- Article
Lipid-Lowering and Hepatoprotective Effects of Basil-Enriched Soybean Oil (BEO) in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice
- Amani Tayebi,
- Mohammadine Moumou and
- Hicham Harnafi
- + 8 authors
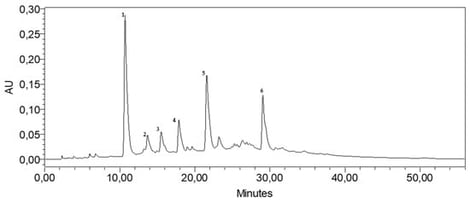
Background: This study investigated the hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective effects of refined soybean oil supplemented with an Ocimum basilicum L. extract, characterized by HPLC and found to be rich in caftaric, caffeic, chicoric, and rosmarinic acids. Methods: After a 12-week model of diet-induced hyperlipidemia, we examined the plasma levels of TC, TG, Glucose, HDL-C, and LDL-C and the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio using enzymatic kits. The Plasma Hepatic and Biliary Marker Analysis was analysed following standardized hospital protocols with quality-controlled instrumentation. Results: The supplementation with Basil-Enriched Oil (BEO) resulted in a notable redistribution of lipids, significantly reducing the plasma total cholesterol (−75%), triglycerides (−96%), and glucose (−22%), while enhancing their hepatic sequestration. This was accompanied by a marked improvement in the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and a reduction in hepatic oxidative stress (measured by MDA). Importantly, BEO preserved liver structure and prevented steatosis, despite inducing an increase in adaptive hepatomegaly. Conclusions: The results reveal a dual mechanism whereby the antioxidant properties of BEO collaborate with reprogrammed lipid metabolism, promoting safe hepatic storage rather than harmful circulating levels. These findings strongly advocate for the extract’s potential as a nutraceutical for addressing hyperlipidemia and related metabolic disorders by targeting both oxidative stress and lipid imbalance. Further research is required to confirm these effects in clinical settings and to confirm its long-term efficacy.
5 February 2026