Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Microbiome in Patients with Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
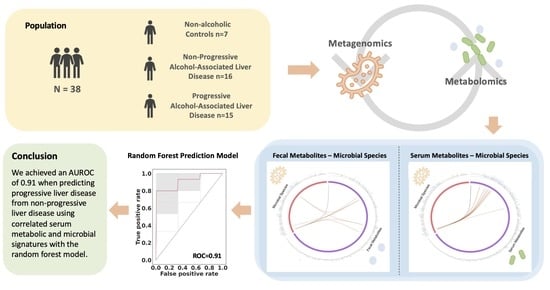
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Microbial Species, Fecal and Serum Metabolites in ALD Patients
2.3. Correlation between Fecal Metabolites and Microbial Species
2.4. Correlation between Serum Metabolites and Microbial Species
2.5. Changes in Correlated Metabolites and Gut Microbes in Three Groups
2.6. Prediction of Progressive Liver Disease Using Correlated Metabolites and Microbial Species
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Untargeted Metabolomics
4.3. Shotgun Metagenomics
4.4. Integrative Analysis of Microbiota and Metabolomics Data
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Shea, R.S.; Dasarathy, S.; McCullough, A.J. Alcoholic Liver Disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-S.; Fan, J.-G.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, B. The Global Burden of Liver Disease: The Major Impact of China. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Marcos, M.; Gattu, A.; Catalano, D.; Szabo, G. Acute Binge Drinking Increases Serum Endotoxin and Bacterial DNA Levels in Healthy Individuals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Shaikh, M.; Zhang, L.; Raeisi, S.; Aloman, C.; Preite, N.Z.; Donohue, T.M.; Fogg, L.; Keshavarzian, A. Diurnal Variations in Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Liver Pathology in Mice: Implications for Alcohol Binge. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 314, G131–G141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic Analyses of Alcohol Induced Pathogenic Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and the Effect of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, E.A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Rangwala, H.; Sikaroodi, M.; Naqvi, A.; Engen, P.A.; Kwasny, M.; Lau, C.K.; Keshavarzian, A. Colonic Microbiome Is Altered in Alcoholism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G966–G978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, R.D.; Dailey, A.; Zaidi, F.; Navarro, K.; Forsyth, C.B.; Mutlu, E.; Engen, P.A.; Keshavarzian, A. Alcohol Induced Alterations to the Human Fecal VOC Metabolome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puri, P.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Christensen, J.E.; Shah, V.H.; Kamath, P.S.; Gores, G.J.; Walker, S.; Comerford, M.; Katz, B.; Borst, A.; et al. The Circulating Microbiome Signature and Inferred Functional Metagenomics in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1284–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, A.-M.; Inamine, T.; Hochrath, K.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Llorente, C.; Bluemel, S.; Hartmann, P.; Xu, J.; Koyama, Y.; et al. Intestinal Fungi Contribute to Development of Alcoholic Liver Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2829–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuomisto, S.; Pessi, T.; Collin, P.; Vuento, R.; Aittoniemi, J.; Karhunen, P.J. Changes in Gut Bacterial Populations and Their Translocation into Liver and Ascites in Alcoholic Liver Cirrhotics. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubinkina, V.B.; Tyakht, A.V.; Odintsova, V.Y.; Yarygin, K.S.; Kovarsky, B.A.; Pavlenko, A.V.; Ischenko, D.S.; Popenko, A.S.; Alexeev, D.G.; Taraskina, A.Y.; et al. Links of Gut Microbiota Composition with Alcohol Dependence Syndrome and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Microbiome 2017, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Farhadi, A.; Jakate, S.M.; Tang, Y.; Shaikh, M.; Keshavarzian, A. Lactobacillus GG Treatment Ameliorates Alcohol-Induced Intestinal Oxidative Stress, Gut Leakiness, and Liver Injury in a Rat Model of Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Kirpich, I.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Barve, S.; McClain, C.J.; Feng, W. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Treatment Potentiates Intestinal Hypoxia-Inducible Factor, Promotes Intestinal Integrity and Ameliorates Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Solovieva, N.V.; Leikhter, S.N.; Shidakova, N.A.; Lebedeva, O.V.; Sidorov, P.I.; Bazhukova, T.A.; Soloviev, A.G.; Barve, S.S.; McClain, C.J.; et al. Probiotics Restore Bowel Flora and Improve Liver Enzymes in Human Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury: A Pilot Study. Alcohol 2008, 42, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stadlbauer, V.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Hodges, S.; Wright, G.A.K.; Davies, N.A.; Jalan, R. Effect of Probiotic Treatment on Deranged Neutrophil Function and Cytokine Responses in Patients with Compensated Alcoholic Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.H.; Suk, K.T.