Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Antibody-Functionalised, PEGylated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Intervention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactions and Products of the Carbon Nanotube System
2.1.1. Synthesis of Aligned MWCNTs and Morphological Evaluation
Aligned MWCNTs Synthesis
Morphological Evaluation of the CNTs
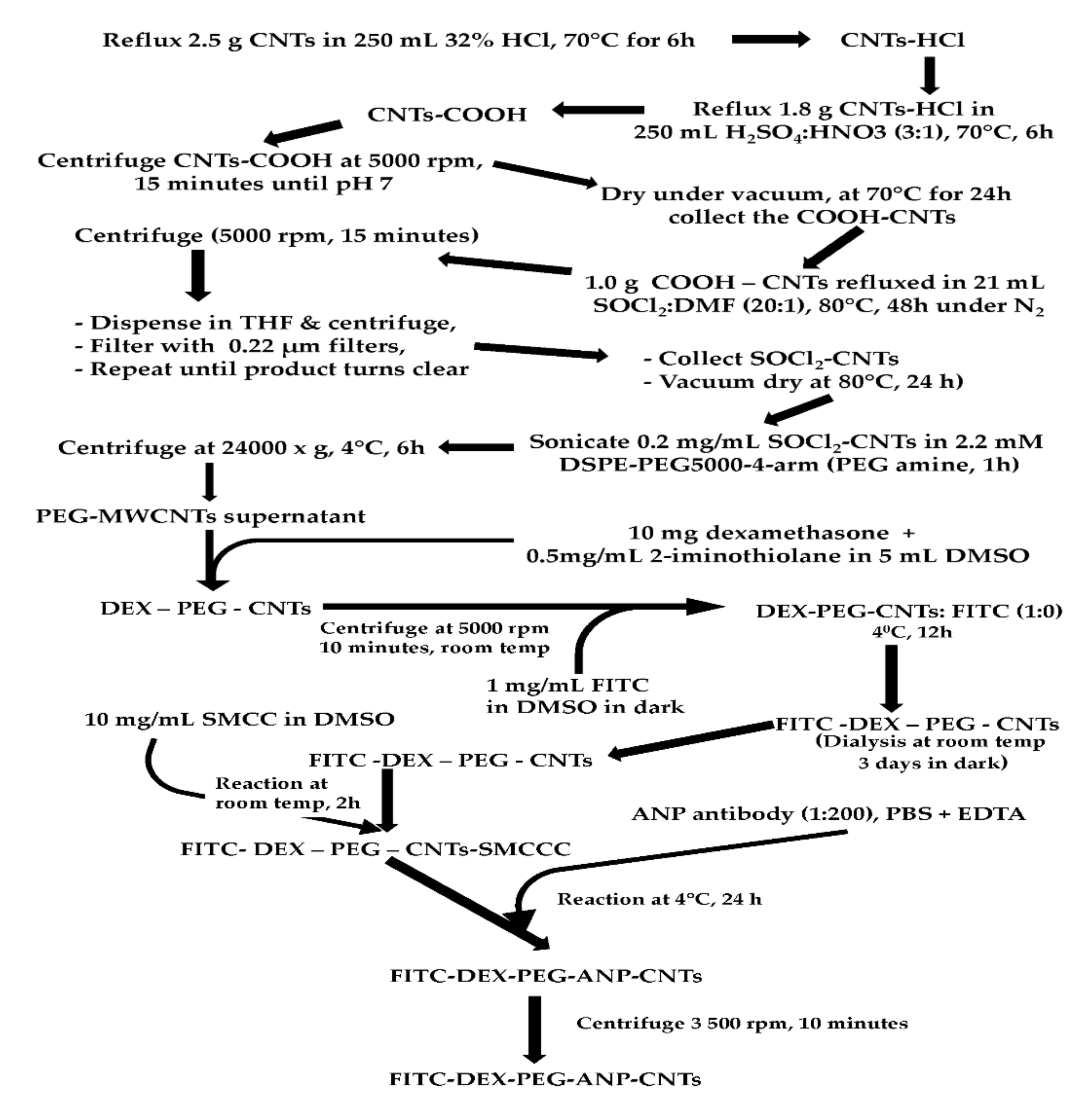
2.1.2. Purification, Acid Functionalization, Acylation and PEGylation of MWCNTs
Purification of the MWCNTs
Carboxylation of the Purified MWCNTs
Acylation of the Carboxylated MWCNTs
PEGylation of the Acylated MWCNTs
2.1.3. Dexamethasone Loading to PEG-CNTs, FITC Labelling and ANP Antibody Conjugation to FITC Labelled PEG-CNTs
Loading of Dexamethasone to PEG-CNTs
FITC Labelling of DEX-PEG-CNTs
ANP Antibody Conjugation
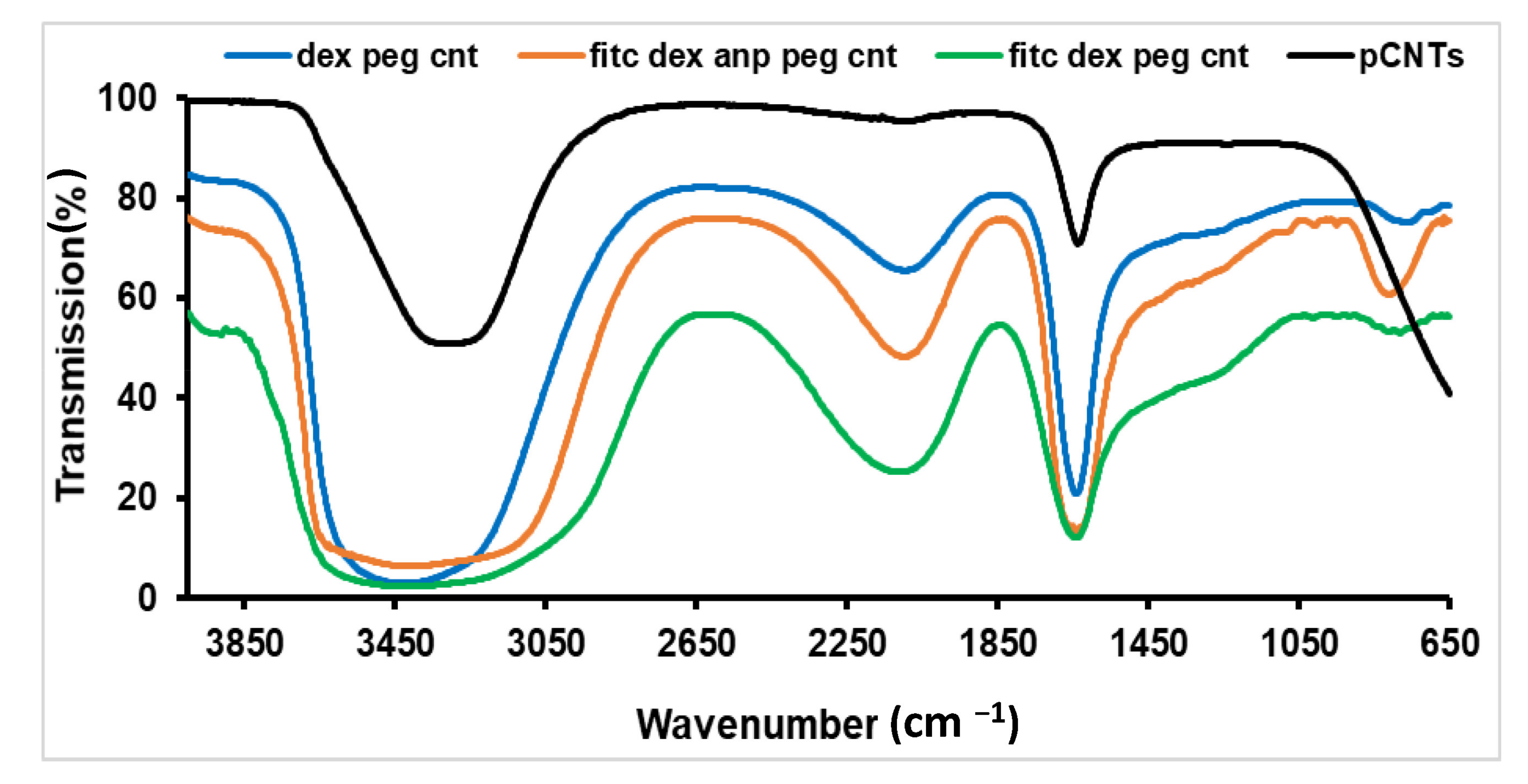
2.1.4. FTIR Spectroscopy of MWCNTs
2.1.5. Raman Spectra of the Functionalised CNTs
2.1.6. UV–Vis and Fluorescence Evaluation in the Functionalised CNTs
2.1.7. Dexamethasone Release Studies
2.2. Biological Properties of the Carbon Nanotube System
2.2.1. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs
2.2.2. Animal Administration and Experimental Design
2.2.3. Unilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion (CCAO) and Neurobehavioural Assessment
2.2.4. Optimization of the Formulation Dose
2.2.5. Treatment of Stroke Rats with the Functionalised Carbon Nanotubes
2.2.6. Tissue Sample Preparation
2.2.7. Determination of Fluorescence Intensity in the Rat Tissues
2.2.8. Histological Evaluation of the Rat Brain Tissue
2.2.9. Determination of Plasma ANP Levels in the Rat Venous Blood
2.2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reactions and Products of the Carbon Nanotube System
3.1.1. SEM and TEM Morphological Evaluation
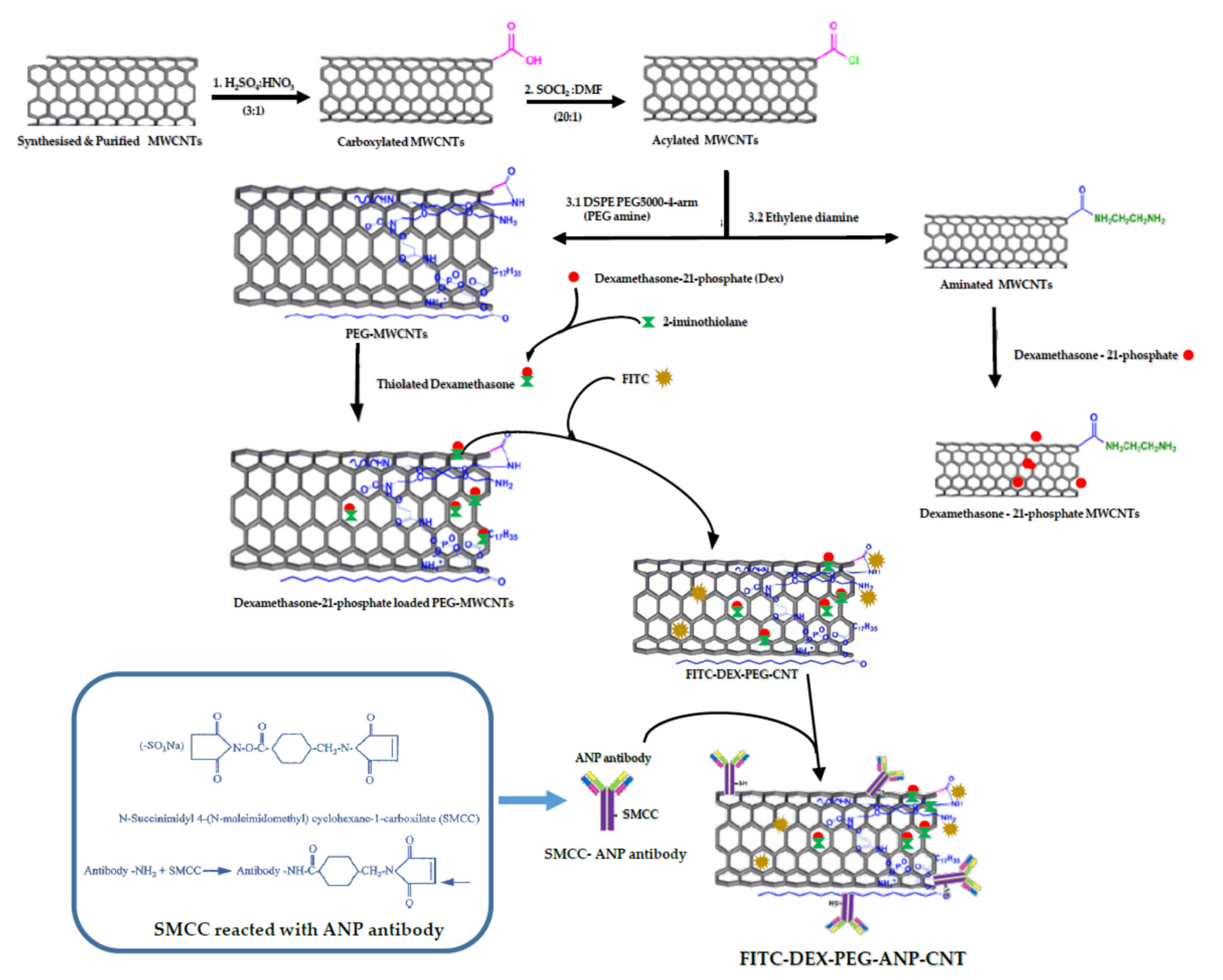
3.1.2. Preparation of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs
3.1.3. Mechanism of ANP Targeting
3.1.4. FTIR Assessment of the Functionalised MWCNTs
