Relationship between Dizziness and the Core Vestibular Projection Injury in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Clinical Evaluation
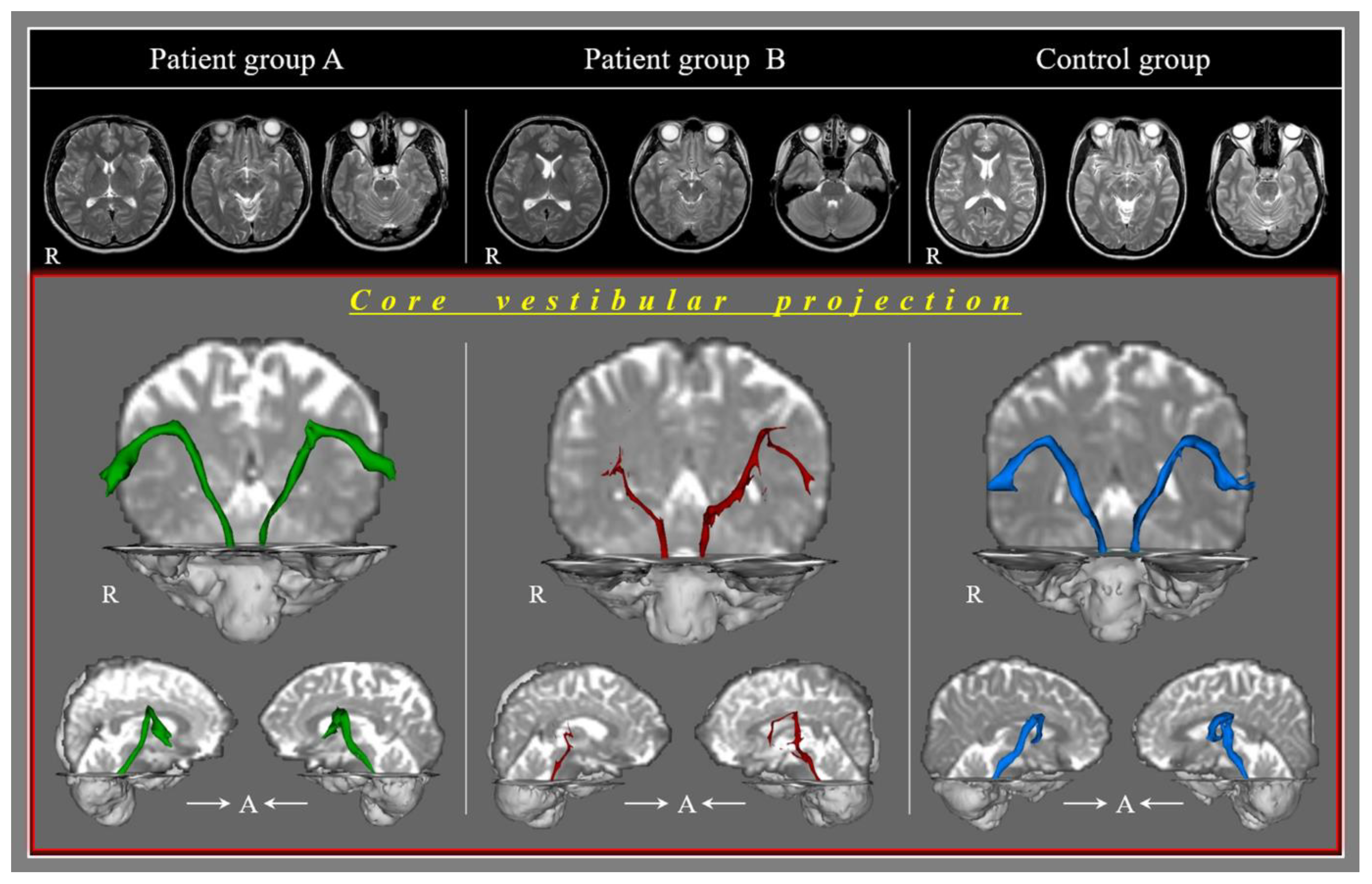
2.3. Diffusion Tensor Tractography
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maskell, F.; Chiarelli, P.; Isles, R. Dizziness after traumatic brain injury: Results from an interview study. Brain Inj. 2007, 21, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maskell, F.; Chiarelli, P.; Isles, R. Dizziness after traumatic brain injury: Overview and measurement in the clinical setting. Brain Inj. 2006, 20, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, R.; Sixt, E.; Landahl, S.; Rosenhall, U. Prevalence of dizziness and vertigo in an urban elderly population. J. Vestib. Res. 2004, 14, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.; Gottshall, K. Physical Therapy Management of the Patient with Vestibular Dysfunction from Head Trauma; Davis Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 504–529. [Google Scholar]
- Fife, T.D.; Giza, C. Posttraumatic vertigo and dizziness. In Seminars in Neurology; Thieme Medical Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 33, pp. 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer, M.E.; Gottshall, K.R.; Moore, R.; Balough, B.J.; Wester, D. Characterizing and treating dizziness after mild head trauma. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Blanke, O. The thalamocortical vestibular system in animals and humans. Brain Res. Rev. 2011, 67, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, A.; Sapru, H.N.; Siegel, H. Essential Neuroscience, 4th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, C.; Serino, A.; Blanke, O. The vestibular system: A spatial reference for bodily self-consciousness. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitier, M.; Besnard, S.; Smith, P.F. Vestibular pathways involved in cognition. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinder, M.E.; Newlands, S.D. Sensory convergence in the parieto-insular vestibular cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 111, 2445–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barmack, N.H. Central vestibular system: Vestibular nuclei and posterior cerebellum. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 60, 511–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, R.; Protti, D.A.; Camp, A.J. Vestibular Interactions in the Thalamus. Front. Neural. Circuits 2015, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maas, A.I.; Stocchetti, N.; Bullock, R. Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.P. Mild traumatic brain injury: Pathophysiology, natural history, and clinical management. Neurology 1995, 45, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruijk, J.R.; Twijnstra, A.; Leffers, P. Diagnostic criteria and differential diagnosis of mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2001, 15, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannsjo, M.; af Geijerstam, J.L.; Johansson, U.; Bring, J.; Borg, J. Prevalence and structure of symptoms at 3 months after mild traumatic brain injury in a national cohort. Brain Inj. 2009, 23, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, A.; de Boussard, C.; Edman, G.; Borg, J. Symptoms and disability until 3 months after mild TBI. Brain Inj. 2006, 20, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Tu, Y.K.; Hua, M.S.; Huang, S.J. The association between the postconcussion symptoms and clinical outcomes for patients with mild traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma 2007, 62, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikmen, S.; McLean, A.; Temkin, N. Neuropsychological and psychosocial consequences of minor head injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1986, 49, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamelian, L.; Feinstein, A. Outcome after mild to moderate traumatic brain injury: The role of dizziness. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, K.; Given, B.; Fabiano, R.; Schutte, D.; von Eye, A.; Davidson, S. Symptoms associated with mild traumatic brain injury/concussion: The role of bother. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2013, 45, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhilali, L.M.; Yaeger, K.; Collins, M.; Fakhran, S. Detection of central white matter injury underlying vestibulopathy after mild traumatic brain injury. Radiology 2014, 272, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keser, Z.; Hasan, K.M.; Mwangi, B.I.; Kamali, A.; Ucisik-Keser, F.E.; Riascos, R.F.; Yozbatiran, N.; Francisco, G.E.; Narayana, P.A. Diffusion tensor imaging of the human cerebellar pathways and their interplay with cerebral macrostructure. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirsch, V.; Keeser, D.; Hergenroeder, T.; Erat, O.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Brandt, T.; Dieterich, M. Structural and functional connectivity mapping of the vestibular circuitry from human brainstem to cortex. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1291–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Halsey, A.; Wang, M.X.; Tornroth-Horsefield, S.; Conner, A.C.; Badaut, J.; Iliff, J.J.; Bill, R.M. Emerging roles for dynamic aquaporin-4 subcellular relocalization in CNS water homeostasis. Brain 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Iliff, J.J.; Bill, R.M. Aquaporin 4 and glymphatic flow have central roles in brain fluid homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshuhri, M.S.; Gallagher, L.; Work, L.M.; Holmes, W.M. Direct imaging of glymphatic transport using H217O MRI. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e141159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, N.J.; Salman, M.M.; Pushie, M.J.; Hou, H.; Meher, V.; Herlo, R.; Peeling, L.; Kelly, M.E. The effects of trifluoperazine on brain edema, aquaporin-4 expression and metabolic markers during the acute phase of stroke using photothrombotic mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; MacDonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting aquaporin-4 subcellular localization to treat central nervous system edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.S.; Jang, S.H.; Kwon, J.W. Central vestibular disorder due to ischemic injury on the parieto-insular vestibular cortex in patients with middle cerebral artery territory infarction: Observational study. Medicine 2017, 96, e9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.S.; Jang, S.H.; Kwon, J.W. Lateral medullary syndrome following injury of the vestibular pathway to the core vestibular cortex: Diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurosci. Lett 2018, 665, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.G.; Chang, C.H.; Jang, S.H. Diagnosis of dizziness due to a core vestibular projection injury in a patient with intracerebral hemorrhage. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, N.S.; Crawford, S.; Wenden, F.J.; Moss, N.E.; Wade, D.T. The rivermead post concussion symptoms questionnaire: A measure of symptoms commonly experienced after head injury and its reliability. J. Neurol. 1995, 242, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23 (Suppl. 1), S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behrens, T.E.; Berg, H.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Rushworth, M.F.; Woolrich, M.W. Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? Neuroimage 2007, 34, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; L. Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; Volume 21, p. 567. [Google Scholar]
- Assaf, Y.; Pasternak, O. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: A review. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, E.; Agosta, F.; Rocca, M.A.; Caputo, D.; Filippi, M. Voxel-based analysis derived from fractional anisotropy images of white matter volume changes with aging. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povlishock, J.T.; Christman, C.W. The pathobiology of traumatically induced axonal injury in animals and humans: A review of current thoughts. J. Neurotrauma 1995, 12, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenton, M.E.; Hamoda, H.M.; Schneiderman, J.S.; Bouix, S.; Pasternak, O.; Rathi, Y.; Vu, M.A.; Purohit, M.P.; Helmer, K.; Koerte, I.; et al. A review of magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging findings in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 137–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H. Traumatic Axonal Injury in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury; InTech: London, UK, 2018; Volume 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Paniak, C.; Reynolds, S.; Phillips, K.; Toller-Lobe, G.; Melnyk, A.; Nagy, J. Patient complaints within 1 month of mild traumatic brain injury: A controlled study. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2002, 17, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, F.; Maurette, P.; Salmi, L.R.; Dartigues, J.F.; Vecsey, J.; Destaillats, J.M.; Erny, P. Prevalence of impairments 5 years after a head injury, and their relationship with disabilities and outcome. Brain Inj. 1996, 10, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartvigsen, J.; Boyle, E.; Cassidy, J.D.; Carroll, L.J. Mild traumatic brain injury after motor vehicle collisions: What are the symptoms and who treats them? A population-based 1-year inception cohort study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, S286–S294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, K.; Ichimaru, K.; Komagata, M.; Yamamoto, K. Cervical vertigo and dizziness after whiplash injury. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.T.; Lai, Y.J.; Chan, J.L. Vertigo with an isolated lesion in brainstem vestibular nucleus and nerve. Neurology 2010, 74, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.S.; Kwon, J.W.; Cho, I.H. Associations between age-related changes in the core vestibular projection pathway and balance ability: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Behav. Neurol. 2020, 2020, 2825108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, K.; Sakai, K.; Akazawa, K.; Yuen, S.; Nishimura, T. MR tractography: A review of its clinical applications. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salman, M.M.; Marsh, G.; Kusters, I.; Delince, M.; Di Caprio, G.; Upadhyayula, S.; de Nola, G.; Hunt, R.; Ohashi, K.G.; Gray, T.; et al. Design and validation of a human brain endothelial microvessel-on-a-chip open microfluidic model enabling advanced optical imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 573775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group A | Group B | Control Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male:female) | 7:8 | 8:20 | 11:18 |
| Mean age, years | 38.7 (10.6) | 39.5 (8.5) | 38.5 (7.3) |
| LOC, minutes | 0.8 (1.7) | 3.8 (7.7) | - |
| PTA, minutes | 4.6 (10.8) | 10.2 (16.9) | - |
| GCS score | 15.0 (0.0) | 15.0 (0.0) | - |
| Mean duration to DTI, months | 5.2 (4.9) | 7.1 (9.3) | - |
| Dizziness score | 0.8 (0.4) | 3.0 (0.7) | - |
| Group A | Group B | Control Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fractional anisotropy | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.43 |
| (0.03) | (0.07) | (0.03) | |
| Mean diffusivity | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.82 |
| (0.05) | (0.06) | (0.05) | |
| Tract volume | 595.53 | 345.59 † | 554.21 |
| (151.51) | (240.22) | (198.15) | |
| Correlation between the dizziness score and diffusion tensor tractography parameters | |||
| Fractional anisotropy | Mean diffusivity | Tract volume | |
| Core vestibular projection | 0.037 | 0.091 | −0.711 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, S.-H.; Bae, C.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kwon, H.-G. Relationship between Dizziness and the Core Vestibular Projection Injury in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112070
Jang S-H, Bae C-H, Kim J-W, Kwon H-G. Relationship between Dizziness and the Core Vestibular Projection Injury in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112070
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Sung-Ho, Chang-Hoon Bae, Jae-Woon Kim, and Hyeok-Gyu Kwon. 2021. "Relationship between Dizziness and the Core Vestibular Projection Injury in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112070
APA StyleJang, S.-H., Bae, C.-H., Kim, J.-W., & Kwon, H.-G. (2021). Relationship between Dizziness and the Core Vestibular Projection Injury in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112070