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Baik, S.K.; Kim, Y.D.; Cheon, G.J.; Choi, D.H.; Ham, Y.L.; Shin, D.H.; et al. Effects of Probiotics (Cultured Lactobacillus Subtilis/Streptococcus Faecium) in the Treatment of Alcoholic Hepatitis: Randomized-Controlled Multicenter Study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Takebayashi, T.; Kurihara, A.; Akiyama, M.; Suzuki, A.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Sugiyama, D.; Kuwabara, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Okamura, T.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Novel Biomarkers of Alcohol Intake and Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Community-Dwelling Men. Env. Health Prev. Med. 2016, 21, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, P.; Hochrath, K.; Horvath, A.; Chen, P.; Seebauer, C.T.; Llorente, C.; Wang, L.; Alnouti, Y.; Fouts, D.E.; Stärkel, P.; et al. Modulation of the Intestinal Bile Acid/Farnesoid X Receptor/Fibroblast Growth Factor 15 Axis Improves Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2150–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Gillevet, P.M.; Sartor, R.B.; Betrapally, N.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Sikaroodi, M.; Takei, H.; Nittono, H.; Zhou, H.; et al. Gut Microbial Composition Can Differentially Regulate Bile Acid Synthesis in Humanized Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Zhao, D.; Takei, H.; Fagan, A.; Hylemon, P.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Nittono, H.; Fiehn, O.; et al. Continued Alcohol Misuse in Human Cirrhosis Is Associated with an Impaired Gut–Liver Axis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, K.; Hartmann, P.; Jih, L.J.; Pizzo, D.P.; Argemi, J.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Coulter, S.; Liddle, C.; Ling, L.; Rossi, S.J.; et al. Dysregulation of Serum Bile Acids and FGF19 in Alcoholic Hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocan, D.; Voican, C.S.; Wrzosek, L.; Hugot, C.; Rainteau, D.; Humbert, L.; Cassard, A.-M.; Perlemuter, G. Bile Acid Homeostasis and Intestinal Dysbiosis in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Aliment Pharm. 2018, 48, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiyama, G.; Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Heuman, D.M.; Kang, D.J.; Takei, H.; Nittono, H.; Ridlon, J.M.; Fuchs, M.; et al. Colonic Inflammation and Secondary Bile Acids in Alcoholic Cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G929–G937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.-A. MixOmics: An R Package for ’omics Feature Selection and Multiple Data Integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Computer Science & Engineering &GZSCCET Bhatinda, Punjab, India; Goel, E.; Abhilasha, E. Random Forest: A Review. IJARCSSE 2017, 7, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, H.; Marchini, J.S.; Padovan, G.J.; dos-Santos, J.E.; Dutra-de-Oliveira, J.E. Amino Acid Patterns in the Plasma and Ascitic Fluid of Cirrhotic Patients. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1985, 18, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T.; Iino, C.; Endo, T.; Mikami, K.; Kimura, M.; Sawada, N.; Nakaji, S.; Fukuda, S. Changed Amino Acids in NAFLD and Liver Fibrosis: A Large Cross-Sectional Study without Influence of Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Rosso, C.; Buzzigoli, E.; Marietti, M.; Della Latta, V.; Ciociaro, D.; Abate, M.L.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M.; et al. Altered Amino Acid Concentrations in NAFLD: Impact of Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, W.-M.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, M.-H.; Cinar, R.; Yi, H.-S.; Eun, H.S.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Glutamate Signaling in Hepatic Stellate Cells Drives Alcoholic Steatosis. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 877–889.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, T.; Suzuki, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kouno, M.; Suzuki, M.; Kato, Y.; Sato, A.; Okabe, K.; Miyashita, M. Clinical Significance of Measuring Plasma Concentrations of Glutamine and Glutamate in Alcoholic Liver Diseases. Alcohol Alcohol. Suppl. 1993, 1A, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y. Probiotic and Glutamine Treatments Attenuate Alcoholic Liver Disease in a Rat Model. Exp. Med. 2019, 18, 4733–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, K.K.; Shukla, P.K.; Mir, H.; Manda, B.; Gangwar, R.; Yadav, N.; McMullen, M.; Nagy, L.E.; Rao, R. Glutamine Supplementation Attenuates Ethanol-Induced Disruption of Apical Junctional Complexes in Colonic Epithelium and Ameliorates Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Fatty Liver in Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossouw, J.E.; Labadarios, D.; Davis, M.; Williams, R. The Degradation of Tryptophan in Severe Liver Disease. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1978, 48, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Shi, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, F.; Chen, Z. A Narrative Review of the Roles of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Tryptophan-2,3-Dioxygenase in Liver Diseases. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginanni Corradini, S.; Zerbinati, C.; Maldarelli, F.; Palmaccio, G.; Parlati, L.; Bottaccioli, A.G.; Molinaro, A.; Poli, E.; Boaz, M.; Serviddio, G.; et al. Plasma Fatty Acid Lipidome Is Associated with Cirrhosis Prognosis and Graft Damage in Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Feng, K.; He, C.; Li, P.; Hu, Y.-J.; Su, H.; Wan, J.-B. Dietary α-Linolenic Acid-Rich Flaxseed Oil Prevents against Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis via Ameliorating Lipid Homeostasis at Adipose Tissue-Liver Axis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Yin, P.; Fan, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Flaxseed Oil Ameliorates Alcoholic Liver Disease via Anti-Inflammation and Modulating Gut Microbiota in Mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alferink, L.J.M.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Erler, N.S.; Vojinovic, D.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; de Knegt, R.J.; Amin, N.; Ikram, M.A.; Janssen, H.L.A.; et al. Microbiomics, Metabolomics, Predicted Metagenomics, and Hepatic Steatosis in a Population-Based Study of 1,355 Adults. Hepatology 2021, 73, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Franceschi, C.; Rampelli, S.; Severgnini, M.; Ostan, R.; Turroni, S.; Consolandi, C.; Quercia, S.; Scurti, M.; Monti, D.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Extreme Longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smirnova, E.; Puri, P.; Muthiah, M.D.; Daitya, K.; Brown, R.; Chalasani, N.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Shah, V.H.; Gelow, K.; Siddiqui, M.S.; et al. Fecal Microbiome Distinguishes Alcohol Consumption from Alcoholic Hepatitis but Does Not Discriminate Disease Severity. Hepatology 2020, 72, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-D.; Peng, X.-B.; Zhao, R.-R.; Ma, C.-Q.; Li, J.-N.; Yao, L.-Q. The Intestinal Microbial Community Dissimilarity in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Cirrhosis Patients with and without at Alcohol Consumption. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Juan-Vergara, H.; Zurek, E.; Ajami, N.J.; Mogollon, C.; Peña, M.; Portnoy, I.; Vélez, J.I.; Cadena-Cruz, C.; Diaz-Olmos, Y.; Hurtado-Gómez, L.; et al. A Lachnospiraceae-Dominated Bacterial Signature in the Fecal Microbiota of HIV-Infected Individuals from Colombia, South America. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowerman, K.L.; Rehman, S.F.; Vaughan, A.; Lachner, N.; Budden, K.F.; Kim, R.Y.; Wood, D.L.A.; Gellatly, S.L.; Shukla, S.D.; Wood, L.G.; et al. Disease-Associated Gut Microbiome and Metabolome Changes in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, Z. Cross-Sectional Studies: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Recommendations. Chest 2020, 158, S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccioni, L.; Gao, B.; Leclercq, S.; Pirlot, B.; Horsmans, Y.; Timary, P.D.; Leclercq, I.; Fouts, D.; Schnabl, B.; Stärkel, P. Intestinal Permeability, Microbial Translocation, Changes in Duodenal and Fecal Microbiota, and Their Associations with Alcoholic Liver Disease Progression in Humans. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1782157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Lue, H.-W.; Podolak, J.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Serawat, A.; Alumkal, J.J.; Fiehn, O.; Thomas, G.V. Multi-Omics Analyses Detail Metabolic Reprogramming in Lipids, Carnitines, and Use of Glycolytic Intermediates between Prostate Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Prostate Adenocarcinoma. Metabolites 2019, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skogerson, K.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. The Volatile Compound BinBase Mass Spectral Database. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-Independent MS/MS Deconvolution for Comprehensive Metabolome Analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFelice, B.C.; Mehta, S.S.; Samra, S.; Čajka, T.; Wancewicz, B.