3.1.5. Raman Evaluation of the Functionalised MWCNTs
3.1.6. UV–Vis Scanning and FEEM Evaluation of the FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs
3.1.7. Dexamethasone Loading and Release Studies
3.1.8. Fluorescence Evaluation of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs
3.2. Biological Properties of the Carbon Nanotube System
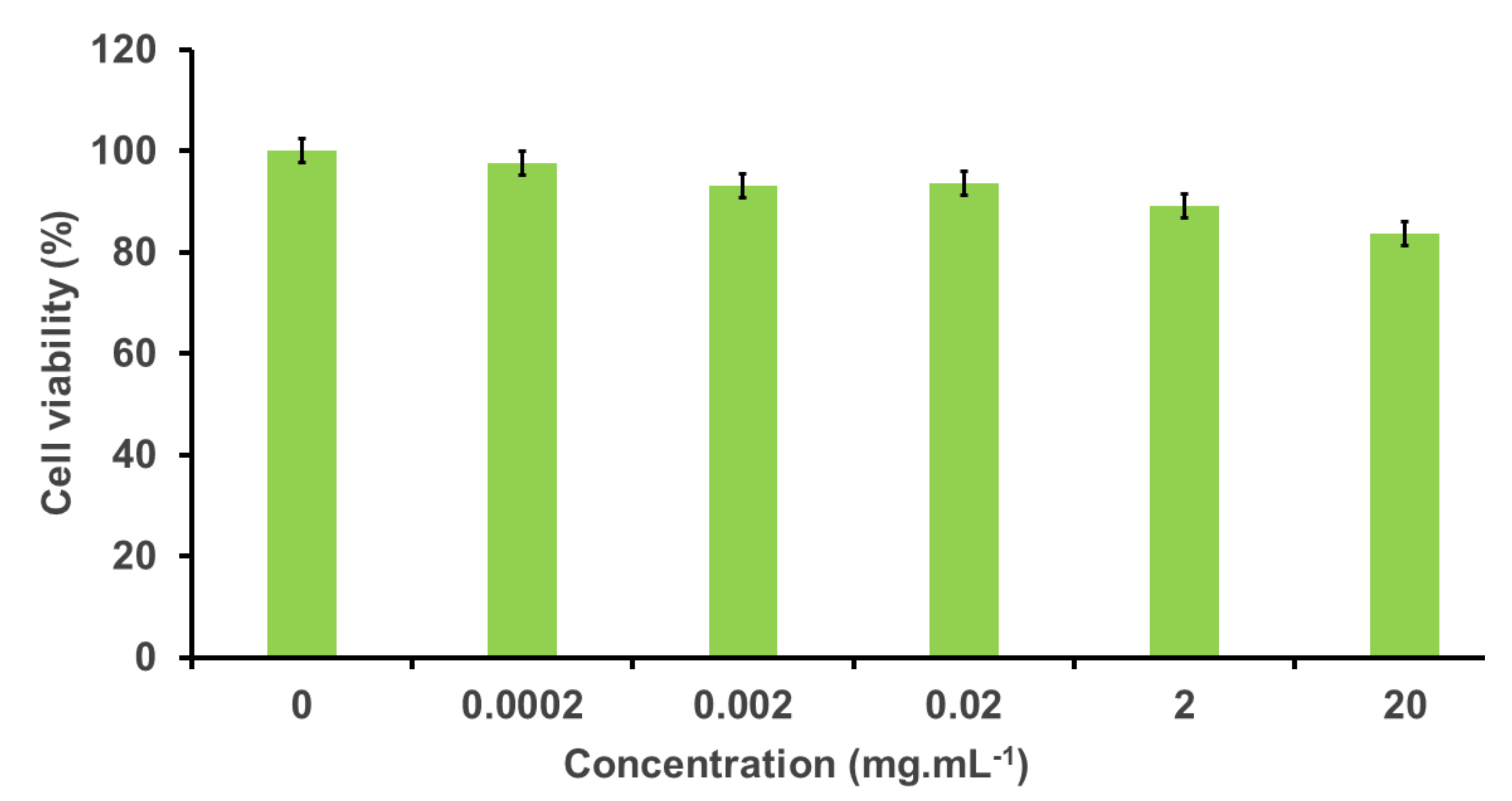
3.2.1. Cytotoxic Effect of the FITC-PEG-ANP-CNTs in PC-12 Cells
3.2.2. Animal Surgery and Neurobehavioural Assessment
3.2.3. Humane Endpoints and Sampling
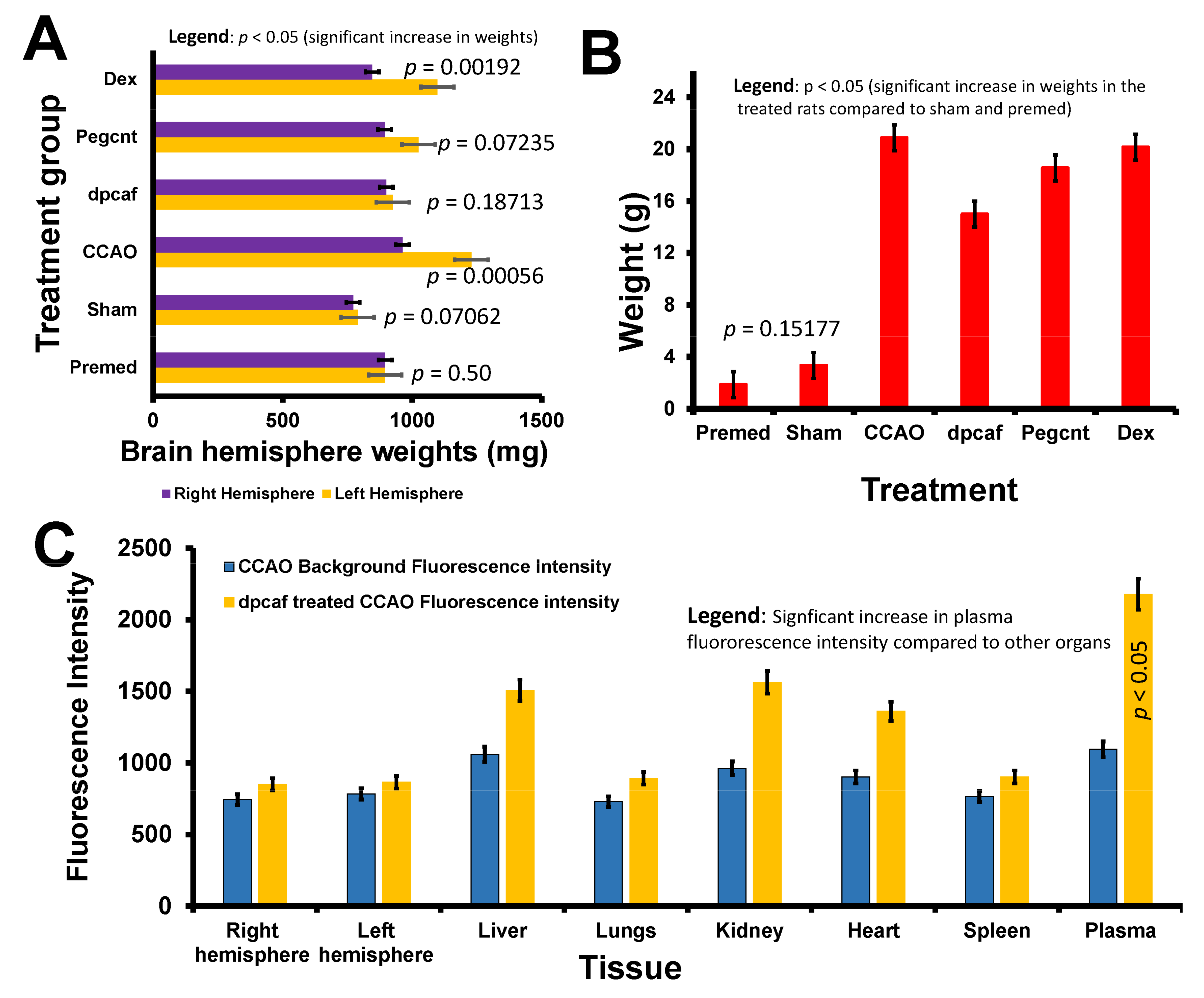
3.2.4. Brain and Total Body Weights following Common Carotid Artery Occlusion and Treatment with the Formulations
3.2.5. Biodistribution of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs Using Absorption Spectroscopy
3.2.6. Biodistribution of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy
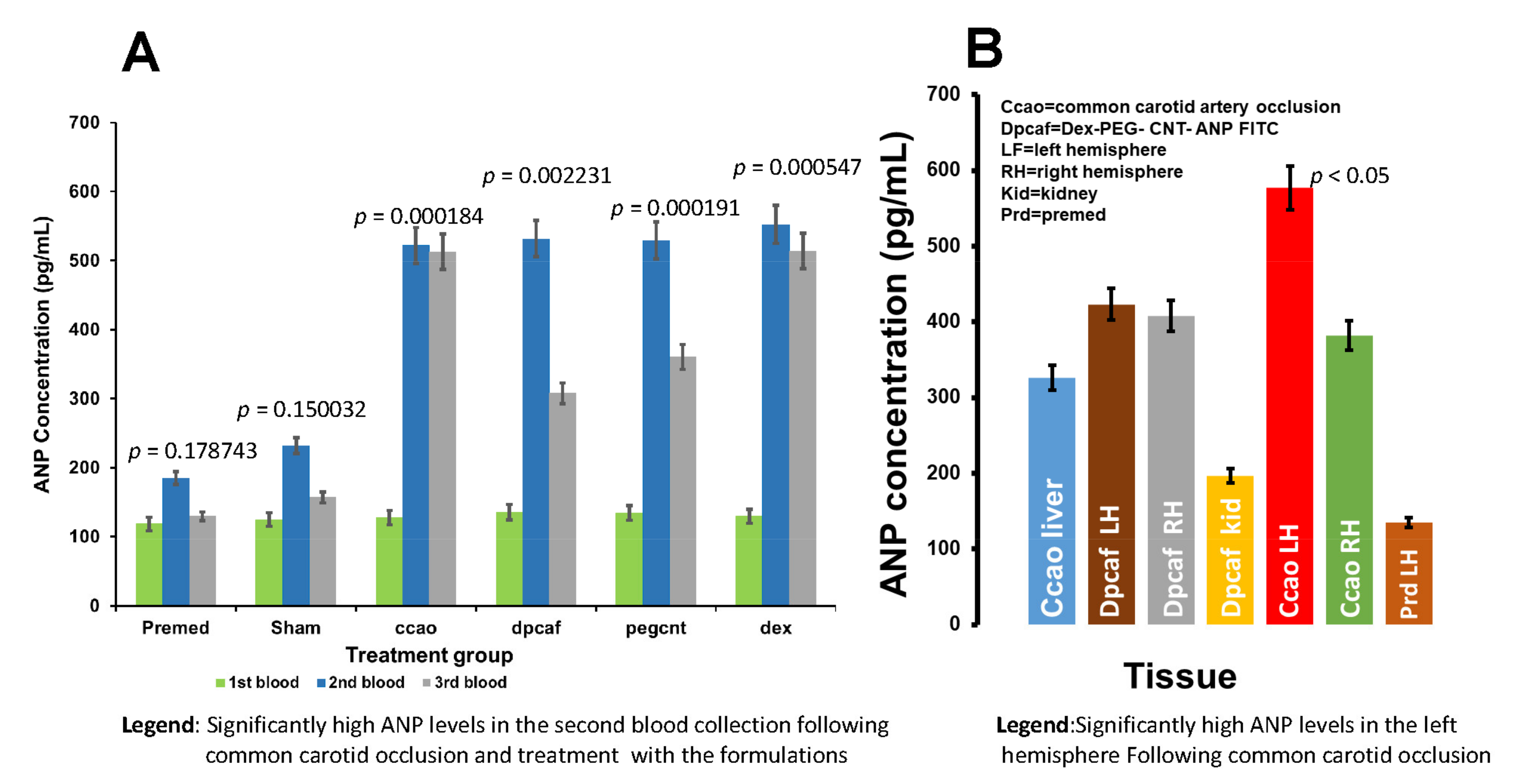
3.2.7. Determination of Plasma ANP Levels in the Rat Venous Blood
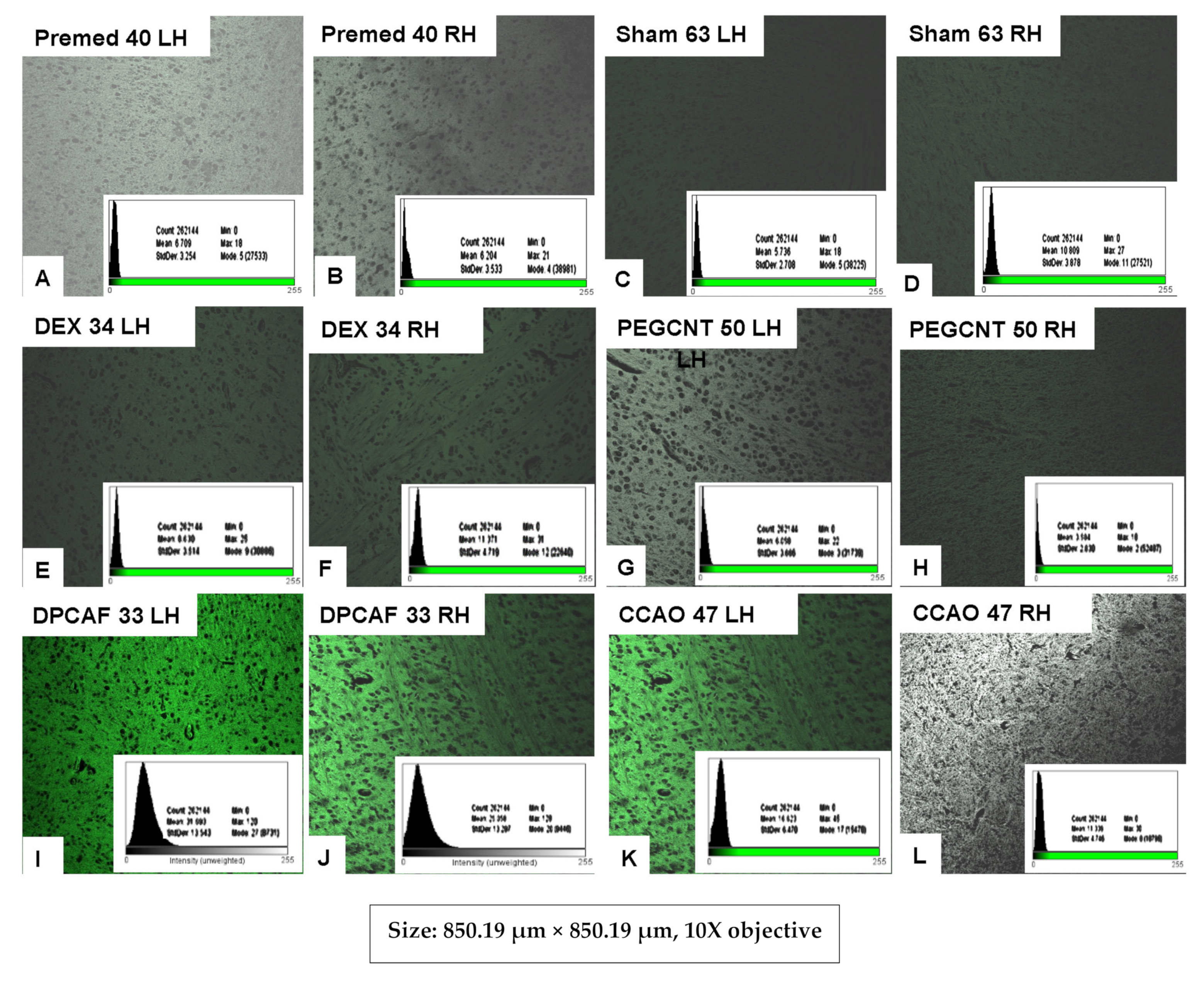
3.2.8. Histological Evaluation of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs Delivery into the Brain by Fluorescence Microscopy
3.2.9. Histological Evaluation of FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs Delivery into the Brain by Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining Technique
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEX | dexamethasone |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| ANP | atrial natriuretic peptide |
| CNTs | carbon nanotubes |
| BNP | brain natriuretic peptide |
| VA-MWCNTs | vertically aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes |
| PEG-CNTs | PEGylated carbon nanotubes |
| ULCCAO | unilateral common carotid artery occlusion |
| PEG-HCC | PEGylated hydrophilic carbon clusters |
| CVD | chemical vapour deposition |
| MCAO | middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| SWCNTs | single-walled carbon nanotubes |
| NPs | natriuretic peptides |
| FEEM | field excitation emission matrix |
