Regulation of Wnt Signaling by FOX Transcription Factors in Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
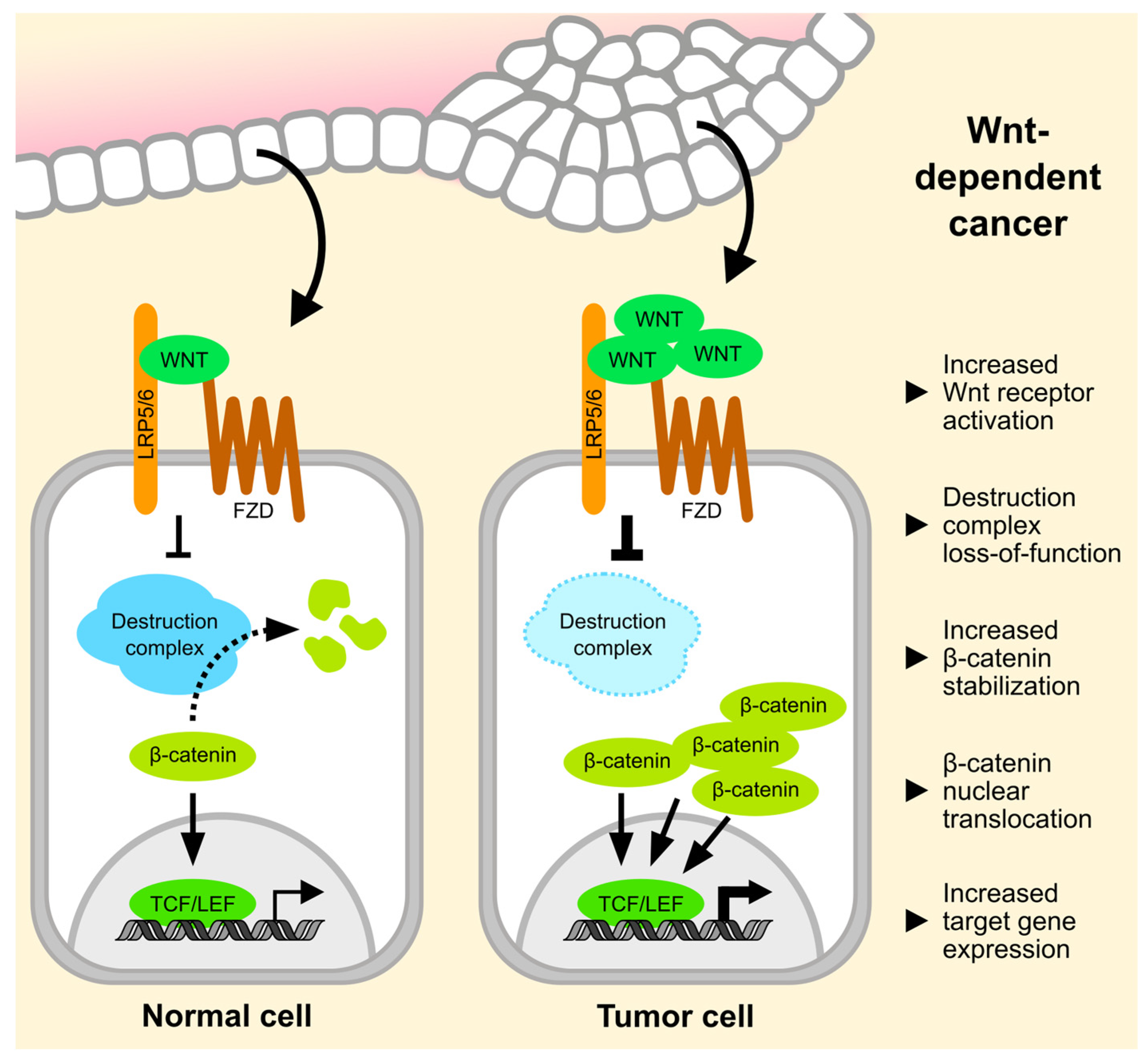
1. Wnt Signaling in Cancer
Regulation of β-catenin-dependent Gene Transcription
2. Forkhead Box Family Transcription Factors
2.1. FOX Transcription Factors Are Wnt Pathway Regulators
2.1.1. Regulation of β-catenin Localization and Stability
2.1.2. Regulation of the Wnt Transcriptional Complex
2.1.3. Regulation of Wnt Ligand Expression
2.1.4. Other Mechanisms of Wnt Pathway Regulation
2.2. Reciprocal Regulation of FOX Transcription Factors by Wnt Signaling
2.3. Common Themes and Open Questions
2.4. Therapeutic Targeting of FOX-dependent Wnt Signaling
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhart, Z.; Angers, S. Wnt Signaling in Development and Tissue Homeostasis. Development 2018, 145, dev146589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonekamp, K.E.; Heo, I.; Artegiani, B.; Asra, P.; van Son, G.; de Ligt, J.; Clevers, H. Identification of Novel Human Wnt Target Genes Using Adult Endodermal Tissue-Derived Organoids. Dev. Biol. 2021, 474, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acebron, S.P.; Niehrs, C. β-Catenin-Independent Roles of Wnt/LRP6 Signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehrs, C. The Complex World of WNT Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackstadt, R.; Hodder, M.C.; Sansom, O.J. WNT and β-Catenin in Cancer: Genes and Therapy. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2020, 4, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt Signaling in Cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijsewijk, F.; Schuermann, M.; Wagenaar, E.; Parren, P.; Weigel, D.; Nusse, R. The Drosophila Homology of the Mouse Mammary Oncogene Int-1 Is Identical to the Segment Polarity Gene Wingless. Cell 1987, 50, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Human Colon and Rectal Cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voloshanenko, O.; Erdmann, G.; Dubash, T.D.; Augustin, I.; Metzig, M.; Moffa, G.; Hundsrucker, C.; Kerr, G.; Sandmann, T.; Anchang, B.; et al. Wnt Secretion Is Required to Maintain High Levels of Wnt Activity in Colon Cancer Cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dow, L.E.; O’Rourke, K.P.; Simon, J.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H.; Lowe, S.W. Apc Restoration Promotes Cellular Differentiation and Reestablishes Crypt Homeostasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murillo-Garzón, V.; Kypta, R. WNT Signalling in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Germinaro, M.; Micsenyi, A.; Monga, N.K.; Bell, A.; Sood, A.; Malhotra, V.; Sood, N.; Midda, V.; Monga, D.K.; et al. Aberrant Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincan, E.; Barker, N. The Upstream Components of the Wnt Signalling Pathway in the Dynamic EMT and MET Associated with Colorectal Cancer Progression. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuberger, J.; Birchmeier, W. Interplay of Cadherin-Mediated Cell Adhesion and Canonical Wnt Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Yu, Y.; Akilli Öztürk, Ö.; Holland, J.D.; Besser, D.; Fritzmann, J.; Wulf-Goldenberg, A.; Eckert, K.; Fichtner, I.; Birchmeier, W. New Wnt/β-Catenin Target Genes Promote Experimental Metastasis and Migration of Colorectal Cancer Cells through Different Signals. Gut 2016, 65, 1690–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Hu, C.Y.; Ford, M.; Kleer, C.G.; Weiss, S.J. Canonical Wnt Signaling Regulates Slug Activity and Links Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition with Epigenetic Breast Cancer 1, Early Onset (BRCA1) Repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16654–16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yook, J.I.; Li, X.-Y.; Ota, I.; Fearon, E.R.; Weiss, S.J. Wnt-Dependent Regulation of the E-cadherin Repressor Snail. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11740–11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohn, A.D.; Moon, R.T. Wnt and Calcium Signaling: β-Catenin-Independent Pathways. Cell Calcium 2005, 38, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Wnt/Planar Cell Polarity Signaling: A New Paradigm for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.-S.; Park, J.-I. Wnt Signaling in Cancer: Therapeutic Targeting of Wnt Signaling beyond Β-Catenin and the Destruction Complex. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting the Wnt/Beta-Catenin Pathway in Cancer: Update on Effectors and Inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, M. Can We Safely Target the WNT Pathway? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alok, A.; Lei, Z.; Jagannathan, N.S.; Kaur, S.; Harmston, N.; Rozen, S.G.; Tucker-Kellogg, L.; Virshup, D.M. Wnt Proteins Synergize to Activate β-Catenin Signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dijksterhuis, J.P.; Baljinnyam, B.; Stanger, K.; Sercan, H.O.; Ji, Y.; Andres, O.; Rubin, J.S.; Hannoush, R.N.; Schulte, G. Systematic Mapping of WNT-FZD Protein Interactions Reveals Functional Selectivity by Distinct WNT-FZD Pairs. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6789–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eubelen, M.; Bostaille, N.; Cabochette, P.; Gauquier, A.; Tebabi, P.; Dumitru, A.C.; Koehler, M.; Gut, P.; Alsteens, D.; Stainier, D.Y. A Molecular Mechanism for Wnt Ligand-Specific Signaling. Science 2018, 361, eaat1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voloshanenko, O.; Gmach, P.; Winter, J.; Kranz, D.; Boutros, M. Mapping of Wnt-Frizzled Interactions by Multiplex CRISPR Targeting of Receptor Gene Families. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 4832–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, N.H.; Franken, P.; Fodde, R. Tumour-Stroma Interactions in Colorectal Cancer: Converging on Beta-Catenin Activation and Cancer Stemness. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosimann, C.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. β-Catenin Hits Chromatin: Regulation of Wnt Target Gene Activation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; de Paiva Alves, E.; Veenstra, G.J.C.; Hoppler, S. Tissue-and Stage-Specific Wnt Target Gene Expression Is Controlled Subsequent to β-Catenin Recruitment to Cis-Regulatory Modules. Development 2016, 143, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Söderholm, S.; Cantù, C. The WNT/β-Catenin Dependent Transcription: A Tissue-Specific Business. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2020, 13, e1511. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, A.-B.; Sinha, A.; Fan, V.B.; Cadigan, K.M. The Wnt Transcriptional Switch: TLE Removal or Inactivation? Bioessays 2018, 40, 1700162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadigan, K.M.; Waterman, M.L. TCF/LEFs and Wnt Signaling in the Nucleus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.-D.; Magon de La Giclais, S.; Alsehly, F.; Hoppler, S. Diverse LEF/TCF Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer Correlates with Altered Wnt-Regulated Transcriptome in a Meta-Analysis of Patient Biopsies. Genes 2020, 11, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, S.; Polena, E.; Gordon, V.; Abdulla, S.; Mahendram, S.; Cao, J.; Blais, A.; Wood, G.A.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; Doble, B.W. A Single TCF Transcription Factor, Regardless of Its Activation Capacity, Is Sufficient for Effective Trilineage Differentiation of ESCs. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2424–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chesire, D.R.; Isaacs, W.B. Ligand-Dependent Inhibition of Β-Catenin/TCF Signaling by Androgen Receptor. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8453–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Truica, C.I.; Byers, S.; Gelmann, E.P. β-Catenin Affects Androgen Receptor Transcriptional Activity and Ligand Specificity. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4709–4713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davidson, K.C.; Adams, A.M.; Goodson, J.M.; McDonald, C.E.; Potter, J.C.; Berndt, J.D.; Biechele, T.L.; Taylor, R.J.; Moon, R.T. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Promotes Differentiation, Not Self-Renewal, of Human Embryonic Stem Cells and Is Repressed by Oct4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4485–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, K.F.; Ng, D.Y.; Jayakumaran, G.; Wood, G.A.; Koide, H.; Doble, B.W. β-Catenin Enhances Oct-4 Activity and Reinforces Pluripotency through a TCF-Independent Mechanism. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gan, X.-Q.; Wang, J.-Y.; Xi, Y.; Wu, Z.-L.; Li, Y.-P.; Li, L. Nuclear Dvl, c-Jun, Beta-Catenin, and TCF Form a Complex Leading to Stabilization of Beta-Catenin-TCF Interaction. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nateri, A.S.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Behrens, A. Interaction of Phosphorylated C-Jun with TCF4 Regulates Intestinal Cancer Development. Nature 2005, 437, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho, R.; Nateri, A.S.; De Vinuesa, A.G.; Aguilera, C.; Nye, E.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Behrens, A. JNK Signalling Modulates Intestinal Homeostasis and Tumourigenesis in Mice. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerli, D.; Borrelli, C.; Jauregi-Miguel, A.; Söderholm, S.; Brütsch, S.; Doumpas, N.; Reichmuth, J.; Murphy-Seiler, F.; Aguet, M.; Basler, K.; et al. TBX3 Acts as Tissue-Specific Component of the Wnt/β-Catenin Transcriptional Complex. eLife 2020, 9, e58123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellak, H.; Wu, S.; Lincoln, T.M. KLF4 and SOX9 Transcription Factors Antagonize Β-Catenin and Inhibit TCF-Activity in Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinha, A.; Fan, V.B.; Ramakrishnan, A.