Monitoring the Levels of Cellular NF-?B Activation States
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Brief Description of the Core NF-κB Pathways and Their Components
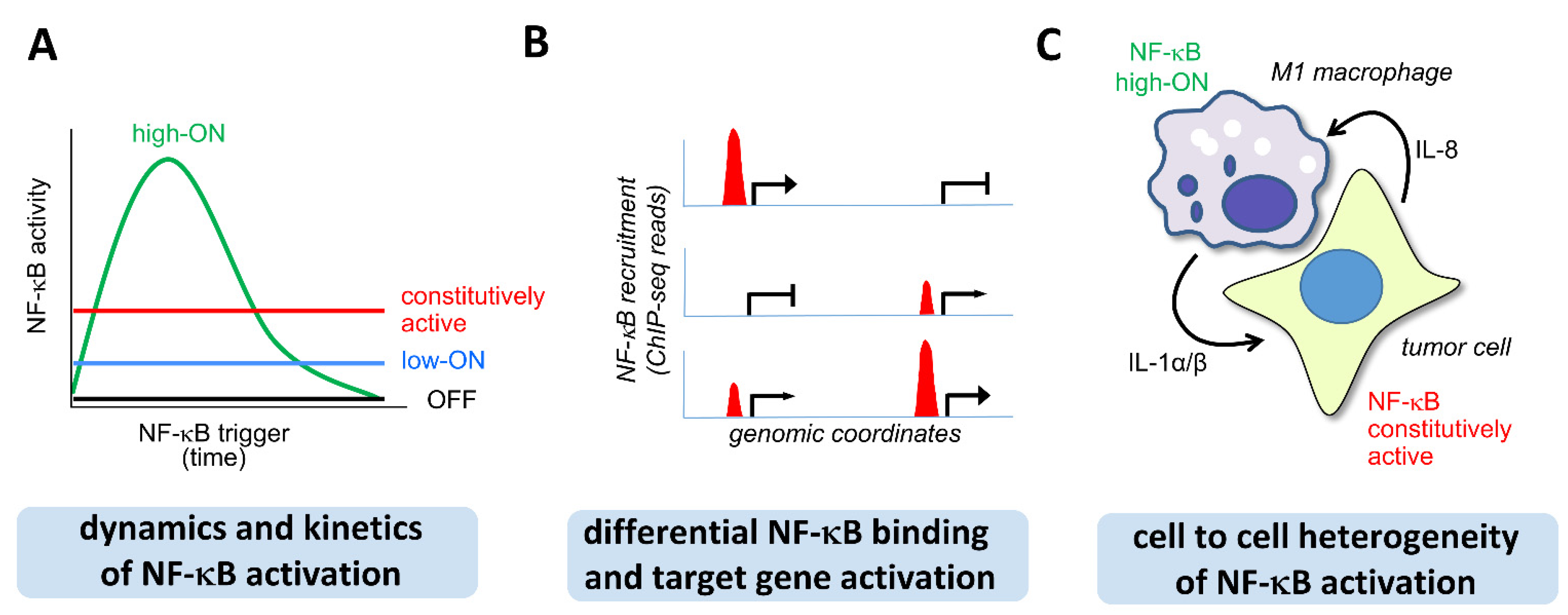
1.2. The Concept of Three Layers of NF-κB Activity
2. Determination of NF-κB Activity
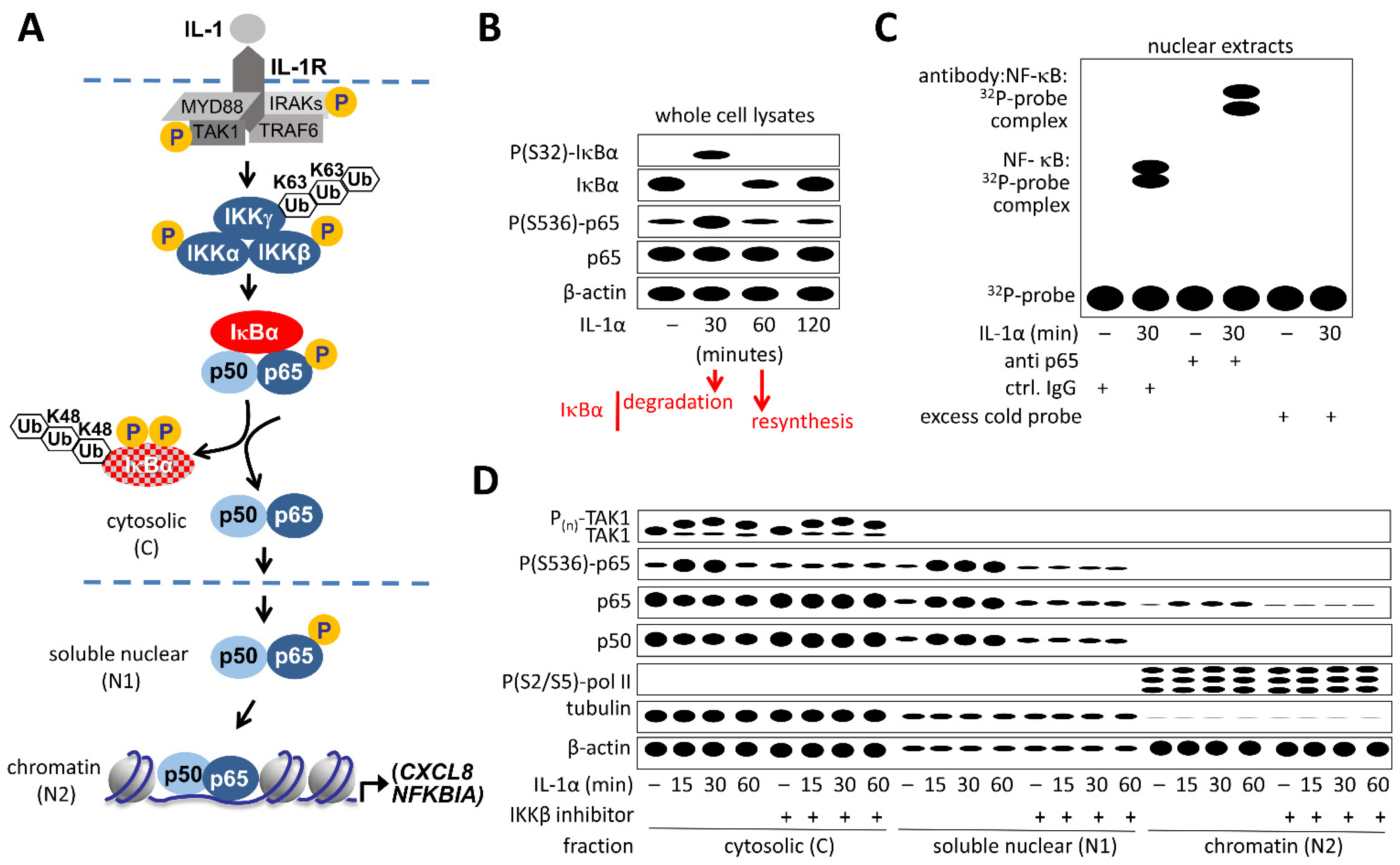
2.1. Detection of NF-κB Pathway Proteins
2.2. Detection of DNA-Bound NF-κB
2.3. Detection of Post-Translational Modifications of NF-κB Pathway Components
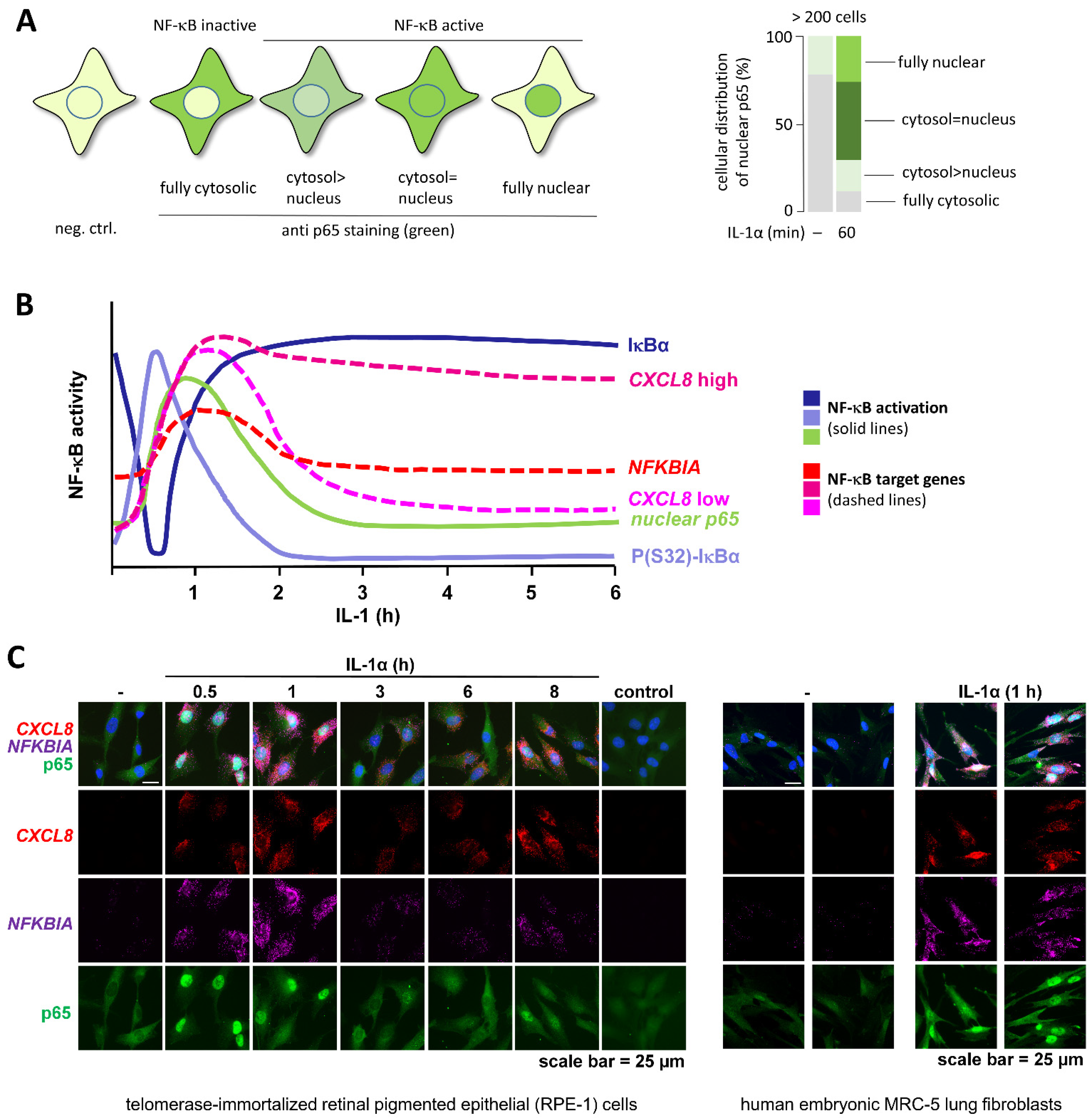
2.4. Detection of Subcellular Localization of NF-κB
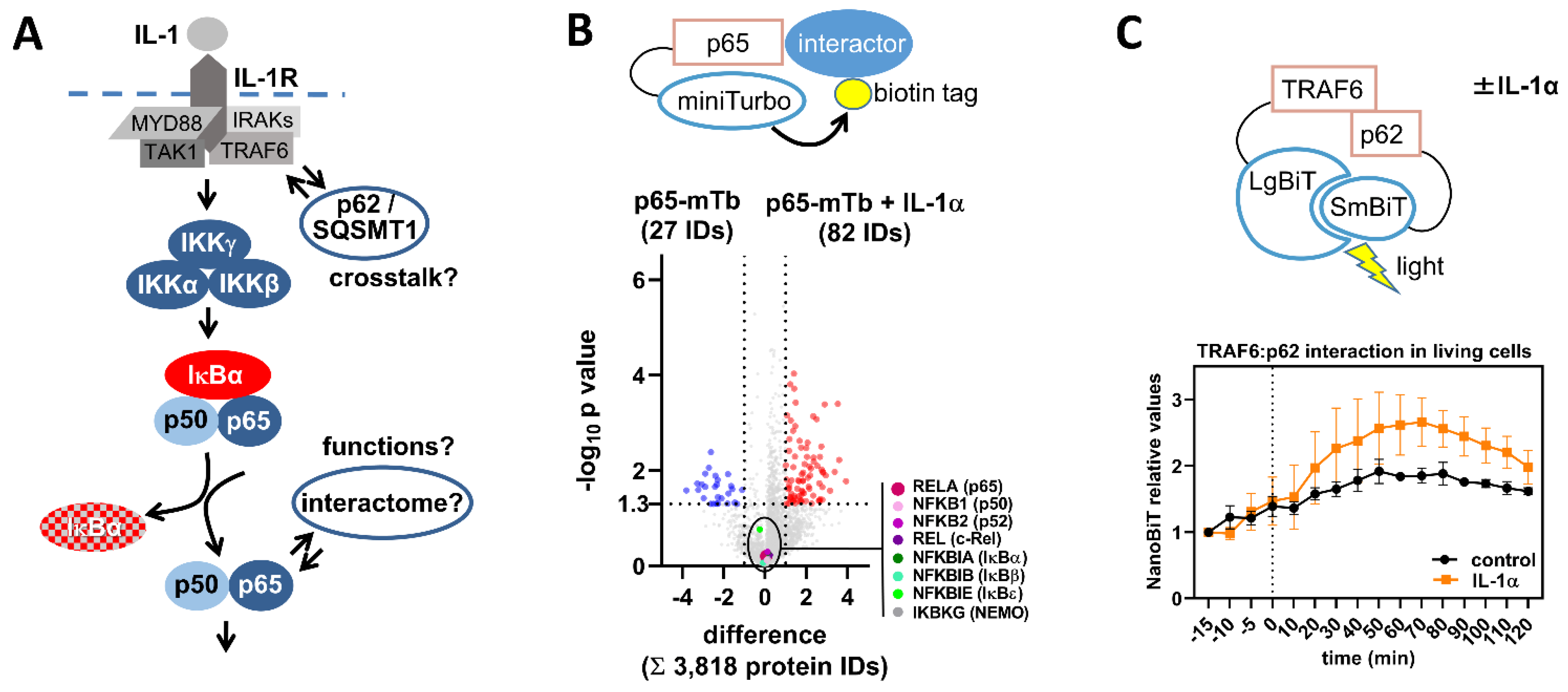
2.5. Detecting NF-κB Activation by Changes in Protein/Protein Interactions
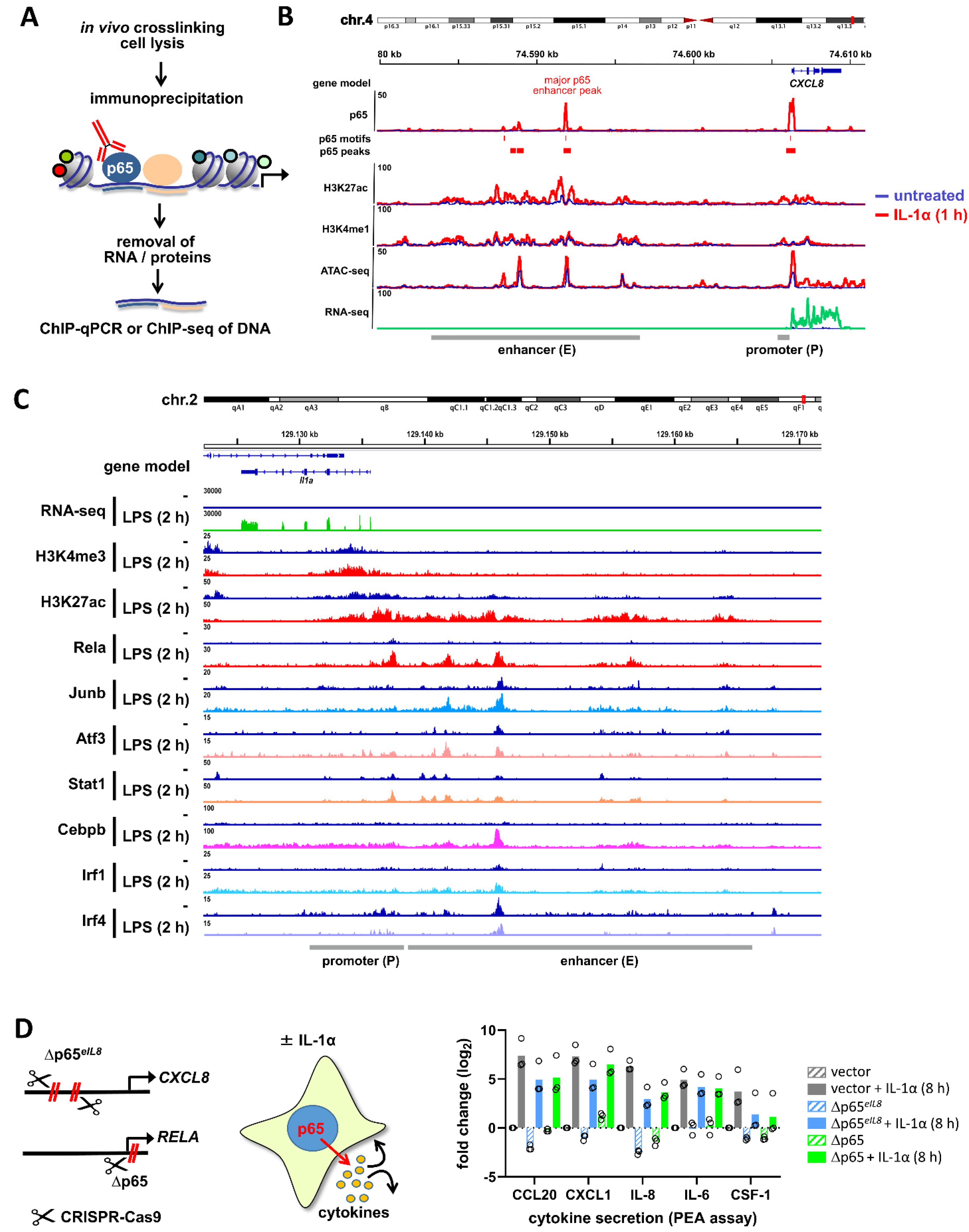
2.6. Detection of NF-κB-Binding in the Chromatin Environment
2.7. Detection of NF-κB-Mediated Gene Expression beyond mRNA
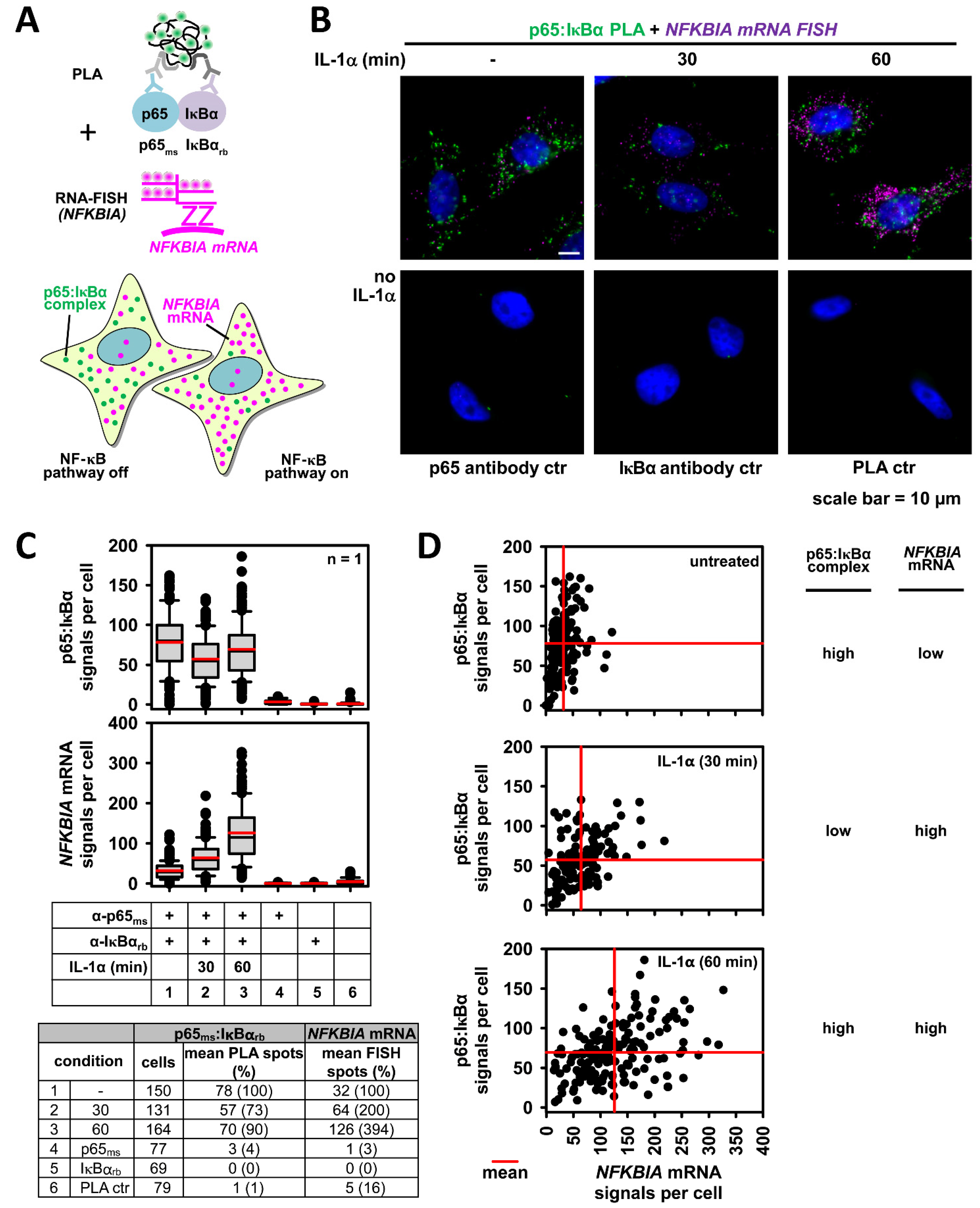
2.8. Advanced Analysis of NF-κB Activation States: Single Cell Detection of NF-κB Protein/Protein Interactions Together with mRNA Expression of NF-κB Target Genes
3. Concluding Remarks
- (1)
- Time-dependent and stimulus-induced degradation and re-synthesis of IκBα
- (2)
- Increase in nuclear p50 and p65
- (3)
- Binding of p50 or p65 to the promoter of NFKBIA (the gene encoding IκBα)
- (4)
- Induced mRNA expression of NFKBIA and other prototypical NF-κB target genes (CXCL8, IL6, TNFAIP3)
- (5)
- Impaired inducible mRNA expression in cells with reduced p65 or p50 protein levels
- (6)
- smRNA-FISH (with or without p50 or p65 IF or p65/IκBα PLA)
- (7)
- ChIP-seq to determine direct regulation of NF-κB target genes
- (1)
- Assessment of the activation status of other signaling systems (JNK, p38, ERK, JAK/STATs, ER stress)
- (2)
- Phosphorylation of IKKα/IKKβ
- (3)
- Phosphorylation of p65 at Ser536 or Ser468
- (4)
- Chromatin accessibility of NF-κB sites in enhancers or promoters of target genes
- (5)
- Motif analyses of NF-κB elements and composite elements
- (6)
- Determination of repressive or active histone marks flanking NF-κB elements
- (7)
- Co-recruitment of typical NF-κB interacting transcription factors
- (8)
- Co-recruitment of transcriptional coactivators/repressors
- (9)
- Genome-wide profiling of mRNA expression in cells lacking NF-κB subunits
- (10)
- Application of protein kinase inhibitors, e.g., TAK1 or IKK inhibitors
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, R.; Baltimore, D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 1986, 46, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-kappaB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D. Post-translational modifications regulating the activity and function of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6717–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smale, S.T. Dimer-specific regulatory mechanisms within the NF-kappaB family of transcription factors. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Stilmann, M.; Arslan, S.C.; Khanna, K.K.; Dittmar, G.; Scheidereit, C. A cytoplasmic ATM-TRAF6-cIAP1 module links nuclear DNA damage signaling to ubiquitin-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, E.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Delhase, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Karin, M. The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for IkappaB phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. Cell 1997, 91, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanarek, N.; London, N.; Schueler-Furman, O.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Ubiquitination and degradation of the inhibitors of NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb.. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathes, E.; O’Dea, E.L.; Hoffmann, A.; Ghosh, G. NF-kappaB dictates the degradation pathway of IkappaBalpha. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senftleben, U.