| SMCC | succinimidyl-4-(N-maleimidomethyl) cyclohexane-1-carboxylate |
| BAR | Bright, Alert and Responsive |
| DSPE-PEG5000-amine | 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[amino(polyethylene glycol)-5000] |
References
- Phipps, M.S.; Cronin, C.A. Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ 2020, 368, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Fan, T.; Zhao, W.; Abbas, G.; Han, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, N.; Liu, N.; Liang, W.; Huang, H.; et al. Bioactive Materials Recent advances in the development of nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2854–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Montaner, J.; Ramiro, L.; Arora, R.; Talwar, P.; Nath, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Pandit, A.K.; Mohania, D.; et al. Blood biomarkers for the diagnosis and differentiation of stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H. N-Terminal Pro – B-Type Natriuretic Peptide as a Risk Biomarker for. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2020, 27, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangnus, T.; Burckhardt, B.B. Potential and Limitations of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide as Biomarker in Pediatric Heart Failure — A Comparative Review. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idzikowska, K. Midregional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide, an important member of the natriuretic peptide family: Potential role in diagnosis and prognosis of cardiovascular disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3017–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Fan, T.; An, J.; Choi, W.; Duo, Y. Chem Soc Rev Emerging combination strategies with phototherapy in cancer nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8065–8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Peng, M.; Lu, R.; Meng, X.; Liang, W.; Li, Z.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, B.; Nie, G.; Xie, N.; et al. Black phosphorus-based photothermal therapy with aCD47-mediated immune checkpoint blockade for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Xing, C.