Inhibition of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase as a Possible Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Aspects of AD
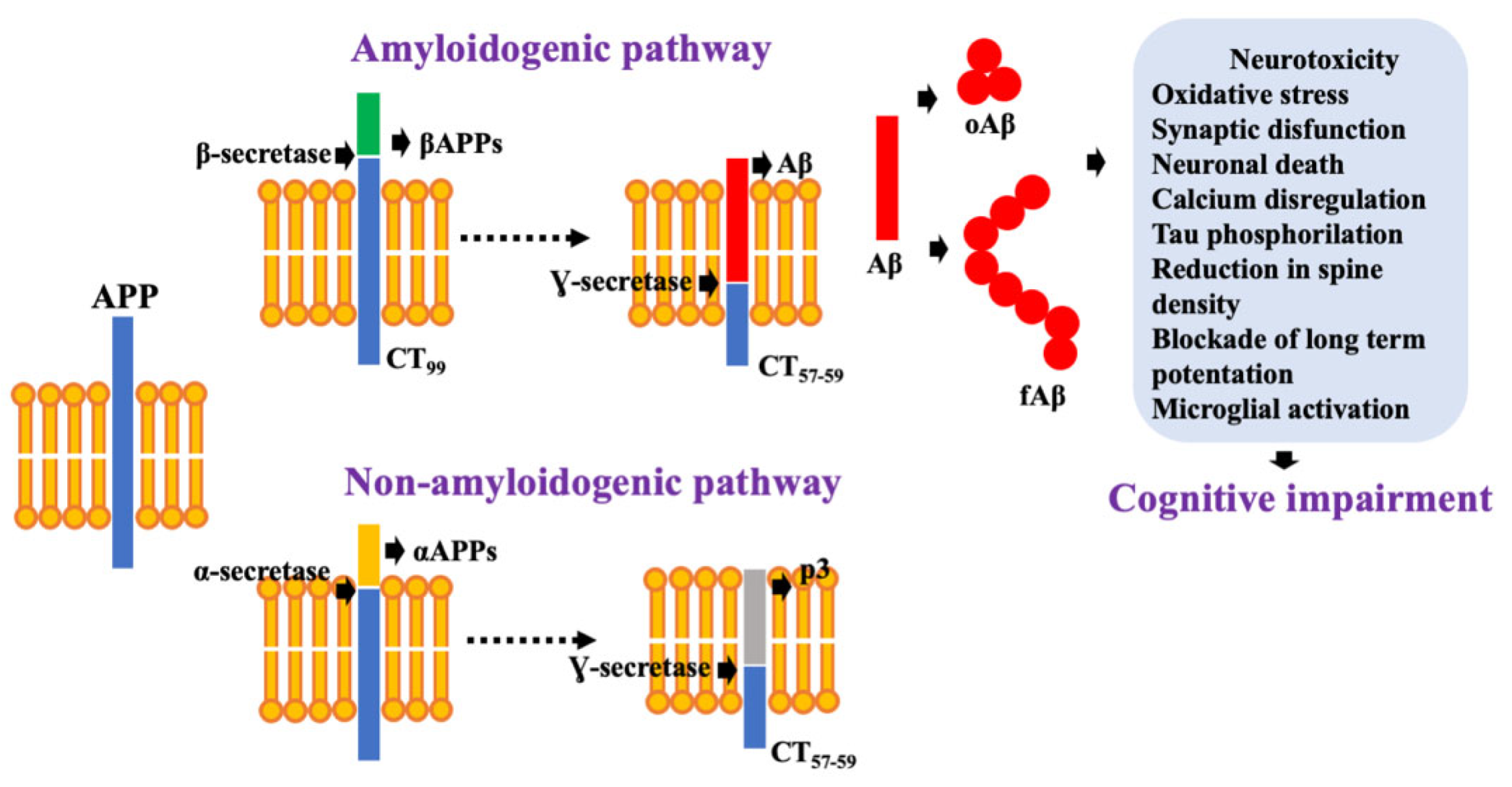
2.1. Aβ as a Neurotoxic Specie
2.2. NFTs Correlate with Cognitive Impairment
3. Dysregulation of the Neurotransmission Systems Involved in AD
3.1. Cholinergic System
3.2. Glutamate and NMDA Receptors
3.3. Serotonergic System
3.4. Noradrenergic System
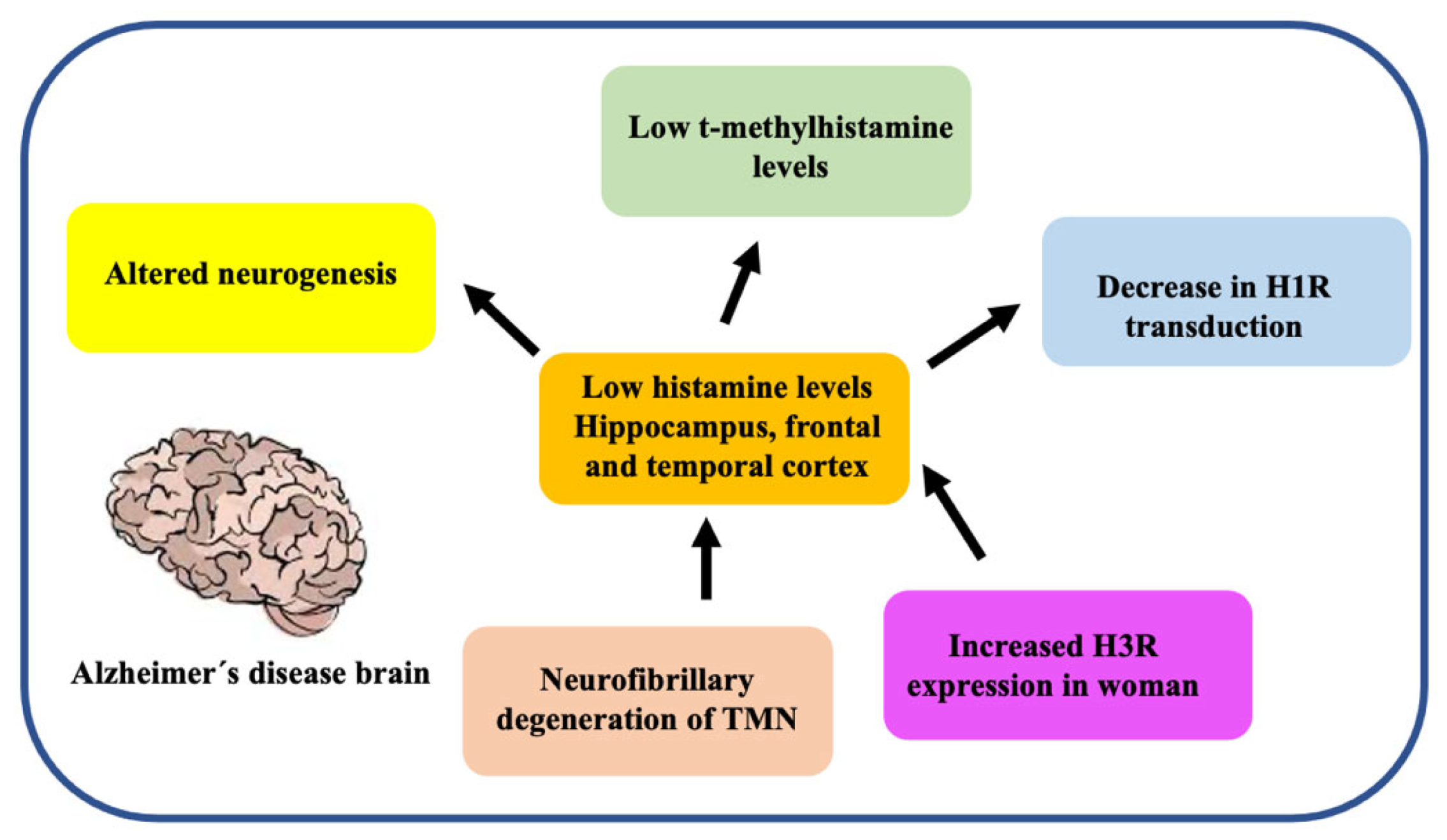
3.5. Histaminergic System
4. Histamine in the Brain
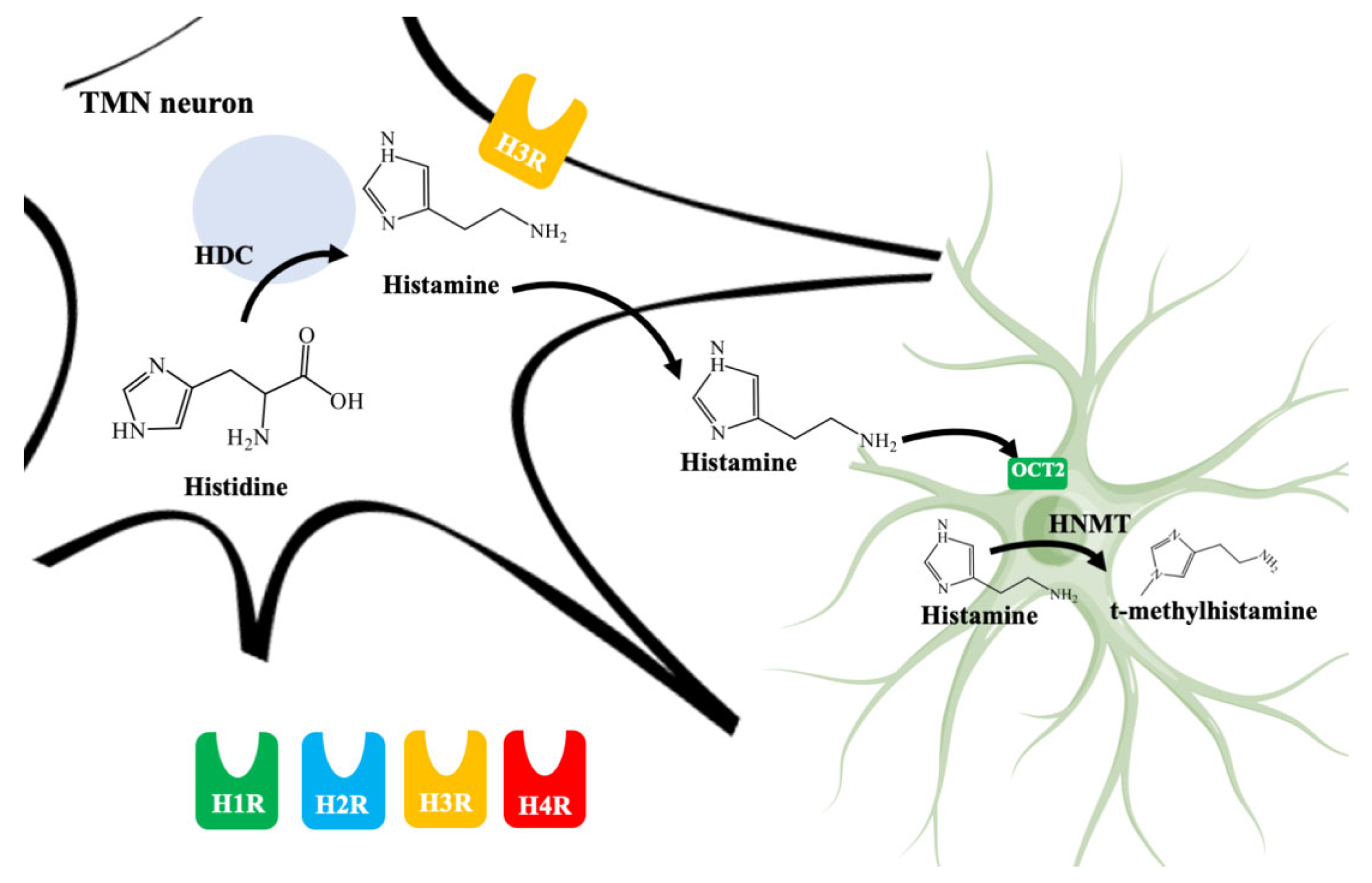
4.1. Histaminergic System in the CNS
4.2. Histamine Receptors
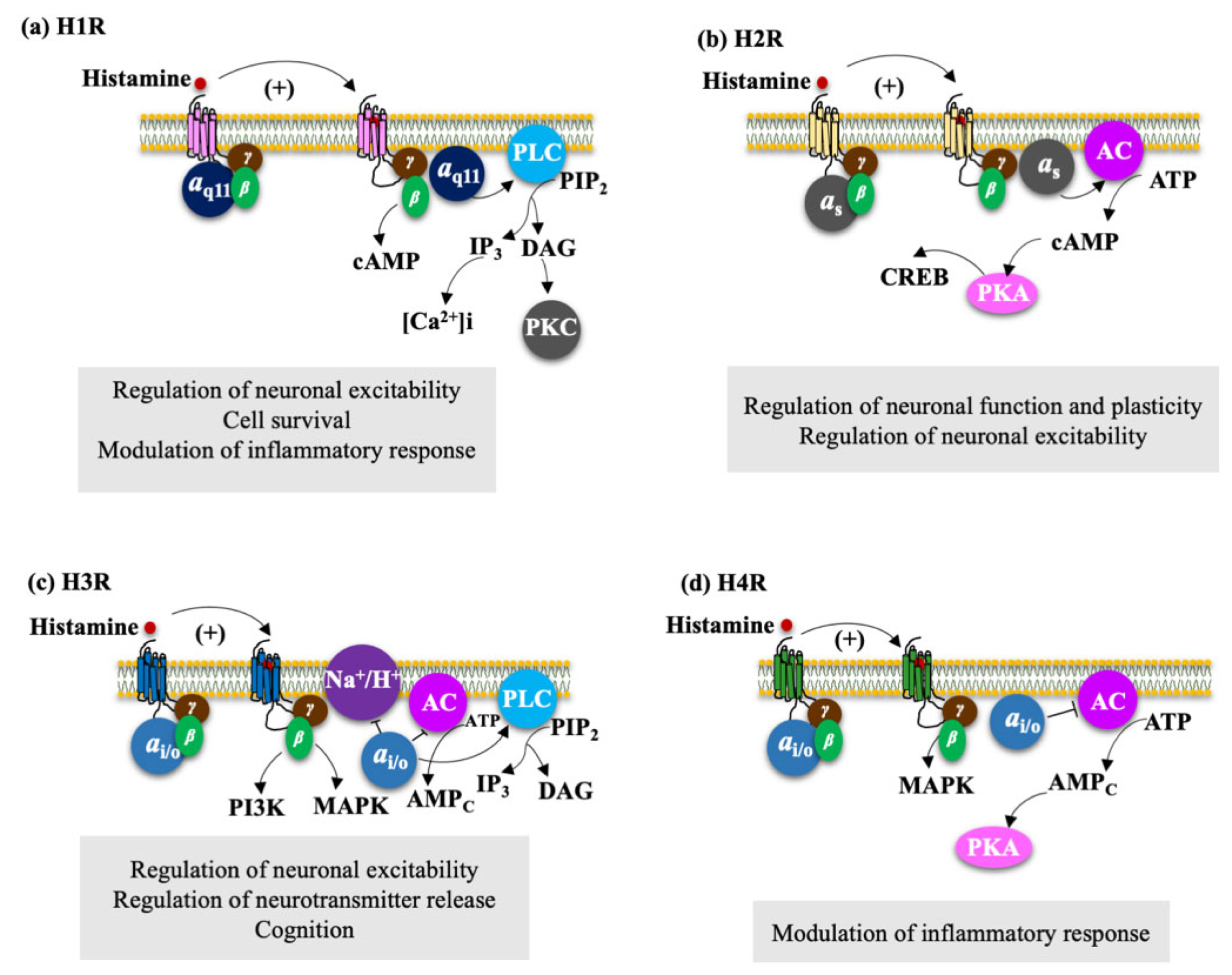
4.2.1. H1R Regulate Neuronal Excitability, Cell Survival, and Modulation of Inflammatory Response
4.2.2. H2R Regulates Neuronal Plasticity and Neuronal Excitability
4.2.3. H3R Regulate Neuronal Excitability, Neurotransmitter Release, and Cognition
4.2.4. H4R Modulate the Inflammatory Response
4.3. Astrocytes Are Involved in Histamine Elimination
5. Increase Histamine Levels in the Brain as an Opportunity to Develop Novel Treatments for AD Patients
5.1. H3R Inverse Agonist/Antagonist
5.2. Inhibition of HNMT
5.3. Beneficial Effects of Increased Histamine Levels in the Brains of AD Patients
5.3.1. Effects on Cognitive Functions and Neuroplasticity
5.3.2. Increase in the Degradation of Extracellular Aβ Insoluble Plaques
5.3.3. Increasing Neuronal Survival and Neurogenesis
5.4. Increasing Histamine Levels Could Be Helpful in Neurodegenerative Diseases
5.5. Potential Adverse Effects by Increasing Histamine Levels
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, G.L.; Samant, N.P. Current Druggable Targets for Therapeutic Control of Alzheimer’s Disease. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2021, 28, 106549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eratne, D.; Loi, S.M.; Farrand, S.; Kelso, W.; Velakoulis, D.; Looi, J.C. Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical Update on Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis. Australas Psychiatry 2018, 26, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.E.; Sekhar, N.; Rajamma, R.G.; Marathakam, A.; Al Mamun, A.; Uddin, M.S.; Mathew, B. Exploring the Role of Aggregated Proteomes in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciarelli, R.; Fedele, E. The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease: It’s Time to Change Our Mind. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L.; Tong, G.; Ballard, C. Treatment Combinations for Alzheimer’s Disease: Current and Future Pharmacotherapy Options. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 67, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Lennon, J.C.; Malkaram, S.A.; Zeng, Y.; Fisher, D.W.; Dong, H. Serotonergic system, cognition, and BPSD in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 704, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, L.M.; Hof, P.R.; Šimić, G. Alterations and Interactions of Subcortical Modulatory Systems in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Brain. Res. 2021, 261, 379–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlomuzica, A.; Dere, D.; Binder, S.; De Souza Silva, M.A.; Huston, J.P.; Dere, E. Neuronal Histamine and Cognitive Symptoms in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, A.G.; Prendergast, A.; Barry, C.; Scully, D.; Upton, N.; Medhurst, A.D.; Regan, C.M. H3 Receptor Antagonism Enhances NCAM PSA-Mediated Plasticity and Improves Memory Consolidation in Odor Discrimination and Delayed Match-to-Position Paradigms. Neuropsychopharmacoly 2009, 34, 2585–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Vasanthan, V.; Fu, W.; Fahlman, R.P.; MacTavish, D.; Jhamandas, J.H. Histamine Induces the Production of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Human Astrocytic Cultures via H1-Receptor Subtype. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1845–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Chen, L.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Lu, M.H.; Wang, Z.T.; Chen, M.; Lu, L.; Huang, W.; et al. Clemastine Attenuates AD-like Pathology in an AD Model Mouse Via Enhancing mTOR-mediated Autophagy. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 342, 113742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, C.; Barata-Antunes, S.; Santos, T.; Ferreiro, E.; Cristóvão, A.C.; Serra-Almeida, C.; Ferreira, R.; Bernardino, L. Histamine Modulates Hippocampal Inflammation and Neurogenesis in Adult Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naganuma, F.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Iida, T.; Miura, Y.; Kárpáti, A.; Matsuzawa, T.; Yanai, A.; Mogi, A.; Mochizuki, T.; et al. Histamine N-methyltransferase Regulates Aggression and the Sleep-wake Cycle. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R. Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Pivac, N. Genetic Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1192, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria Lopez, J.A.; González, H.M.; Léger, G.C. Alzheimer’s Disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 167, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.A.; Hadziselimovic, A.; Sanders, C.R. The Vexing Complexity of the Amyloidogenic Pathway. Protein. Sci. 2019, 28, 1177–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, G.; Holtzman, D.M. Amyloid-β and Tau at the Crossroads of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1184, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Arias, Á.; Paredes, J.M.; di Biase, C.; Cuerva, J.M.; Giron, M.D.; Salto, R.; González-Vera, J.A.; Orte, A. Seeding and Growth of β-Amyloid Aggregates Upon Interaction with Neuronal Cell Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. Amyloid β Oligomers in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis, Treatment, and Diagnosis. Acta. Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyure, K.A.; Durham, R.; Stewart, W.F.; Smialek, J.E.; Troncoso, J.C. Intraneuronal Aβ-Amyloid Precedes Development of Amyloid Plaques in Down Syndrome. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2001, 125, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.M.; Klyubin, I.; Shankar, G.M.; Townsend, M.; Fadeeva, J.V.; Betts, V.; Podlisny, M.B.; Cleary, J.P.; Ashe, K.H.; Rowan, M.J.; et al. The Role of Cell-Derived Oligomers of Aβ in Alzheimer’s Disease and Avenues for Therapeutic Intervention. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Selkoe, D.J. A Mechanistic Hypothesis for the Impairment of Synaptic Plasticity by Soluble Aβ Oligomers from Alzheimer’s brain. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Ochani, M.; Amella, C.A.; Tanovic, M.; Susarla, S.; Li, J.H.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Ulloa, L.; et al. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor A7 Subunit Is an Essential Regulator of Inflammation. Nature 2003, 421, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, N.N.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Sharma, M.; Luo, W. The Complexity of Tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 705, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The Neuropathological Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Boyd-Kimball, D. Oxidative Stress, Amyloid-β Peptide, and Altered Key Molecular Pathways in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, C.; Buée, L.; Blum, D. Tau and Neuroinflammation: What Impact for Alzheimer’s Disease and Tauopathies? Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegmann, S.; Biernat, J.; Mandelkow, E. A Current View on Tau Protein Phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2021, 69, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pîrşcoveanu, D.F.V.; Pirici, I.; Tudorică, V.; Bălşeanu, T.A.; Albu, V.C.; Bondari, S.; Bumbea, A.M.; Pîrşcoveanu, M. Tau protein in neurodegenerative diseases—A review. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, B.R.; Reed, M.N.; Su, J.; Penrod, R.D.; Kotilinek, L.A.; Grant, M.K.; Pitstick, R.; Carlson, G.A.; Lanier, L.M.; Yuan, L.-L.; et al. Tau Mislocalization to Dendritic Spines Mediates Synaptic Dysfunction Independently of Neurodegeneration. Neuron 2010, 68, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Thangavel, R.; Sharma, V.M.; Litersky, J.M.; Bhaskar, K.; Fang, S.M.; Do, L.H.; Andreadis, A.; Van Hoesen, G.; Ksiezak-Reding, H. Phosphorylation of Tau by Fyn: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.M.; Cuello, A.C.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Farlow, M.R.; Snyder, P.J.; Giacobini, E.; Khachaturian, Z.S. Revisiting the Cholinergic Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Emerging Evidence from Translational and Clinical Research. J. Prev. Alzheimers. Dis. 2019, 6, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán-García, E.D.; Márquez-Gómez, R.; Barrón-González, M.; Pérez-Capistran, T.; Rosales-Hernández, M.C.; Pinto-Almazán, R.; Soriano-Ursúa, M.A. Monoamines and their Derivatives on GPCRs: Potential Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer. Res. 2019, 16, 871–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandimalla, R.; Reddy, P.H. Therapeutics of Neurotransmitters in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1049–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Rao, J.; Canción, Y.; Chen, S.; Xue, C.; Abrazo, L.X.; Chen, J. Altered Functional Connectivity of the Basal Nucleus of Meynert in Subjective Cognitive Impairment, Early Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M. Cholinergic Circuitry of the Human Nucleus Basalis and its Fate in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 4124–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.K.; Tomlinson, B.E.; Blessed, G.; Bergmann, K.; Gibson, P.H.; Perry, R.H. Correlation of Cholinergic Abnormalities with Senile Plaques and Mental Test Scores in Senile Dementia. Br. Med. J. 1978, 2, 1457–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Rodriguez, J.J.; Pacheco-Herrero, M.; Thyssen, D.; Murillo-Carretero, M.I.; Berrocoso, E.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Bacskai, B.J.; Garcia-Alloza, M. Rapid β-Amyloid Deposition and Cognitive Impairment After Cholinergic Denervation in APP/PS1 Mice. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, F.; Gauthier, S. Update on the Pharmacological Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y. Molecular Mechanism of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation—Towards Multiscale Understanding of Learning and Memory. Neurosci. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E. Pro-Survival Signalling from the NMDA Receptor. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleich, S.; Römer, K.; Wiltfang, J.; Kornhuber, J. Glutamate and the Glutamate Receptor System: A Target for Drug Action. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2003, 18, S33–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. The NMDA Receptor Antagonist Memantine as a Symptomatological and Neuroprotective Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease: Preclinical Evidence. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2003, 18, S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, A.J. Invertebrate serotonin receptors: A Molecular Perspective on Classification and Pharmacology. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb184838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, T.; Park, S.; Jayathilake, K.; Roy, A.; Ertugrul, A.; Meltzer, H.Y. Effect of Buspirone, a Serotonin1A Partial Aagonist, on Cognitive Function in Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 95, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.K.P.; Tsang, S.W.Y.; Francis, P.T.; Keene, J.; Hope, T.; Esiri, M.M.; Spence, I.; Chen, C.P.L.