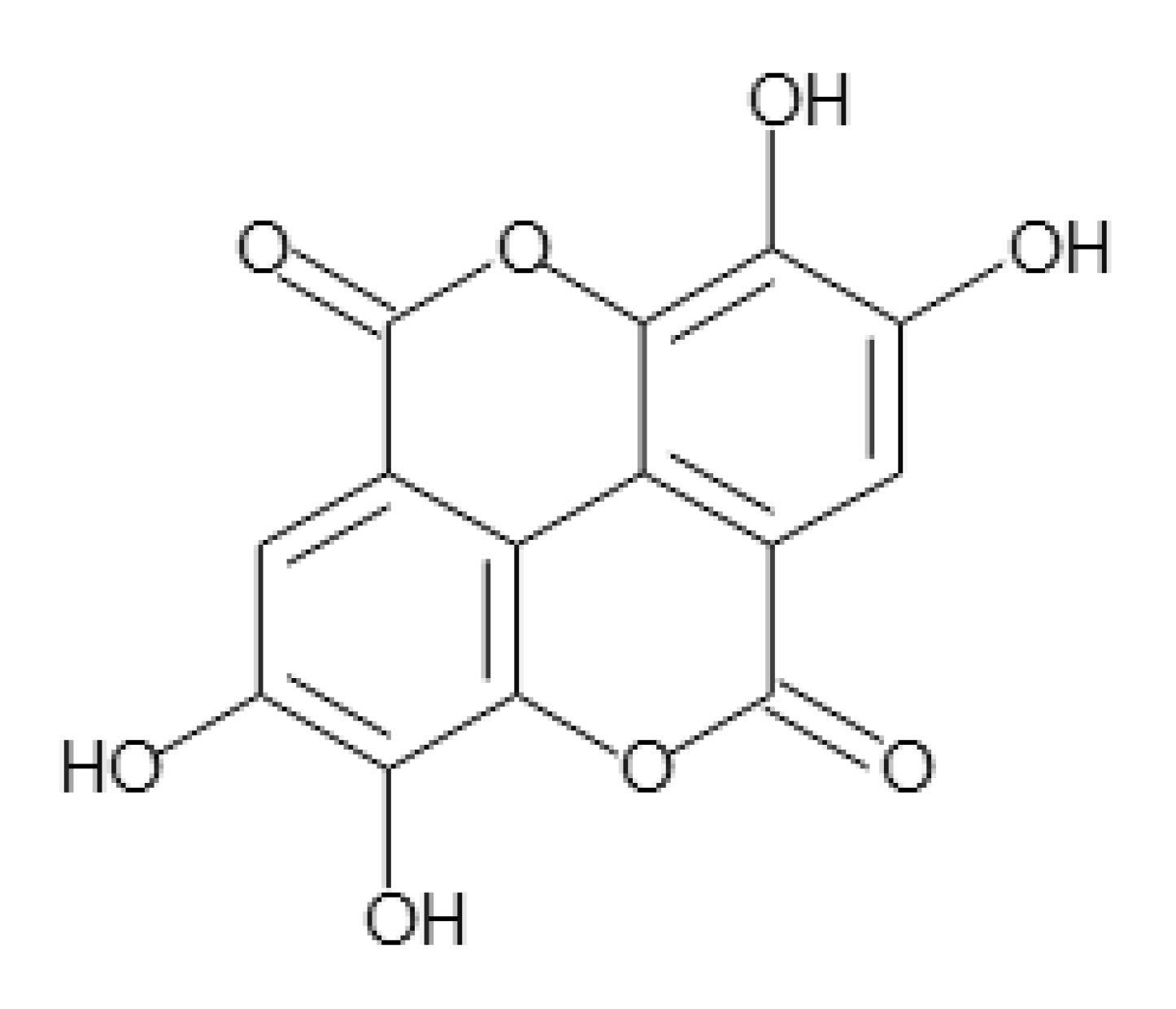
:1. Introduction
2. Results
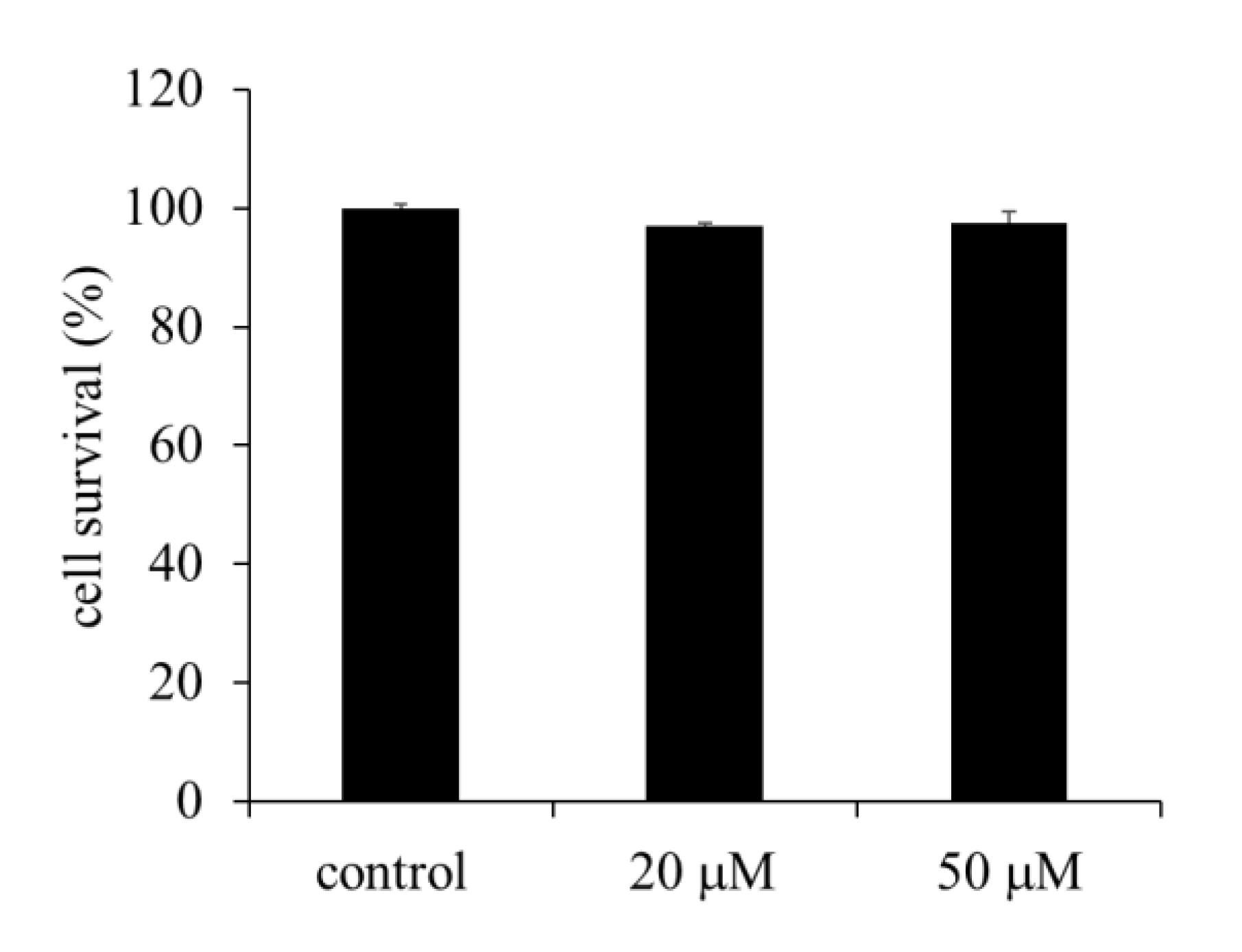
2.1. Effect of EA on the Viability of HepG2 Cells
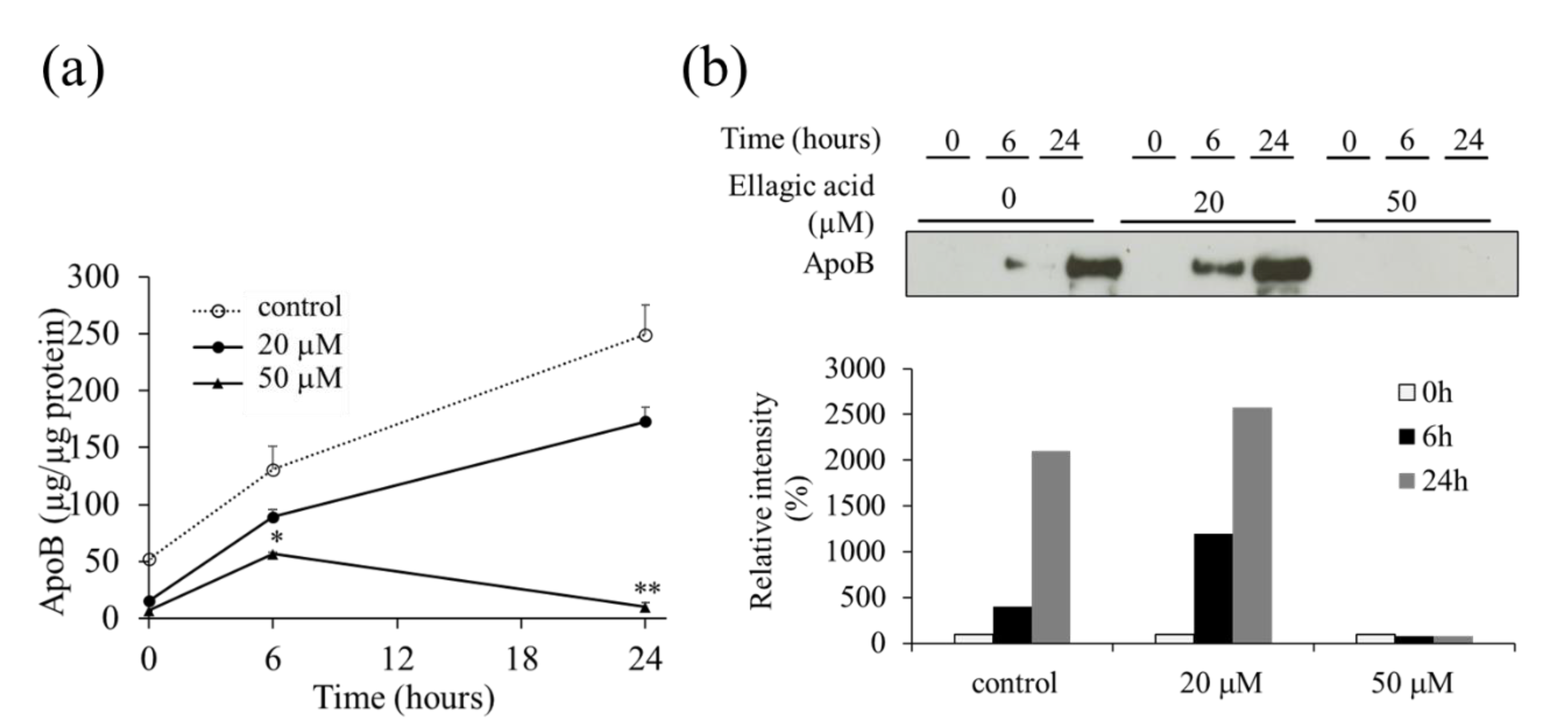
2.2. Effect of EA on the Secretion of VLDL (apoB) from HepG2 Cells
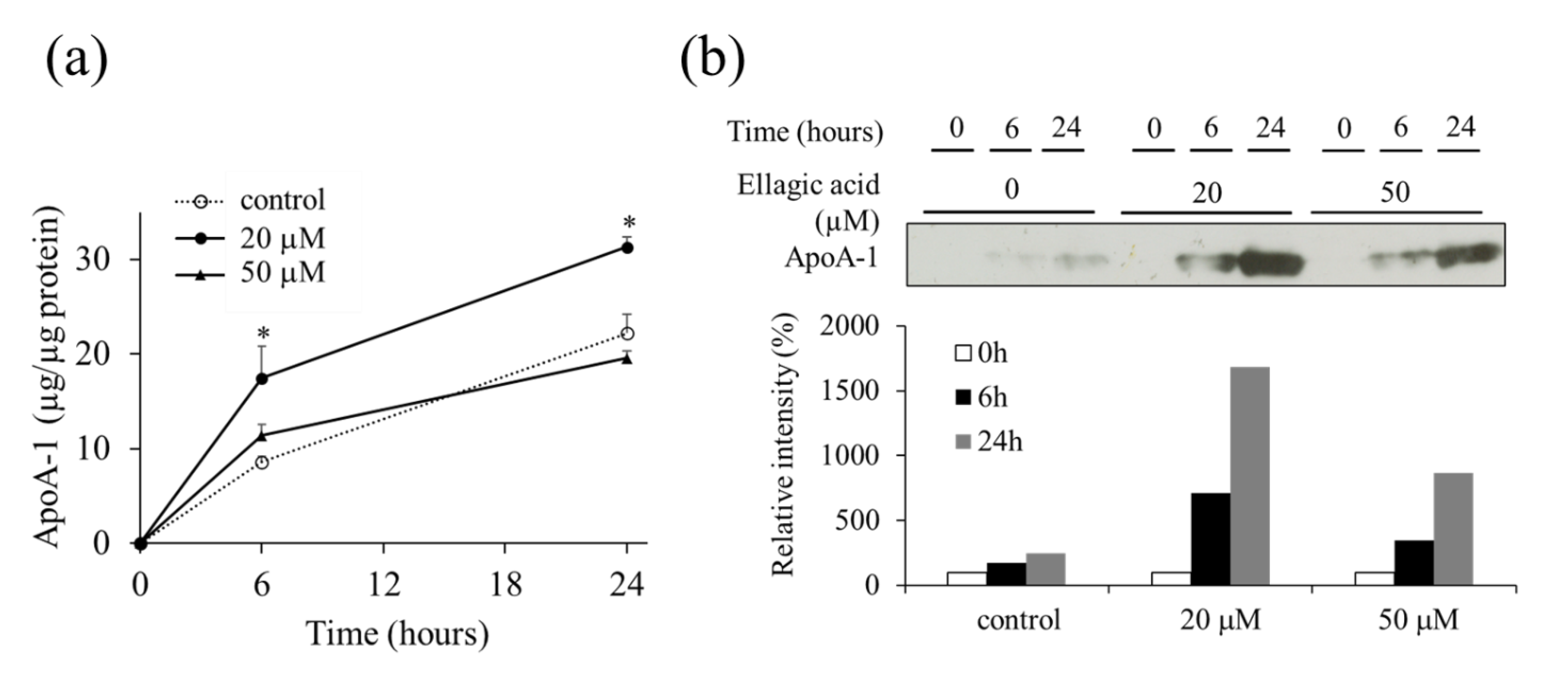
2.3. Effect of EA on the Secretion of apoA-1 from HepG2 Cells
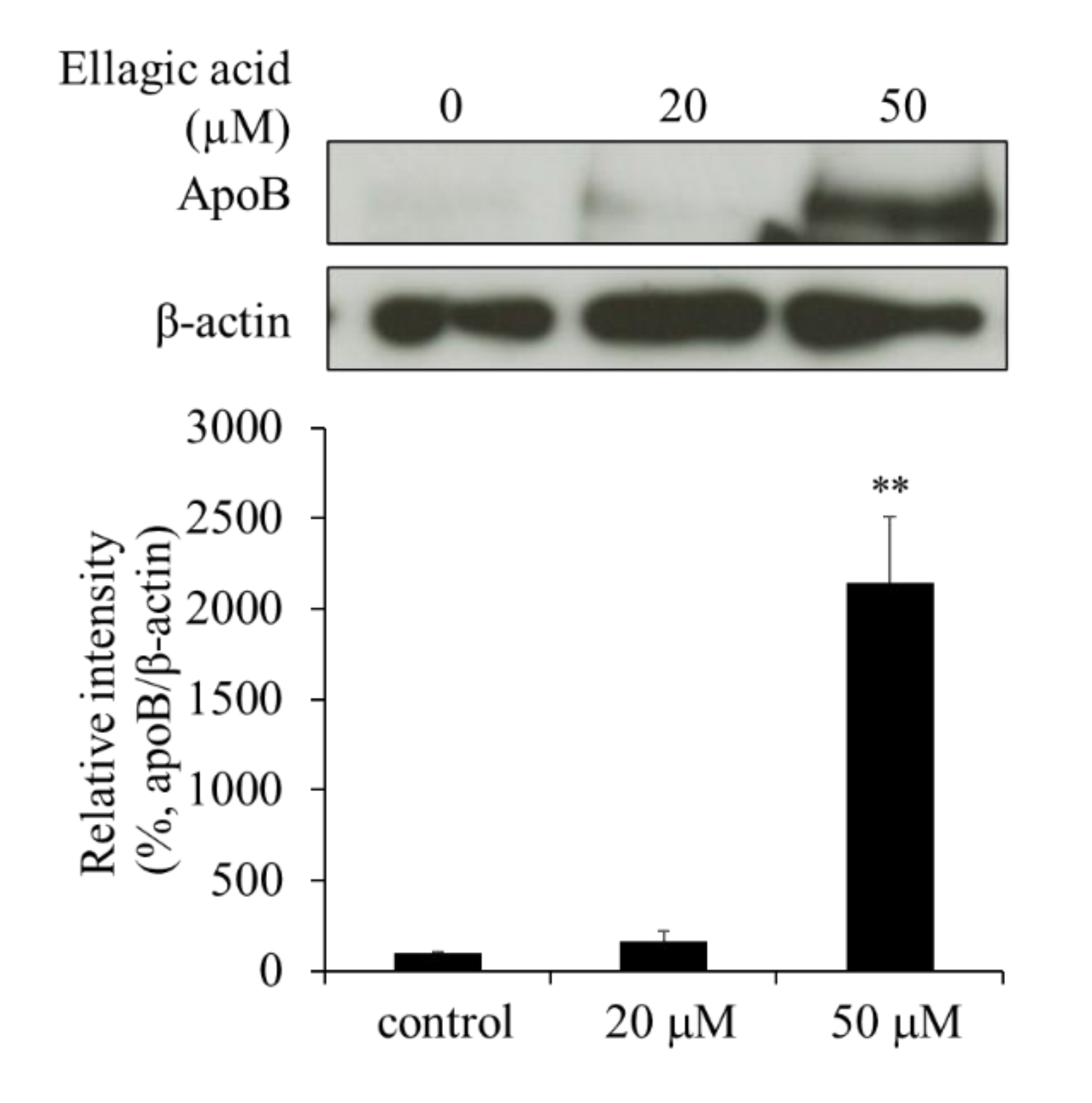
2.4. Effect of EA on apoB Levels in HepG2 Cells
2.5. Effect of EA on apoA-1 Levels in HepG2 Cells
2.6. Effect of EA on Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein (MTP) Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture and Sample Treatment
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. ELISA for Determination of apoB and apoA-1 Levels in the Culture Medium
4.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zannis, V.I.; Cole, F.S.; Jackson, C.L.; Kurnit, D.M.; Karathanasis, S.K. Distribution of apolipoprotein A-I, C-II, C-III, and E mRNA in fetal human tissues. Time-dependent induction of apolipoprotein E mRNA by cultures of human monocyte-macrophages. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 4450–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunzell, J.D.; Hokanson, J.E. Low-density and high-density lipoprotein subspecies and risk for premature coronary artery disease. Amer. J. Med. 1999, 107, 16S–18S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ho, N.; Santos, C.; Dubois, P.; Mamo, J.; Croft, K.; Allister, E. Red wine polyphenolics increase LDL receptor expression and activity and suppress the secretion of ApoB100 from human HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.I.