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, B.; et al. Two-Dimensional Borophene: Properties, Fabrication, and Promising Applications. Research 2020, 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Naure 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, Z. Carbon nanotubes in biology and medicine: An overview. Chinese Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Zhan, L.; Juanjuan, B.; Jing, W.; Jianjun, W.; Taoli, S.; Yi, G.; Wangsuo, W. Biodistribution of co-exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes and nanodiamonds in mice. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobsen, N.R.; Møller, P.; Clausen, P.A.; Saber, A.T.; Micheletti, C.; Jensen, K.A. Biodistribution of Carbon Nanotubes in Animal Models. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komane, P.P.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E. Functionalized, Vertically Super-Aligned Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Potential Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedaghat, S. Synthesis and Modification of Carboxylated Multi Wall Nanotubes with Atenolol. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 2014, 4, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Luis, A.; De Barros, B.; Cristian, D.; Soares, F.; Nicole, S.; Alisaraie, L. Functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes: Cellular uptake, biodistribution and applications in drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, S.Y.; Mandel, A.; Seifalian, A.M. A concise review of carbon nanotube’s toxicology. Nano Rev. 2013, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajid, M.I.; Jamshaid, U.; Jamshaid, T.; Zafar, N.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Carbon nanotubes from synthesis to in vivo biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzar, N.; Hasan, R.; Tyagi, M.; Yadav, N.; Narang, J. Carbon nanotube - A review on Synthesis, Properties and plethora of applications in the field of biomedical science. Sensors Int. 2020, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tangboriboon, N. Carbon and Carbon Nanotube Drug Delivery and Its Characterization, Properties, and Applications. Nanocarriers Drug Deliv. 2019, 2019, 451–467. [Google Scholar]