-H. Postmortem Serotoninergic Correlates of Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, J.; Baron, J.C.; Dubois, B.; Crouzel, C.; Fiorelli, M.; Attar-Levy, D.; Pillon, B.; Fournier, D.; Vidailhet, M.; Agid, Y. Loss of Brain 5-HT2 Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. In Vivo Assessment with Positron Emission Tomography and [18F]Setoperone. Brain 1993, 116, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodovitsyna, O.; Flamini, M.; Chandler, D. Noradrenergic Modulation of Cognition in Health and Disease. Neural. Plast. 2017, 2017, 6031478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekar, L.K.; Wei, H.S.; Nedergaard, M. The Locus Coeruleus-Norepinephrine Network Optimizes the Coupling of Cerebral Blood Volume with Oxygen Demand. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow. Metab. 2012, 32, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagena, H.; Hansen, N.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Beta-Adrenergic Control of Hippocampal Function: Subserving the Choreography of Synaptic Information Storage and Memory. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 1349–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yanai, K. Histaminergic Neurons in the Tuberomammillary Nucleus as a Control Centre for Wakefulness. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 750–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scammell, T.E.; Jackson, A.; Franks, N.P.; Wisden, W.; Dauvilliers, Y. Histamine: Neural Circuits and New Medications. Sleep 2019, 42, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Selbach, O. Histamine in the Nervous System. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Pollard, H.; Ruat, M. Histaminergic Transmission in the Mammalian Brain. Physiol. Rev. 1991, 71, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, P. The Basics of Histamine Biology. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 106, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.T. The Interplay of Neurotransmitters in Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Spectr. 2005, 10, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Rinne, J.; Kuokkanen, K.; Eriksson, K.S.; Sallmen, T.; Kalimo, H.; Relja, M. Neuronal Histamine Deficit in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroscience 1997, 82, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Eser, R.A.; Ehrenberg, A.J.; Morales, D.; Petersen, C.; Kudlacek, J.; Dunlop, S.R.; Theofilas, P.; Resende, E.D.P.F.; Cosme, C.; et al. Profound Degeneration of Wake-Promoting Neurons in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naddafi, F.; Mirshafiey, A. The Neglected Role of Histamine in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 2013, 28, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motawaj, M.; Peoc’h, K.; Callebert, J.; Arrang, J.-M. CSF Levels of the Histamine Metabolite Tele-Methylhistamine Are Only Slightly Decreased in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 22, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Bossers, K.; Unmehopa, U.; Bao, A.-M.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations in the Histaminergic System in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Postmortem Study. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2585–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Yanai, K.; Okamura, N.; Meguro, K.; Arai, H.; Itoh, M.; Iwata, R.; Ido, T.; Watanabe, T.; Sasaki, H. Histamine H1 Receptors in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Assessed by Positron Emission Tomography. Neuroscience 2000, 99, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.H.; Neumann, D.; Seifert, R. Modulation of Behavior by the Histaminergic System: Lessons from HDC-, H3R- and H4R-Deficient Mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, E.; Zlomuzica, A.; De Souza Silva, M.A.; Ruocco, L.A.; Sadile, A.G.; Huston, J.P. Neuronal Histamine and the Interplay of Memory, Reinforcement and Emotions. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 215, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, E.; De Souza-Silva, M.A.; Spieler, R.E.; Lin, J.S.; Ohtsu, H.; Haas, H.L.; Huston, J.P. Changes in Motoric, Exploratory and Emotional Behaviours and Neuronal Acetylcholine Content and 5-HT Turnover in Histidine Decarboxylase-KO Mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Michelsen, K.A.; Wu, M.; Morozova, E.; Panula, P.; Alreja, M. Histamine Innervation and Activation of Septohippocampal GABAergic Neurones: Involvement of Local ACh Release: Histamine and the Septohippocampal Pathway. J. Physiol. 2004, 561, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.; Santos, T.; Gonçalves, J.; Baltazar, G.; Ferreira, L.; Agasse, F.; Bernardino, L. Histamine Modulates Microglia Function. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouterlood, F.G.; Sauren, Y.M.H.F.; Steinbusch, H.W.M. Histaminergic Neurons in the Rat Brain: Correlative Immunocytochemistry, Golgi Impregnation, and Electron Microscopy. J. Comp. Neurol. 1986, 252, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, H.; Watanabe, T.; Köhler, C. Morphological Analysis of the Tuberomammmillary Nucleus in the Rat Brain: Delineation of Subgroups with Antibody Again L-Histidine Decarboxylase as a Marker: Tuberomammilliary nucleus in rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987, 263, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouterlood, F.G.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Luiten, P.G.M.; Bol, J.G.J.M. Projection from the Prefrontal Cortex to Histaminergic Cell Groups in the Posterior Hypothalamic Region of the Rat. Anterograde Tracing with Phaseolus Vulgaris Leucoagglutinin Combined with Immunocytochemistry of Histidine Decarboxylase. Brain Res. 1987, 406, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouterlood, F.G.; Gaykema, R.P.A. Innervation of Histaminergic Neurons in the Posterior Hypothalamic Region by Medial Preoptic Neurons. Anterograde Tracing with Phaseolus Vulgaris Leucoagglutinin Combined with Immunocytochemistry of Histidine Decarboxylase in the Rat. Brain Res. 1988, 455, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, H.; Blomqvist, A.; Köohler, C. Origin of Neuronal Inputs to the Region of the Tuberomammillary Nucleus of the Rat Brain: Neuronal inputs to Tuberomammillary Nuclear Region. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 311, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherin, J.E.; Elmquist, J.K.; Torrealba, F.; Saper, C.B. Innervation of Histaminergic Tuberomammillary Neurons by GABAergic and Galaninergic Neurons in the Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus of the Rat. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4705–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Alamilla, G.; Márquez-Gómez, R.; García-Gálvez, A.-M.; Morales-Figueroa, G.-E.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. The Histamine H3 Receptor: Structure, Pharmacology, and Function. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelin, R.; Schuldiner, S. Vesicular Neurotransmitter Transporters. In Neurotransmitter Transporters. Contemporary Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Reith, M.E.A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 313–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Takagi, H.; Takeda, N.; Kubota, Y.; Tohyama, M.; Watanabe, T.; Wada, H. Fine Structure of Histaminergic Neurons in the Caudal Magnocellular Nucleus of the Rat as Demonstrated by Immunocytochemistry Using Histidine Decarboxylase as a Marker. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 229, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhar, M.J.; Taylor, K.M.; Snyder, S.H. The Subcellular Localization of Histamine and Histamine Methyltransferase in Rat Brain. J. Neurochem. 1971, 18, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Schwartz, J.-C. Auto-Inhibition of Brain Histamine Release Mediated by a Novel Class (H3) of Histamine Receptor. Nature 1983, 302, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavadai, E.; Hsuan-Liang, L.; Jian-Hua, Z.; Wilson, C.; Dar, S.L.; Chih-Kuang, C.; Wei-Bor, T.; Yih, H. Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening and Docking Studies to Identify Novel HNMT inhibitors. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 493–503. [Google Scholar]
- Debacker, M.D.; Gommeren, W.; Moereels, H.; Nobels, G.; Vangompel, P.; Leysen, J.E.; Luyten, W.H.M.L. Genomic Cloning, Heterologous Expression and Pharmacological Characterization of a Human Histamine H1 Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1993, 197, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.S.L.; Tran, V.T.; Snyder, S.H. Heterogeneity of Histamine Hi-Receptors: Species Variations In [3H]Mepyramine Binding of Brain Membranes. J. Neurochem. 1979, 32, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mir, M.I.; Pollard, H.; Moreau, J.; Arrang, J.M.; Ruat, M.; Traiffort, E.; Schwartz, J.C.; Palacios, J.M. Three Histamine Receptors (H1, H2 and H3) Visualized in the Brain of Human and Non-Human Primates. Brain Res. 1990, 526, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kárpáti, A.; Yoshikawa, T.; Naganuma, F.; Matsuzawa, T.; Kitano, H.; Yamada, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Futatsugi, A.; Mikoshiba, K.; Yanai, K. Histamine H1 Receptor on Astrocytes and Neurons Controls Distinct Aspects of Mouse Behaviour. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dong, H.; Li, N.; Qian, Y.; Jin, W. Histamine Upregulates the Expression of Histamine Receptors and Increases the Neuroprotective Effect of Astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopoldt, D.; Harteneck, C.; Nürnberg, B. G Proteins Endogenously Expressed in Sf 9 Cells: Interactions with Mammalian Histamine Receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 356, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, K.S.; Sergeeva, O.; Brown, R.E.; Haas, H.L. Orexin/Hypocretin Excites the Histaminergic Neurons of the Tuberomammillary Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9273–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, O.A.; Amberger, B.T.; Eriksson, K.S.; Scherer, A.; Haas, H.L. Co-Ordinated Expression of 5-HT2C Receptors with the NCX1 Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger in Histaminergic Neurones: NCX and 5-HT2C Receptors in Hypothalamus. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bárbara, A.; Aceves, J.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. Histamine H1 Receptors in Rat Dorsal Raphe Nucleus: Pharmacological Characterisation and Linking to Increased Neuronal Activity. Brain Res. 2002, 954, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Jasso, L.-E.; Bahena-Trujillo, R.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. Histamine H1 Receptors and Inositol Phosphate Formation in Rat Thalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 225, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Reymann, K.G.; Brown, R.E. In Vivo Electrophysiological Investigations into the Role of Histamine in the Dentate Gyrus of the Rat. Neuroscience 1998, 84, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbach, O.; Brown, R.E.; Haas, H.L. Long-Term Increase of Hippocampal Excitability by Histamine and Cyclic AMP. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Tome, P.; Brera, B.; Arevalo, M.A.; de Ceballos, M.L. Beta-Amyloid 25–35 Inhibits Glutamate Uptake in Cultured Neurons and Astrocytes: Modulation of Uptake as a Survival Mechanism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 15, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P. Histamine receptors, agonists, and antagonists in health and disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 180, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzsimons, C.P.; Lazar-Molnar, E.; Tomoskozi, Z.; Buzás, E.; Rivera, E.S.; Falus, A. Histamine Deficiency Induces Tissue-Specific Down-regulation of Histamine H2 Receptor Expression in Histidine Decarboxylase Knockout Mice. FEBS Lett. 2001, 508, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, R.M.; Slack, B.E.; Wurtman, R.J.; Growdon, J.H. Release of Alzheimer Amyloid Precursor Derivatives Stimulated by Activation of Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Science 1992, 258, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedarzani, P.; Storm, J.F. Pka Mediates the Effects of Monoamine Transmitters on the K+ Current Underlying the Slow Spike Frequency Adaptation in Hippocampal Neurons. Neuron 1993, 11, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Roland, B.L.; Wilson, S.J.; Jiang, X.; Pyati, J.; Huvar, A.; Jackson, M.R.; Erlander, M.G. Cloning and Functional Expression of the Human Histamine H3 Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 55, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, C.; Heron, A.; Cochois, V.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Ligneau, X.; Schwartz, J.-C.; Arrang, J.-M. A Detailed Mapping of the Histamine H3 Receptor and Its Gene Transcripts in Rat Brain. Neuroscience 2002, 114, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.R.; Eriksson, K.S.; Brown, R.E.; Haas, H.L. The Mechanism of Spontaneous Firing in Histamine Neurons. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 124, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Delgado, D.; Torrent, A.; Gómez-Ramírez, J.; de Esch, I.; Blanco, I.; Ortiz, J. Constitutive Activity of H3 Autoreceptors Modulates Histamine Synthesis in Rat Brain through the CAMP/PKA Pathway. Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Werthwein, S.; Zentner, J. Histamine H3 Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of Noradrenaline Release in the Human Brain. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 13, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandina, P.; Giorgetti, M.; Bartolini, L.; Cecchi, M.; Timmerman, H.; Leurs, R.; Pepeu, G.; Giovannini, M.G. Inhibition of Cortical Acetylcholine Release and Cognitive Performance by Histamine H3 Receptor Activation in Rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 119, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Rhee, J.; Watanabe, T.; Akaike, N.; Akaike, N. Histaminergic Modulation of GABAergic Transmission in Rat Ventromedial Hypothalamic Neurones. J. Physiol. 2001, 534, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.E.; Haas, H.L. On the Mechanism of Histaminergic Inhibition of Glutamate Release in the Rat Dentate Gyrus. J. Physiol. 1999, 515, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garduño-Torres, B.; Treviño, M.; Gutiérrez, R.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. Pre-Synaptic Histamine H3 Receptors Regulate Glutamate, but Not GABA Release in Rat Thalamus. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, T.; Shibata, M.; Inoue, M.; Kaya, H.; Takahashi, H. Regulation of Substance P Release Mediated via Prejunctional Histamine H3 Receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 273, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.M.F.; Crossthwaite, A.J. Higher-Order Organization and Regulation of Adenylyl Cyclases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, G.; Bakker, R.A.; Leurs, R. Molecular Aspects of the Histamine H3 Receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Willigen, G.; Nieuwland, R.; Nürnberg, B.; Gorter, G.; Akkerman, J.-W.N. Negative Regulation of the Platelet Na+/H+ Exchanger by Trimeric G-Proteins: G-Protein Regulation of the Platelet NHE-1. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 7102–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E. Advances in H1-antihistamines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, M.; Bücheler, M.M.; Philipp, M.; Lohse, M.J.; Hein, L. Activation and Deactivation Kinetics of A2A- and A2C-Adrenergic Receptor-Activated G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying K+ Channel Currents. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47512–47517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drutel, G.; Peitsaro, N.; Karlstedt, K.; Wieland, K.; Smit, M.J.; Timmerman, H.; Panula, P.; Leurs, R. Identification of Rat H3 Receptor Isoforms with Different Brain Expression and Signaling Properties. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Clemente, C.; Osorio-Espinoza, A.; Escamilla-Sánchez, J.; Leurs, R.; Arias, J.-M.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. A Single-Point Mutation (Ala280Val) in the Third Intracellular Loop Alters the Signalling Properties of the Human Histamine H3 Receptor Stably Expressed in CHO-K1 Cells: A280V Mutation and H3 Receptor Function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, G.; Sallmen, T.; Passani, M.B.; Mariottini, C.; Wendelin, D.; Lozada, A.; Marle, A.V.; Navis, M.; Blandina, P.; Bakker, R.A.; et al. The Akt/GSK-3beta Axis as a New Signaling Pathway of the Histamine H(3) Receptor. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgaud, J.L.; Oudart, N. Bronchodilatation of Guinea-Pig Perfused Bronchioles Induced by the H3-Receptor for Histamine: Role of Epithelium. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 109, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, M.; Alpert, R.; Jenkinson, S.; Gladue, R.P.; Foo, S.; Trim, S.; Peter, B.; Trevethick, M.; Fidock, M. Identification of A Histamine H4 Receptor on Human Eosinophils—Role in Eosinophil Chemotaxis. J. Recept. Signal. Transduct. 2002, 22, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passani, M.B.; Blandina, P. Histamine receptors in the CNS as Targets for Therapeutic Intervention. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Itadani, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Ohta, M.; Tanaka, K. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a New Human Histamine Receptor, HH4R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Shapiro, D.A.; George, S.R.; Setola, V.; Lee, D.K.; Cheng, R.; Rauser, L.; Lee, S.P.; Lynch, K.R.; Roth, B.L.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Member of the Histamine Receptor Family. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Michalovich, D.; Wu, H.-L.; Tan, K.B.; Dytko, G.M.; Mannan, I.J.; Boyce, R.; Alston, J.; Tierney, L.A.; Li, X.; et al. Cloning, Expression, and Pharmacological Characterization of a Novel Human Histamine Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, E.W.E.; Araaj, B.A.; Prabhata, W.R.; Prihandoko, R.; Nijmeijer, S.; Tobin, A.B.; Leurs, R.; Vischer, H.F. Differential Role of Serines and Threonines in Intracellular Loop 3 and C-Terminal Tail of the Histamine H4 Receptor in β-Arrestin and G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase Interaction, Internalization, and Signaling. Farmacología ACS Cienc. Traslacional 2020, 3, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakhova, M.I.; Nikkel, A.L.; Manelli, A.M.; Hsieh, G.C.; Esbenshade, T.A.; Brioni, J.D.; Bitner, R.S. Localization of Histamine H4 Receptors in the Central Nervous System of Human and Rat. Brain Res. 2009, 1250, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Chazot, P.L.; Cowart, M.; Gutzmer, R.; Leurs, R.; Liu, W.L.S.; Stark, H.; Thurmond, R.L.; Haas, H.L. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCVIII. Histamine Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 601–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, D.M.; Krz, M.; Lipnik-Stangelj, M. Histamine and Astrocyte Function. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerit, S.; Fidan, E.; Macas, J.; Czupalla, C.J.; Figueiredo, R.; Vijikumar, A.; Yalcin, B.H.; Thom, S.; Winter, P.; Gerhardt, H.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Wnt Growth Factors are Required for Endothelial Blood-Brain Barrier Maintenance. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Yanai, K. Histamine Clearance Through Polyspecific Transporters in the Brain. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 241, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.S.; Kitahama, K.; Fort, P.; Panula, P.; Denney, R.M.; Jouvet, M. Histaminergic System in the Cat Hypothalamus with Reference to Type B Monoamine Oxidase. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 330, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Bao, A.-M.; Swaab, D.F. Changes in Histidine Decarboxylase, Histamine N-Methyltransferase and Histamine Receptors in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. In Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Hattori, Y., Seifert, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 241, pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yanai, K. Analysis of brain histamine clearance using genetically engineered mice. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi 2018, 152, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martin, E.; Martínez, C.; Serrador, M.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Navacerrada, F.; Esguevillas, G.; García-Albea, E.; Agúndez, J.A.G.; Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J. Polimorfismo de histamina-N-metiltransferasa y riesgo de migraña. Headeach 2008, 48, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; García-Martín, E.; Agúndez, J.A.G. Thr105Ile (Rs11558538) Polymorphism in the Histamine N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) Gene and Risk for Parkinson Disease: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Association of Histamine N-Methyltransferase Thr105Ile Polymorphism with Parkinson’s Disease and Schizophrenia in Han Chinese: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; McCann, D.; Grimshaw, K.; Parker, K.M.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.; Holloway, J.W.; Warner, J.O. The Role of Histamine Degradation Gene Polymorphisms in Moderating the Effects of Food Additives on Children’s ADHD Symptoms. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meza-Velázquez, R.; López-Márquez, F.; Espinosa-Padilla, S.; Rivera-Guillen, M.; Ávila-Hernández, J.; Rosales-González, M. Association of Diamine Oxidase and Histamine N-Methyltransferase Polymorphisms with Presence of Migraine in a Group of Mexican Mothers of Children with Allergies. Neurologia 2017, 32, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasović-Šušnjara, I.; Palada, V.; Marinović-Terzić, I.; Mimica, N.; Marin, J.; Muck-Seler, D.; Mustapić, M.; Presečki, P.; Pivac, N.; Folnegović-Šmalc, V.; et al. No Association between Histamine N-Methyltransferase Functional Polymorphism Thr105Ile and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 489, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellermayer, B.; Polgar, N.; Pal, J.; Banati, M.; Maasz, A.; Kisfali, P.; Hosszu, Z.; Juhasz, A.; Jensen, H.B.; Tordai, A.; et al. Association of Myasthenia Gravis with Polymorphisms in the Gene of Histamine N-Methyltransferase. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, R.; Harrington, C.; Mahler, A.; Beresford, I.; Maruff, P.; Lowy, M.; Nicholls, A.; Boardley, R.; Berges, A.; Nathan, P.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, 16-Week Study of the H3 Receptor Antagonist, GSK239512 as a Monotherapy in Subjects with Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2014, 11, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provensi, G.; Costa, A.; Passani, M.B.; Blandina, P. Donepezil, an Acetylcholine Esterase inhibitor, and ABT-239, a Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist/Inverse Agonist, Require the Integrity of Brain Histamine System to Exert Biochemical and Procognitive Effects in the Mouse. Neuropharmacology 2016, 109, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gálvez, A.M.; Arias-Montaño, J.A. Isoformas del Receptor a Histamina H3 Humano: Generación, Expresión en el Sistema Nervioso Central (SNC) e Implicaciones Funcionales [Isoforms of the Human Histamine H3 Receptor: Generation, Expression in the Central Nervous System and Functional Implications]. Gac Med. Mex. 2016, 152, 94–102. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zuo, Y.X.; Jiang, R.T. Astrocyte Morphology: Diversity, Plasticity, and Role in Neurological Diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yanai, K. Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafałowska, U.; Waśkiewicz, J.; Albrecht, J. Is Neurotransmitter Histamine Predominantly Inactivated in Astrocytes? Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 80, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, E.; Sakurai, E.; Oreland, L.; Nishiyama, S.; Kato, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yanai, K. Evidence for the Presence of Histamine Uptake into the Synaptosomes of Rat Brain. Pharmacology 2006, 78, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, K.M.; Henry, D.P. Histamine N-Methyltransferase. In Neurotransmitter Enzymes. Neuromethods; (Series 1: Neurochemistry); Boulton, A.A., Baker, G.B., Yu, P.H., Eds.; Humana Press: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1986; Volume 5, pp. 147–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Mori, S.; Takahashi, H.K.; Kanke, T.; Wake, H.; Nishibori, M. Effect of Amodiaquine, a Histamine N-Methyltransferase Inhibitor, on Propionibacterium Acnes and Lipopolysaccharide-induced Hepatitis in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 558, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitanaka, N.; Hall, F.S.; Kobori, S.; Kushiha, S.; Oyama, H.; Sasaoka, Y.; Takechi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Tomita, K.; Igarashi, K.; et al. Metoprine, a Histamine N-methyltransferase Inhibitor, Attenuates Methamphetamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion via Activation of Histaminergic Neurotransmission in Mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 209, 173257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duch, D.S.; Bowers, S.W.; Nichol, C.A. Elevation of Brain Histamine Levels by Diaminopyrimidine Inhibitors of Histamine N-Methyl Transferase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1978, 27, 1507–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.C.; Gertner, S.B. Evidence for a Role of Endogenous Histamine in Central Cardiovascular Regulation: Inhibition of Histamine-N-Methyltransferase by SKF 91488. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1981, 216, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Taraschenko, O.D.; Barnes, W.G.; Herrick-Davis, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Boyd, D.L.; Hough, L.B. Actions of Tacrine and Galanthamine on Histamine-N-methyltransferase. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 27, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, J.S.; Da Silva, W.C.; Da Silveira, C.K.B.; Köhler, C.A.; Izquierdo, I.; Cammarota, M. Histamine Facilitates Consolidation of Fear Extinction. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nurhan, A.D.; Gani, M.A.; Budiatin, A.S.; Siswodihardjo, S.; Khotib, J. Molecular Docking Studies of Nigella sativa L and Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb Secondary Metabolites Against Histamine N-methyltransferase with their ADMET Prediction. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 32, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, W.; Sawato, T.; Kitano, H.; Shinozaki, Y.; Arisawa, M.; Saito, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Optically Active Iodohelicene Derivatives Exhibit Histamine N-methyl Transferase Inhibitory Activity. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.R.; Sawada, K.; Nishibori, M.; Cheng, X. Structural Basis for Inhibition of Histamine N-methyltransferase by Various Drugs. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passani, M.B.; Bacciottini, L.; Mannaioni, P.F.; Blandina, P. Central Histaminergic System and Cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajda, M.; Łażewska, D.; Godyń, J.; Zaręba, P.; Kuder, K.; Hagenow, S.; Łątka, K.; Stawarska, E.; Stark, H.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. Search for New Multi-target Compounds Against Alzheimer’s Disease Among Histamine H3 Receptor Ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrée, O.; Buschert, J.; Zhang, W.; Arolt, V.; Dere, E.; Zlomuzica, A. Impaired Spatial Learning and Reduced Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Histamine H1-Receptor Knockout Mice. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, C.; Song, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; You, J.; Sun, F.; et al. Activation of CREB-mediated autophagy by thioperamide ameliorates β-amyloid pathology and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haig, G.M.; Pritchett, Y.; Meier, A.; Othman, A.A.; Hall, C.; Gault, L.M.; Lenz, R.A. A Randomized Study of H3 Antagonist ABT-288 in Mild-To-Moderate Alzheimer’s Dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Ipponi, A.; Bartolini, A.; Schunack, W. Antiamnesic Effect of Metoprine and of Selective Histamine H(1) Receptor Agonists in a Modified Mouse Passive Avoidance Test. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 288, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knakker, B.; Oláh, V.; Trunk, A.; Lendvai, B.; Lévay, G.; Hernadi, I. Delay-dependent Cholinergic Modulation of Visual Short-term Memory in Rhesus Macaques. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 396, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provensi, G.; Costa, A.; Izquierdo, I.; Blandina, P.; Passani, M.B. Brain Histamine Modulates Recognition Memory: Possible Implications in Major Cognitive Disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.L.; Dai, H.B.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z. Reversing effect of histamine on neurotoxicity induced by beta-amyloid1-42. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2007, 36, 146–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cumming, P.; Vincent, S.R. Inhibition of Histamine-N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) by Fragments of 9-Amino-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroacridine (Tacrine) and by β-Carbolines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 44, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawaj, M.; Burban, A.; Davenas, E.; Arrang, J.-M. Activation of Brain Histaminergic Neurotransmission: A Mechanism for Cognitive Effects of Memantine in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, G.; Velasco, I.; García-López, G.; Solís, K.H.; Flores-Herrera, H.; Díaz, N.F.; Molina-Hernández, A. Histamine Is Required during Neural Stem Cell Proliferation to Increase Neuron Differentiation. Neuroscience 2012, 216, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurič, D.M.; Mele, T.; Carman-Kržan, M. Involvement of Histaminergic Receptor Mechanisms in the Stimulation of NT-3 Synthesis in Astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Hernández, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, G.; Escobedo-Ávila, I.; Velasco, I. Histamine Up-Regulates Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 and Increases FOXP2 Neurons in Cultured Neural Precursors by Histamine Type 1 Receptor Activation: Conceivable Role of Histamine in Neurogenesis during Cortical Development In Vivo. Neural. Dev. 2013, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Hernández, A.; Velasco, I. Histamine Induces Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Neuronal Differentiation by Activation of Distinct Histamine Receptors. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpy, M.J.; Bogan, R.K. Update on the Pharmacologic Management of Narcolepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Implications. Sleep. Med. 2020, 68, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Siegel, J.M. Interactions of the Histamine and Hypocretin Systems in CNS Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Dogra, S.; Sona, C.; Umrao, D.; Rashid, M.; Singh, S.K.; Wahajuddin, M.; Yadav, P.N. Chronic Histamine 3 receptor Antagonism Alleviates Depression Like Conditions in Mice Via Modulation of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor and Hypothalamus-pituitary Aadrenal Axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 101, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deindl, P.; Peri-Jerkan, S.; Deichmann, K.; Niggemann, B.; Lau, S.; Sommerfeld, C.; Sengler, C.; Muller, S.; Wahn, U.; Nickel, R.; et al. No Association of Histamine-N-methyltransferase Polymorphism with Asthma or Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness in Two German Pediatric Populations. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 16, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Mei, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J. C314T Polymorphism in Histamine N-methyltransferase Gene and Susceptibility to Duodenal Ulcer in Chinese population. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 389, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Inhibitor | IC50 | Effects on Histamine Brain Levels | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
Metoprine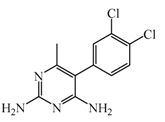 | 100 nM | Metoprine administered at 10 mg/kg (orally) can increase histamine levels, being the highest 5 h after administration and correlates with peak drug levels in the brain. Histamine levels are still elevated more than 2-fold 4 h after administration of the drug. | [144] |
Amodiaquine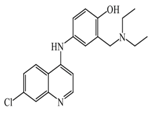 | 400 nM | Antimalarian agent, potent HNMT inhibitor by in vitro studies. However, amodiquine did not change the endogenous histamine level in the rat brain. | [148] |
Quinacrine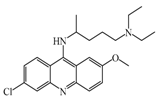 | 160 nM | Quinacrine, a drug that inhibits HNMT in vitro, has little or no effect on the levels in vivo of histamine. | [149] |
Etoprine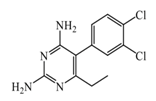 | 760 nM | Etoprine inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Etoprine can cross the BBB; however, its effect on histamine brain level has not been explored. | [150] |
Dimaprit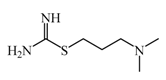 | 8 μM | Dimaprit, an H2R antagonist, is a potent HNMT inhibitor. Dimatiprit increases histamine brain levels after intracerebroventricularly administration in rats. | [151] |
SKF91488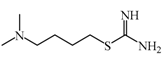 | 1.85 μM | Due to the low permeability of the BBB SKF91488, research for this compound has been limited. | [152] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Clemente, C.; Nicolás-Vázquez, M.I.; Mera Jiménez, E.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M. Inhibition of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase as a Possible Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101408
Flores-Clemente C, Nicolás-Vázquez MI, Mera Jiménez E, Hernández-Rodríguez M. Inhibition of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase as a Possible Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(10):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101408
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Clemente, Cecilia, María Inés Nicolás-Vázquez, Elvia Mera Jiménez, and Maricarmen Hernández-Rodríguez. 2021. "Inhibition of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase as a Possible Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease" Biomolecules 11, no. 10: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101408
APA StyleFlores-Clemente, C., Nicolás-Vázquez, M. I., Mera Jiménez, E., & Hernández-Rodríguez, M. (2021). Inhibition of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase as a Possible Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules, 11(10), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101408