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Fiehn, O. Mass Spectral Feature List Optimizer (MS-FLO): A Tool to Minimize False Positive Peak Reports in Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS) Data Processing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3250–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Emami, A.; Zhou, R.; Lang, S.; Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Loomba, R.; Brenner, D.; Stärkel, P.; et al. Functional Microbial Responses to Alcohol Abstinence in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Truong, D.T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Tickle, T.L.; Scholz, M.; Weingart, G.; Pasolli, E.; Tett, A.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. MetaPhlAn2 for Enhanced Metagenomic Taxonomic Profiling. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzosa, E.A.; McIver, L.J.; Rahnavard, G.; Thompson, L.R.; Schirmer, M.; Weingart, G.; Lipson, K.S.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G.; Segata, N.; et al. Species-Level Functional Profiling of Metagenomes and Metatranscriptomes. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, W.K.; Paley, S.; Subhraveti, P.; Karp, P.D. The MetaCyc Database of Metabolic Pathways and Enzymes—A 2019 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D445–D453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lê Cao, K.-A.; González, I.; Déjean, S. IntegrOmics: An R Package to Unravel Relationships between Two Omics Datasets. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2855–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Shannon, C.P.; Gautier, B.; Rohart, F.; Vacher, M.; Tebbutt, S.J.; Lê Cao, K.-A. DIABLO: An Integrative Approach for Identifying Key Molecular Drivers from Multi-Omics Assays. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Non-Alcoholic Controls | Non-Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease | Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical parameter | ||||
| Total n | 7 | 16 | 15 | |
| Age, years, n = 38 | 52 (37–71) | 37 (27–58) | 42 (28–59) | 0.096 |
| Body Mass Index (BMI), kg/m2, n = 38 | 23 (19–29) | 22 (19–31) | 24 (18–31) | 0.437 |
| Gender (male), n (%), n = 38 | 6 (86) | 11 (69) | 13 (87) | 0.421 |
| Laboratory parameter | ||||
| Albumin (g/dL), n = 27 | 4.7 (4.2–5.2) | 4.8 (3.9–5.2) | 0.519 | |
| ALT (U/L), n = 31 | 19.5 (11–37) | 77 (37–184) | <0.001 | |
| AST (U/L), n = 31 | 25.5 (15–36) | 78 (46–283) | <0.001 | |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL), n = 28 | 0.3 (0.2–1.1) | 0.5 (0.3–0.8) | 0.049 | |
| GGT (U/L), n = 28 | 31 (4–213) | 121 (11–952) | 0.021 | |
| Platelet counts (×109/L), n = 27 | 268 (165–339) | 222 (21–434) | 0.286 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL), n = 28 | 0.8 (0.5–0.95) | 0.8 (0.6–1.2) | 0.433 | |
| International normalized ratio, n = 28 | 1.0 (0.9–1.2) | 0.9 (0.8–1.0) | 0.128 | |
| Fibroscan (kpa), n = 30 | 4.9 (3.1–6.8) | 6.1 (3.9–7.0) | 0.262 | |
| CAP, (dB/m), n = 31 CAP > 250 dB/m, n (%) | 254.5 (148–325) 9 (56) | 311 (222–381) 15 (93) | 0.001 | |
| CK18-M65 (U/L), n = 30 | 332 (158–616) | 592 (316–1576) | <0.001 |
| Acidaminococcus fermentans | Lachnospiraceae bacterium 8_1_57FAA | Coprococcus sp. ART55/1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-methylglutarylcarnitine | 0.5513 | 0.5446 | 0.6061 |
| carbamazepine | 0.5729 | 0.5593 | 0.6227 |
| phenylalanine | −0.5991 | −0.5645 | −0.6292 |
| linolenic acid | 0.6671 | 0.6246 | 0.6963 |
| cystine | 0.6008 | 0.5393 | 0.6021 |
| Odoribacter splanchnicus | Coprococcus sp. ART55/1 | |
|---|---|---|
| (R)-butyrylcarnitine | 0.5975 | 0.6111 |
| 2-O-methylcytidine | 0.6520 | 0.6606 |
| 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid | 0.6065 | 0.6182 |
| glutamine | 0.6629 | 0.6681 |
| guanosine | 0.6160 | 0.6256 |
| inosine | 0.6376 | 0.6481 |
| kynurenic acid | 0.6291 | 0.6404 |
| glutamic acid | −0.6085 | −0.6075 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, N.; Shen, W.; Stärkel, P.; Schnabl, B. Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Microbiome in Patients with Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Metabolites 2021, 11, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110766
Gao B, Zhu Y, Gao N, Shen W, Stärkel P, Schnabl B. Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Microbiome in Patients with Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Metabolites. 2021; 11(11):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110766
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Bei, Yixin Zhu, Nan Gao, Weishou Shen, Peter Stärkel, and Bernd Schnabl. 2021. "Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Microbiome in Patients with Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease" Metabolites 11, no. 11: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110766
APA StyleGao, B., Zhu, Y., Gao, N., Shen, W., Stärkel, P., & Schnabl, B. (2021). Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Microbiome in Patients with Progressive Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Metabolites, 11(11), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110766