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, G.; Greten, F.R.; Krahn, G.; Bonizzi, G.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C.; et al. Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science 2001, 293, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, F.; Schmitz, M.L. Autoregulatory feedback loops terminating the NF-kappaB response. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertz, I.; Dixit, V. A20—A bipartite ubiquitin editing enzyme with immunoregulatory potential. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 809, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Verstrepen, L.; Verhelst, K.; van Loo, G.; Carpentier, I.; Ley, S.C.; Beyaert, R. Expression, biological activities and mechanisms of action of A20 (TNFAIP3). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.C.; Ganchi, P.A.; Ballard, D.W.; Greene, W.C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: Evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science 1993, 259, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.L.; Fujita, T.; Liou, H.C.; Nolan, G.P.; Baltimore, D. The p65 subunit of NF-kappa B regulates I kappa B by two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerre, S.; Corley, R.B. Constitutive nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B in B cells in the absence of I kappa B degradation. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt, C.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Neumann, H.; Wekerle, H.; Baeuerle, P.A. Constitutive NF-kappa B activity in neurons. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 3981–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basavarajappa, S.C.; Ramakrishnan, P. Regulation of B-cell function by NF-kappaB c-Rel in health and disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3325–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichy, E.D.; Ma, N.; Sidibe, D.; Loro, E.; Kocan, J.; Chen, D.Z.; Khurana, T.S.; Hasty, P.; Mourkioti, F. Persistent NF-kappaB activation in muscle stem cells induces proliferation-independent telomere shortening. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paun, A.; Claudio, E.; Siebenlist, U.K. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during early bone marrow development results in loss of B cells at the pro-B-cell stage. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Phelan, J.D.; Wright, G.W.; Haupl, B.; Huang, D.W.; Shaffer, A.L., 3rd; Young, R.M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yu, X.; et al. Regulation of B cell receptor-dependent NF-kappaB signaling by the tumor suppressor KLHL14. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6092–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracht, M.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Schmitz, M.L. Mutual regulation of metabolic processes and proinflammatory NF-kappaB signaling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, E.L.; Barken, D.; Peralta, R.Q.; Tran, K.T.; Werner, S.L.; Kearns, J.D.; Levchenko, A.; Hoffmann, A. A homeostatic model of IkappaB metabolism to control constitutive NF-kappaB activity. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 8, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Neriah, Y.; Karin, M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.; Charles, K.A.; Mantovani, A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakshatri, H.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Martin, D.A.; Goulet, R.J., Jr.; Sledge, G.W., Jr. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natoli, G.; Saccani, S.; Bosisio, D.; Marazzi, I. Interactions of NF-kappaB with chromatin: The art of being at the right place at the right time. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Natarajan, R. PU.1 and C/EBP(alpha) synergistically program distinct response to NF-kappaB activation through establishing monocyte specific enhancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5290–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Hitz, B.C.