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Holcroft, D.M.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant activity of pomegranate juice and its relationship with phenolic composition and processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.D.; Mehta, R.; Yu, W.; Neeman, I.; Livney, T.; Amichay, A.; Poirier, D.; Nicholls, P.; Kirby, A.; Jiang, W.; et al. Chemopreventive and adjuvant therapeutic potential of pomegranate (Punica granatum) for human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2002, 71, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblat, M.; Hayek, T.; Aviram, M. Anti-oxidative effects of pomegranate juice (PJ) consumption by diabetic patients on serum and on macrophages. Atherosclerosis. 2006, 187, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaillzadeh, A.; Tahbaz, F.; Gaieni, I.; Alavi-Majd, H.; Azadbakht, L. Cholesterol-lowering effect of concentrated pomegranate juice consumption in type II diabetic patients with hyperglycemia. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2006, 76, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino-Wakagi, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Uzawa, Y.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T.; Kawamura, Y. Ellagic acid in pomegranate suppresses resistin secretion by a novel regulatory mechanism involving the degradation of intracellular resistin protein in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.A.; Wetterau, J.R.; Gregg, R.E. Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein: A protein complex required for the assembly of lipoprotein particles. Trends Cell Biol. 1995, 5, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterau, J.R.; Aggerbeck, L.P.; Bouma, M.E.; Eisenberg, C.; Munck, A.; Hermier, M.; Schmitz, J.; Gay, G.; Rader, D.J.; Gregg, R.E. Absence of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in individuals with abetalipoproteinemia. Science 1992, 258, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Xiong, T.; Liu, P.; Guo, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, F.; Tang, Y.; Yao, P. Quercetin ameliorates HFD-induced NAFLD by promoting hepatic VLDL assembly and lipophagy via the IRE1a/XBP1s pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Assini, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Allister, E.M.; Sutherland, B.G.; Koppes, J.B.; Sawyez, C.G.; Edwards, J.Y.; Telford, D.E.; Charbonneau, A.; et al. Nobiletin attenuates VLDL overproduction, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in mice with diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2011, 60, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borradaile, N.M.; de Dreu, L.E.; Barrett, P.H.; Behrsin, C.D.; Huff, M.W. Hepatocyte ApoB-containing lipoprotein secretion is decreased by the grapefruit flavonoid, naringenin, via inhibition of MTP-mediated microsomal triglyceride accumulation. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borradaile, N.M.; de Dreu, L.E.; Huff, M.W. Inhibition of net HepG2 cell apolipoprotein B secretion by the citrus flavonoid naringenin involves activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, independent of insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubota, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Nagaoka, S. Ellagic acid affects mRNA expression levels of genes that regulate cholesterol metabolism in HepG2 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shin, J.Y.; Oh, J.M.; Jung, C.H.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, K.J.; Ryu, J.Y.; Shin, J.; et al. Dissection of SNARE-driven membrane fusion and neuroexocytosis by wedging small hydrophobic molecules into the SNARE zipper. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010, 107, 22145–22150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Davidson, W.S.; Fayad, Z.A.; Fuster, V.; Goldstein, J.; Hellerstein, M.; Jiang, X.C.; Phillips, M.C.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Cholesterol efflux and atheroprotection: Advancing the concept of reverse cholesterol transport. Circulation 2012, 125, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Translation of high-density lipoprotein function into clinical practice: Current prospects and future challenges. Circulation 2013, 128, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navab, M.; Hama, S.Y.; Cooke, C.J.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Chaddha, M.; Jin, L.; Subbanagounder, G.; Faull, K.F.; Reddy, S.T.; Miller, N.E.; et al. Normal high density lipoprotein inhibits three steps in the formation of mildly oxidized low density lipoprotein: Step 1. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, R.K.; Tsukamoto, K.; Chun, S.H.; Usher, D.; Puré, E.; Rader, D.J. Regression of atherosclerosis induced by liver-directed gene transfer of apolipoprotein A-I in mice. Circulation. 1999, 100, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rong, R.; Ramachandran, S.; Penumetcha, M.; Khan, N.; Parthasarathy, S. Dietary oxidized fatty acids may enhance intestinal apolipoprotein A-I production. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Nishii, S.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T.; Kawamura, Y. Ellagic acid improves hepatic steatosis and serum lipid composition through reduction of serum resistin levels and transcriptional activation of hepatic ppara in obese, diabetic KK-Ay mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chung, Y.W.; Jung, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, K.Y.; Jang, J.K.; Ham, M.; Kang, H.; Pack, C.G.; Mihara, H.; et al. Apolipoprotein E-mediated regulation of selenoprotein P transportation via exosomes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2367–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Ling, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xia, P. Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis via microRNA-1. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, Z.; Huin, W.K.; Hisham, M.D.B.; Ng, J.X. Effects of pomegranate on lipid profiles: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Complementary Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbingie, O.A.; Onakpoya, I.J.; Spencer, E.A. Evidence for the effectiveness of pomegranate supplementation for blood pressure management is weak: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Nutr. Research. 2017, 46, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liao, D.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y. Lack of efficacy of pomegranate supplementation for glucose management, insulin levels and sensitivity: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahebkar, A.; Ferri, C.; Giorgini, P.; Bo, S.; Nachtigal, P.; Grassi, D. Effects of pomegranate juice on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; McClees, S.F.; Afaq, F. Pomegranate for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer: An Update. Molecules 2017, 22, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlachojannis, C.; Erne, P.; Schoenenberger, A.W.; Chrubasik-Hausmann, S. A critical evaluation of the clinical evidence for pomegranate preparations in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučić, V.; Grabež, M.; Trchounian, A.; Arsić, A. Composition and potential health benefits of pomegranate: A review. Curr. Pharm. Design. 2019, 25, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Rasekhmagham, R.; Kord-Varkaneh, H.; Santos, H.O.; Yao, G. The effects of pomegranate supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Complementary Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ieda, A.; Wada, M.; Moriyasu, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Ellagic Acid Suppresses ApoB Secretion and Enhances ApoA-1 Secretion from Human Hepatoma Cells, HepG2. Molecules 2021, 26, 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133885
Ieda A, Wada M, Moriyasu Y, Okuno Y, Zaima N, Moriyama T. Ellagic Acid Suppresses ApoB Secretion and Enhances ApoA-1 Secretion from Human Hepatoma Cells, HepG2. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133885
Chicago/Turabian StyleIeda, Ayana, Maki Wada, Yuuki Moriyasu, Yuuko Okuno, Nobuhiro Zaima, and Tatsuya Moriyama. 2021. "Ellagic Acid Suppresses ApoB Secretion and Enhances ApoA-1 Secretion from Human Hepatoma Cells, HepG2" Molecules 26, no. 13: 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133885
APA StyleIeda, A., Wada, M., Moriyasu, Y., Okuno, Y., Zaima, N., & Moriyama, T. (2021). Ellagic Acid Suppresses ApoB Secretion and Enhances ApoA-1 Secretion from Human Hepatoma Cells, HepG2. Molecules, 26(13), 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133885