- Martincic, M.; Tobias, G. Filled carbon nanotubes in biomedical imaging and drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Cellular Toxicity and Immunological Effects of Carbon-based Nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komane, P.P.; Kumar, P.; Marimuthu, T.; du Toit, L.C.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Dexamethasone-loaded, pegylated, vertically aligned, multiwalled carbon nanotubes for potential ischemic stroke intervention. Molecules 2018, 23, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.J.; Velho, S.; Amaral, M.H. Functionalizing nanoparticles with cancer-targeting antibodies: A comparison of strategies. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 180–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, K.; Davis, C.; Sherlock, S.; Cao, Q.; Chen, X.; Dai, H. Drug delivery with carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6652–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brambilla, R.; Couch, Y.; Lykke, K. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience The effect of stroke on immune function. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, Z. Nanomaterials for Medical Applications; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; p. 1042789. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Park, J.G.; Leonhardt, B.E.; Zhang, S.; Liang, R. Continuous Synthesis of Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Assisted Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roozbahani, M.; Kharaziha, M.; Emadi, R. pH sensitive dexamethasone encapsulated laponite nanoplatelets: Release mechanism and cytotoxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamine, B.; Karimi, I.; Salimi, A.; Mazdarani, P.; Becker, L.A. Neurobehavioral toxicity of carbon nanotubes in mice: Focus on brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein. Toxic. Ind. Heal. 2017, 33, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Dewangan, H.K. PEGYLATION: An important approach for novel drug delivery system. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 32, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Alaaeldin, E.; Hussein, A.; Sarhan, A.H. Liposomes and PEGylated liposomes as drug delivery system. J. Adv. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 3, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Orgah, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Protection against acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by QiShenYiQi via neuroinflammatory network mobilization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.C.; Linske, M.A.; Stafford, K.C. Humane use of cardiac puncture for non-terminal phlebotomy of wild-caught and released Peromyscus spp. Animals 2020, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavarajah, R.; Mudimbaimannar, V.K.; Elizabeth, J.; Rao, U.K.; Ranganathan, K. Chemical and physical basics of routine formaldehyde fixation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2012, 16, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haque, Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Khan, M.Z.I.; Hussan, M.T.; Alam, M.M. Alcohol-based fixatives can better preserve tissue morphology than formalin. Int. J. Morphol. 2020, 38, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, R.H.; Derry, P.J.; Rea, H.C.; Dalmeida, W.V.; Nilewski, L.G.; Sikkema, W.K.A.; Mandava, P.; Tsai, A.L.; Mendoza, K.; Berka, V.; et al. Efficacy of novel carbon nanoparticle antioxidant therapy in a severe model of Reversible middle cerebral artery stroke in acutely hyperglycemic rats. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmar, M.; Spruss, T.; Schuierer, G.; Horn, M. External carotid artery territory ischemia impairs outcome in the endovascular filament model of middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 2003, 34, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Nanomedicine for ischemic stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyon, W.S.; Gray, D.T.; Barnes, C.A.; Rosa, M.; Gilissen, E.P. An Alternative to Dye-Based Approaches to Remove Background Autofluorescence From Primate Brain Tissue. Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colino, C.I.; Lanao, J.M.; Gutierrez-Millan, C. Targeting of Hepatic Macrophages by Therapeutic Nanoparticles. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ching, P.; Wong, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, A. The renal and cardiovascular effects of natriuretic peptides. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2017, 41, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkikallio, A.M.; Mäkikallio, T.H.; Korpelainen, J.T.; Vuolteenaho, O.; Tapanainen, J.M.; Ylitalo, K.; Sotaniemi, K.A.; Huikuri, H.V.; Myllylä, V.V. Natriuretic peptides and mortality after stroke. Stroke 2005, 36, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Morales, M.A.; Castelló-Ruiz, M.; Burguete, M.C.; Jover-Mengual, T.; Aliena-Valero, A.; Centeno, J.M.; Alborch, E.; Salom, J.B.; Torregrosa, G.; Miranda, F.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective role of atrial natriuretic peptide in experimental acute ischemic stroke. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 472, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monici, M. Cell and tissue autofluorescence research and diagnostic applications. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 11, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Xie, W.; Xu, Q.; Liang, T.; Xu, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Neuroprotective effects of radix scrophulariae on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via MAPK pathways. Molecules 2018, 23, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Ma, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F. Normobaric oxygen inhibits AQP4 and NHE1 expression in experimental focal ischemic stroke. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoblaugh, S.E.; Himmel, L.E. Keeping Score: Semiquantitative and Quantitative Scoring Approaches to Genetically Engineered and Xenograft Mouse Models of Cancer. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