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Kagda, M.S.; Lam, B.; Myers, Z.; Sud, P.; Jou, J.; Lin, K.; et al. New developments on the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) data portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D882–D889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, S.; Meier-Soelch, J.; Kracht, M.; Schmitz, M.L. Regulation of Transcription Factor NF-kappaB in Its Natural Habitat: The Nucleus. Cells 2021, 10, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazzi, I.; Greenbaum, B.D.; Low, D.H.P.; Guccione, E. Chromatin dependencies in cancer and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Pittol, J.M.; Oruba, A.; Mittler, G.; Saccani, S.; van Essen, D. Zbtb7a is a transducer for the control of promoter accessibility by NF-kappa B and multiple other transcription factors. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diermeier, S.; Kolovos, P.; Heizinger, L.; Schwartz, U.; Georgomanolis, T.; Zirkel, A.; Wedemann, G.; Grosveld, F.; Knoch, T.A.; Merkl, R.; et al. TNFalpha signalling primes chromatin for NF-kappaB binding and induces rapid and widespread nucleosome repositioning. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogatsky, I.; Adelman, K. Preparing the First Responders: Building the Inflammatory Transcriptome from the Ground Up. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smale, S.T.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Natoli, G. Chromatin contributions to the regulation of innate immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoglio, F.; Simonatto, M.; Polletti, S.; Liu, X.; Smale, S.T.; Barozzi, I.; Natoli, G. Dissection of acute stimulus-inducible nucleosome remodeling in mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harper, C.V.; Woodcock, D.J.; Lam, C.; Garcia-Albornoz, M.; Adamson, A.; Ashall, L.; Rowe, W.; Downton, P.; Schmidt, L.; West, S.; et al. Temperature regulates NF-kappaB dynamics and function through timing of A20 transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5243–E5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashall, L.; Horton, C.A.; Nelson, D.E.; Paszek, P.; Harper, C.V.; Sillitoe, K.; Ryan, S.; Spiller, D.G.; Unitt, J.F.; Broomhead, D.S.; et al. Pulsatile stimulation determines timing and specificity of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Science 2009, 324, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zambrano, S.; Loffreda, A.; Carelli, E.; Stefanelli, G.; Colombo, F.; Bertrand, E.; Tacchetti, C.; Agresti, A.; Bianchi, M.E.; Molina, N.; et al. First Responders Shape a Prompt and Sharp NF-kappaB-Mediated Transcriptional Response to TNF-alpha. iScience 2020, 23, 101529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.W.; Pacholewska, A.; Patel, H.; Dashora, H.; Sung, M.H. Integrative analysis suggests cell type-specific decoding of NF-kappaB dynamics. Sci. Signal 2020, 13, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, J.J.; Chuang, Y.; Bagheri, N.; Leonard, J.N. Macrophages employ quorum licensing to regulate collective activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.A.; Yao, F.; Wong, J.J.; George, J.; Xu, H.; Chiu, K.P.; Sung, W.K.; Lipovich, L.; Vega, V.B.; Chen, J.; et al. Genome-wide mapping of RELA(p65) binding identifies E2F1 as a transcriptional activator recruited by NF-kappaB upon TLR4 activation. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wang, J. Characterization of genome-wide binding of NF-kappaB in TNFalpha-stimulated HeLa cells. Gene 2013, 526, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mitra, A.; Dojer, N.; Fu, S.; Rowicka, M.; Brasier, A.R. A probabilistic approach to learn chromatin architecture and accurate inference of the NF-kappaB/RelA regulatory network using ChIP-Seq. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7240–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garber, M.; Yosef, N.; Goren, A.; Raychowdhury, R.; Thielke, A.; Guttman, M.; Robinson, J.; Minie, B.; Chevrier, N.; Itzhaki, Z.; et al. A high-throughput chromatin immunoprecipitation approach reveals principles of dynamic gene regulation in mammals. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, F.; Li, Y.; Dixon, J.R.; Selvaraj, S.; Ye, Z.; Lee, A.Y.; Yen, C.A.; Schmitt, A.D.; Espinoza, C.A.; Ren, B. A high-resolution map of the three-dimensional chromatin interactome in human cells. Nature 2013, 503, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasowski, M.; Grubert, F.; Heffelfinger, C.; Hariharan, M.; Asabere, A.; Waszak, S.M.; Habegger, L.; Rozowsky, J.; Shi, M.; Urban, A.E.; et al. Variation in transcription factor binding among humans. Science 2010, 328, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Barrera, L.A.; Ersing, I.; Willox, B.; Schmidt, S.C.; Greenfeld, H.; Zhou, H.; Mollo, S.B.; Shi, T.T.; Takasaki, K.; et al. The NF-kappaB genomic landscape in lymphoblastoid B cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolovos, P.; Georgomanolis, T.; Koeferle, A.; Larkin, J.D.; Brant, L.; Nikolicc, M.; Gusmao, E.G.; Zirkel, A.; Knoch, T.A.; van Ijcken, W.F.; et al. Binding of nuclear factor kappaB to noncanonical consensus sites reveals its multimodal role during the early inflammatory response. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaestel, M.; Kotlyarov, A.; Kracht, M. Targeting innate immunity protein kinase signalling in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2009, 8, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Z.B.; Kofahl, B.; Beaudette, P.; Baum, K.; Ipenberg, I.; Weih, F.; Wolf, J.; Dittmar, G.; Scheidereit, C. Quantitative dissection and modeling of the NF-kappaB p100-p105 module reveals interdependent precursor proteolysis. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1756–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver Metzig, M.; Tang, Y.; Mitchell, S.; Taylor, B.; Foreman, R.; Wollman, R.; Hoffmann, A. An incoherent feedforward loop interprets NFkappaB/RelA dynamics to determine TNF-induced necroptosis decisions. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Leung, T.H.; Baltimore, D. Genetic analysis of NF-kappaB/Rel transcription factors defines functional specificities. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5530–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Levchenko, A.; Scott, M.L.; Baltimore, D. The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: Temporal control and selective gene activation. Science 2002, 298, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.; Park, S.; Kanno, T.; Franzoso, G.; Siebenlist, U. Mutual regulation of the transcriptional activator NF-kappa B and its inhibitor, I kappa B-alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2532–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Martin, R.; Vanhove, B.; Cheng, Q.; Hofer, E.; Csizmadia, V.; Winkler, H.; Bach, F.H. Cytokine-inducible expression in endothelial cells of an I kappa B alpha-like gene is regulated by NF kappa B. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2773–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiterer, S.S.; Meier-Soelch, J.; Georgomanolis, T.; Mizi, A.; Beyerlein, A.; Weiser, H.; Brant, L.; Mayr-Buro, C.; Jurida, L.; Beuerlein, K.; et al. Distinct IL-1alpha-responsive enhancers promote acute and coordinated changes in chromatin topology in a hierarchical manner. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnichenko, M.; Mikuda, N.; Hopken, U.E.; Kargel, E.; Uyar, B.; Tufan, A.B.; Milanovic, M.; Sun, W.; Krahn, I.; Schleich, K.; et al. Transcriptional repression of NFKBIA triggers constitutive IKK- and proteasome-independent p65/RelA activation in senescence. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourbakhsh, M.; Kalble, S.; Dorrie, A.; Hauser, H.; Resch, K.; Kracht, M. The NF-kappa b repressing factor is involved in basal repression and interleukin (IL)-1-induced activation of IL-8 transcription by binding to a conserved NF-kappa b-flanking sequence element. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4501–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jurida, L.; Soelch, J.; Bartkuhn, M.; Handschick, K.; Muller, H.; Newel, D.; Weber, A.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Schneider, H.; Bhuju, S.; et al. The Activation of IL-1-Induced Enhancers Depends on TAK1 Kinase Activity and NF-kappaB p65. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krappmann, D.; Scheidereit, C. Regulation of NF-kappa B activity by I kappa B alpha and I kappa B beta stability. Immunobiology 1997, 198, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinova, O.V.; Hoffmann, A.; Ghosh, G. The Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 proteins p105 and p100 function as the core of high-molecular-weight heterogeneous complexes. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poppe, M.; Wittig, S.; Jurida, L.; Bartkuhn, M.; Wilhelm, J.; Muller, H.; Beuerlein, K.; Karl, N.; Bhuju, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; et al. The NF-kappaB-dependent and -independent transcriptome and chromatin landscapes of human coronavirus 229E-infected cells. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zabel, U.; Baeuerle, P.A. Purified human I kappa B can rapidly dissociate the complex of the NF-kappa B transcription factor with its cognate DNA. Cell 1990, 61, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, U.; Schreck, R.; Baeuerle, P.A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Teixeira, A.; Oikonomopoulos, S.; Humburg, P.; Lone, I.N.; Saliba, D.; Siggers, T.; Bulyk, M.; Angelov, D.; Dimitrov, S.; et al. Extensive characterization of NF-kappaB binding uncovers non-canonical motifs and advances the interpretation of genetic functional traits. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Lu, D.; Ye, S.; Ye, H.; Zhu, L.; Feng, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Hu, Q. A simplified probe preparation for ELISA-based NF-kappaB activity assay. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2005, 65, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradere, J.P.; Hernandez, C.; Koppe, C.; Friedman, R.A.; Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. Negative regulation of NF-kappaB p65 activity by serine 536 phosphorylation. Sci. Signal 2016, 9, ra85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, H.; Chiba, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Sugita, T.; Toriumi, W. IkappaB kinases phosphorylate NF-kappaB p65 subunit on serine 536 in the transactivation domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30353–30356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buss, H.; Dorrie, A.; Schmitz, M.L.; Hoffmann, E.; Resch, K.; Kracht, M. Constitutive and interleukin-1-inducible phosphorylation of p65 NF-{kappa}B at serine 536 is mediated by multiple protein kinases including I{kappa}B kinase (IKK)-{alpha}, IKK{beta}, IKK{epsilon}, TRAF family member-associated (TANK)-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), and an unknown kinase and couples p65 to TATA-binding protein-associated factor II31-mediated interleukin-8 transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 55633–55643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pando, M.P.; Verma, I.M. Signal-dependent and -independent degradation of free and NF-kappa B-bound IkappaBalpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21278–21286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, P.; Jolly, M.K.; Jia, D.; Mooney, S.M.; Bhargava, A.; Kagohara, L.T.; Chen, Y.; Hao, P.; He, Y.; Veltri, R.W.; et al. Phosphorylation-induced conformational dynamics in an intrinsically disordered protein and potential role in phenotypic heterogeneity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2644–E2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanovic, M.; Kracht, M.; Schmitz, M.L. The cytokine-induced conformational switch of nuclear factor kappaB p65 is mediated by p65 phosphorylation. Biochem. J. 2014, 457, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabapathy, K.; Lane, D.P. Understanding p53 functions through p53 antibodies. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngo, K.A.; Kishimoto, K.; Davis-Turak, J.; Pimplaskar, A.; Cheng, Z.; Spreafico, R.; Chen, E.Y.; Tam, A.; Ghosh, G.; Mitchell, S.; et al. Dissecting the Regulatory Strategies of NF-kappaB RelA Target Genes in the Inflammatory Response Reveals Differential Transactivation Logics. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2758–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, M.L.; dos Santos Silva, M.A.; Altmann, H.; Czisch, M.; Holak, T.A.; Baeuerle, P.A. Structural and functional analysis of the NF-kappa B p65 C terminus. An acidic and modular transactivation domain with the potential to adopt an alpha-helical conformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 25613–25620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.L.; Baeuerle, P.A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 3805–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handschick, K.; Beuerlein, K.; Jurida, L.; Bartkuhn, M.; Muller, H.; Soelch, J.; Weber, A.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Schneider, H.; Scharfe, M.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 is a chromatin-bound cofactor for NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riedlinger, T.; Liefke, R.; Meier-Soelch, J.; Jurida, L.; Nist, A.; Stiewe, T.; Kracht, M.; Schmitz, M.L. NF-kappaB p65 dimerization and DNA-binding is important for inflammatory gene expression. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4188–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Stark, L.A. Crosstalk between NF-kappaB and Nucleoli in the Regulation of Cellular Homeostasis. Cells 2018, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jobe, F.; Simpson, J.; Hawes, P.; Guzman, E.; Bailey, D. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Sequesters NF-kappaB Subunit p65 to Cytoplasmic Inclusion Bodies To Inhibit Innate Immune Signaling. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01380–e01420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.E.; Ihekwaba, A.E.; Elliott, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Gibney, C.A.; Foreman, B.E.; Nelson, G.; See, V.; Horton, C.A.; Spiller, D.G.; et al. Oscillations in NF-kappaB signaling control the dynamics of gene expression. Science 2004, 306, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, E.W.; Chakraborty, S.; Presman, D.M.; Tomassoni Ardori, F.; Oh, K.S.; Kaileh, M.; Tessarollo, L.; Sung, M.H. Assaying Homodimers of NF-kappaB in Live Single Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, J.A.; Birbach, A.; Hofer-Warbinek, R.; Pengg, M.; Burner, U.; Furtmuller, P.G.; Binder, B.R.; de Martin, R. Dynamics of NF kappa B and Ikappa Balpha studied with green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion proteins. Investigation of GFP-p65 binding to DNa by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17035–17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birbach, A.; Gold, P.; Binder, B.R.; Hofer, E.; de Martin, R.; Schmid, J.A. Signaling molecules of the NF-kappa B pathway shuttle constitutively between cytoplasm and nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10842–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwmeester, T.; Bauch, A.; Ruffner, H.; Angrand, P.O.; Bergamini, G.; Croughton, K.; Cruciat, C.; Eberhard, D.; Gagneur, J.; Ghidelli, S.; et al. A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmack, G.; Schorpp, K.; Kutzner, K.; Gehring, T.; Brenke, J.K.; Hadian, K.; Krappmann, D. YOD1/TRAF6 association balances p62-dependent IL-1 signaling to NF-kappaB. Elife 2017, 6, e22416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branon, T.C.; Bosch, J.A.; Sanchez, A.D.; Udeshi, N.D.; Svinkina, T.; Carr, S.A.; Feldman, J.L.; Perrimon, N.; Ting, A.Y. Efficient proximity labeling in living cells and organisms with TurboID. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, D.G.; Scott, K.L.; Campos, A.R.; Roux, K.J. Comparative Application of BioID and TurboID for Protein-Proximity Biotinylation. Cells 2020, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.I.; Jensen, S.C.; Noble, K.A.; Kc, B.; Roux, K.H.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Roux, K.J. An improved smaller biotin ligase for BioID proximity labeling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.I.; Roux, K.J. Filling the Void: Proximity-Based Labeling of Proteins in Living Cells. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, T.J.; Zhao, J.; Stains, C.I. Utilizing split-NanoLuc luciferase fragments as luminescent probes for protein solubility in living cells. Methods Enzymol. 2019, 622, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, V.A.; Sun, J.M.; Li, L.; Davie, J.R. Chromatin immunoprecipitation: A tool for studying histone acetylation and transcription factor binding. Methods 2003, 31, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.C.; Bass, V.L.; Bullock, M.E.; Chavali, A.K.; Lee, R.E.C.; Mothes, W.; Gaudet, S.; Miller-Jensen, K. NF-kappaB-Chromatin Interactions Drive Diverse Phenotypes by Modulating Transcriptional Noise. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meers, M.P.; Bryson, T.D.; Henikoff, J.G.; Henikoff, S. Improved CUT&RUN chromatin profiling tools. Elife 2019, 8, e46314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya-Okur, H.S.; Wu, S.J.; Codomo, C.A.; Pledger, E.S.; Bryson, T.D.; Henikoff, J.G.; Ahmad, K.; Henikoff, S. CUT&Tag for efficient epigenomic profiling of small samples and single cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, M.D.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of an IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex. Cell 1998, 95, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaltschmidt, C.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Henkel, T.; Stockinger, H.; Baeuerle, P.A. Selective recognition of the activated form of transcription factor NF-kappa B by a monoclonal antibody. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1995, 376, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, M.J.; Cheung, K.; Falk, J.; Panagiotopoulos, A.C.; Cosimini, C.; O'Brien, S.; Teja-Putri, K.; Neill, G.; Deehan, D.J.; Young, D.A. Dynamic chromatin accessibility landscape changes following interleukin-1 stimulation. Epigenetics 2021, 16, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. ATAC-seq: A Method for Assaying Chromatin Accessibility Genome-Wide. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2015, 109, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Essen, D.; Engist, B.; Natoli, G.; Saccani, S. Two modes of transcriptional activation at native promoters by NF-kappaB p65. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziesche, E.; Kettner-Buhrow, D.; Weber, A.; Wittwer, T.; Jurida, L.; Soelch, J.; Muller, H.; Newel, D.; Kronich, P.; Schneider, H.; et al. The coactivator role of histone deacetylase 3 in IL-1-signaling involves deacetylation of p65 NF-kappaB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlsen, H.; Moskaug, J.O.; Fromm, S.H.; Blomhoff, R. In vivo imaging of NF-kappa B activity. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier-Soelch, J.; Jurida, L.; Weber, A.; Newel, D.; Kim, J.; Braun, T.; Schmitz, M.L.; Kracht, M. RNAi-Based Identification of Gene-Specific Nuclear Cofactor Networks Regulating Interleukin-1 Target Genes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, P. Intrinsic mRNA stability helps compose the inflammatory symphony. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P. Post-transcriptional control of cytokine production. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Baltimore, D. The stability of mRNA influences the temporal order of the induction of genes encoding inflammatory molecules. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nickel, W.; Rabouille, C. Mechanisms of regulated unconventional protein secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabouille, C. Pathways of Unconventional Protein Secretion. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuhler, K.; Schipper, K.; Poschmann, G. Unconventional protein secretion: The hidden pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom 2019, 1867, 140272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilman, T.; Michaloglou, C.; Vredeveld, L.C.; Douma, S.; van Doorn, R.; Desmet, C.J.; Aarden, L.A.; Mooi, W.J.; Peeper, D.S. Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell 2008, 133, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnas, O.; Jovanovic, M.; Eisenhaure, T.M.; Herbst, R.H.; Dixit, A.; Ye, C.J.; Przybylski, D.; Platt, R.J.; Tirosh, I.; Sanjana, N.E.; et al. A Genome-wide CRISPR Screen in Primary Immune Cells to Dissect Regulatory Networks. Cell 2015, 162, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assarsson, E.; Lundberg, M.; Holmquist, G.; Bjorkesten, J.; Thorsen, S.B.; Ekman, D.; Eriksson, A.; Rennel Dickens, E.; Ohlsson, S.; Edfeldt, G.; et al. Homogenous 96-plex PEA immunoassay exhibiting high sensitivity, specificity, and excellent scalability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredriksson, S.; Gullberg, M.; Jarvius, J.; Olsson, C.; Pietras, K.; Gustafsdottir, S.M.; Ostman, A.; Landegren, U. Protein detection using proximity-dependent DNA ligation assays. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr-Buro, C.; Schlereth, E.; Beuerlein, K.; Tenekeci, U.; Meier-Soelch, J.; Schmitz, M.L.; Kracht, M. Single-Cell Analysis of Multiple Steps of Dynamic NF-kappaB Regulation in Interleukin-1alpha-Triggered Tumor Cells Using Proximity Ligation Assays. Cancers 2019, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konermann, S.; Brigham, M.D.; Trevino, A.E.; Joung, J.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Barcena, C.; Hsu, P.D.; Habib, N.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Nishimasu, H.; et al. Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex. Nature 2015, 517, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamson, A.; Boddington, C.; Downton, P.; Rowe, W.; Bagnall, J.; Lam, C.; Maya-Mendoza, A.; Schmidt, L.; Harper, C.V.; Spiller, D.G.; et al. Signal transduction controls heterogeneous NF-kappaB dynamics and target gene expression through cytokine-specific refractory states. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meier-Soelch, J.; Mayr-Buro, C.; Juli, J.; Leib, L.; Linne, U.; Dreute, J.; Papantonis, A.; Schmitz, M.L.; Kracht, M. Monitoring the Levels of Cellular NF-?B Activation States. Cancers 2021, 13, 5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215351
Meier-Soelch J, Mayr-Buro C, Juli J, Leib L, Linne U, Dreute J, Papantonis A, Schmitz ML, Kracht M. Monitoring the Levels of Cellular NF-?B Activation States. Cancers. 2021; 13(21):5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215351
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeier-Soelch, Johanna, Christin Mayr-Buro, Jana Juli, Lisa Leib, Uwe Linne, Jan Dreute, Argyris Papantonis, M. Lienhard Schmitz, and Michael Kracht. 2021. "Monitoring the Levels of Cellular NF-?B Activation States" Cancers 13, no. 21: 5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215351
APA StyleMeier-Soelch, J., Mayr-Buro, C., Juli, J., Leib, L., Linne, U., Dreute, J., Papantonis, A., Schmitz, M. L., & Kracht, M. (2021). Monitoring the Levels of Cellular NF-?B Activation States. Cancers, 13(21), 5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215351