-B.; Engelhardt, N.; Kennell, J.; Cadigan, K.M. Repression of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling by SOX9 and Mastermind-Like Transcriptional Coactivator 2. Sci Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, L.; Chen, W.; Song, H.; Day, T.F.; Yang, Y. Sox9 Inhibits Wnt Signaling by Promoting β-Catenin Phosphorylation in the Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3323–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastide, P.; Darido, C.; Pannequin, J.; Kist, R.; Robine, S.; Marty-Double, C.; Bibeau, F.; Scherer, G.; Joubert, D.; Hollande, F. Sox9 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Is Required for Paneth Cell Differentiation in the Intestinal Epithelium. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannenhalli, S.; Kaestner, K.H. The Evolution of Fox Genes and Their Role in Development and Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, L.; Todeschini, A.-L.; Veitia, R.A. Forkhead Transcription Factors in Health and Disease. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golson, M.L.; Kaestner, K.H. Fox Transcription Factors: From Development to Disease. Development 2016, 143, 4558–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, E.W.F.; Brosens, J.J.; Gomes, A.R.; Koo, C.-Y. Forkhead Box Proteins: Tuning Forks for Transcriptional Harmony. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myatt, S.S.; Lam, E.W.-F. The Emerging Roles of Forkhead Box (Fox) Proteins in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ji, Z.; Webber, A.; Sharrocks, A.D. Genome-Wide Binding Studies Reveal DNA Binding Specificity Mechanisms and Functional Interplay amongst Forkhead Transcription Factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1566–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolma, A.; Yan, J.; Whitington, T.; Toivonen, J.; Nitta, K.R.; Rastas, P.; Morgunova, E.; Enge, M.; Taipale, M.; Wei, G.; et al. DNA-Binding Specificities of Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2013, 152, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, S.; Gisselbrecht, S.S.; Rogers, J.M.; Hartl, D.L.; Bulyk, M.L. DNA-Binding Specificity Changes in the Evolution of Forkhead Transcription Factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12349–12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Malovannaya, A.; Xi, Y.; Li, W.; Guerra, R.; Hawke, D.H.; Qin, J.; Chen, J. Proteomic Analyses Reveal Distinct Chromatin-Associated and Soluble Transcription Factor Complexes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moparthi, L.; Koch, S. A Uniform Expression Library for the Exploration of FOX Transcription Factor Biology. Differentiation 2020, 115, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna-Martinez, M.; Epp, F.; Kahles, H.; Ramos-Lopez, E.; Hinsch, N.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Selkinski, I.; Grünwald, F.; Holzer, K.; Bechstein, W.O. FOXE1 Association with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Its Progression. Thyroid 2014, 24, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trueba, S.S.; Augé, J.l.; Mattei, G.r.; Etchevers, H.; Martinovic, J.; Czernichow, P.; Vekemans, M.; Polak, M.; Attié-Bitach, T. PAX8, TITF1, and FOXE1 Gene Expression Patterns during Human Development: New Insights into Human Thyroid Development and Thyroid Dysgenesis-Associated Malformations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moparthi, L.; Pizzolato, G.; Koch, S. Wnt Activator FOXB2 Drives the Neuroendocrine Differentiation of Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22189–22195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; He, W.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, R. FOXC1 Induces Cancer Stem Cell-Like Properties through Upregulation of Beta-Catenin in NSCLC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Zhou, B.; Qu, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, Y.; Chung, S.; Tanaka, H.; Yang, W.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cui, X. FOXC1-Induced Non-Canonical WNT5A-MMP7 Signaling Regulates Invasiveness in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Yao, W.; Wang, W.; Shi, B.; Yuan, F.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. FOXC1 Negatively Regulates DKK1 Expression to Promote Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation through Activation of Wnt Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozo, M.C.; Aspuria, P.J.; Cheon, D.J.; Walts, A.E.; Berel, D.; Miura, N.; Karlan, B.Y.; Orsulic, S. Foxc2 Induces Wnt4 and Bmp4 Expression during Muscle Regeneration and Osteogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lai, J.; Su, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J. FOXE1 Supports the Tumor Promotion of Gli2 on Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma by the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17739–17748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesin, C.; Peres, J.N.; Johansson, M.; Snowden, V.; Cording, A.; Papalopulu, N.; Houart, C. Integration of Telencephalic Wnt and Hedgehog Signaling Center Activities by Foxg1. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Mo, Z.; Lian, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Peng, L.; Xie, C. Forkhead Box (FOX) G1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Activating Wnt Signal through Forming T-Cell Factor-4/Beta-Catenin/FOXG1 Complex. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afouda, B.A.; Nakamura, Y.; Shaw, S.; Charney, R.M.; Paraiso, K.D.; Blitz, I.L.; Cho, K.W.Y.; Hoppler, S. Foxh1/Nodal Defines Context-Specific Direct Maternal Wnt/β-Catenin Target Gene Regulation in Early Development. iScience 2020, 23, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Huang, L. Benzyl Isothiocyanate Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Tumorigenesis via Repression of the FoxH1-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 17601–17611. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Fan, J.; Wu, J. Forkhead box protein J1 (FOXJ1) Is Overexpressed in Colorectal Cancer and Promotes Nuclear Translocation of β-Catenin in SW620 Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Lee, M.; Jun, S.; Aziz, K.E.; Feng, L.; Tran, M.K.; Li, N.; McCrea, P.D.; Park, J.-I.; et al. FOXKs Promote Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling by Translocating DVL into the Nucleus. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, J.; Gong, A.; Yu, G.; Zhou, A.; Lin, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Gottardi, C.J. Wnt-Induced Deubiquitination Foxm1 Ensures Nucleus β-Catenin Transactivation. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Wei, P.; Gong, A.; Chiu, W.-T.; Lee, H.-T.; Colman, H.; Huang, H.; Xue, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. FoxM1 Promotes β-Catenin Nuclear Localization and Controls Wnt Target-Gene Expression and Glioma Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, M.P.; Stopford, C.M.; Cederlund, M.; Fang, F.; Jahn, C.; Rabinowitz, A.D.; Goldfarb, D.; Graham, D.M.; Yan, F.; Deal, A.M.; et al. FOXP1 Potentiates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Ng, C.S.H.; Yang, S.-L.; Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Dong, Y.; Du, J.; Long, X.; et al. FOXP3 Promotes Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and EMT in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagati, A.; Bianchi-Smiraglia, A.; Moparthy, S.; Kolesnikova, K.; Fink, E.E.; Lipchick, B.C.; Kolesnikova, M.; Jowdy, P.; Polechetti, A.; Mahpour, A.; et al. Melanoma Suppressor Functions of the Carcinoma Oncogene FOXQ1. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2820–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, M.; Ai, T.; Cai, B. FOXQ1 Promotes the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling by Binding with ANXA2. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-H.; Cui, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.-M.; Liu, J. Down-Regulation of FOXR2 Inhibits Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion through the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormestad, M.; Astorga, J.; Landgren, H.; Wang, T.; Johansson, B.R.; Miura, N.; Carlsson, P. Foxf1 and Foxf2 Control Murine Gut Development by Limiting Mesenchymal Wnt Signaling and Promoting Extracellular Matrix Production. Development 2006, 133, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashimori, A.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, W.; Nakatsu, G.; Ng, S.S.M.; Arakawa, T.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; Yu, J. Forkhead Box F2 Suppresses Gastric Cancer through a Novel FOXF2–IRF2BPL–β-Catenin Signaling Axis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nik, A.M.; Reyahi, A.; Pontén, F.; Carlsson, P. Foxf2 in Intestinal Fibroblasts Reduces Numbers of Lgr5+ Stem Cells and Adenoma Formation by Inhibiting Wnt Signaling. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perreault, N.; Katz, J.P.; Sackett, S.D.; Kaestner, K.H. Foxl1 Controls the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Modulating the Expression of Proteoglycans in the Gut. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43328–43333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, H.; Xiao, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D. Loss of FOXN3 in Colon Cancer Activates Beta-Catenin/TCF Signaling and Promotes the Growth and Migration of Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9783–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Dong, X.; Xue, Y.; Jia, X.; Song, W.; Li, Q. FOXO1-Regulated lncRNA LINC01197 Inhibits Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation by Restraining Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeboom, D.; Essers, M.A.; Polderman, P.E.; Voets, E.; Smits, L.M.; Boudewijn, M.T. Interaction of FOXO with β-Catenin Inhibits β-Catenin/T Cell Factor Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9224–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Yin, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, G.; Deng, M.; Zhang, G.; Bu, X.; Cai, S.; Du, J.; He, Z. FOXO3a Modulates WNT/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppresses Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, L.; Shu, Y.; Wan, B. Overexpression of FOXS1 in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines Inhibits Proliferation, Metastasis, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Tumor Through Downregulating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Huang, S. FoxM1 and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Glioma Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5658–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. FOX (M1) News—It Is Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raychaudhuri, P.; Park, H.J. FoxM1: A Master Regulator of Tumor Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4329–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gartel, A.L. FOXM1 in Cancer: Interactions and Vulnerabilities. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3135–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quan, M.; Cui, J.; Xia, T.; Jia, Z.; Xie, D.; Wei, D.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Xie, K. Merlin/NF2 Suppresses Pancreatic Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Attenuating the FOXM1-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4778–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, H.N.; Braunstein, S.E.; Phillips, J.J.; Pekmezci, M.; Tomlin, B.A.; Wu, A.; Reis, G.F.; Magill, S.T.; Zhang, J.; Feng, F.Y. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling Identifies FOXM1 as a Key Transcription Factor for Meningioma Proliferation. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3672–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Xing, Z.; Ma, C.; Xiong, W.; Zhu, X.; He, X. FOXG1 Expression Is Elevated in Glioma and Inhibits Glioma Cell Apoptosis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verginelli, F.; Perin, A.; Dali, R.; Fung, K.H.; Lo, R.; Longatti, P.; Guiot, M.-C.; Del Maestro, R.F.; Rossi, S.; Di Porzio, U. Transcription Factors FOXG1 and Groucho/TLE Promote Glioblastoma Growth. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abedalthagafi, M.S.; Wu, M.P.; Merrill, P.H.; Du, Z.; Woo, T.; Sheu, S.H.; Hurwitz, S.; Ligon, K.L.; Santagata, S. Decreased FOXJ1 Expression and Its Ciliogenesis Programme in Aggressive Ependymoma and Choroid Plexus Tumours. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.W.; Huang, X.D.; Li, H.C.; He, S.; Ni, R.Z.; Chen, C.H.; Peng, C.; Wu, G.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, Y.Y. Expression of FOXJ1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Correlation with Patients’ Prognosis and Tumor Cell Proliferation. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Luo, Z.; Kang, Q.; Deng, D.; Wang, Q.; Peng, H.; Wang, S.; Wei, Z. FOXQ1 Mediates the Crosstalk between TGF-β and Wnt Signaling Pathways in the Progression of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lee, S.T.; Karuturi, R.M.; Hooi, S.C.; Yu, Q. FOXQ1 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Cancers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3076–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galli, L.M.; Barnes, T.; Cheng, T.; Acosta, L.; Anglade, A.; Willert, K.; Nusse, R.; Burrus, L.W. Differential Inhibition of Wnt-3a by Sfrp-1, Sfrp-2, and Sfrp-3. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tago, K.; Nakamura, T.; Nishita, M.; Hyodo, J.; Nagai, S.; Murata, Y.; Adachi, S.; Ohwada, S.; Morishita, Y.; Shibuya, H.; et al. Inhibition of Wnt Signaling by ICAT, a Novel Beta-Catenin-Interacting Protein. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Koon, H.B.; Ippolito, G.C.; Banham, A.H.; Tucker, P.W. FOXP1: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.; Rodova, M.; Miska, E.A.; Calvet, J.P.; Kouzarides, T. Acetylation of β-Catenin by CREB-Binding Protein (CBP). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25562–25567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, G.; Gui, T.; Bourgeois, B.; Koyani, C.N.; Ulz, P.; Heitzer, E.; von Lewinski, D.; Burgering, B.M.; Malle, E.; Madl, T. β-Catenin Regulates FOXP2 Transcriptional Activity Via Multiple Binding Sites. FEBS J. 2020, 288, 3261–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.; Han, L.; Martin-Millan, M.; O’Brien, C.A.; Manolagas, S.C. Oxidative Stress Antagonizes Wnt Signaling in Osteoblast Precursors by Diverting Beta-Catenin from T Cell Factor- to Forkhead Box O-mediated Transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27298–27305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Essers, M.A.G.; de Vries-Smits, L.M.M.; Barker, N.; Polderman, P.E.; Burgering, B.M.T.; Korswagen, H.C. Functional Interaction Between β-Catenin and FOXO in Oxidative Stress Signaling. Science 2005, 308, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlstone, A.; Clevers, H. T-Cell Factors: Turn-Ons and Turn-Offs. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, M.E.; Brunet, A. FOXO Transcription Factors. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R113–R114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhan, M.; Wang, H.; Gaur, U.; Little, P.J.; Xu, J.; Zheng, W. FOXO Signaling Pathways as Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenbaum, S.P.; Ordóñez-Morán, P.; Puig, I.; Chicote, I.; Arqués, O.; Landolfi, S.; Fernández, Y.; Herance, J.R.; Gispert, J.D.; Mendizabal, L. β-Catenin Confers Resistance to PI3K and AKT Inhibitors and Subverts FOXO3a to Promote Metastasis in Colon Cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doumpas, N.; Lampart, F.; Robinson, M.D.; Lentini, A.; Nestor, C.E.; Cantù, C.; Basler, K. TCF/LEF Dependent and Independent Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Target Genes. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e98873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhai, J.; Yan, C.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Brown, J.A.; Fang, Y. Recent Advances in Understanding FOXN3 in Breast Cancer, and Other Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Ma, R.; Xu, Y.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Yue, J.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Qi, D. Wnt2 Promotes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Activating WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Oue, N.; Sato, A.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsubara, A.; Yasui, W.; Kikuchi, A. Wnt5a Signaling Is Involved in the Aggressiveness of Prostate Cancer and Expression of Metalloproteinase. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshioka, S.; King, M.L.; Ran, S.; Okuda, H.; MacLean, J.A.; McAsey, M.E.; Sugino, N.; Brard, L.; Watabe, K.; Hayashi, K. WNT7A Regulates Tumor Growth and Progression in Ovarian Cancer through the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.-S.; Jun, S.; Lee, S.H.; Sharma, A.; Park, J.-I. Wnt2 Complements Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37257–37268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klarmann, G.J.; Decker, A.; Farrar, W.L. Epigenetic Gene Silencing in the Wnt Pathway in Breast Cancer. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, K.H.; Schütz, G.; Monaghan, A.P. Expression of the Winged Helix Genes Fkh-4 and Fkh-5 Defines Domains in the Central Nervous System. Mech. Dev. 1996, 55, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.-W. Emerging Roles and Mechanisms of FOXC2 in Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 479, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiao, H.; Ye, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, N.; Li, T.; Lin, J.; Qi, L.; Wu, P. FOXC2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Directly Targeting MET. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4379–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Shang, R.; Yao, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. WNT4 Secreted by Tumor Tissues Promotes Tumor Progression in Colorectal Cancer by Activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichberger, T.; Regl, G.; Ikram, M.S.; Neill, G.W.; Philpott, M.P.; Aberger, F.; Frischauf, A.-M. FOXE1, a New Transcriptional Target of GLI2 Is Expressed in Human Epidermis and Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martynoga, B.; Morrison, H.; Price, D.J.; Mason, J.O. Foxg1 Is Required for Specification of Ventral Telencephalon and Region-Specific Regulation of Dorsal Telencephalic Precursor Proliferation and Apoptosis. Dev. Biol. 2005, 283, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, Y.; Rahman, M.F.U.; Vyatkin, Y.; Azatyan, A.; St. Laurent, G.; Kapranov, P.; Zaphiropoulos, P.G. Identification of Novel GLI1 Target Genes and Regulatory Circuits in Human Cancer Cells. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1718–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruciat, C.-M.; Niehrs, C. Secreted and Transmembrane Wnt Inhibitors and Activators. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a015081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Sada, R.; Takada, N.; Harada, A.; Doki, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Kikuchi, A. The Dickkopf1 and FOXM1 Positive Feedback Loop Promotes Tumor Growth in Pancreatic and Esophageal Cancers. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4486–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xiong, W.; Dou, K.; Ran, Q. Knockdown of FOXK1 Suppresses Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Prostate Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2017, 25, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestal de Moraes, G.; Carneiro, L.d.T.; Maia, R.C.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Sharrocks, A.D. FOXK2 Transcription Factor and Its Emerging Roles in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, L.; Peng, Y.; Huang, X. RUFY3 Interaction with FOXK1 Promotes Invasion and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Chen, Y.-G. Dishevelled: The Hub of Wnt Signaling. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habas, R.; Dawid, I.B. Dishevelled and Wnt Signaling: Is the Nucleus the Final Frontier? J. Biol. 2005, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, R.; van Kerkhof, P.; Jordens, I.; Malinauskas, T.; Pusapati, G.V.; McKenna, J.K.; Li, D.; Carette, J.E.; Ho, M.; Siebold, C. R-Spondins Engage Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans to Potentiate WNT Signaling. eLife 2020, 9, e54469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertao, Z.; Jianhui, C.; Chuangqi, C.; Changjiang, Q.; Sile, C.; Yulong, H.; Shirong, C.; Hui, W. Low Level of FOXL1 Indicates a Worse Prognosis for Gastric Cancer Patients. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11331–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; He, P.; Gaedcke, J.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Ried, T.; Yfantis, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Hanna, N.; Alexander, H.R.; Hussain, S.P. FOXL1, a Novel Candidate Tumor Suppressor, Inhibits Tumor Aggressiveness and Predicts Outcome in Human Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5416–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbst, A.; Jurinovic, V.; Krebs, S.; Thieme, S.E.; Blum, H.; Göke, B.; Kolligs, F.T. Comprehensive Analysis of β-Catenin Target Genes in Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Lines with Deregulated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, J.; Bentz, S.; Sengstag, T.; Shastri, V.P.; Anderle, P. FOXQ1, a Novel Target of the Wnt Pathway and a New Marker for Activation of Wnt Signaling in Solid Tumors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60051. [Google Scholar]
- Villacorte, M.; Suzuki, K.; Hirasawa, A.; Ohkawa, Y.; Suyama, M.; Maruyama, T.; Aoki, D.; Ogino, Y.; Miyagawa, S.; Terabayashi, T.; et al. β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Foxa2 Expression during Endometrial Hyperplasia Formation. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3477–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, Z.M.; Yang, S.; Chen, F.; Yeh, Y.; Khater, N.; Jin, R.; Matusik, R.; Yu, X. Foxa2 Activates the Transcription of Androgen Receptor Target Genes in Castrate Resistant Prostatic Tumors. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2018, 6, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Tuteja, G.; Schug, J.; Kaestner, K.H. Foxa1 and Foxa2 Are Essential for Sexual Dimorphism in Liver Cancer. Cell 2012, 148, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balciunaite, G.; Keller, M.P.; Balciunaite, E.; Piali, L.; Zuklys, S.; Mathieu, Y.D.; Gill, J.; Boyd, R.; Sussman, D.J.; Holländer, G.A. Wnt Glycoproteins Regulate the Expression of Foxn1, the Gene Defective in Nude Mice. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, A.; Xu, X.; Lin, X. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Directly Regulates Foxj1 Expression and Ciliogenesis in Zebrafish Kupffer’s Vesicle. Development 2012, 139, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssens, S.; Van Den Broek, O.; Davenport, I.R.; Akkers, R.C.; Liu, F.; Veenstra, G.J.C.; Hoppler, S.; Vleminckx, K.; Destrée, O. The Wnt Signaling Mediator Tcf1 Is Required for Expression of Foxd3 during Xenopus Gastrulation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savage, J.; Voronova, A.; Mehta, V.; Sendi-Mukasa, F.; Skerjanc, I.S. Canonical Wnt Signaling Regulates Foxc1/2 Expression in P19 Cells. Differentiation 2010, 79, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Bellon, M.; Nicot, C. FBXW7: A Critical Tumor Suppressor of Human Cancers. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larroux, C.; Luke, G.N.; Koopman, P.; Rokhsar, D.S.; Shimeld, S.M.; Degnan, B.M. Genesis and Expansion of Metazoan Transcription Factor Gene Classes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, S.Q.; Finnerty, J.R.; Martindale, M.Q. Protein Evolution: Structure-Function Relationships of the Oncogene Beta-Catenin in the Evolution of Multicellular Animals. J. Exp. Zool. Part. B. Mol. Dev. Evol. 2003, 295B, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.M.; van Amerongen, R.; Nusse, R. Generating Cellular Diversity and Spatial Form: Wnt Signaling and the Evolution of Multicellular Animals. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arqués, O.; Chicote, I.; Puig, I.; Tenbaum, S.P.; Argilés, G.; Dienstmann, R.; Fernández, N.; Caratù, G.; Matito, J.; Silberschmidt, D. Tankyrase Inhibition Blocks Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Reverts Resistance to PI3K and AKT Inhibitors in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, S.; Milewski, D.; Pradhan, A.; Rama, N.; Rice, K.; Le, T.; Flick, M.J.; Vaz, S.; Zhao, X.; Setchell, K.D.; et al. The FOXM1 Inhibitor RCM-1 Decreases Carcinogenesis and Nuclear β-Catenin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An Enhanced Web Server for Large-Scale Expression Profiling and Interactive Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; 4.1.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]



| FOX | Relevance for Cancer Biology | Proposed Function in Wnt Signaling | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wnt pathway activators | |||
| FOXB2 | Putative oncogene in prostate cancer | Induces various Wnt ligands | [60] |
| FOXC1 | Increases proliferation and metastasis in many cancer types | Induces CTNNB1 1 and WNT5A; represses Wnt inhibitor DKK1 | [61,62,63] |
| FOXC2 | Increases proliferation and metastasis in many cancer types | Induces WNT4 | [64] |
| FOXE1 | Mutation associated with thyroid cancer | May induce WNT5A | [65] |
| FOXG1 | Associated with cancer progression in glioma and hepatocellular carcinoma | Binds and stabilizes β-catenin; promotes TCF7L2 activity; inhibits Wnt ligand expression during development | [66,67] |
| FOXH1 | Drives cell proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia | Synergizes with β-catenin in target gene expression; may induce CTNNB1 | [68,69] |
| FOXJ1 | Associated with tumor progression in many cancer types | May stabilize β-catenin via inhibition of APC | [70] |
| FOXK1 | Increases proliferation and metastasis in many cancer types | Promotes nuclear translocation of Wnt scaffold protein DVL | [71] |
| FOXK2 | Context-dependent oncogene or tumor suppressor | Promotes nuclear translocation of Wnt scaffold protein DVL | [71] |
| FOXM1 | Major oncogene in many cancer types | Promotes β-catenin nuclear translocation; stabilizes β-catenin/TCF7L2 interaction; synergizes in target gene expression | [72,73] |
| FOXP1 | Context-dependent oncogene or tumor suppressor | Activates β-catenin via CBP-dependent acetylation; synergizes in target gene expression | [74] |
| FOXP3 | Context-dependent oncogene or tumor suppressor | Synergizes with β-catenin/TCF7L2 in target gene expression | [75] |
| FOXQ1 | Promotes metastasis in carcinomas; tumor suppressor in melanomas | Induces Wnt ligands; may promote β-catenin nuclear translocation via annexin A2 | [76,77] |
| FOXR2 | Oncogene in many cancer types | Unclear | [78] |
| Wnt pathway inhibitors | |||
| FOXF1 | Context-dependent oncogene or tumor suppressor | May inhibit WNT5A | [79] |
| FOXF2 | Tumor suppressor in gastric and cervical cancer | May inhibit WNT5A and induce Wnt inhibitor SFRP1; promotes β-catenin degradation | [79,80,81] |
| FOXL1 | Tumor suppressor in multiple types of cancer | May reduce proteoglycan co-receptor levels | [82] |
| FOXN3 | Inhibits proliferation and migration in multiple types of cancer | Inhibits β-catenin/TCF7L2 interaction | [83] |
| FOXO1 | Tumor suppressor in multiple types of cancer | Inhibits β-catenin/TCF7L2 interaction, possibly via LINC01197 | [84] |
| FOXO3 | Tumor suppressor in multiple types of cancer | Inhibits β-catenin/TCF7L2 interaction by competitive binding | [85,86] |
| FOXO4 | Tumor suppressor in multiple types of cancer | Inhibits β-catenin/TCF7L2 interaction by competitive binding | [85] |
| FOXS1 | Putative tumor suppressor in breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma | May inhibit CTNNB1 expression | [87] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koch, S. Regulation of Wnt Signaling by FOX Transcription Factors in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143446
Koch S. Regulation of Wnt Signaling by FOX Transcription Factors in Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(14):3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143446
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoch, Stefan. 2021. "Regulation of Wnt Signaling by FOX Transcription Factors in Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 14: 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143446
APA StyleKoch, S. (2021). Regulation of Wnt Signaling by FOX Transcription Factors in Cancer. Cancers, 13(14), 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143446