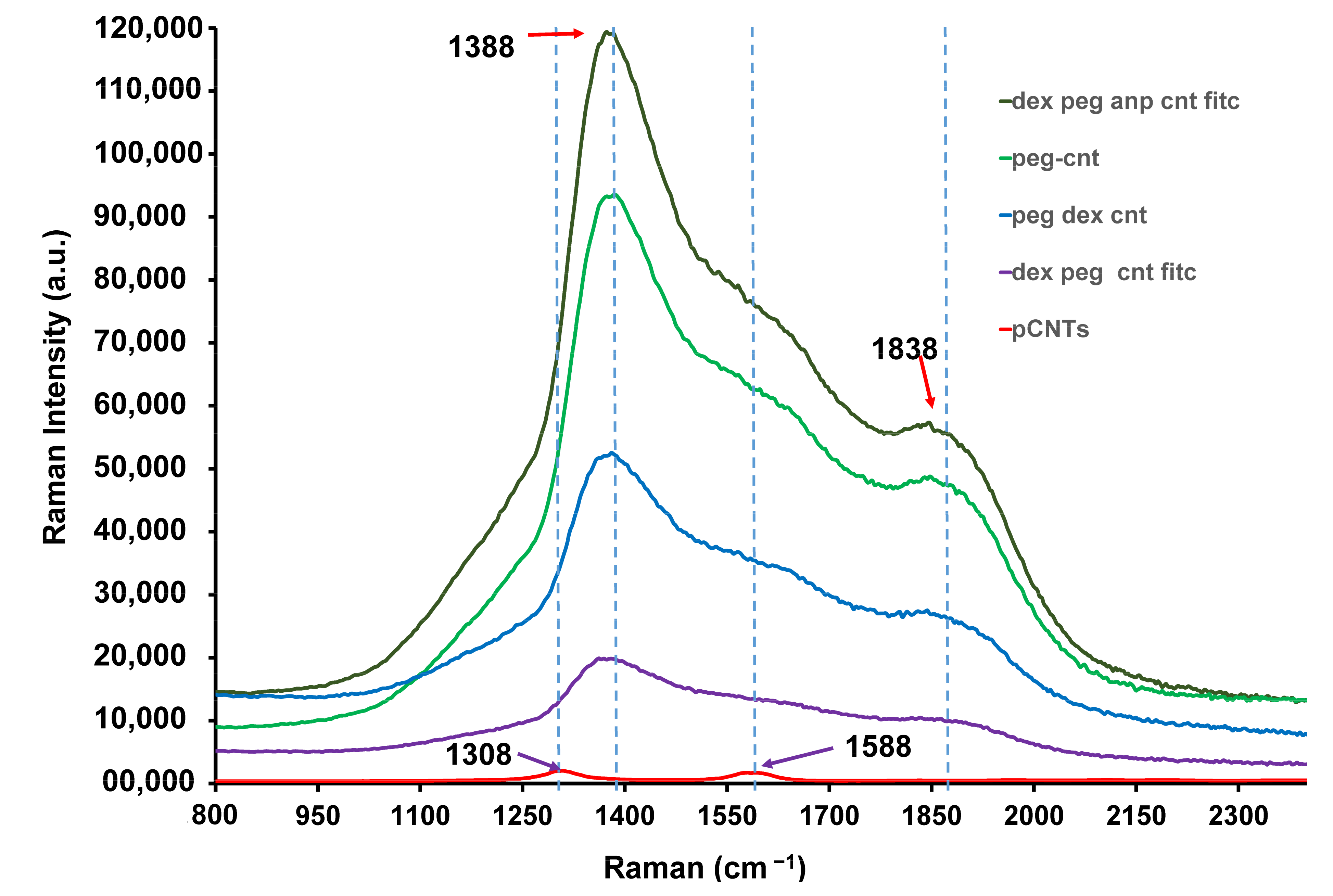




| MWCNT Type | D Band Intensity ×103 | G Band Intensity ×103 | Intensity Increase | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D Band | G Band | |||
| Pristine CNTs | 1.18 | 1.63 | - | - |
| FITC-Dex-PEG CNTs | 19.60 | 9.81 | 10× | 6× |
| Dex-PEG-CNTs | 51.30 | 26.60 | 27× | 16× |
| PEG-CNTs | 92.30 | 47.80 | 49× | 29× |
| FITC-ANP-Dex-PEG-CNTs | 118 | 55.60 | 63× | 34× |
| Healthy Rats | Premed | Sham | CCAO | FITC-DEX-PEG-ANP-CNTs | PEG-CNT | DEX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komane, P.P.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Antibody-Functionalised, PEGylated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Intervention. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091357
Komane PP, Kumar P, Choonara YE. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Antibody-Functionalised, PEGylated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Intervention. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(9):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091357
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomane, Patrick P., Pradeep Kumar, and Yahya E. Choonara. 2021. "Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Antibody-Functionalised, PEGylated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Intervention" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 9: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091357
APA StyleKomane, P. P., Kumar, P., & Choonara, Y. E. (2021). Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Antibody-Functionalised, PEGylated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Intervention. Pharmaceutics, 13(9), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091357







